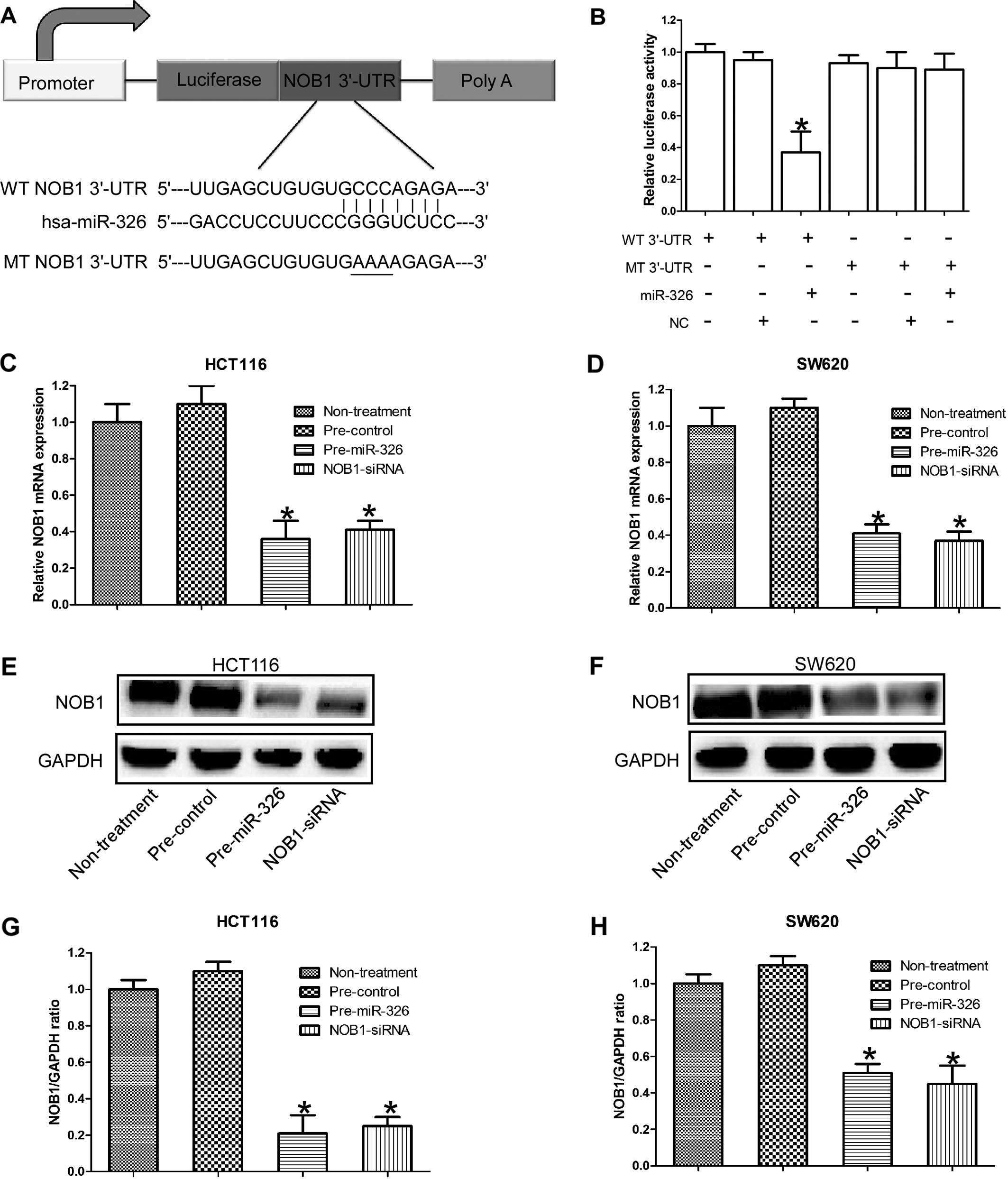
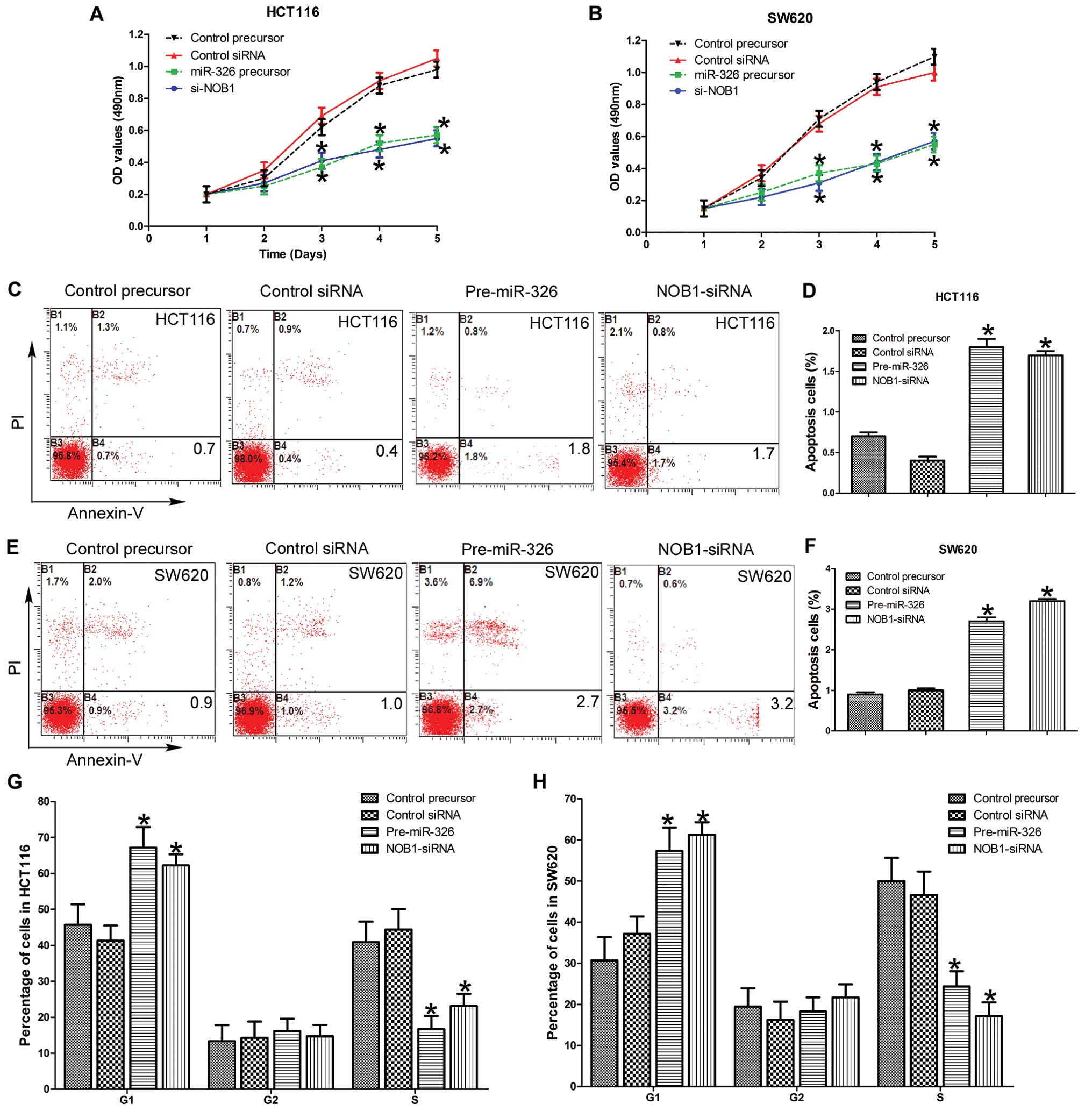
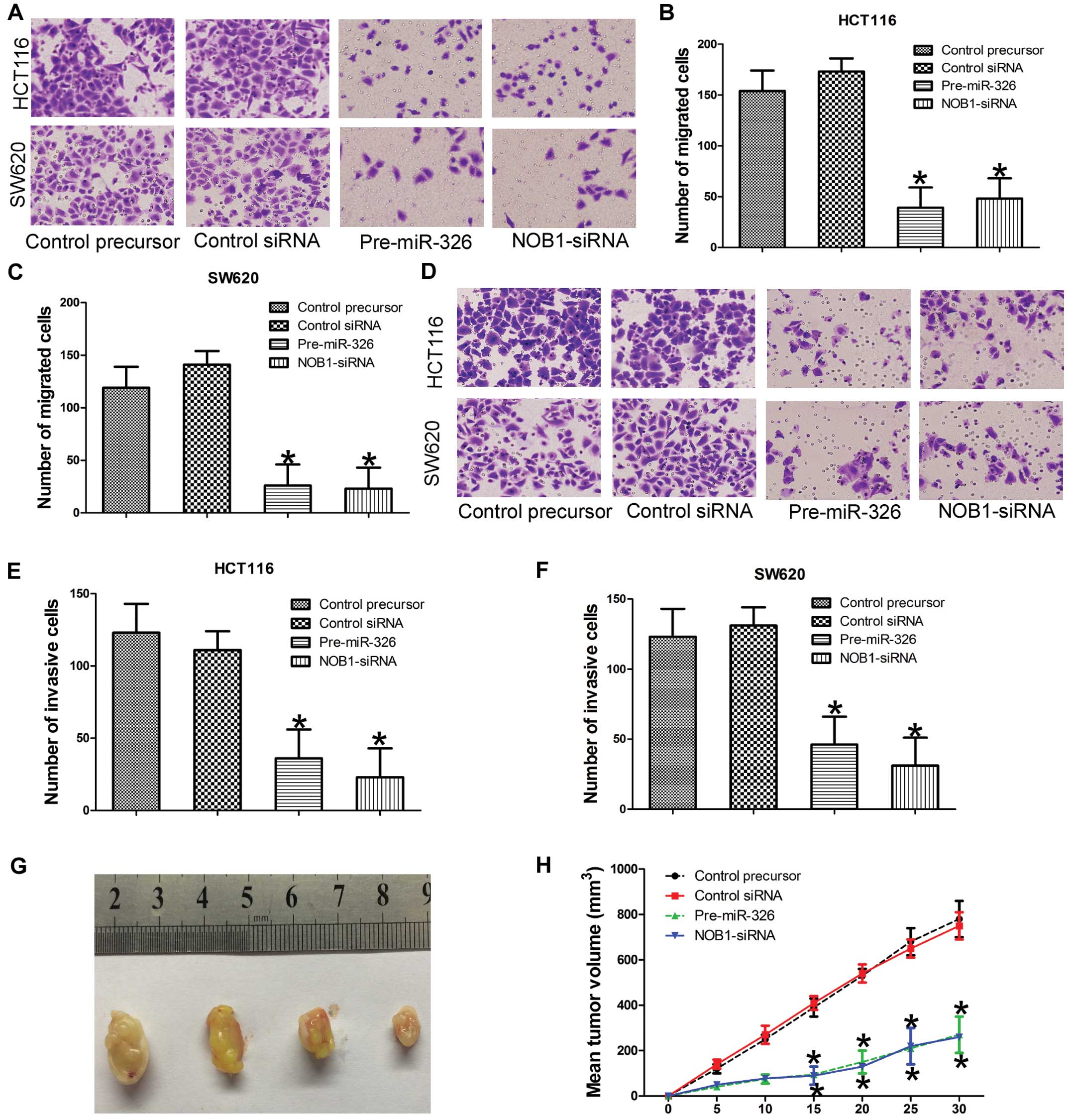
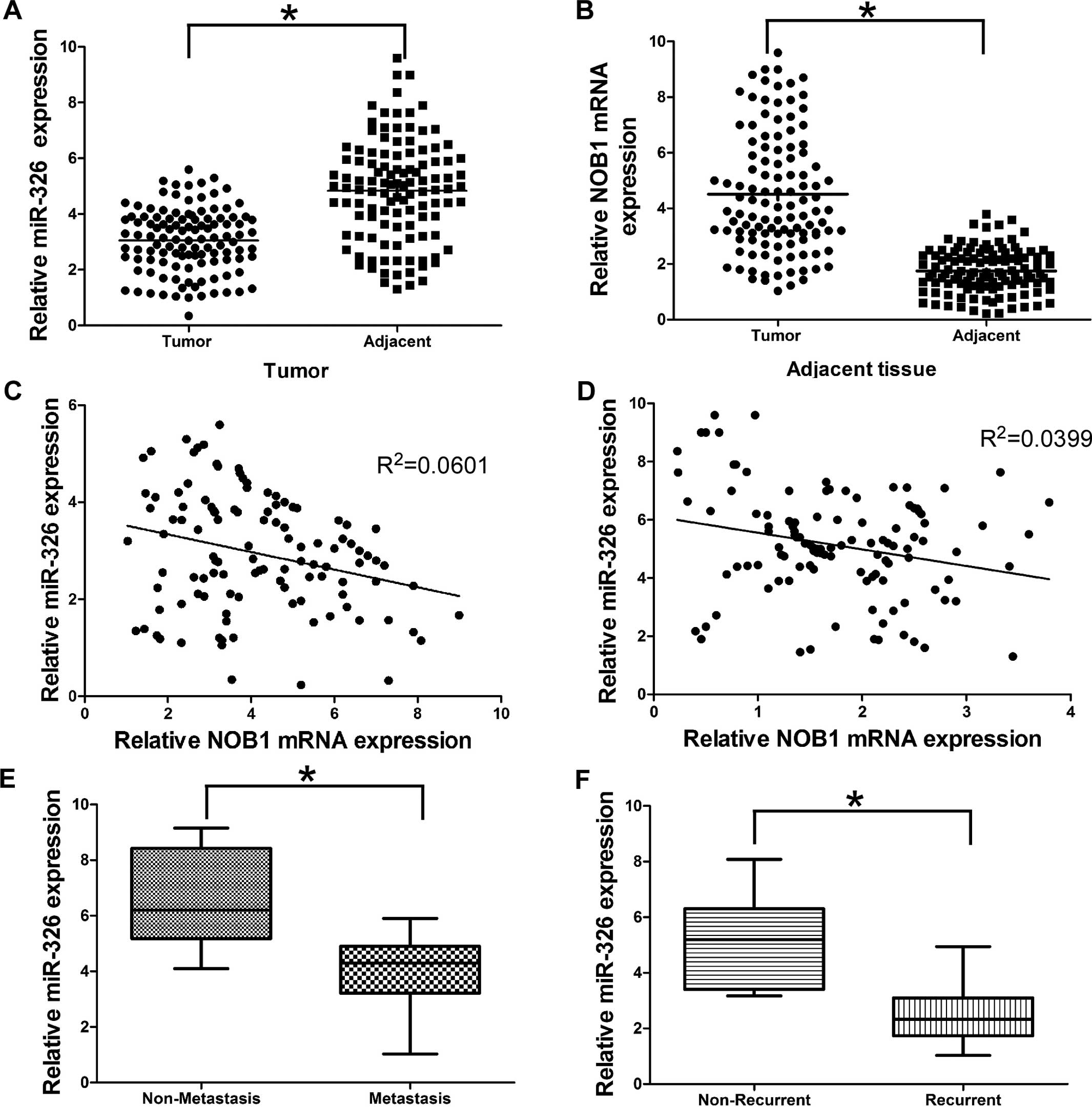
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR and
Jacks T: Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular
transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 39:673–677. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Zhang H, Yang J,
Peng J, Liu W and Qin H: miR-150 as a potential biomarker
associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colorectal
cancer. Gut. 61:1447–1453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Almeida MI, Nicoloso MS, Zeng L, et al:
Strand-specific miR-28-5p and miR-28-3p have distinct effects in
colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 142:886–896.e9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pichler M, Ress AL, Winter E, Stiegelbauer
V, Karbiener M, Schwarzenbacher D, Scheideler M, Ivan C, Jahn SW,
Kiesslich T, et al: MiR-200a regulates epithelial to mesenchymal
transition-related gene expression and determines prognosis in
colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 110:1614–1621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun HB, Chen X, Ji H, Wu T, Lu HW, Zhang
Y, Li H and Li YM: miR-494 is an independent prognostic factor and
promotes cell migration and invasion in colorectal cancer by
directly targeting PTEN. Int J Oncol. 45:2486–2494. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou J, Xu T, Yan Y, Qin R, Wang H, Zhang
X, Huang Y, Wang Y, Lu Y, Fu D, et al: MicroRNA-326 functions as a
tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting the Nin one binding protein
(NOB1). PLoS One. 8:e684692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du W, Liu X, Chen L, et al: Targeting the
SMO oncogene by miR-326 inhibits glioma biological behaviors and
stemness. Neuro Oncol. 17:243–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Miele E, Laneve
P, Po A, Pelloni M, Paganelli A, Di Marcotullio L, Caffarelli E,
Screpanti I, et al: Concerted microRNA control of Hedgehog
signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO
J. 27:2616–2627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H,
Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD and Patel T:
Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to
chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
Gastroenterology. 130:2113–2129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Hajifathali A,
Tavirani MR, Zomorod MS, Ghadiani M and Soleimani M: Targeting of
the signal transducer Smo links microRNA-326 to the oncogenic
Hedgehog pathway in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells. Int
J Cancer. 133:579–589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Makarova KS, Aravind L, Galperin MY,
Grishin NV, Tatusov RL, Wolf YI and Koonin EV: Comparative genomics
of the Archaea (Euryarchaeota): Evolution of conserved protein
families, the stable core, and the variable shell. Genome Res.
9:608–628. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Ni J, Zhou G, Yuan J, Ren W, Shan
Y, Tang W, Yu L and Zhao S: Cloning, expression and
characterization of the human NOB1 gene. Mol Biol Rep. 32:185–189.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fatica A, Oeffinger M, Dlakić M and
Tollervey D: Nob1p is required for cleavage of the 3′ end of 18S
rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1798–1807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang WY, Chen DH, Ning L and Wang LW:
siRNA mediated silencing of NIN1/RPN12 binding protein 1 homolog
inhibits proliferation and growth of breast cancer cells. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 13:1823–1827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin Y, Peng S, Yu H, Teng H and Cui M:
RNAi-mediated downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the growth and
colony-formation ability of human ovarian cancer cells. Med Oncol.
29:311–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Ma C, Qian M, Wen Z, Jing H and Qian
D: Downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the proliferation and tumor
growth of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol
Rep. 31:1271–1276. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Z, Guo Q, Shi A, Xie F and Lu Q:
Downregulation of NIN/RPN12 binding protein inhibit the growth of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 39:501–507.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He XW, Tao F, Luo SS and Yu XK: Effect of
lentivirus-mediated NOB1 gene silencing by RNA interference on
proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer cells. Zhonghua
Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 15:1182–1186. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao F and Wang W: MicroRNA-96 promotes the
proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and targets tumor protein
p53 inducible nuclear protein S1, forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1)
and FOXO3a. Mol Med Rep. 11:1200–1206. 2015.
|
|
21
|
Xue G, Yan HL, Zhang Y, Hao LQ, Zhu XT,
Mei Q and Sun SH: c-Myc-mediated repression of miR-15-16 in hypoxia
is induced by increased HIF-2α and promotes tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis by upregulating FGF2. Oncogene. Apr 7–2014.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fernandez S, Risolino M, Mandia N, et al:
miR-340 inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by
targeting multiple negative regulators of p27 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncogene. 0:2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li T, Yang J, Lv X, Liu K, Gao C, Xing Y
and Xi T: miR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of
colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Biotechnol Lett.
36:1743–1752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu DP and He XW: Expression of NOB1 and
its significance in colorectal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 32:420–422. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Huang H, Yuan B, Zhuang LY, Luo TP
and Zhang Q: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of NOB1 suppresses the
proliferation of colon cancer cells. Z Gastroenterol. 52:429–435.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meng W, Wang PS, Liu J, Xue S, Wang GM,
Meng XY and Chen G: Adenovirus-mediated siRNA targeting NOB1
inhibits tumor growth and enhances radiosensitivity of human
papillary thyroid carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
32:2411–2420. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Granneman S, Nandineni MR and Baserga SJ:
The putative NTPase Fap7 mediates cytoplasmic 20S pre-rRNA
processing through a direct interaction with Rps14. Mol Cell Biol.
25:10352–10364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raychaudhuri S, Fontanes V, Barat B and
Dasgupta A: Activation of ribosomal RNA transcription by hepatitis
C virus involves upstream binding factor phosphorylation via
induction of cyclin D1. Cancer Res. 69:2057–2064. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meraner J, Lechner M, Loidl A,
Goralik-Schramel M, Voit R, Grummt I and Loidl P: Acetylation of
UBF changes during the cell cycle and regulates the interaction of
UBF with RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:1798–1806. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fasanaro P, Capogrossi MC and Martelli F:
Regulation of the endothelial cell cycle by the
ubiquitin-proteasome system. Cardiovasc Res. 85:272–280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xu G, Bernaudo S, Fu G, Lee DY, Yang BB
and Peng C: Cyclin G2 is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway and mediates the antiproliferative effect of activin
receptor-like kinase 7. Mol Biol Cell. 19:4968–4979. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li W, Liu M, Feng Y, Xu YF, Huang YF, Che
JP, Wang GC, Yao XD and Zheng JH: Downregulated miR-646 in clear
cell renal carcinoma correlated with tumour metastasis by targeting
the nin one binding protein (NOB1). Br J Cancer. 111:1188–1200.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z,
Quan C, Zhou L, Hu Y, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: MiR-139-5p inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR
and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 5:851–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kjersem JB, Ikdahl T, Lingjaerde OC, Guren
T, Tveit KM and Kure EH: Plasma microRNAs predicting clinical
outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving
first-line oxaliplatin-based treatment. Mol Oncol. 8:59–67. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
No authors listed. MicroRNA miR-133
represses HERG K+ channel expression contributing to QT
prolongation in diabetic hearts. J Biol Chem. 286:286562011.
|