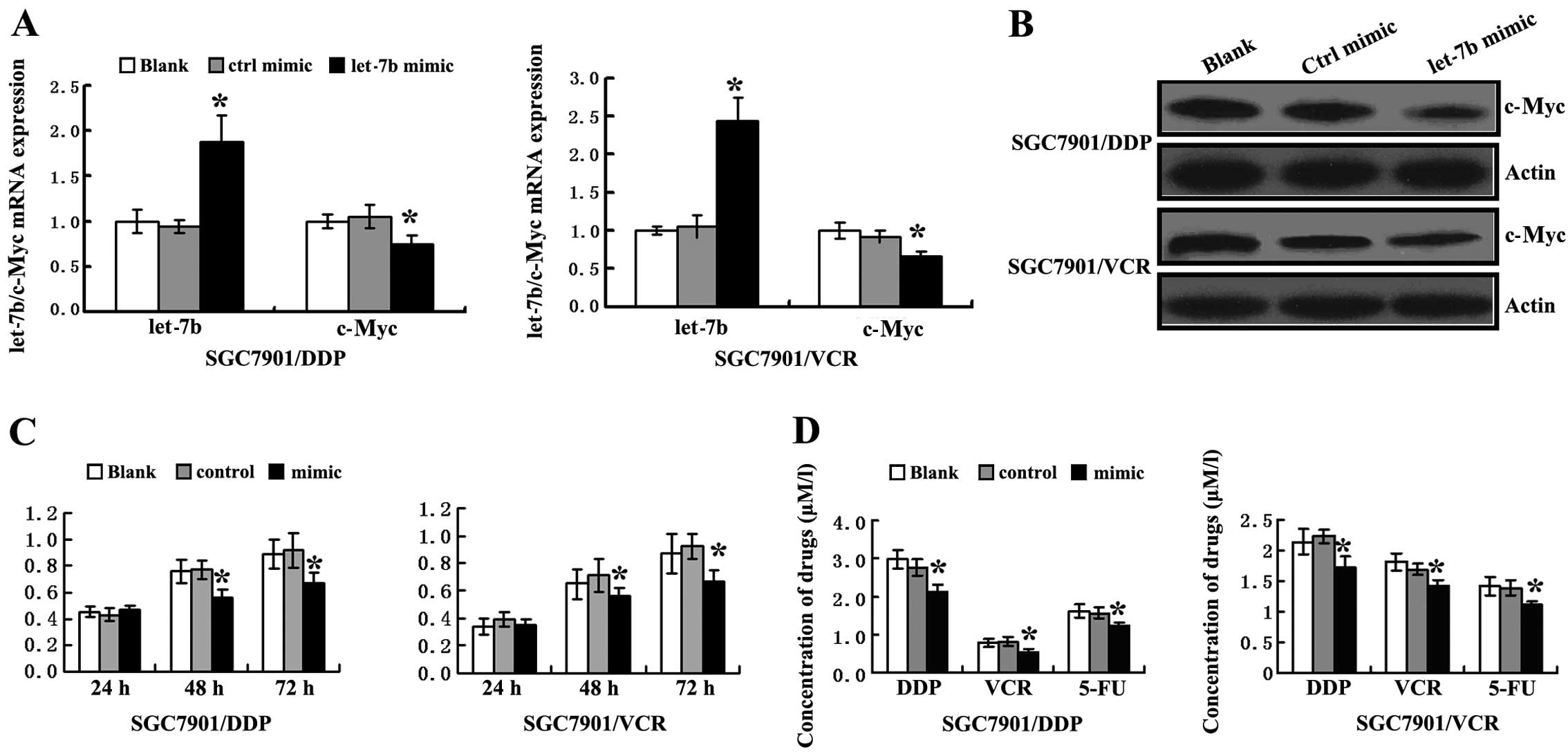
|
1
|
Lee JH, Kim KM, Cheong JH and Noh SH:
Current management and future strategies of gastric cancer. Yonsei
Med J. 53:248–257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hudler P: Genetic aspects of gastric
cancer instability. Sci World J. 2012:7619092012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Verdecchia A, Corazziari I, Gatta G, Lisi
D, Faivre J and Forman D; EUROCARE Working Group. Explaining
gastric cancer survival differences among European countries. Int J
Cancer. 109:737–741. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bonenkamp JJ, Hermans J, Sasako M, et al:
Extended lymphnode dissection for gastric cancer. N Engl J Med.
340:908–914. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaneko S and Yoshimura T: Time trend
analysis of gastric cancer incidence in Japan by histological
types, 1975–1989. Br J Cancer. 84:400–405. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan D and Liu X: New progresses in
researches on multidrug resistance in gastric cancer. Chin J
Digest. 20:77–78. 2000.
|
|
7
|
Milne AN, Sitarz R, Carvalho R, Carneiro F
and Offerhaus GJ: Early onset gastric cancer: on the road to
unraveling gastric carcinogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 7:15–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eilers M and Eisenman RN: Myc’s broad
reach. Genes Dev. 22:2755–2766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Herkert B and Eilers M: Transcriptional
repression: the dark side of myc. Genes Cancer. 1:580–586. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Miller MD, Thomas SD, Islam A, Muench D
and Sedoris K: C-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5546–5553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walker TL, White JD, Esdale WJ, Burton MA
and DeCruz EE: Tumour cells surviving in vivo cisplatin
chemotherapy display elevated cmyc expression. Br J Cancer.
73:610–614. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marazzi L, Parodi MT, Martino DD, Ferrari
S and Tonini GP: Coordinate change of c-myc, transferrin receptor
and H3 gene expression precedes induction of haemoglobin-producing
cells of the leukaemia K562 cell line treated with
cisdiamminedichlo-roplatinum II. Anticancer Res. 11:947–952.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kashani-Sabet M, Lu Y, Leong L, Haedicke K
and Scanlon KJ: Differential oncogene amplification in tumour cells
from a patient treated with cisplatin and 5-FU. Eur J Cancer.
26:383–390. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vandenboom TG II, Li Y, Philip PA and
Sarkar FH: MicroRNA and cancer: tiny molecules with major
implications. Curr Genomics. 9:97–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peter ME: Regulating cancer stem cells the
miR way. Cell Stem Cell. 6:4–6. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, et al: miR-200
expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth
factor receptor therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5060–5072. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bourguignon LY, Spevak CC, Wong G, Xia W
and Gilad E: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with protein kinase
C(epsilon) promotes oncogenic signaling by the stem cell marker
Nanog and the Production of microRNA-21, leading to down-regulation
of the tumor suppressor protein PDCD4, anti-apoptosis, and
chemotherapy resistance in breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem.
284:26533–26546. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, et al:
MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roush S and Slack FJ: The let-7 family of
microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 18:505–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: The tumor suppressor
microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev.
21:1025–1030. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR and
Jacks T: Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular
transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 39:673–677. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang N, Kaur S, Volinia S, et al: MicroRNA
microarray identifies Let-7i as a novel biomarker and therapeutic
target in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
68:10307–10314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim CH, Kim HK, Rettig RL, et al: miRNA
signature associated with outcome of gastric cancer patients
following chemotherapy. BMC Med Genomics. 4:792001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Broxterman HJ, Gotink KJ and Verheul HM:
Understanding the causes of multidrug resistance in cancer: a
comparison of doxorubicin and sunitinib. Drug Resist Updat.
12:114–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fojo T: Multiple paths to a drug
resistance phenotype: mutations, translocations, deletions and
amplification of coding genes or promoter regions, epigenetic
changes and microRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 10:59–67. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gatti L and Zunino F: Overview of tumor
cell chemoresistance mechanisms. Methods Mol Med. 111:127–148.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan D, Zhang X, Chen X, et al: Bird’s-eye
view on gastric cancer research of the past 25 years. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:360–365. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chuman Y, Sumizawa T, Takebayashi Y, et
al: Expression of the multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP)
gene in human colorectal, gastric and non-small-cell lung
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 66:274–279. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsuhashi N, Saio M, Matsuo A, Sugiyama Y
and Saji S: The evaluation of gastric cancer sensitivity to
5-FU/CDDP in terms of induction of apoptosis: Time- and p53
expression-dependency of anti-cancer drugs. Oncol Rep. 14:609–615.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ning H, Li T, Zhao L, et al: TRF2 promotes
multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:950–956. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang L, Guo F, Wang Y, et al:
MicroRNA-200c regulates the sensitivity of chemotherapy of gastric
cancer SGC7901/DDP cells by directly targeting RhoE. Pathol Oncol
Res. 20:93–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yan LH, Wang XT, Yang J, et al: Reversal
of multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by CDX2
downregulation. World J Gastroenterol. 19:4155–4165. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eitan R, Kushnir M, Lithwick-Yanai G, et
al: Tumor microRNA expression patterns associated with resistance
to platinum based chemotherapy and survival in ovarian cancer
patients. Gynecol Oncol. 114:253–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Zuo J, Liu Y, Gao H and Liu W:
Inhibitory effects of miRNA-200c on chemotherapy-resistance and
cell proliferation of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells. Chin J
Cancer. 29:1006–1011. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, et al:
MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth
in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:9762–9770. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et
al: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rybak A, Fuchs H, Smirnova L, et al: A
feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7
maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat Cell Biol.
10:987–993. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang XJ, Lin XJ, Zhong XM, et al: Double
negative feedback loop between reprogramming factor LIN28 and
microRNA let-7 regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cancer
stem cells. Cancer Res. 70:9463–9472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chang TC, Zeitels LR, Hwang HW, et al:
Lin-28B transactivation is necessary for Myc-mediated let-7
repression and proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:3384–3389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cotterman R and Knoepfler PS: N-Myc
regulates expression of pluripotency genes in neuroblastoma
including lif, klf2, klf4, and lin28b. PLoS One. 4:e57992009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Molenaar JJ, Domingo-Fernández R, Ebus ME,
et al: LIN28B induces neuroblastoma and enhances MYCN levels via
let-7 suppression. Nat Genet. 44:1199–1206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Laurenti E, Varnum-Finney B, Wilson A, et
al: Hematopoietic stem cell function and survival depend on c-Myc
and N-Myc activity. Cell Stem Cell. 3:611–624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stanton BR, Perkins AS, Tessarollo L,
Sassoon DA and Parada LF: Loss of Nmyc function results in
embryonic lethality and failure of the epithelial component of the
embryo to develop. Gene Dev. 6:2235–2247. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Konopleva M, Tabe Y, Zeng Z and Andreeff
M: Therapeutic targeting of micro environmental interactions in
leukemia: mechanisms and approaches. Drug Resist Updat. 12:103–113.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S and Sarkar FH:
Emerging role of Notch in stem cells and cancer. Cancer Lett.
279:8–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Wang ZW, Li YW, Ahmad A, et al: Targeting
miRNAs involved in cancer stem cell and EMT regulation: an emerging
concept in overcoming drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
13:109–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ahmed N, Abubaker K, Findlay J and Quinn
M: Cancerous ovarian stem cells: obscure targets for therapy but
relevant to chemoresistance. J Cell Biochem. 114:21–34. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|