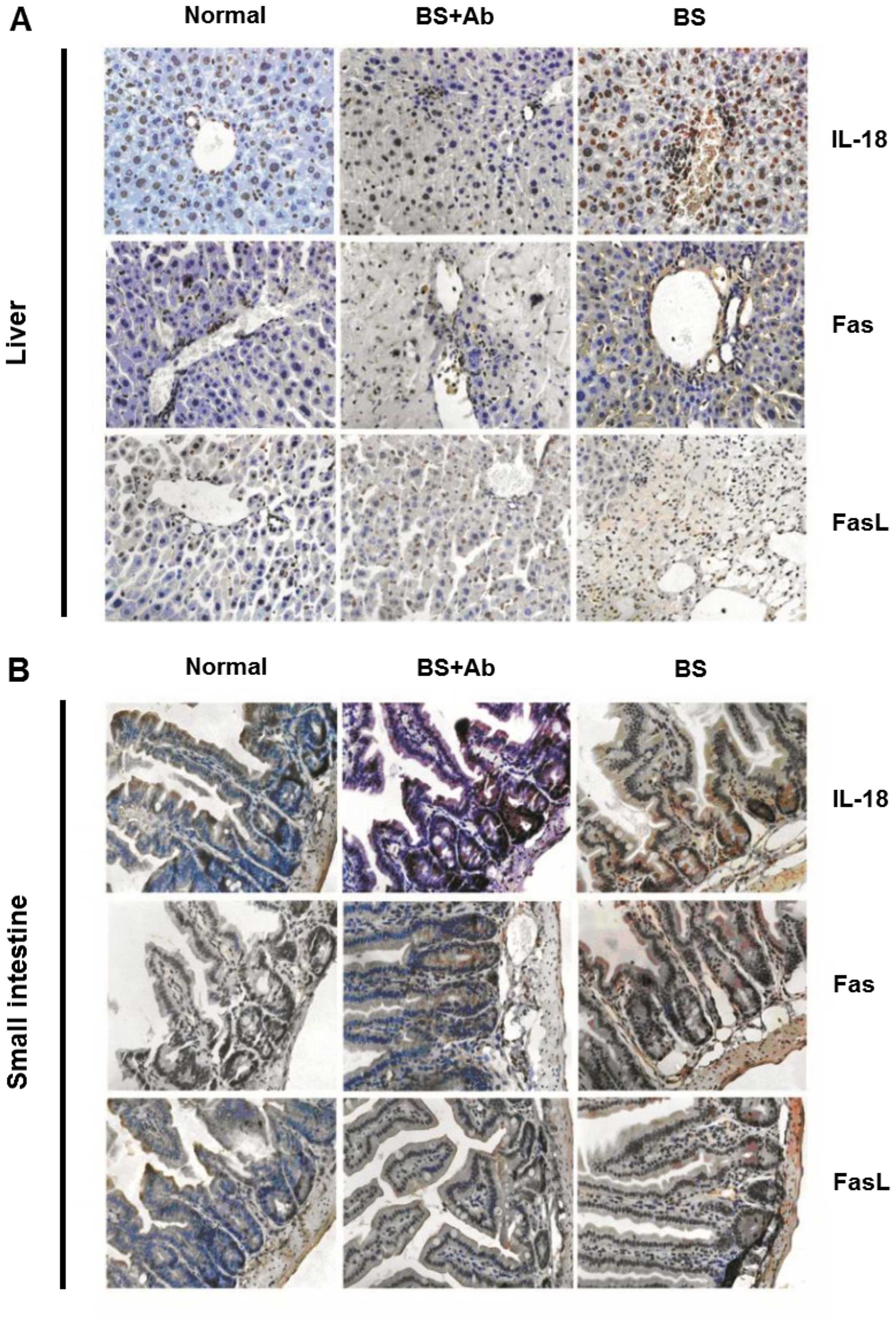
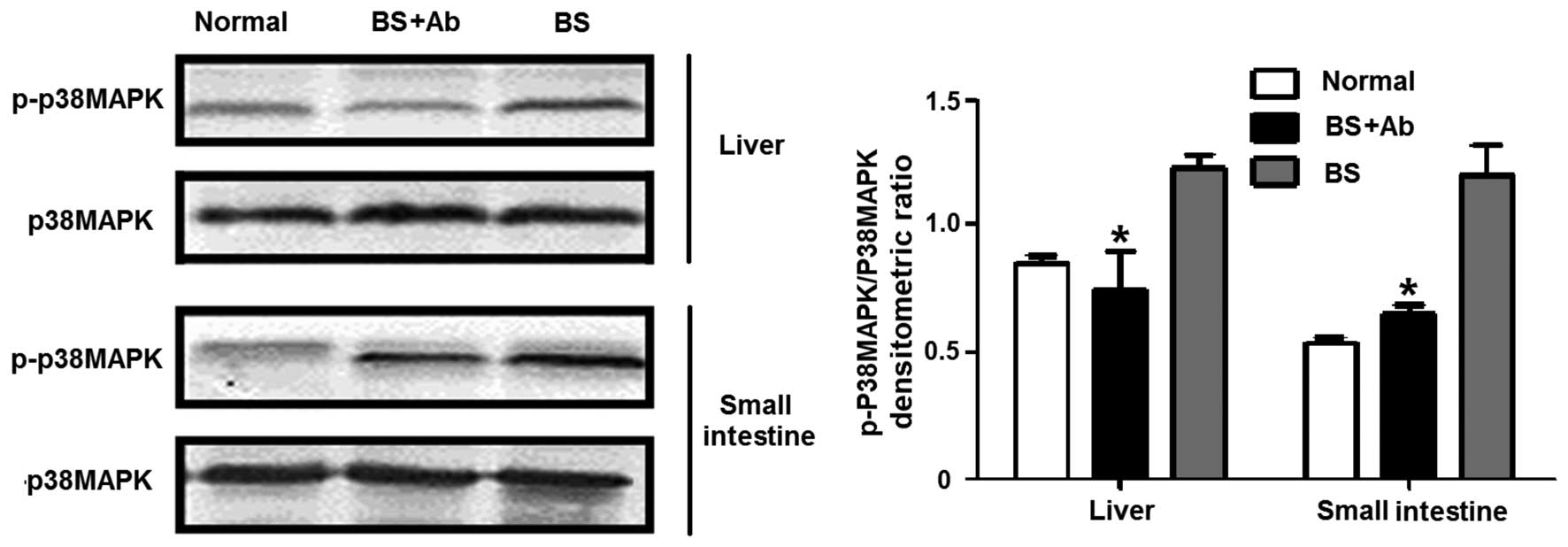
|
1
|
Storb R: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem
cell transplantation - yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Exp Hematol.
31:1–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P and Holler
E: Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 373:1550–1561. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tobin LM, Healy ME, English K and Mahon
BP: Human mesenchymal stem cells suppress donor CD4(+) T cell
proliferation and reduce pathology in a humanized mouse model of
acute graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 172:333–348.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reddy P: Pathophysiology of acute
graft-versus-host disease. Hematol Oncol. 21:149–161. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Antin JH and Ferrara JL: Cytokine
dysregulation and acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood.
80:2964–2968. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Levine JE, Paczesny S and Sarantopoulos S:
Clinical applications for biomarkers of acute and chronic
graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 18(Suppl
1): S116–S124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan B, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Cheng H, Wu Y, Song
G, Chen W, Zeng L and Xu K: Deviated balance between Th1 and Th17
cells exacerbates acute graft-versus-host disease in mice.
Cytokine. 68:69–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tawara I, Maeda Y, Sun Y, Lowler KP, Liu
C, Toubai T, McKenzie AN and Reddy P: Combined Th2 cytokine
deficiency in donor T cells aggravates experimental acute
graft-vs-host disease. Exp Hematol. 36:988–996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reddy P, Arora M, Guimond M and Mackall
CL: GVHD: A continuing barrier to the safety of allogeneic
transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 15(Suppl 1):
162–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmaltz C, Alpdogan O, Horndasch KJ,
Muriglan SJ, Kappel BJ, Teshima T, Ferrara JL, Burakoff SJ and van
den Brink MR: Differential use of Fas ligand and perforin cytotoxic
pathways by donor T cells in graft-versus-host disease and
graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood. 97:2886–2895. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maeda Y, Levy RB, Reddy P, Liu C,
Clouthier SG, Teshima T and Ferrara JL: Both perforin and Fas
ligand are required for the regulation of alloreactive
CD8+ T cells during acute graft-versus-host disease.
Blood. 105:2023–2027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fremond CM, Togbe D, Doz E, Rose S,
Vasseur V, Maillet I, Jacobs M, Ryffel B and Quesniaux VF: IL-1
receptor-mediated signal is an essential component of
MyD88-dependent innate response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection. J Immunol. 179:1178–1189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chandrasekar B, Vemula K, Surabhi RM,
Li-Weber M, Owen-Schaub LB, Jensen LE and Mummidi S: Activation of
intrinsic and extrinsic proapoptotic signaling pathways in
interleukin-18-mediated human cardiac endothelial cell death. J
Biol Chem. 279:20221–20233. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu Y, Sakamaki S, Kuroda H, Kusakabe T,
Konuma Y, Akiyama T, Fujimi A, Takemoto N, Nishiie K, Matsunaga T,
et al: Prevention of lethal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice
by oral administration of T helper 1 inhibitor, TAK-603. Blood.
97:1123–1130. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cooke KR, Kobzik L, Martin TR, Brewer J,
Delmonte J Jr, Crawford JM and Ferrara JL: An experimental model of
idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: I.
The roles of minor H antigens and endotoxin. Blood. 88:3230–3239.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro
CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ and Littman DR: The orphan
nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of
proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell.
126:1121–1133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Tawara I, Toubai T and Reddy P:
Pathophysiology of acute graft-versus-host disease: Recent
advances. Transl Res. 150:197–214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilson SP and Cassel SL:
Inflammasome-mediated autoinflammatory disorders. Postgrad Med.
122:125–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miossec P: IL-17 and Th17 cells in human
inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect. 11:625–630. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nishimoto N and Kishimoto T: Interleukin
6: From bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2:619–626.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vogelsang GB, Lee L and Bensen-Kennedy DM:
Pathogenesis and treatment of graft-versus-host disease after bone
marrow transplant. Annu Rev Med. 54:29–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Reddy P, Teshima T, Kukuruga M, Ordemann
R, Liu C, Lowler K and Ferrara JL: Interleukin-18 regulates acute
graft-versus-host disease by enhancing Fas-mediated donor T cell
apoptosis. J Exp Med. 194:1433–1440. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wasem C, Frutschi C, Arnold D, Vallan C,
Lin T, Green DR, Mueller C and Brunner T: Accumulation and
activation-induced release of preformed Fas (CD95) ligand during
the pathogenesis of experimental graft-versus-host disease. J
Immunol. 167:2936–2941. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yi T, Zhao D, Lin CL, Zhang C, Chen Y,
Todorov I, LeBon T, Kandeel F, Forman S and Zeng D: Absence of
donor Th17 leads to augmented Th1 differentiation and exacerbated
acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 112:2101–2110. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kalina U, Kauschat D, Koyama N,
Nuernberger H, Ballas K, Koschmieder S, Bug G, Hofmann WK, Hoelzer
D and Ottmann OG: IL-18 activates STAT3 in the natural killer cell
line 92, augments cytotoxic activity, and mediates IFN-gamma
production by the stress kinase p38 and by the extracellular
regulated kinases p44erk−1 and p42erk−21. J
Immunol. 165:1307–1313. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Calvani N, Tucci M, Richards HB, Tartaglia
P and Silvestris F: Th1 cytokines in the pathogenesis of lupus
nephritis: The role of IL-18. Autoimmun Rev. 4:542–548. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gracie JA, Forsey RJ, Chan WL, Gilmour A,
Leung BP, Greer MR, Kennedy K, Carter R, Wei XQ, Xu D, et al: A
proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin
Invest. 104:1393–1401. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller WP, Srinivasan S,
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Singh K, Sen S, Hamby K, Deane T, Stempora
L, Beus J, Turner A, et al: GVHD after haploidentical
transplantation: A novel, MHC-defined rhesus macaque model
identifies CD28− CD8+ T cells as a reservoir
of breakthrough T-cell proliferation during costimulation blockade
and sirolimus-based immunosuppression. Blood. 116:5403–5418. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arnold D, Wasem C, Juillard P, Graber P,
Cima I, Frutschi C, Herren S, Jakob S, Alouani S, Mueller C, et al:
IL-18-independent cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation and IFN-gamma
production during experimental acute graft-versus-host disease. Int
Immunol. 14:503–511. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang MJ, Homer RJ, Gallo A, Lee CG,
Crothers KA, Cho SJ, Rochester C, Cain H, Chupp G, Yoon HJ, et al:
IL-18 is induced and IL-18 receptor alpha plays a critical role in
the pathogenesis of cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary emphysema and
inflammation. J Immunol. 178:1948–1959. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Halpern MD, Khailova L, Molla-Hosseini D,
Arganbright K, Reynolds C, Yajima M, Hoshiba J and Dvorak B:
Decreased development of necrotizing enterocolitis in
IL-18-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
294:G20–G26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T and Hume
DA: Interferon-gamma: An overview of signals, mechanisms and
functions. J Leukoc Biol. 75:163–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Olee T, Hashimoto S, Quach J and Lotz M:
IL-18 is produced by articular chondrocytes and induces
proinflammatory and catabolic responses. J Immunol. 162:1096–1100.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|