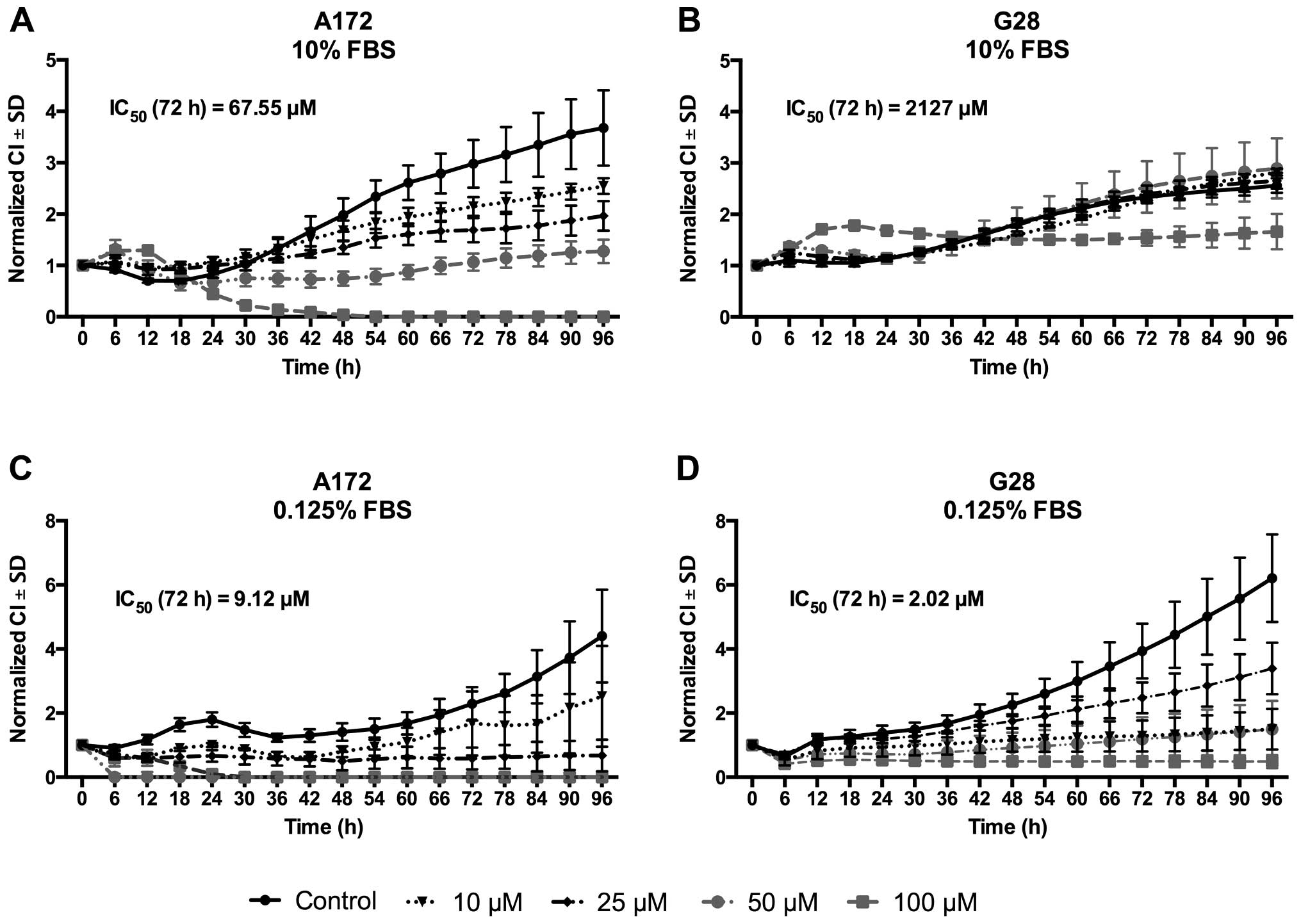
|
1
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch
DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK and DePinho RA: Malignant glioma: Genetics
and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hengstschläger M, Hölzl G and
Hengstschläger-Ottnad E: Different regulation of c-Myc- and
E2F-1-induced apoptosis during the ongoing cell cycle. Oncogene.
18:843–848. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiffer D, Cavalla P, Migheli A, Chiò A,
Giordana MT, Marino S and Attanasio A: Apoptosis and cell
proliferation in human neuroepithelial tumors. Neurosci Lett.
195:81–84. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Costello JF, Plass C, Arap W, Chapman VM,
held WA, Berger MS, Su Huang HJ and Cavenee WK: Cyclin-dependent
kinase 6 (CDK6) amplification in human gliomas identified using
two-dimensional separation of genomic DNA. Cancer Res.
57:1250–1254. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dirks PB, Hubbard SL, Murakami M and Rutka
JT: Cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase expression in human
astrocytoma cell lines. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 56:291–300. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Olson JJ, Barnett D, Yang J, Assietti R,
Cotsonis G and James CD: Gene amplification as a prognostic factor
in primary brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 4:215–222.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ono Y, Tamiya T, Ichikawa T, Kunishio K,
Matsumoto K, Furuta T, Ohmoto T, Ueki K and Louis DN: Malignant
astrocytomas with homozygous CDKN2/p16 gene deletions have higher
Ki-67 proliferation indices. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
55:1026–1031. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rollbrocker B, Waha A, Louis DN, Wiestler
OD and von Deimling A: Amplification of the cyclin-dependent kinase
4 (CDK4) gene is associated with high cdk4 protein levels in
glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. 92:70–74. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Srivenugopal KS and Ali-Osman F: Deletions
and rearrangements inactivate the p16INK4 gene in human glioma
cells. Oncogene. 12:2029–2034. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP,
Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG and Moulinoux JP:
Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and
selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and
cdk5. Eur J Biochem. 243:527–536. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schutte B, Nieland L, Van Engeland M,
Henfling ME, Meijer L and Ramaekers FC: The effect of the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor olomoucine on cell cycle
kinetics. Exp Cell Res. 236:4–15. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nair BC, Vallabhaneni S, Tekmal RR and
Vadlamudi RK: Roscovitine confers tumor suppressive effect on
therapy-resistant breast tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res.
13:R802011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pizarro JG, Folch J, Junyent F, Verdaguer
E, Auladell C, Beas-Zarate C, Pallàs M and Camins A: Antiapoptotic
effects of roscovitine on camptothecin-induced DNA damage in
neuro-blastoma cells. Apoptosis. 16:536–550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arısan ED, Coker A and Palavan-Ünsal N:
Polyamine depletion enhances the roscovitine-induced apoptosis
through the activation of mitochondria in HCT116 colon carcinoma
cells. Amino Acids. 42:655–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cho SJ, Kim YJ, Surh YJ, Kim BM and Lee
SK: Ibulocydine is a novel prodrug Cdk inhibitor that effectively
induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
286:19662–19671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu NA, Jiang H, Ben-Shlomo A, Wawrowsky
K, Fan XM, Lin S and Melmed S: Targeting zebrafish and murine
pituitary corti-cotroph tumors with a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)
inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:8414–8419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Coley HM, Safuwan NA, Chivers P,
Papacharalbous E, Giannopoulos T, Butler-Manuel S, Madhuri K,
Lovell DP and Crook T: The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
p57(Kip2) is epigenetically regulated in carboplatin resistance and
results in collateral sensitivity to the CDK inhibitor seliciclib
in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:482–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wellwood J and Taylor K: Central nervous
system prophylaxis in haematological malignancies. Intern Med J.
32:252–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sallam H, Jimenez P, Song H, Vita M,
Cedazo-Minguez A and Hassan M: Age-dependent pharmacokinetics and
effect of rosco-vitine on Cdk5 and Erk1/2 in the rat brain.
Pharmacol Res. 58:32–37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yakisich JS, Sidén A, Idoyaga Vargas V,
Eneroth P and Cruz M: Early inhibition of DNA synthesis in the
developing rat cerebral cortex by the purine analogues olomoucine
and roscovitine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 243:674–677. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McClue SJ and Stuart I: Metabolism of the
trisubstituted purine cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib
(R-roscovitine) in vitro and in vivo. Drug Metab Dispos.
36:561–570. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dhavan R and Tsai LH: A decade of CDK5.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:749–759. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hassan M, Sallam H and Hassan Z: The role
of pharmaco kinetics and pharmacodynamics in early drug development
with reference to the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)
inhibitor-roscovitine. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 11:165–178.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paprskárová M, Krystof V, Jorda R, Dzubák
P, Hajdúch M, Wesierska-Gadek J and Strnad M: Functional p53 in
cells contributes to the anticancer effect of the cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitor roscovitine. J Cell Biochem. 107:428–437. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wesierska-Gadek J, Borza A, Komina O and
Maurer M: Impact of roscovitine, a selective CDK inhibitor, on
cancer cells: Bi-functionality increases its therapeutic potential.
Acta Biochim Pol. 56:495–501. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Alvi AJ, Austen B, Weston VJ, Fegan C,
MacCallum D, Gianella-Borradori A, Lane DP, Hubank M, Powell JE,
Wei W, et al: A novel CDK inhibitor, CYC202 (R-roscovitine),
overcomes the defect in p53-dependent apoptosis in B-CLL by
down-regulation of genes involved in transcription regulation and
survival. Blood. 105:4484–4491. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Slovackova J, Smarda J and Smardova J:
Roscovitine-induced apoptosis of H1299 cells depends on functional
status of p53. Neoplasma. 59:606–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lim YM, Yamasaki Y and Tsuda L: Ebi
alleviates excessive growth signaling through multiple epigenetic
functions in Drosophila. Genes Cells. 18:909–920. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Węsierska-Gądek J, Gritsch D, Zulehner N,
Komina O and Maurer M: Roscovitine, a selective CDK inhibitor,
reduces the basal and estrogen-induced phosphorylation of ER-α in
human ER-positive breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:761–772.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bach S, Knockaert M, Reinhardt J, Lozach
O, Schmitt S, Baratte B, Koken M, Coburn SP, Tang L, Jiang T, et
al: Roscovitine targets, protein kinases and pyridoxal kinase. J
Biol Chem. 280:31208–31219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Whittaker SR, Walton MI, Garrett MD and
Workman P: The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202
(R-roscovitine) inhibits retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation,
causes loss of cyclin D1, and activates the mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway. Cancer Res. 64:262–272. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bertoli C, Klier S, McGowan C, Wittenberg
C and de Bruin RA: Chk1 inhibits e2F6 repressor function in
response to replication stress to maintain cell-cycle
transcription. Curr Biol. 23:1629–1637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fischer PM and Lane DP: inhibitors of
cyclin-dependent kinases as anti-cancer therapeutics. Curr Med
Chem. 7:1213–1245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
MacCallum DE, Melville J, Frame S, Watt K,
Anderson S, Gianella-Borradori A, Lane DP and Green SR: Seliciclib
(CYC202, R-Roscovitine) induces cell death in multiple myeloma
cells by inhibition of RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription
and down-regulation of Mcl-1. Cancer Res. 65:5399–5407. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Erguven M, Bilir A, Yazihan N, Korkmaz S,
Aktas E, Ovalioglu C, Dundar T and Seyithanoglu H: Imatinib
mesylate decreases the cytotoxic effect of roscovitine on human
glioblastoma cells in vitro and the role of midkine. Oncol Lett.
3:200–208. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Whittaker SR, Te Poele RH, Chan F,
Linardopoulos S, Walton MI, Garrett MD and Workman P: The
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib (R-roscovitine;
CYC202) decreases the expression of mitotic control genes and
prevents entry into mitosis. Cell Cycle. 6:3114–3131. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murphy ÁC, Weyhenmeyer B, Noonan J,
Kilbride SM, Schimansky S, Loh KP, Kögel D, Letai AG, Prehn JH and
Murphy BM: Modulation of Mcl-1 sensitizes glioblastoma to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 19:629–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Pawlik TM and Keyomarsi K: Role of cell
cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 59:928–942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sato Y, Kurose A, Ogawa A, Ogasawara K,
Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z and Sawai T: Diversity of DNA damage
response of astrocytes and glioblastoma cell lines with various p53
status to treatment with etoposide and temozolomide. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:452–457. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Akudugu J, Gäde G and Böhm L: Cytotoxicity
of azadirachtin A in human glioblastoma cell lines. Life Sci.
68:1153–1160. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang T, Jiang T, Zhang F, Li C, Zhou YA,
Zhu YF and Li XF: Involvement of p21Waf1/Cip1 cleavage
during roscovitine-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 23:239–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Schmidt M and Fan z: Protection against
chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity by cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors (CKI) in CKI-responsive cells compared with
CKI-unresponsive cells. Oncogene. 20:6164–6171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gartel AL and Tyner AL: The role of the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:639–649. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Neyns B, D'haeseleer M, Rogiers A, Van de
Cauter J, Chaskis C, Michotte A and Strik H: The role of cytotoxic
drugs in the treatment of central nervous system gliomas. Acta
Neurol Belg. 110:1–14. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|