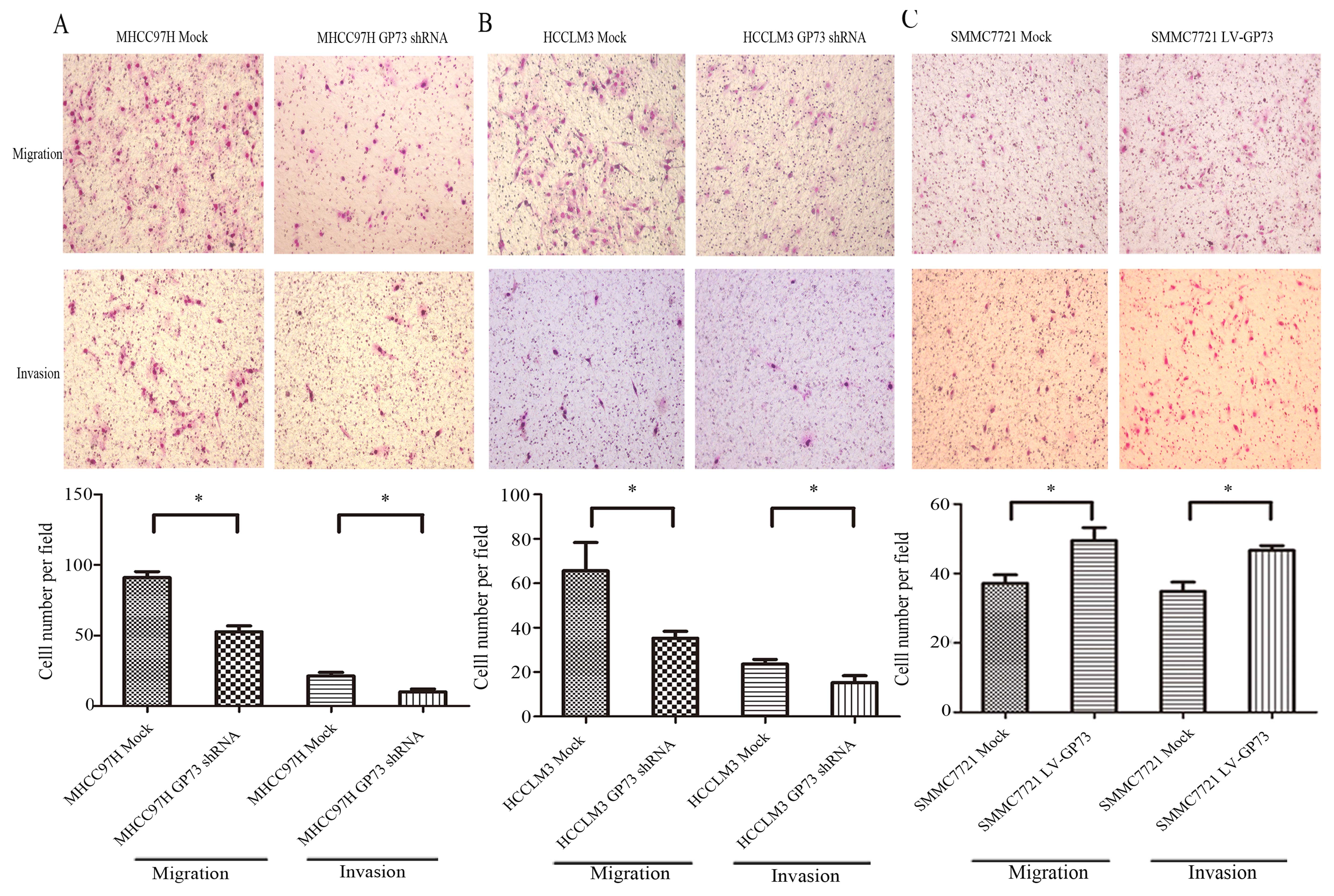
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun C, Sun L, Jiang K, Gao DM, Kang XN,
Wang C, Zhang S, Huang S, Qin X, Li Y, et al: NANOG promotes liver
cancer cell invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through NODAL/SMAD3 signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:1099–1108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wen W, Ding J, Sun W, Fu J, Chen Y, Wu K,
Ning B, Han T, Huang L, Chen C, et al: Cyclin G1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt
signaling facilitates liver cancer progression. Hepatology.
55:1787–1798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iftikhar R, Kladney RD, Havlioglu N,
Schmitt-Gräff A, Gusmirovic I, Solomon H, Luxon BA, Bacon BR and
Fimmel CJ: Disease- and cell-specific expression of GP73 in human
liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1087–1095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kladney RD, Bulla GA, Guo L, Mason AL,
Tollefson AE, Simon DJ, Koutoubi Z and Fimmel CJ: GP73, a novel
Golgi-localized protein upregulated by viral infection. Gene.
249:53–65. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kladney RD, Cui X, Bulla GA, Brunt EM and
Fimmel CJ: Expression of GP73, a resident Golgi membrane protein,
in viral and nonviral liver disease. Hepatology. 35:1431–1440.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bachert C, Fimmel C and Linstedt AD:
Endosomal trafficking and proprotein convertase cleavage of cis
Golgi protein GP73 produces marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Traffic. 8:1415–1423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giannelli G and Antonaci S: New frontiers
in biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis.
38:854–859. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marrero JA, Romano PR, Nikolaeva O, Steel
L, Mehta A, Fimmel CJ, Comunale MA, D'Amelio A, Lok AS and Block
TM: GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker
for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 43:1007–1012. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Riener MO, Stenner F, Liewen H, Soll C,
Breitenstein S, Pestalozzi BC, Samaras P, Probst-Hensch N,
Hellerbrand C, Müllhaupt B, et al: Golgi phosphoprotein 2 (GOLPH2)
expression in liver tumors and its value as a serum marker in
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 49:1602–1609. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ozkan H, Erdal H, Tutkak H, Karaeren Z,
Yakut M, Yüksel O and Köklü S: Diagnostic and prognostic validity
of Golgi protein 73 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion.
83:83–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tian L, Wang Y, Xu D, Gui J, Jia X, Tong
H, Wen X, Dong Z and Tian Y: Serological AFP/Golgi protein 73 could
be a new diagnostic parameter of hepatic diseases. Int J Cancer.
129:1923–1931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wright LM, Yong S, Picken MM, Rockey D and
Fimmel CJ: Decreased survival and hepato-renal pathology in mice
with C-terminally truncated GP73 (GOLPH2). Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
2:34–47. 2009.
|
|
18
|
Sun Y, Yang H, Mao Y, Xu H, Zhang J, Li G,
Lu X, Sang X, Zhao H, Zhong S, et al: Increased Golgi protein 73
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue correlates with tumor
aggression but not survival. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1207–1212.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bao YX, Cao Q, Yang Y, Mao R, Xiao L,
Zhang H, Zhao HR and Wen H: Expression and prognostic significance
of golgiglyco-protein73 (GP73) with epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) related molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC). Diagn Pathol. 8:1972013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Masunaga R1, Kohno H, Dhar DK, Ohno S,
Shibakita M, Kinugasa S, Yoshimura H, Tachibana M, Kubota H and
Nagasue N: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression correlates with tumor
neovascularization and prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4064–4068. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao Y, Yang H, Xu H, Lu X, Sang X, Du S,
Zhao H, Chen W, Xu Y, Chi T, et al: Golgi protein 73 (GOLPH2) is a
valuable serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
59:1687–1693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei H, Li B, Zhang R, Hao X, Huang Y, Qiao
Y, Hou J and Li X and Li X: Serum GP73, a marker for evaluating
progression in patients with chronic HBV infections. PLoS One.
8:e538622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H, Wetten S, Li L, St Jean PL, Upmanyu
R, Surh L, Hosford D, Barnes MR, Briley JD, Borrie M, et al:
Candidate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide
association study of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 65:45–53.
2008.
|
|
24
|
Wright LM, Huster D, Lutsenko S, Wrba F,
Ferenci P and Fimmel CJ: Hepatocyte GP73 expression in Wilson
disease. J Hepatol. 51:557–564. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo JH, Yu YP, Cieply K, Lin F, Deflavia
P, Dhir R, Finkelstein S, Michalopoulos G and Becich M: Gene
expression analysis of prostate cancers. Mol Carcinog. 33:25–35.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laxman B, Morris DS, Yu J, Siddiqui J, Cao
J, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Tsodikov A, Wei JT, Tomlins SA, et al: A
first-generation multiplex biomarker analysis of urine for the
early detection of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:645–649. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kristiansen G, Fritzsche FR, Wassermann K,
Jäger C, Tölls A, Lein M, Stephan C, Jung K, Pilarsky C, Dietel M,
et al: GOLPH2 protein expression as a novel tissue biomarker for
prostate cancer: Implications for tissue-based diagnostics. Br J
Cancer. 99:939–948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fritzsche FR, Riener MO, Dietel M, Moch H,
Jung K and Kristiansen G: GOLPH2 expression in renal cell cancer.
BMC Urol. 8:152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang F, Gu Y, Li X, Wang W, He J and Peng
T: Up-regulated Golgi phosphoprotein 2 (GOLPH2) expression in lung
adenocarcinoma tissue. Clin Biochem. 43:983–991. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Block TM, Comunale MA, Lowman M, Steel LF,
Romano PR, Fimmel C, Tennant BC, London WT, Evans AA, Blumberg BS,
et al: Use of targeted glycoproteomics to identify serum
glycoproteins that correlate with liver cancer in woodchucks and
humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:779–784. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu L, Li L, Xie H, Gu Y and Peng T: The
Golgi localization of GOLPH2 (GP73/GOLM1) is determined by the
transmembrane and cytoplamic sequences. PLoS One. 6:e282072011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen MH, Jan YH, Chang PM, Chuang YJ, Yeh
YC, Lei HJ, Hsiao M, Huang SF, Huang CY and Chau GY: Expression of
GOLM1 correlates with prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Ann Surg Oncol. 20(Suppl 3): S616–S624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shan SG, Gao YT, Xu YJ, Huang Y, Zhang Q,
Zhai DK, Li JB, Wang FM, Jing X, Du Z, et al: Gradually increased
Golgi protein 73 expression in the progression of benign liver
diseases to precancerous lesions and hepatocellular carcinoma
correlates with prognosis of patients. Hepatol Res. 43:1199–1210.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schrohl AS, Holten-Andersen M, Sweep F,
Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Foekens J and Brünner N; European
Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Receptor
and Biomarker Group: Tumor markers: From laboratory to clinical
utility. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2:378–387. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cui B, Zhang S, Chen L, Yu J, Widhopf GF
II, Fecteau JF, Rassenti LZ and Kipps TJ: Targeting ROR1 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Res.
73:3649–3660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kang Y and Pantel K: Tumor cell
dissemination: Emerging biological insights from animal models and
cancer patients. Cancer Cell. 23:573–581. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang K, Corsa CA, Ponik SM, Prior JL,
Piwnica-Worms D, Eliceiri KW, Keely PJ and Longmore GD: The
collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 2 stabilizes SNAIL1 to
facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 15:677–687.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang C, Jiang K, Kang X, Gao D, Sun C, Li
Y, Sun L, Zhang S, Liu X, Wu W, et al: Tumor-derived secretory
clusterin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and facilitates
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:2308–2320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|