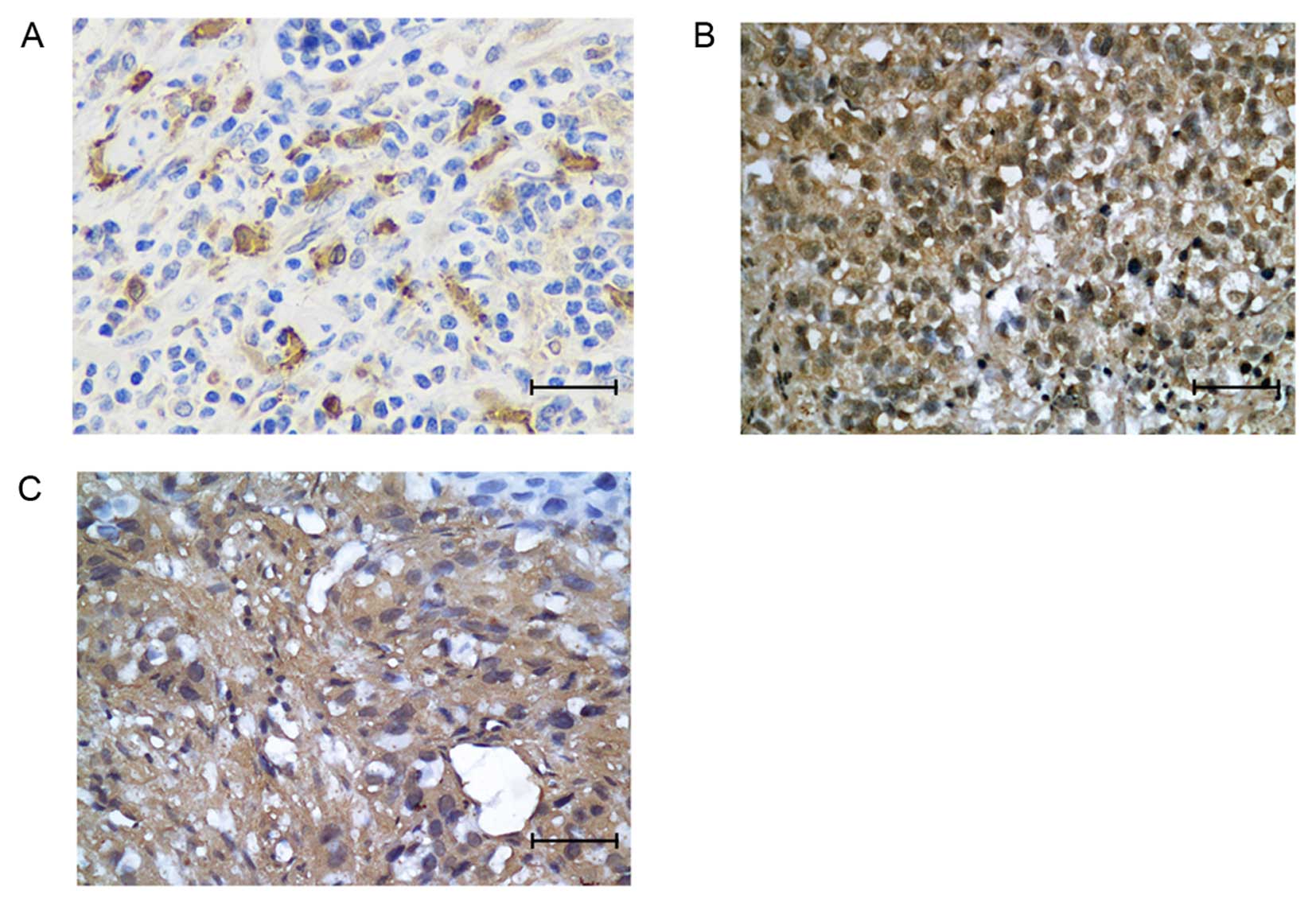
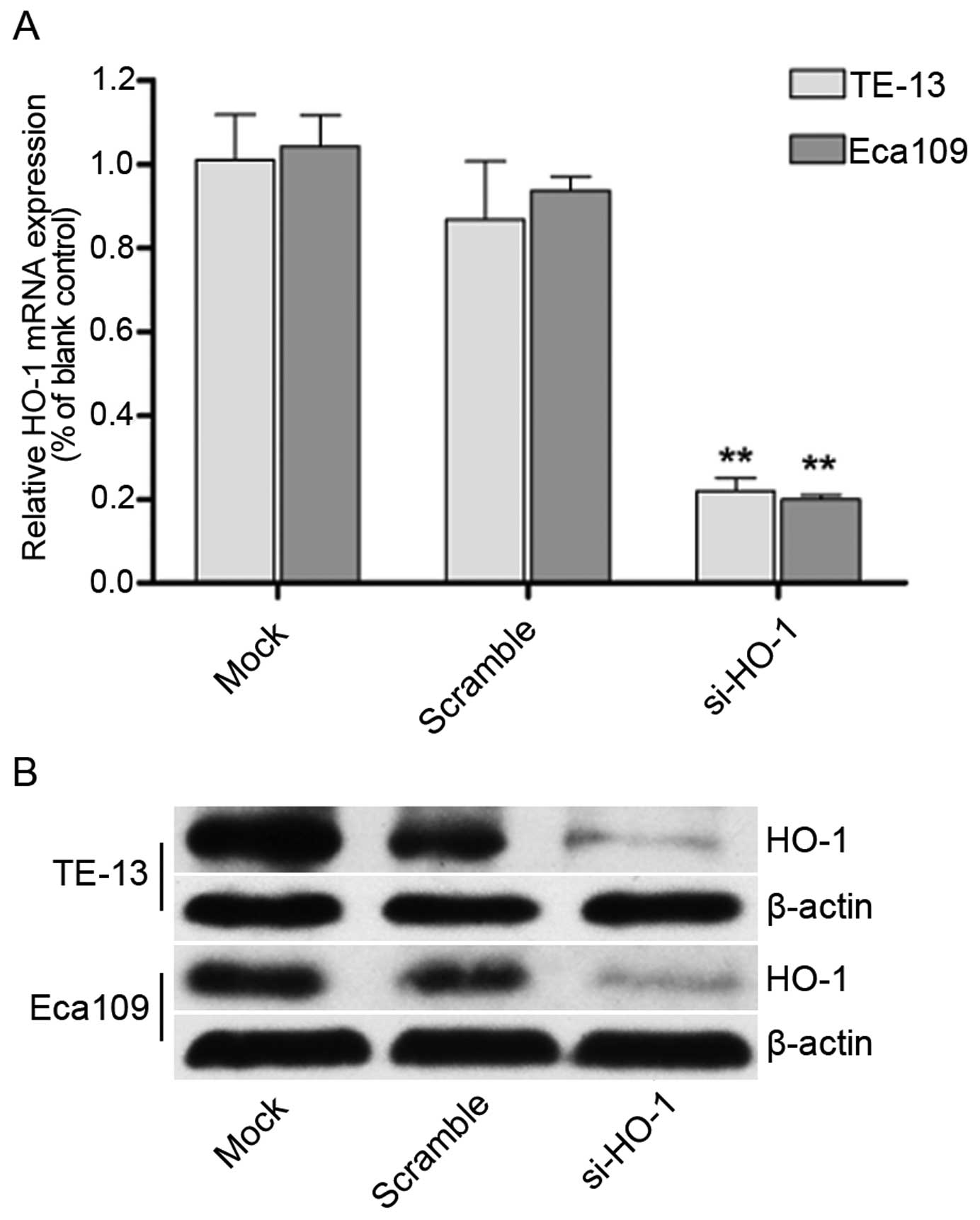
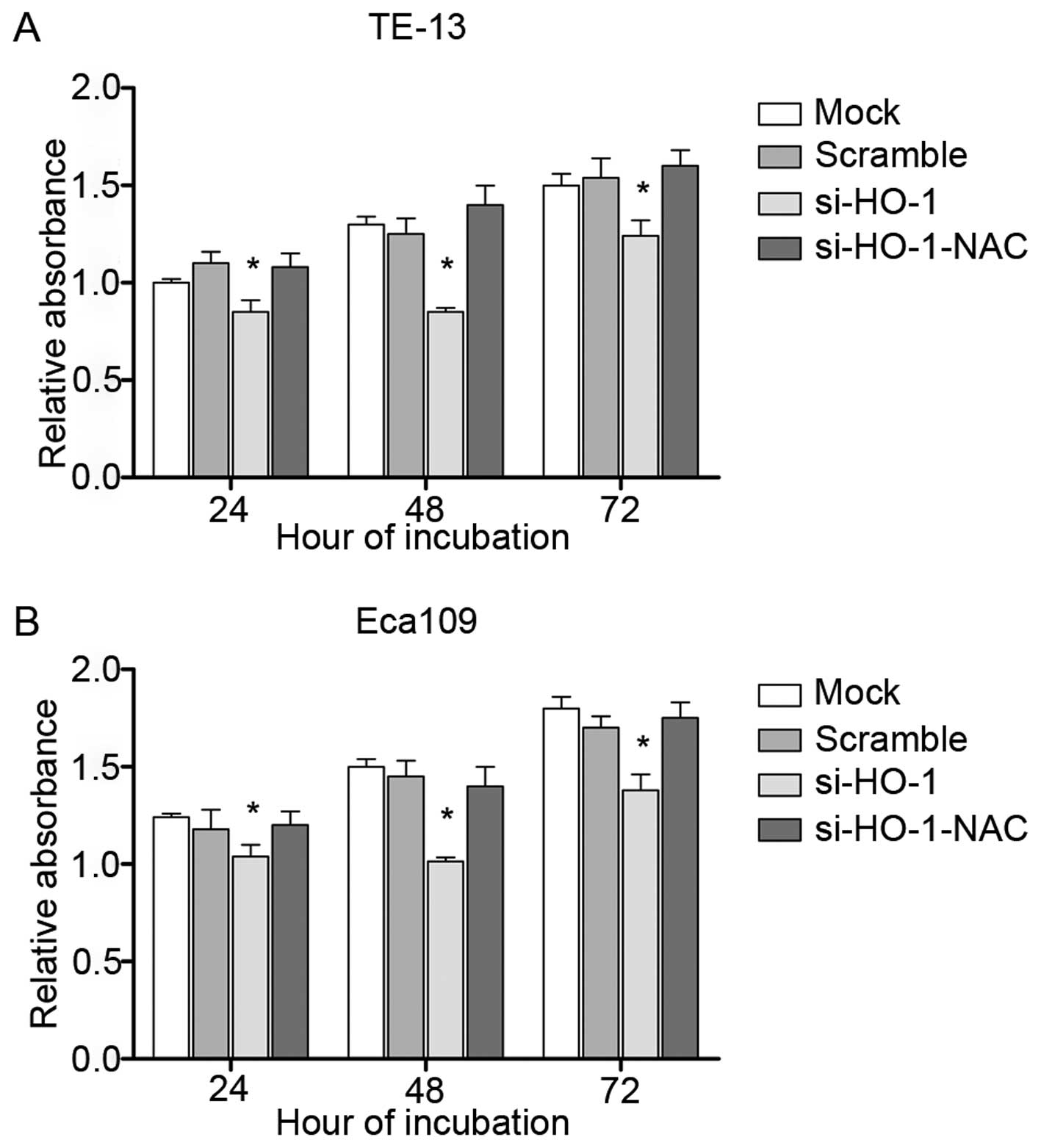
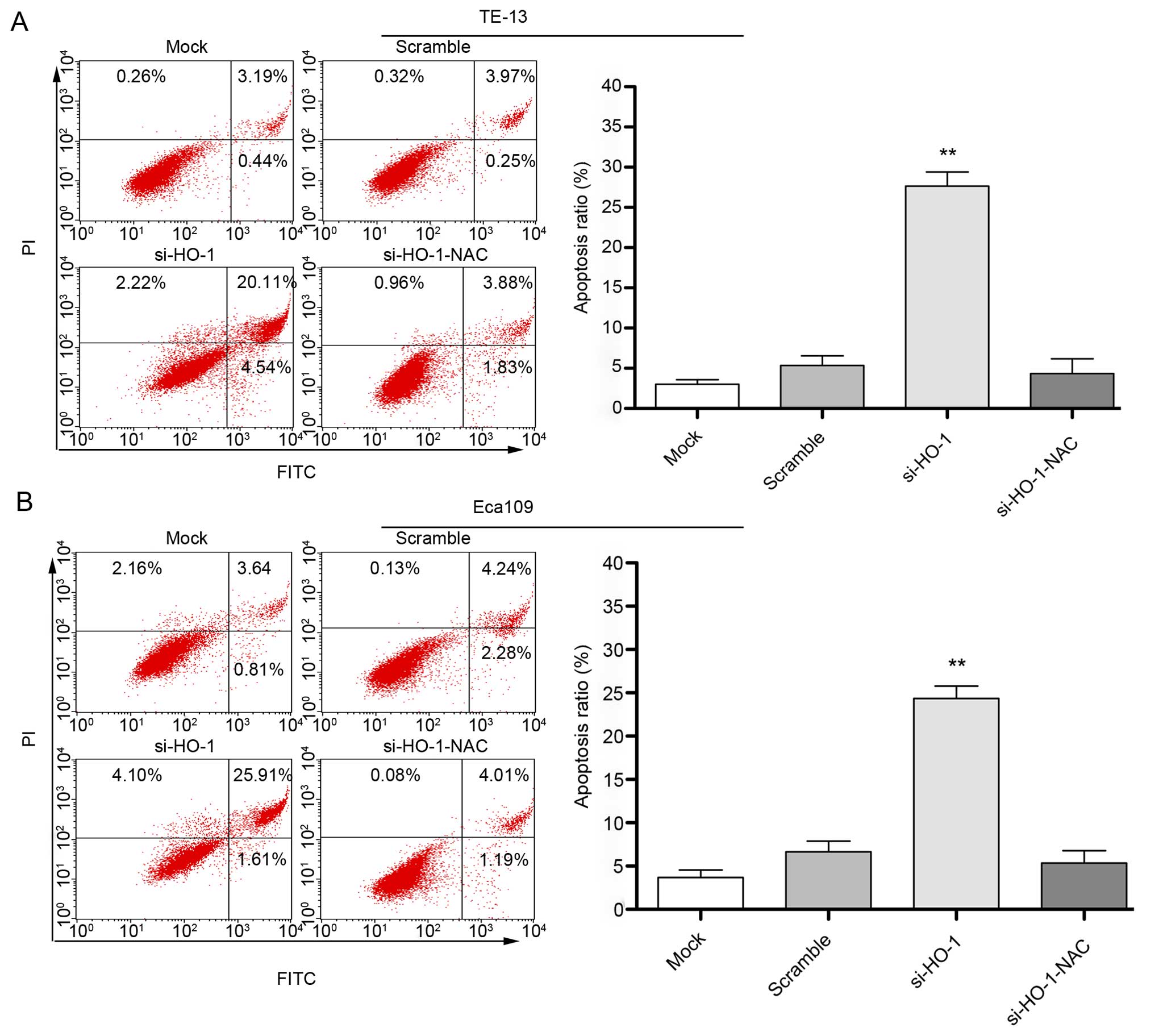
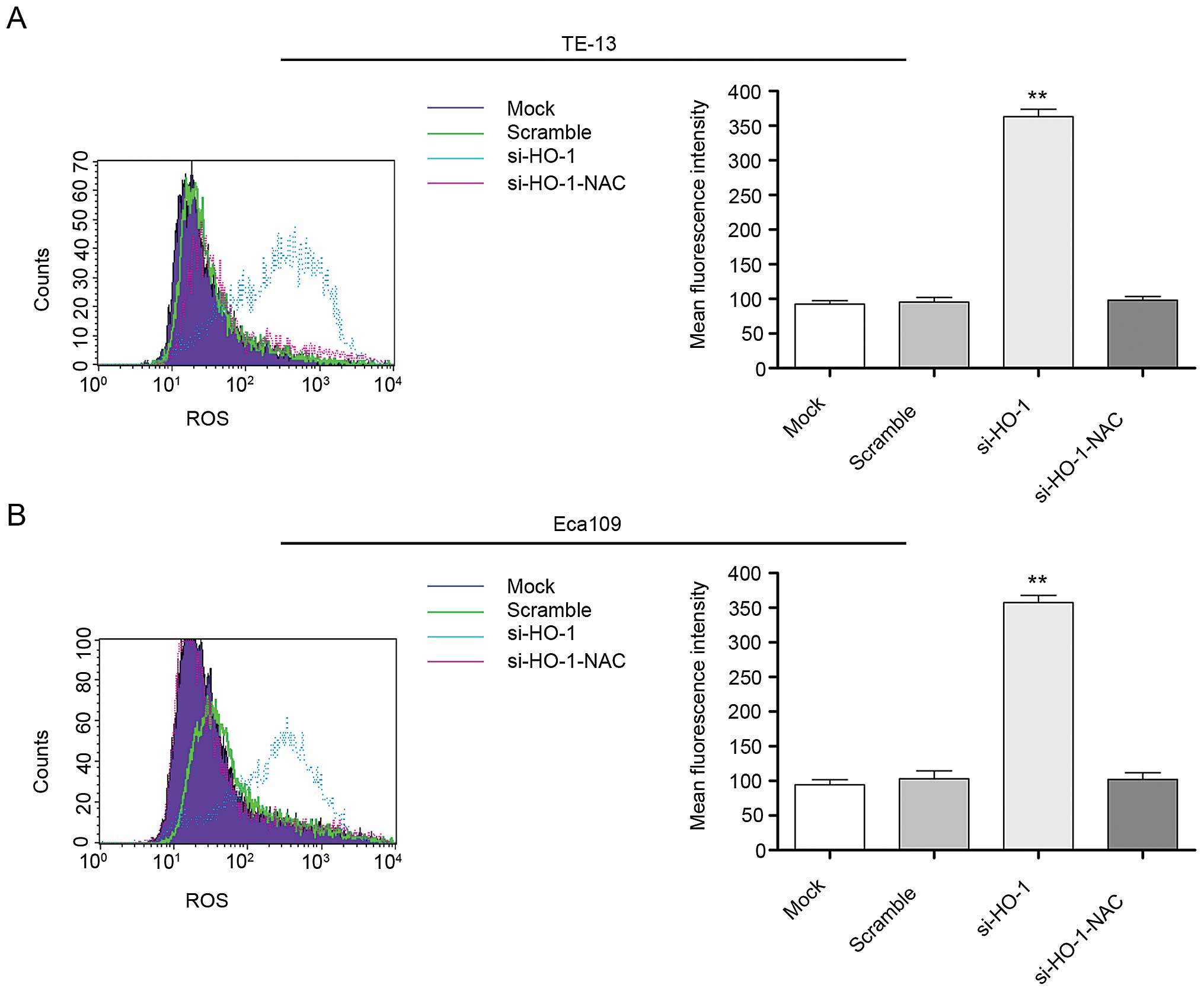
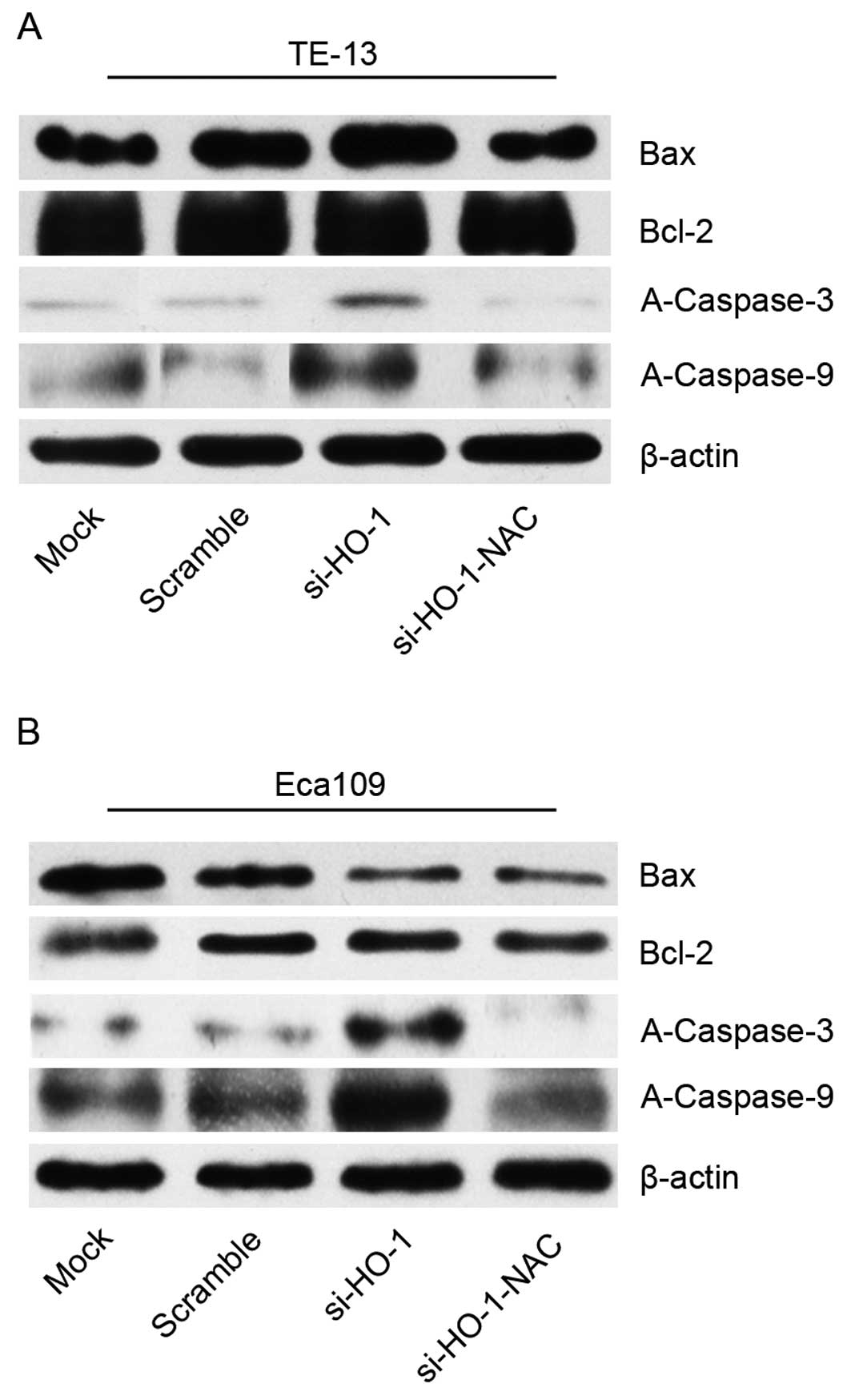
|
1
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Heasman SA, Zaitseva L, Bowles KM,
Rushworth SA and Macewan DJ: Protection of acute myeloid leukaemia
cells from apoptosis induced by front-line chemotherapeutics is
mediated by haem oxygenase-1. Oncotarget. 2:658–668. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tibullo D, Barbagallo I, Giallongo C, La
Cava P, Parrinello N, Vanella L, Stagno F, Palumbo GA, Li Volti G
and Di Raimondo F: Nuclear translocation of heme oxygenase-1
confers resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
Curr Pharm Des. 19:2765–2770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Na HK and Surh YJ: Oncogenic potential of
Nrf2 and its principal target protein heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic
Biol Med. 67:353–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wegiel B, Nemeth Z, Correa-Costa M, Bulmer
AC and Otterbein LE: Heme oxygenase-1: A metabolic nike. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 20:1709–1722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Hu JL, Xiao L, Li ZY, Wang Q, Chang Y and
Jin Y: Upregulation of HO-1 is accompanied by activation of p38MAPK
and mTOR in human oesophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Cell Biol
Int. 37:584–592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang SL, Liu LP, Jiang JX, Xiong ZF, He QJ
and Wu C: The correlation of expression levels of HIF-1α and HIF-2α
in hepatocellular carcinoma with capsular invasion, portal vein
tumor thrombi and patients' clinical outcome. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
44:159–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang S, Hannafon BN, Wolf RF, Zhou J,
Avery JE, Wu J, Lind SE and Ding WQ: Characterization of
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-induced heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)
expression in human cancer cells: The importance of enhanced BTB
and CNC homology 1 (Bach1) degradation. J Nutr Biochem. 25:515–525.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noh SJ, Bae JS, Jamiyandorj U, Park HS,
Kwon KS, Jung SH, Youn HJ, Lee H, Park BH, Chung MJ, et al:
Expression of nerve growth factor and heme oxygenase-1 predict poor
survival of breast carcinoma patients. BMC Cancer. 13:5162013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin Y, Liu Q, Wang B, Chen G, Xu L and
Zhou H: Expression and function of heme oxygenase-1 in human
gastric cancer. Exp Biol Med. 237:362–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Degese MS, Mendizabal JE, Gandini NA,
Gutkind JS, Molinolo A, Hewitt SM, Curino AC, Coso OA and
Facchinetti MM: Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) and its correlation with clinical data. Lung
Cancer. 77:168–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyake M, Fujimoto K, Anai S, Ohnishi S,
Kuwada M, Nakai Y, Inoue T, Matsumura Y, Tomioka A, Ikeda T, et al:
Heme oxygenase-1 promotes angiogenesis in urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Oncol Rep. 25:653–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ben Mosbah I, Mouchel Y, Pajaud J, Ribault
C, Lucas C, Laurent A, Boudjema K, Morel F, Corlu A and Compagnon
P: Pretreatment with mangafodipir improves liver graft tolerance to
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. PloS One. 7:e502352012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen W, Balakrishnan K, Kuang Y, Han Y, Fu
M, Gandhi V and Peng X: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) inducible DNA
cross-linking agents and their effect on cancer cells and normal
lymphocytes. J Med Chem. 57:4498–4510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lien GS, Wu MS, Bien MY, Chen CH, Lin CH
and Chen BC: Epidermal growth factor stimulates nuclear factor-κB
activation and heme oxygenase-1 expression via c-Src, NADPH
oxidase, PI3K, and Akt in human colon cancer cells. PloS One.
9:e1048912014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lin PH, Lan WM and Chau LY: TRC8
suppresses tumorigenesis through targeting heme oxygenase-1 for
ubiquitination and degradation. Oncogene. 32:2325–2334. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sanchez-Alvarez R, Martinez-Outschoorn UE,
Lin Z, Lamb R, Hulit J, Howell A, Sotgia F, Rubin E and Lisanti MP:
Ethanol exposure induces the cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype
and lethal tumor metabolism: Implications for breast cancer
prevention. Cell Cycle. 12:289–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Hambright HG, Meng P, Kumar AP and Ghosh
R: Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis disrupts oxidative
stress-mediated survival of melanoma cells. Oncotarget.
6:7195–7208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Josefsson EC, Burnett DL, Lebois M,
Debrincat MA, White MJ, Henley KJ, Lane RM, Moujalled D, Preston
SP, O'Reilly LA, et al: Platelet production proceeds independently
of the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways. Nat Commun.
5:34552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oh BS, Shin EA, Jung JH, Jung DB, Kim B,
Shim BS, Yazdi MC, Iranshahi M and Kim SH: Apoptotic effect of
galbanic acid via activation of caspases and inhibition of Mcl-1 in
H460 non-small lung carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 29:844–849.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang L, Li L, He X, Yi Q, He B, Cao J,
Pan W and Gu Z: Overcoming drug-resistant lung cancer by paclitaxel
loaded dual-functional liposomes with mitochondria targeting and
pH-response. Biomaterials. 52:126–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi YH, Kang YJ, Kim SH, Sung B, Kim DH,
Hwang SY, Kim M, Lim HS, Yoon JH, Moon HR, et al: MHY-449 induces
apoptotic cell death through ROS- and caspase-dependent pathways in
AGS human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res. 75(Suppl 15):
S17732015. View Article : Google Scholar
|