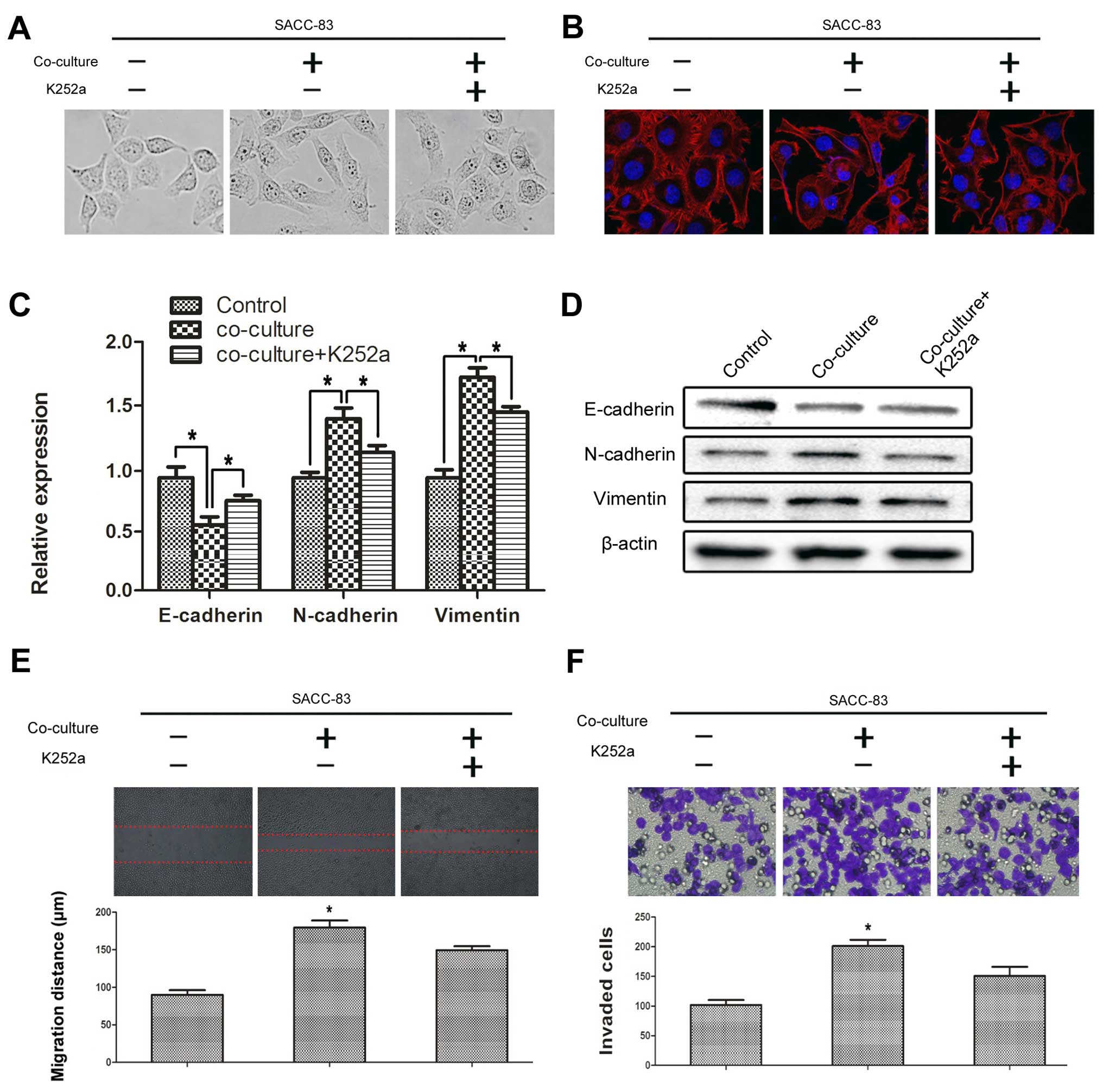
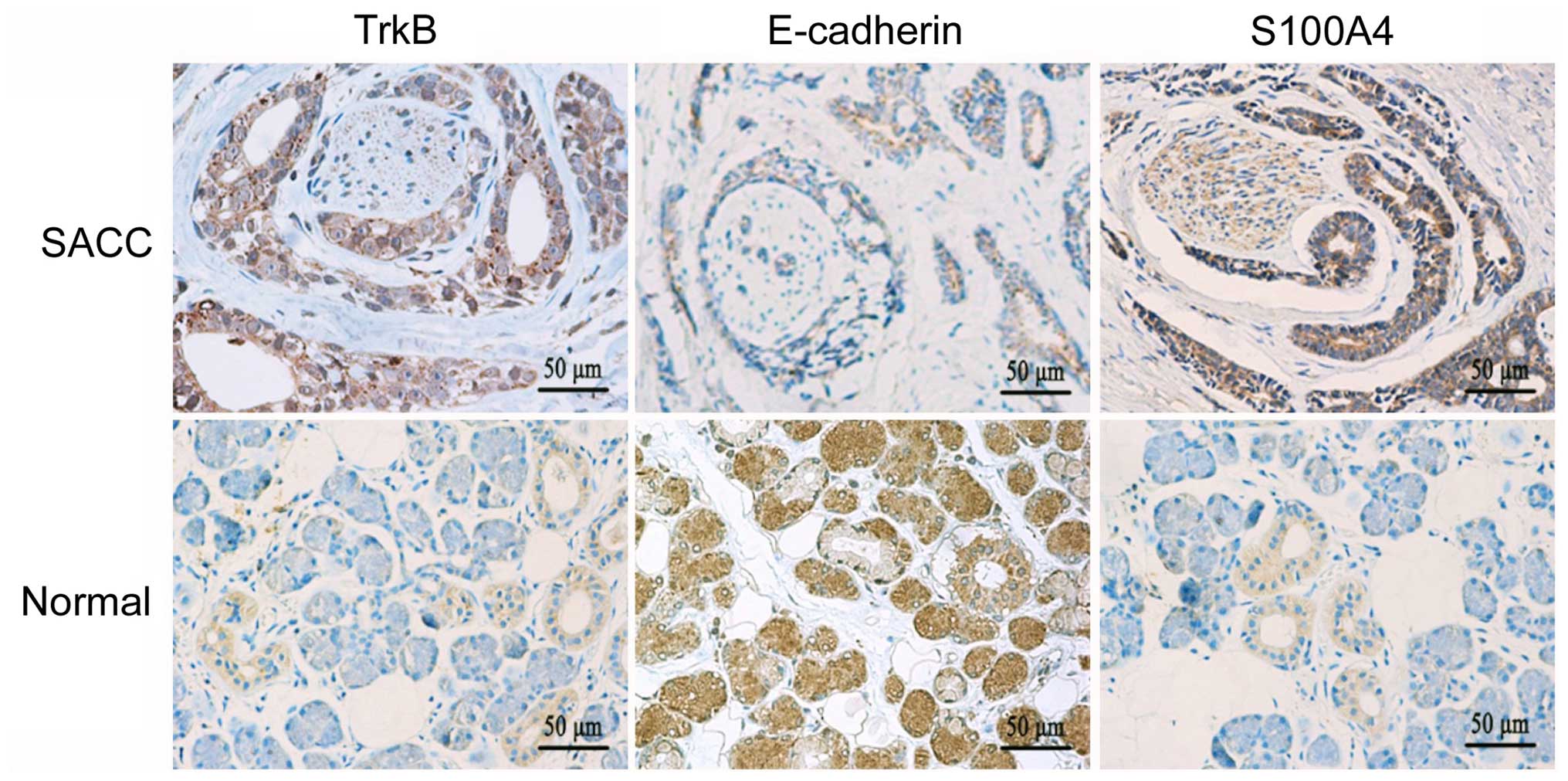
|
1
|
Tian Z, Li L, Wang L, Hu Y and Li J:
Salivary gland neoplasms in oral and maxillofacial regions: A
23-year retrospective study of 6982 cases in an eastern Chinese
population. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 39:235–242. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ,
Vander Poorten V, Triantafyllou A, Hunt JL, Strojan P, Rinaldo A,
Haigentz M Jr, Takes RP, et al: Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the
head and neck - An update. Oral Oncol. 51:652–661. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Amit M, Binenbaum Y, Trejo-Leider L,
Sharma K, Ramer N, Ramer I, Agbetoba A, Miles B, Yang X, Lei D, et
al: International collaborative validation of intraneural invasion
as a prognostic marker in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and
neck. Head Neck. 37:1038–1045. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jessen KR, Mirsky R and Lloyd AC: Schwann
cells: Development and role in nerve repair. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 7:a0204872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Benarroch EE: Brain-derived neurotrophic
factor: Regulation, effects, and potential clinical relevance.
Neurology. 84:1693–1704. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang X, Martin TA and Jiang WG: Biological
influence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on breast cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1541–1546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tanaka K, Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y,
Saigusa S, Kawamura M, Araki T, Uchida K, Mohri Y and Kusunoki M:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced
tropo-myosin-related kinase B (Trk B) signaling is a potential
therapeutic target for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e964102014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jia S, Wang W, Hu Z, Shan C, Wang L, Wu B,
Yang Z, Yang X and Lei D: BDNF mediated TrkB activation contributes
to the EMT progression and the poor prognosis in human salivary
adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 51:64–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee SJ, Choi SY, Kim WJ, Ji M, Lee TG, Son
BR, Yoon SM, Sung R, Lee EJ, Youn SJ, et al: Combined aberrant
expression of E-cadherin and S100A4, but not β-catenin is
associated with disease-free survival and overall survival in
colorectal cancer patients. Diagn Pathol. 8:992013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang X, Jing D, Liu L, Shen Z, Ju J, Ma C
and Sun M: Downregulation of p53 promotes in vitro perineural
invasive activity of human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like changes. Oncol Rep.
33:1650–1656. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Demir IE, Boldis A, Pfitzinger PL, Teller
S, Brunner E, Klose N, Kehl T, Maak M, Lesina M, Laschinger M, et
al: Investigation of Schwann cells at neoplastic cell sites before
the onset of cancer invasion. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:1062014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen W, Dong S, Zhou J and Sun M:
Investigation of myoepi-thelial cell differentiation into
Schwann-like cells in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma associated
with perineural invasion. Mol Med Rep. 6:755–759. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tao Y: Isolation and culture of Schwann
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1018:93–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang X, Zhang P, Ma Q, Kong L, Li Y, Liu B
and Lei D: EMMPRIN silencing inhibits proliferation and perineural
invasion of human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells in vitro
and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:85–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang X, Zhang P, Ma Q, Kong L, Li Y, Liu B
and Lei D: EMMPRIN contributes to the in vitro invasion of human
salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1123–1127.
2012.
|
|
17
|
Dantas AN, de Morais EF, Macedo RA, Tinoco
JM and Morais ML: Clinical-pathological characteristics and
perineural invasion in adenoid cystic carcinoma: A systematic
review. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol (Engl Ed). 8:329–335. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Bapat AA, Hostetter G, Von Hoff DD and Han
H: Perineural invasion and associated pain in pancreatic cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:695–707. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moreira DM, Fleshner NE and Freedland SJ:
Baseline perineural invasion is associated with shorter time to
progression in men with prostate cancer undergoing active
surveillance: Results from the REDEEM study. J Urol. May
16–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Takemura Y, Imai S, Kojima H, Katagi M,
Yamakawa I, Kasahara T, Urabe H, Terashima T, Yasuda H, Chan L, et
al: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor from bone marrow-derived
cells promotes post-injury repair of peripheral nerve. PLoS One.
7:e445922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kupferman ME, Jiffar T, El-Naggar A,
Yilmaz T, Zhou G, Xie T, Feng L, Wang J, Holsinger FC, Yu D, et al:
TrkB induces EMT and has a key role in invasion of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:2047–2059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lam CT, Yang ZF, Lau CK, Tam KH, Fan ST
and Poon RT: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes
tumorigenesis via induction of neovascularization: Implication in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3123–3133. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanaka K, Shimura T, Kitajima T, Kondo S,
Ide S, Okugawa Y, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Araki T, et al:
Tropomyosin-related receptor kinase B at the invasive front and
tumour cell dedifferentiation in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
110:2923–2934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bill R and Christofori G: The relevance of
EMT in breast cancer metastasis: Correlation or causality? FEBS
Lett. 589:1577–1587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang W, Gu W, Qiu R, Shen C, YaohaoWu EY,
Zhang J, Zhou J, Guo Y, Li Z, Deng J, et al: miRNA-101 suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting HMGA2 in
pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. May
7–2015.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
26
|
Rudisch A, Dewhurst MR, Horga LG, Kramer
N, Harrer N, Dong M, van der Kuip H, Wernitznig A, Bernthaler A,
Dolznig H, et al: High EMT signature score of invasive non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells correlates with NFκB driven
colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2/GM-CSF) secretion by neighboring
stromal fibroblasts. PLoS One. 10:e01242832015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ricci A, De Vitis C, Noto A, Fattore L,
Mariotta S, Cherubini E, Roscilli G, Liguori G, Scognamiglio G,
Rocco G, et al: TrkB is responsible for EMT transition in malignant
pleural effusions derived cultures from adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Cell Cycle. 12:1696–1703. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Izquierdo F, Suárez-Vilela D and Honrado
E: Perineurial cells in granular cell tumors and neoplasms with
perineural invasion: An immunohistochemical study. Am J
Dermatopathol. 34:800–809. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park K, Chen Z, MacDonald TY, Siddiqui J,
Ye H, Erbersdobler A, Shevchuk MM, Robinson BD, Sanda MG,
Chinnaiyan AM, et al: Prostate cancer with Paneth cell-like
neuroendocrine differentiation has recognizable histomorphology and
harbors AURKA gene amplification. Hum Pathol. 45:2136–2143. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kwon SY, Bae YK, Gu MJ, Choi JE, Kang SH,
Lee SJ, Kim A, Jung HR, Kang SH, Oh HK, et al: Neuroendocrine
differentiation correlates with hormone receptor expression and
decreased survival in patients with invasive breast carcinoma.
Histopathology. 64:647–659. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reed RJ and Leonard DD: Neurotropic
melanoma. A variant of desmoplastic melanoma. Am J Surg Pathol.
3:301–311. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iwamoto S, Burrows RC, Agoff SN, Piepkorn
M, Bothwell M and Schmidt R: The p75 neurotrophin receptor,
relative to other Schwann cell and melanoma markers, is abundantly
expressed in spindled melanomas. Am J Dermatopathol. 23:288–294.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|