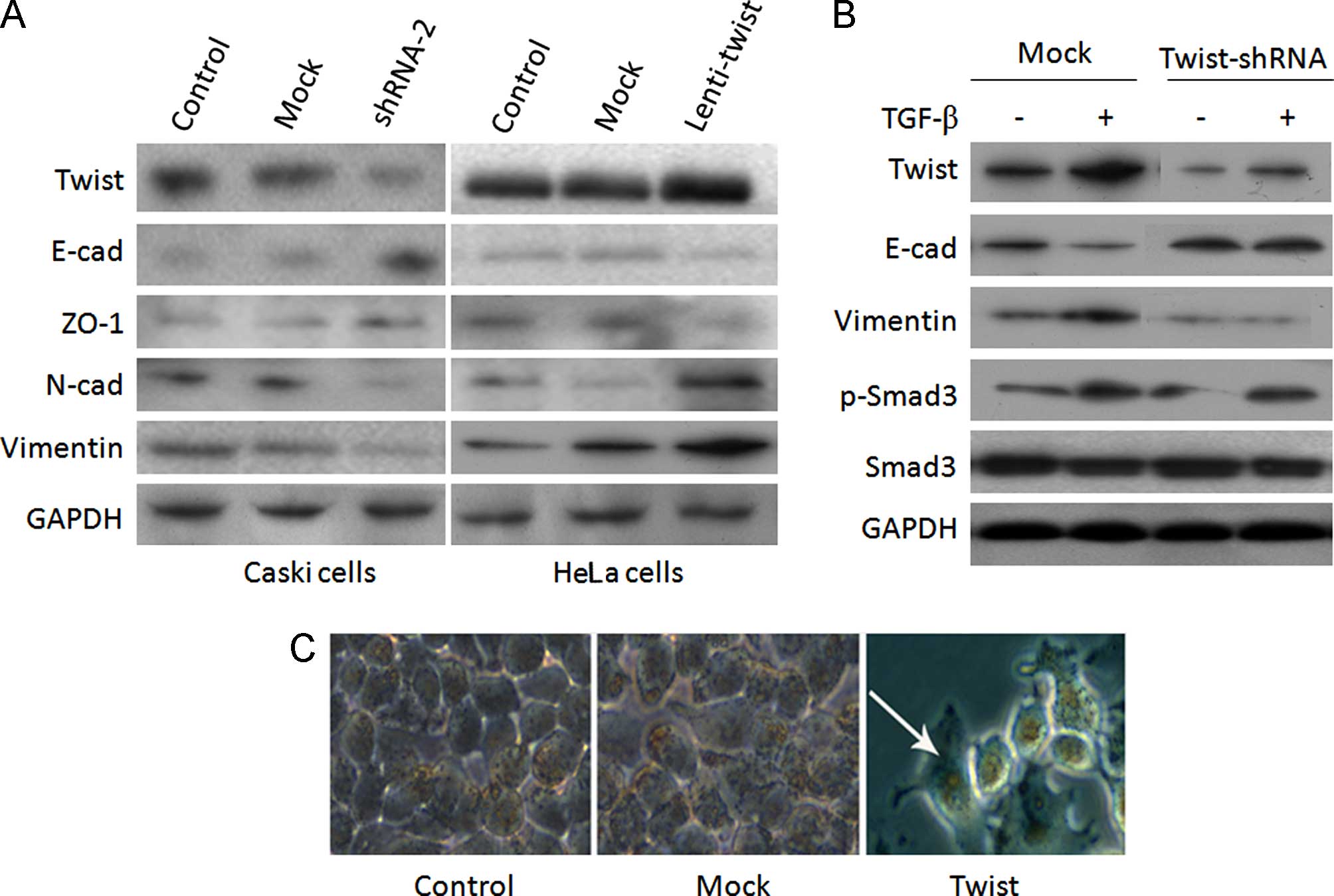
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Alemany L, de Sanjosé S, Tous S, Quint W,
Vallejos C, Shin HR, Bravo LE, Alonso P, Lima MA, Guimerà N, et al:
RIS HPV TT Study Group: Time trends of human papillomavirus types
in invasive cervical cancer, from 1940 to 2007. Int J Cancer.
135:88–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang L, Ci P, Shi J, Zhai K, Feng X,
Colombara D, Wang W, Qiao Y, Chen W and Wu Y: Distribution of
genital wart human papillomavirus genotypes in China: A
multi-center study. J Med Virol. 85:1765–1774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wen Y, Pan XF, Zhao ZM, Chen F, Fu CJ, Li
SQ, Zhao Y, Chang H, Xue QP and Yang CX: Knowledge of human
papillomavirus (HPV) infection, cervical cancer, and HPV vaccine
and its correlates among medical students in Southwest China: A
multi-center cross-sectional survey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5773–5779. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang Y and Massagué J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Christiansen JJ and Rajasekaran AK:
Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite
for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 66:8319–8326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bao W, Qiu H, Yang T, Luo X, Zhang H and
Wan X: Upregulation of TrkB promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and anoikis resistance in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS
One. 8:e706162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Castanon I and Baylies MK: A Twist in
fate: Evolutionary comparison of Twist structure and function.
Gene. 287:11–22. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen ZF and Behringer RR: Twist is
required in head mesenchyme for cranial neural tube morphogenesis.
Genes Dev. 9:686–699. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
El Ghouzzi V, Legeai-Mallet L, Aresta S,
Benoist C, Munnich A, de Gunzburg J and Bonaventure J:
Saethre-Chotzen mutations cause Twist protein degradation or
impaired nuclear location. Hum Mol Genet. 9:813–819. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yousfi M, Lasmoles F, El Ghouzzi V and
Marie PJ: Twist haploinsufficiency in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
induces calvarial osteoblast apoptosis due to increased TNFalpha
expression and caspase-2 activation. Hum Mol Genet. 11:359–369.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mironchik Y, Winnard PT Jr, Vesuna F, Kato
Y, Wildes F, Pathak AP, Kominsky S, Artemov D, Bhujwalla Z, Van
Diest P, et al: Twist overexpression induces in vivo angiogenesis
and correlates with chromosomal instability in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:10801–10809. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wallerand H, Robert G, Pasticier G, Ravaud
A, Ballanger P, Reiter RE and Ferrière JM: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing factor Twist is an
attractive target in advanced and/or metastatic bladder and
prostate cancers. Urol Oncol. 28:473–479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhu DY, Guo QS, Li YL, Cui B, Guo J, Liu
JX and Li P: Twist1 correlates with poor differentiation and
progression in gastric adenocarcinoma via elevation of FGFR2
expression. World J Gastroenterol. 20:18306–18315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhu K, Chen L, Han X and Wang J and Wang
J: Short hairpin RNA targeting Twist1 suppresses cell proliferation
and improves chemosensitivity to cisplatin in HeLa human cervical
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1027–1034. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tirumani SH, Shanbhogue AK and Prasad SR:
Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of endometrial and
cervical carcinomas. Radiol Clin North Am. 51:1087–1110. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bao W, Wang HH, Tian FJ, He XY, Qiu MT,
Wang JY, Zhang HJ, Wang LH and Wan XP: A TrkB-STAT3-miR-204-5p
regulatory circuitry controls proliferation and invasion of
endometrial carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 12:1552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shibata K, Kajiyama H, Ino K, Terauchi M,
Yamamoto E, Nawa A, Nomura S and Kikkawa F: Twist expression in
patients with cervical cancer is associated with poor disease
outcome. Ann Oncol. 19:81–85. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hou CH, Lin FL, Hou SM and Liu JF: Cyr61
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis of
osteosarcoma by Raf-1/MEK/ERK/Elk-1/TWIST-1 signaling pathway. Mol
Cancer. 13:2362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choo KB, Huang CJ, Chen CM, Han CP and au
LC: Jun-B oncogene aberrations in cervical cancer cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 93:249–253. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ndubisi B, Sanz S, Lu L, Podczaski E,
Benrubi G and Masood S: The prognostic value of HER-2/neu oncogene
in cervical cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 27:396–401. 1997.
|
|
25
|
Mehdi SJ, Alam MS, Batra S and Rizvi MM:
Allelic loss of 6q25-27, the PARKIN tumor suppressor gene locus, in
cervical carcinoma. Med Oncol. 28:1520–1526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rizvi MM, Alam MS, Ali A, Mehdi SJ, Batra
S and Mandal AK: Aberrant promoter methylation and inactivation of
PTEN gene in cervical carcinoma from Indian population. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 137:1255–1262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Alam MS, Ali A, Mehdi SJ, Alyasiri NS,
Kazim Z, Batra S, Mandal AK and Rizvi MM: HPV typing and its
relation with apoptosis in cervical carcinoma from Indian
population. Tumour Biol. 33:17–22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rughooputh S, Manraj S, Eddoo R and
Greenwell P: Expression of the c-myc oncogene and the presence of
HPV 18: Possible surrogate markers for cervical cancer? Br J Biomed
Sci. 66:74–78. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee MY, Chou CY, Tang MJ and Shen MR:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: Correlation
with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4743–4750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Qian W, Zhang J, Dong Y, Shi C, Liu
Z and Wu S: The indicative function of Twist2 and E-cadherin in HPV
oncogene-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 33:639–650. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Wang T, Li Y, Wang W, Tuerhanjiang A, Wu
Z, Yang R, Yuan M, Ma D, Wang W and Wang S: Twist2, the key Twist
isoform related to prognosis, promotes invasion of cervical cancer
by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and blocking
senescence. Hum Pathol. 45:1839–1846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG and Schumacher
U: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focus on metastatic cascade,
alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol
Cancer. 12:1072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Wang W, Wang W, Yang R, Wang T, Su
T, Weng D, Tao T, Li W, Ma D, et al: Correlation of TWIST2
up-regulation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition during
tumorigenesis and progression of cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
124:112–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Its role in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356(2 Pt B): 321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fang X, Cai Y, Liu J, Wang Z, Wu Q, Zhang
Z, Yang CJ, Yuan L and Ouyang G: Twist2 contributes to breast
cancer progression by promoting an epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem-like cell self-renewal. Oncogene.
30:4707–4720. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lamouille S and Derynck R: Cell size and
invasion in TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition
is regulated by activation of the mToR pathway. J Cell Biol.
178:437–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Comerci JT Jr, Runowicz CD, Flanders KC,
De Victoria C, Fields AL, Kadish AS and Goldberg GL: Altered
expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in cervical
neoplasia as an early biomarker in carcinogenesis of the uterine
cervix. Cancer. 77:1107–1114. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kloth JN, Fleuren GJ, Oosting J, de
Menezes RX, Eilers PH, Kenter GG and Gorter A: Substantial changes
in gene expression of Wnt, MAPK and TNFalpha pathways induced by
TGF-beta1 in cervical cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis.
26:1493–1502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|