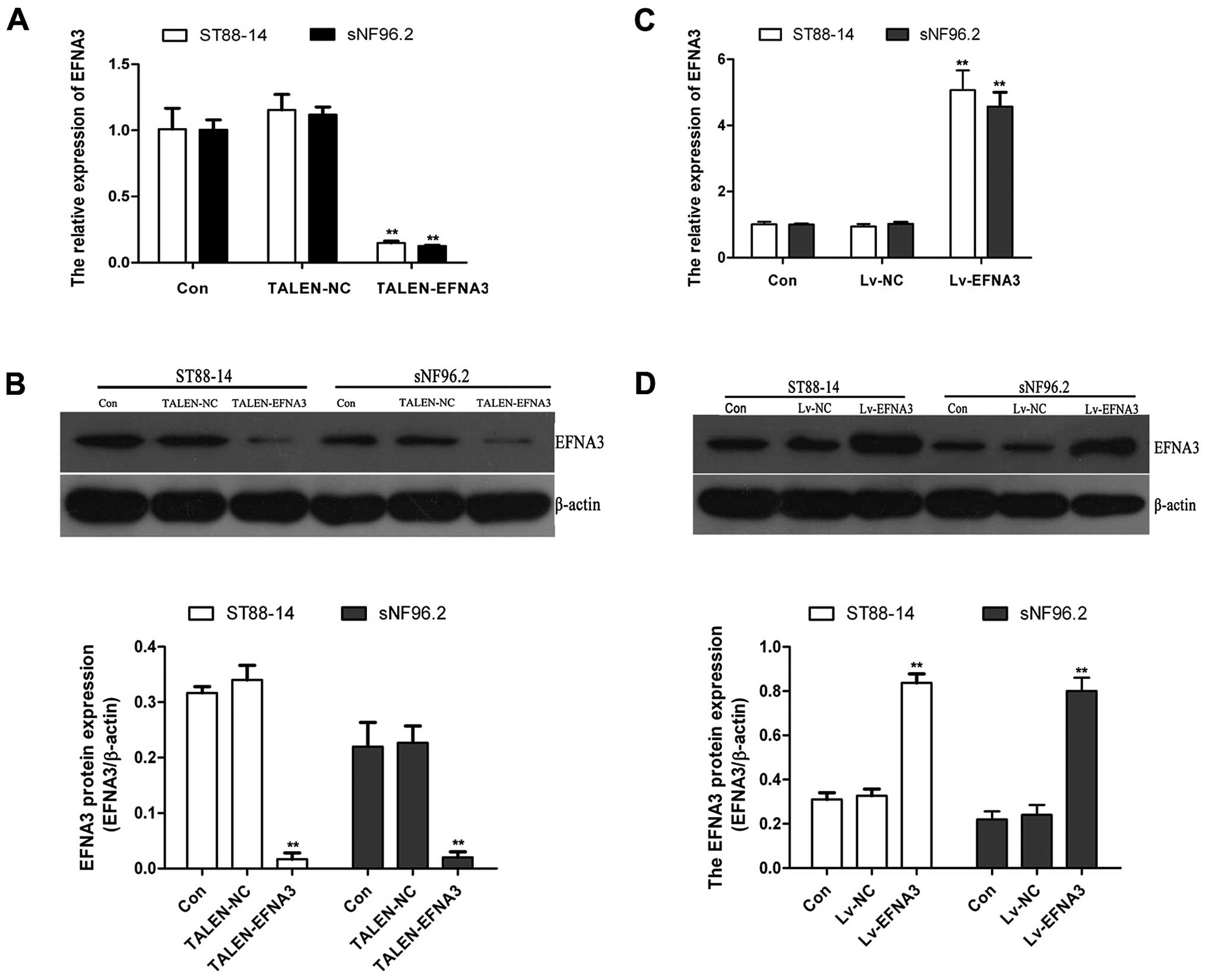
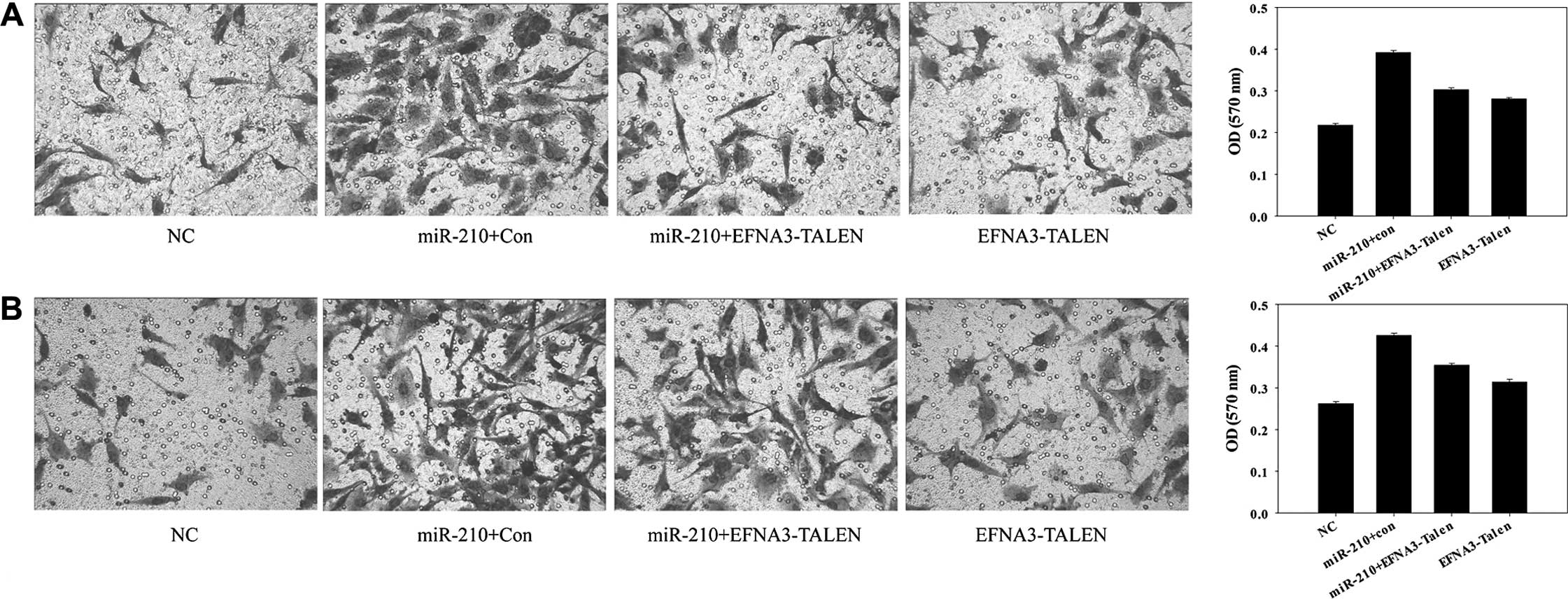
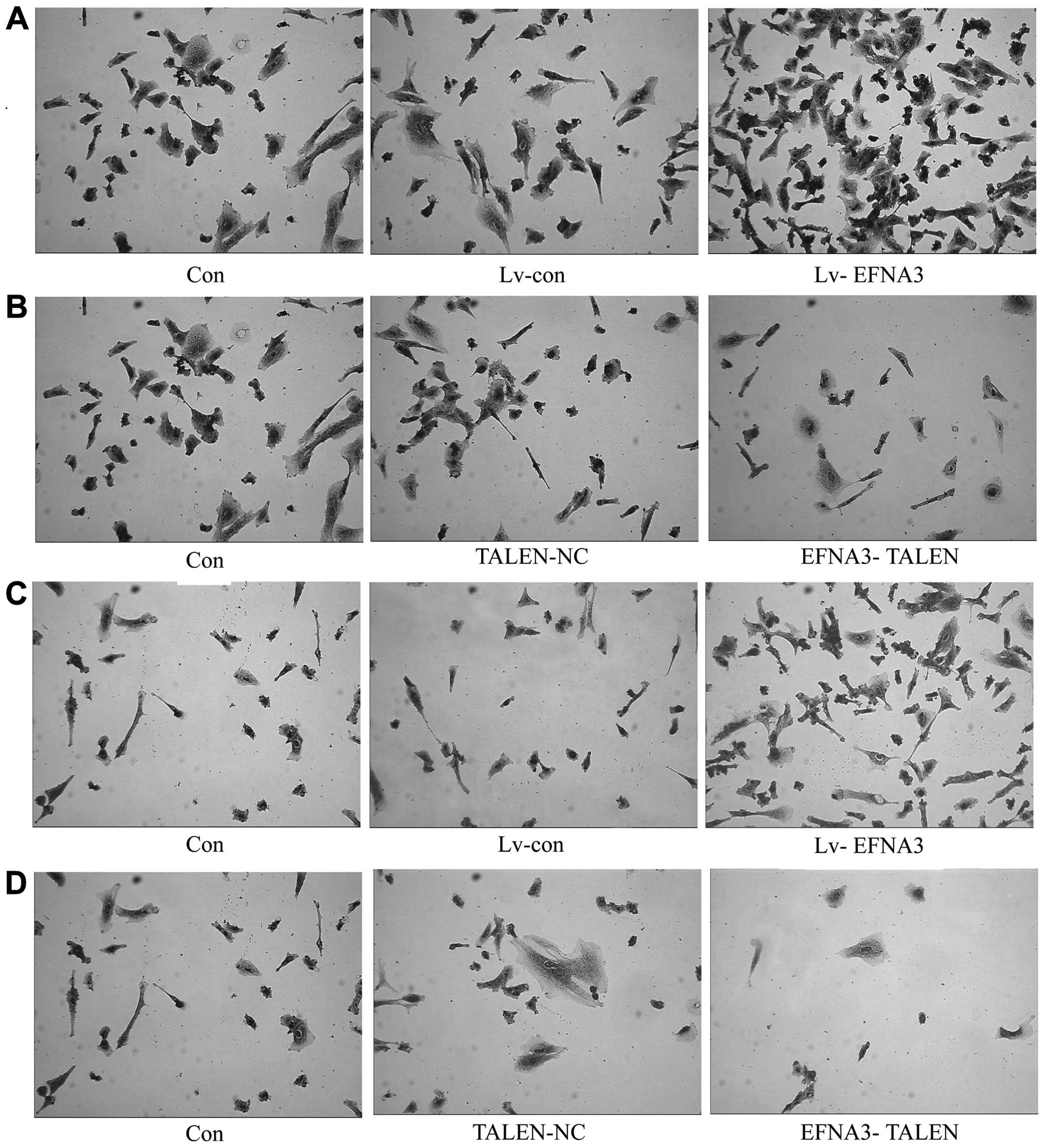
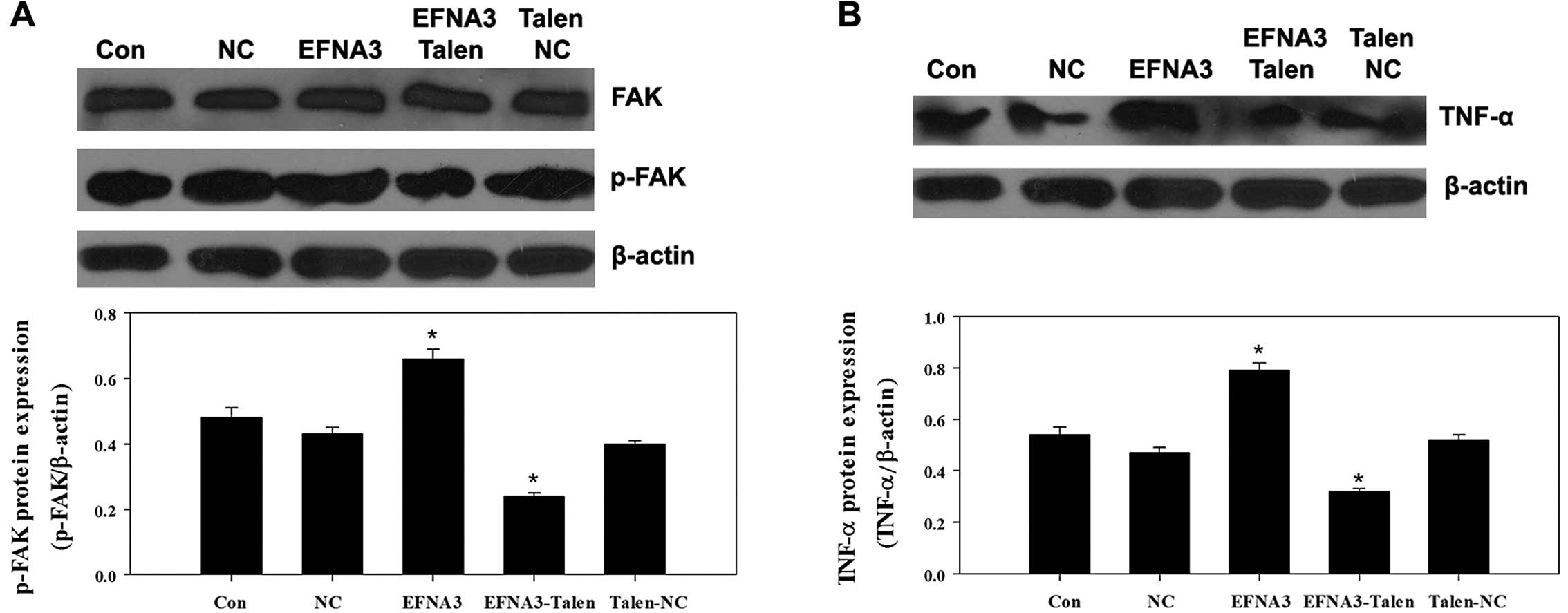
|
1
|
Wang Z, Yin B, Wang B, Ma Z, Liu W and Lv
G: MicroRNA-210 promotes proliferation and invasion of peripheral
nerve sheath tumor cells targeting EFNA3. Oncol Res. 21:145–154.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Itani S, Kunisada T, Morimoto Y, Yoshida
A, Sasaki T, Ito S, Ouchida M, Sugihara S, Shimizu K and Ozaki T:
MicroRNA-21 correlates with tumorigenesis in malignant peripheral
nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) via programmed cell death protein 4
(PDCD4). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1501–1509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Doorn PF, Molenaar WM, Buter J and
Hoekstra HJ: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in patients
with and without neurofibromatosis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 21:78–82.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ingham S, Huson SM, Moran A, Wylie J,
Leahy M and Evans DG: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in
NF1: improved survival in women and in recent years. Eur J Cancer.
47:2723–2728. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Evans DG, Baser ME, McGaughran J, Sharif
S, Howard E and Moran A: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours
in neurofibromatosis 1. J Med Genet. 39:311–314. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Héroult M, Schaffner F and Augustin HG:
Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during
angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 312:642–650.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kuijper S, Turner CJ and Adams RH:
Regulation of angiogenesis by Eph-ephrin interactions. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 17:145–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Irie F, Okuno M, Matsumoto K, Pasquale EB
and Yamaguchi Y: Heparan sulfate regulates ephrin-A3/EphA receptor
signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:12307–12312. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Surawska H, Ma PC and Salgia R: The role
of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
15:419–433. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Böhme B, Holtrich U, Wolf G, Luzius H,
Grzeschik KH, Strebhardt K and Rübsamen-Waigmann H: PCR mediated
detection of a new human receptor-tyrosine-kinase, HEK 2. Oncogene.
8:2857–2862. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fox BP and Kandpal RP: Invasiveness of
breast carcinoma cells and transcript profile: Eph receptors and
ephrin ligands as molecular markers of potential diagnostic and
prognostic application. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 318:882–892.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Walker-Daniels J, Coffman K, Azimi M, Rhim
JS, Bostwick DG, Snyder P, Kerns BJ, Waters DJ and Kinch MS:
Overexpression of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase in prostate cancer.
Prostate. 41:275–280. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu S, Lin S, Hu D, Feng Y, Tan Y and Peng
Y: Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and
miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical
outcome of glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med. 11:102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Redova M, Poprach A, Besse A, Iliev R,
Nekvindova J, Lakomy R, Radova L, Svoboda M, Dolezel J, Vyzula R,
et al: MiR-210 expression in tumor tissue and in vitro effects of
its silencing in renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:481–491.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Puisségur MP, Mazure NM, Bertero T,
Pradelli L, Grosso S, Robbe-Sermesant K, Maurin T, Lebrigand K,
Cardinaud B, Hofman V, et al: miR-210 is overexpressed in late
stages of lung cancer and mediates mitochondrial alterations
associated with modulation of HIF-1 activity. Cell Death Differ.
18:465–478. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong L, Yang J, Han Y, Lu Q, Cao J and
Syed L: High expression of miR-210 predicts poor survival in
patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Gene. 507:135–138.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rothé F, Ignatiadis M, Chaboteaux C,
Haibe-Kains B, Kheddoumi N, Majjaj S, Badran B, Fayyad-Kazan H,
Desmedt C, Harris AL, et al: Global microRNA expression profiling
identifies miR-210 associated with tumor proliferation, invasion
and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. PLoS One. 6:e209802011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan SY and Loscalzo J: MicroRNA-210: a
unique and pleiotropic hypoxamir. Cell Cycle. 9:1072–1083. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui H, Grosso S, Schelter F, Mari B and
Krüger A: On the pro-metastatic stress response to cancer
therapies: evidence for a positive co-operation between TIMP-1,
HIF-1α, and miR-210. Front Pharmacol. 3:1342012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Presneau N, Eskandarpour M, Shemais T,
Henderson S, Halai D, Tirabosco R and Flanagan AM: MicroRNA
profiling of peripheral nerve sheath tumours identifies miR-29c as
a tumour suppressor gene involved in tumour progression. Br J
Cancer. 108:964–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Kim YK, Wee G, Park J, Kim J, Baek D, Kim
JS and Kim VN: TALEN-based knockout library for human microRNAs.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:1458–1464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boch J: TALEs of genome targeting. Nat
Biotechnol. 29:135–136. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arocho A, Chen B, Ladanyi M and Pan Q:
Validation of the 2-DeltaDeltaCt calculation as an alternate method
of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts.
Diagn Mol Pathol. 15:56–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Doyle EL, Booher NJ, Standage DS, Voytas
DF, Brendel VP, Vandyk JK and Bogdanove AJ: TAL Effector-Nucleotide
Targeter (TALE-NT) 2.0: tools for TAL effector design and target
prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:W117–W122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sanjana NE, Cong L, Zhou Y, Cunniff MM,
Feng G and Zhang F: A transcription activator-like effector toolbox
for genome engineering. Nat Protoc. 7:171–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pulkkinen K, Malm T, Turunen M, Koistinaho
J and Ylä-Herttuala S: Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro
and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially
regulated by miR-210. FEBS Lett. 582:2397–2401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kullander K, Mather NK, Diella F, Dottori
M, Boyd AW and Klein R: Kinase-dependent and kinase-independent
functions of EphA4 receptors in major axon tract formation in vivo.
Neuron. 29:73–84. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cutforth T, Moring L, Mendelsohn M, Nemes
A, Shah NM, Kim MM, Frisén J and Axel R: Axonal ephrin-As and
odorant receptors: coordinate determination of the olfactory
sensory map. Cell. 114:311–322. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cang J, Kaneko M, Yamada J, Woods G,
Stryker MP and Feldheim DA: Ephrin-as guide the formation of
functional maps in the visual cortex. Neuron. 48:577–589. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murai KK, Nguyen LN, Irie F, Yamaguchi Y
and Pasquale EB: Control of hippocampal dendritic spine morphology
through ephrin-A3/EphA4 signaling. Nat Neurosci. 6:153–160. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Iiizumi M, Hosokawa M, Takehara A, Chung
S, Nakamura T, Katagiri T, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O,
Nakamura Y, et al: EphA4 receptor, overexpressed in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma, promotes cancer cell growth. Cancer Sci.
97:1211–1216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Georgiou GK, Igglezou M, Sainis I, Vareli
K, Batsis H, Briasoulis E and Fatouros M: Impact of breast cancer
surgery on angiogenesis circulating biomarkers: a prospective
longitudinal study. World J Surg Oncol. 11:2132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Lorenzi M, Pescatori
M, Brioschi M, Kulshreshtha R, Banfi C, Stubbs A, Calin GA, Ivan M,
et al: An integrated approach for experimental target
identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J Biol Chem.
284:35134–35143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao J and Guan JL: Signal transduction by
focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:35–49.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miao H, Burnett E, Kinch M, Simon E and
Wang B: Activation of EphA2 kinase suppresses integrin function and
causes focal-adhesion-kinase dephosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol.
2:62–69. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brantley DM, Cheng N, Thompson EJ, Lin Q,
Brekken RA, Thorpe PE, Muraoka RS, Cerretti DP, Pozzi A, Jackson D,
et al: Soluble Eph A receptors inhibit tumor angiogenesis and
progression in vivo. Oncogene. 21:7011–7026. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kallergi G, Agelaki S, Markomanolaki H,
Georgoulias V and Stournaras C: Activation of FAK/PI3K/Rac1
signaling controls actin reorganization and inhibits cell motility
in human cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 20:977–986. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lim Y, Park H, Jeon J, Han I, Kim J, Jho
EH and Oh ES: Focal adhesion kinase is negatively regulated by
phosphorylation at tyrosine 407. J Biol Chem. 282:10398–10404.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|