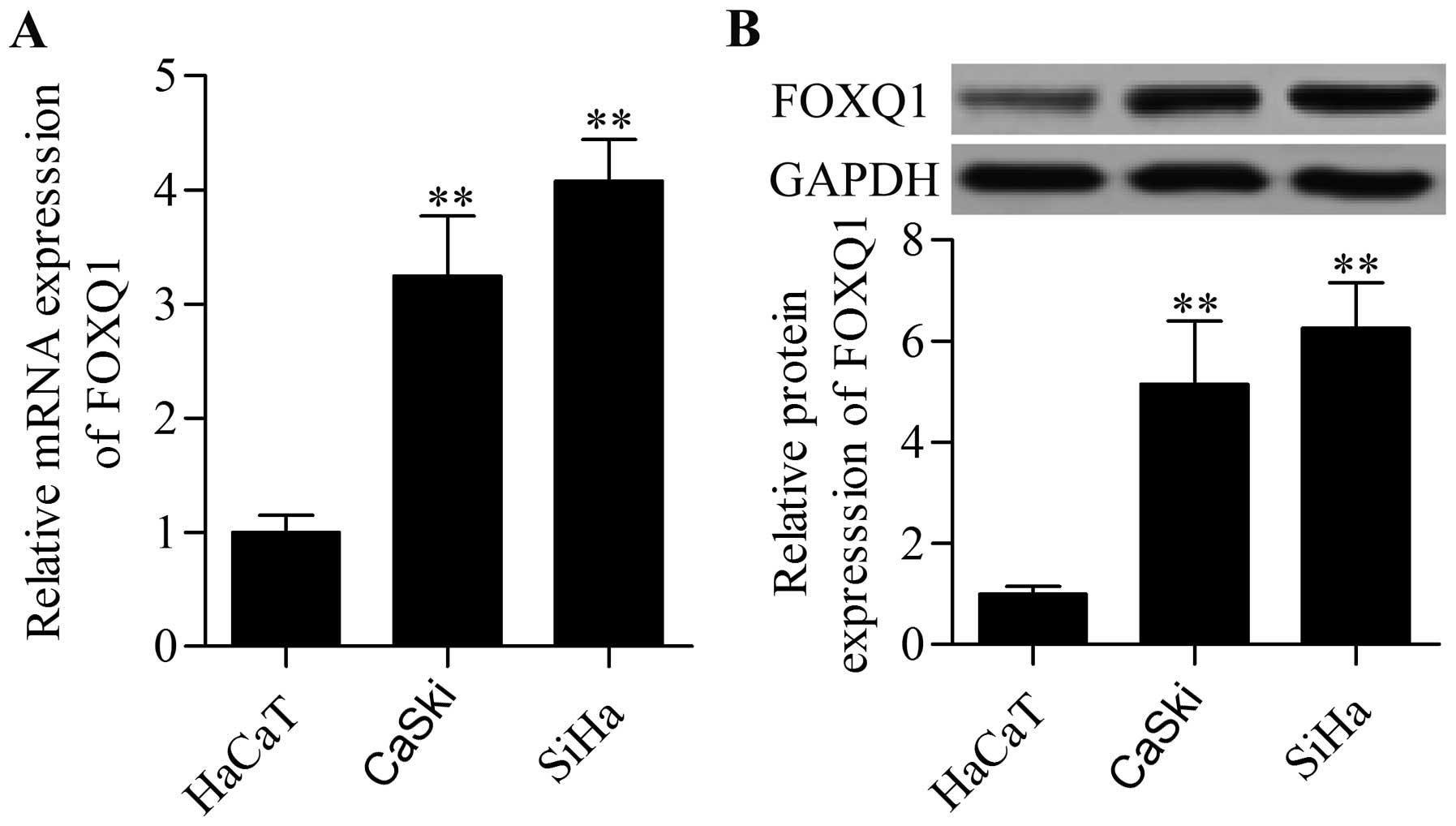
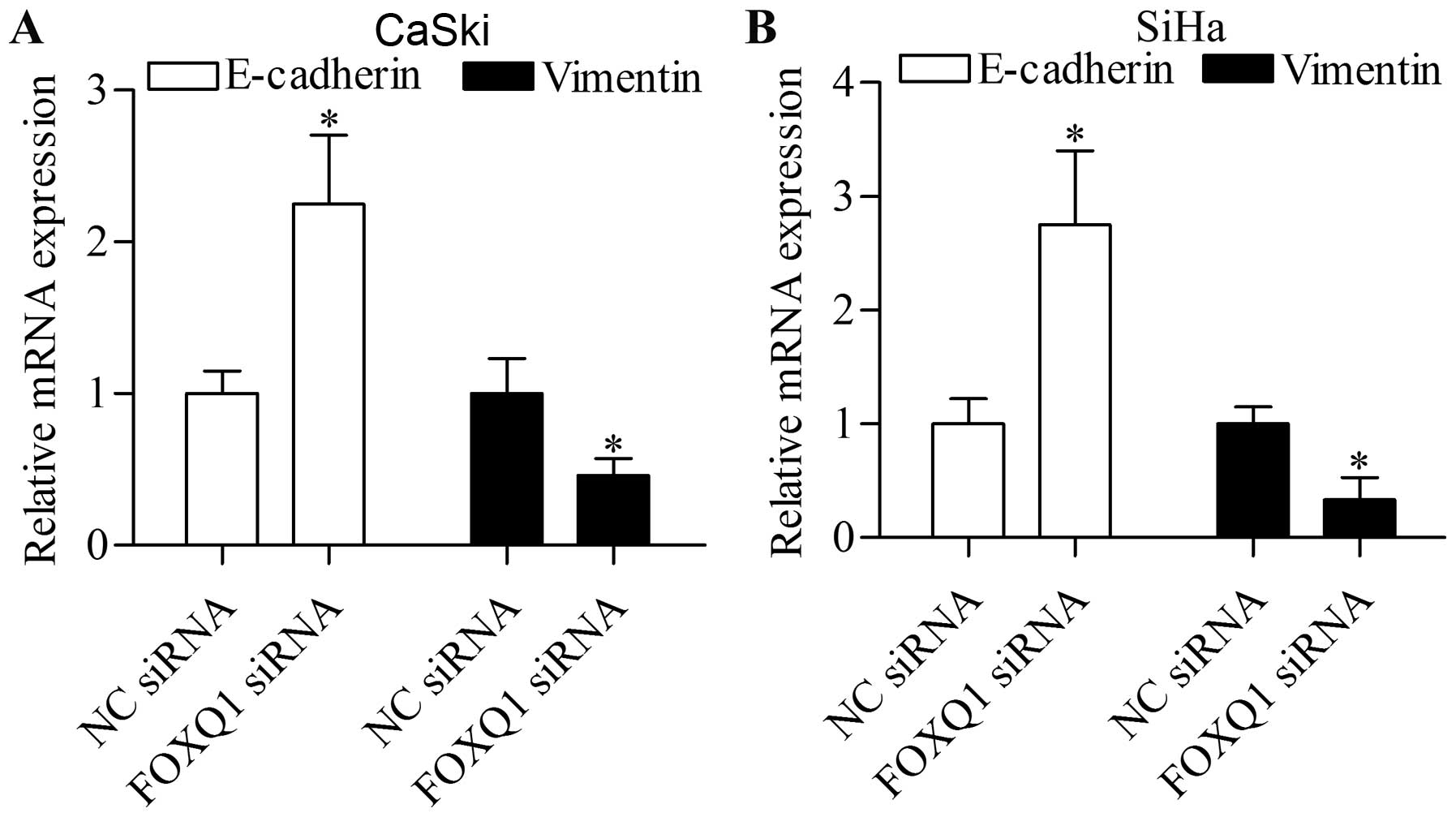
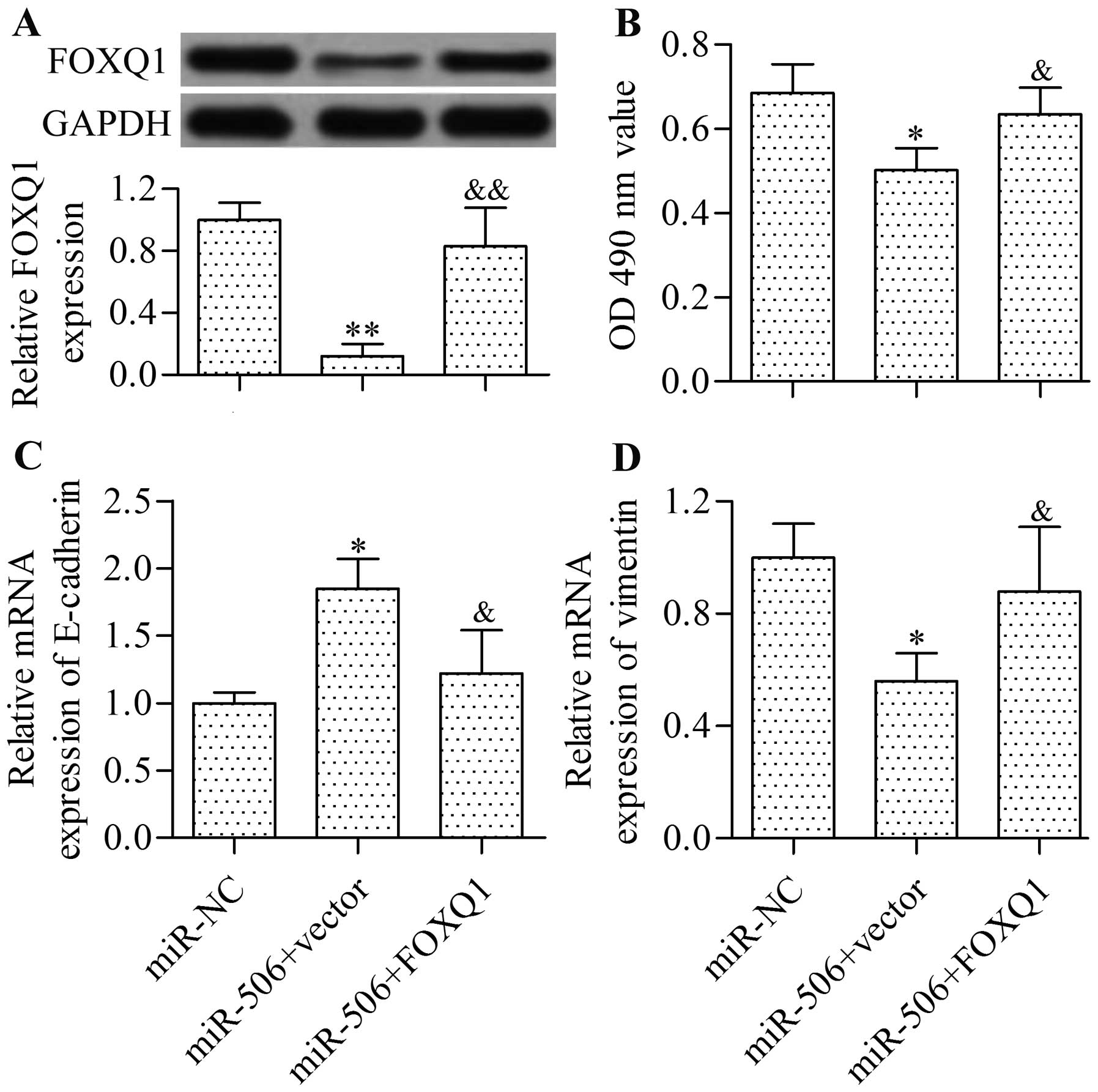
|
1
|
Ojesina AI, Lichtenstein L, Freeman SS,
Pedamallu CS, Imaz-Rosshandler I, Pugh TJ, Cherniack AD, Ambrogio
L, Cibulskis K, Bertelsen B, et al: Landscape of genomic
alterations in cervical carcinomas. Nature. 506:371–375. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rob L, Halaska M and Robova H:
Nerve-sparing and individually tailored surgery for cervical
cancer. Lancet Oncol. 11:292–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lam EW, Brosens JJ, Gomes AR and Koo CY:
Forkhead box proteins: Tuning forks for transcriptional harmony.
Nat Rev Cancer. 13:482–495. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pei Y, Wang P, Liu H, He F and Ming L:
FOXQ1 promotes esophageal cancer proliferation and metastasis by
negatively modulating CDH1. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:89–94. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, Zhang L, Qi X,
Chen Z, Shang X, Nie Y and Wu K: Forkhead box Q1 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by transactivating ZEB2 and
VersicanV1 expression. Hepatology. 59:958–973. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun HT, Cheng SX, Tu Y, Li XH and Zhang S:
FoxQ1 promotes glioma cells proliferation and migration by
regulating NRXN3 expression. PLoS One. 8:e556932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiao Y, Jiang X, Lee ST, Karuturi RK, Hooi
SC and Yu Q: FOXQ1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human cancers. Cancer Res. 71:3076–3086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feng J, Xu L, Ni S, Gu J, Zhu H, Wang H,
Zhang S, Zhang W and Huang J: Involvement of FoxQ1 in NSCLC through
regulating EMT and increasing chemosensitivity. Oncotarget.
5:9689–9702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scheel C, Onder T, Karnoub A and Weinberg
RA: Adaptation versus selection: The origins of metastatic
behavior. Cancer Res. 67:11476–11480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:740–746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaneda H, Arao T, Tanaka K, Tamura D,
Aomatsu K, Kudo K, Sakai K, De Velasco MA, Matsumoto K, Fujita Y,
et al: FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and enhances
tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:2053–2063. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bieller A, Pasche B, Frank S, Gläser B,
Kunz J, Witt K and Zoll B: Isolation and characterization of the
human forkhead gene FOXQ1. DNA Cell Biol. 20:555–561. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Zhang X, Zhu H, Wang X, Ni S and
Huang J: FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT.
PLoS One. 7:e399372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang SH, Yan XZ, Wang BL, Jin HF, Yao LP,
Li YN, Chen M, Nie YZ, Wang X, Guo XG, et al: Increased expression
of FOXQ1 is a prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 34:2605–2609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao M, Shih IEM and Wang TL: The role of
forkhead box Q1 transcription factor in ovarian epithelial
carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13881–13893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Meng F, Liu G, Zhang B, Zhu J, Wu
F, Ethier SP, Miller F and Wu G: Forkhead transcription factor
foxq1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer
metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:1292–1301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi XB, Tepper CG and deVere White RW:
Cancerous miRNAs and their regulation. Cell Cycle. 7:1529–1538.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Li B and Xie X: The roles and
clinical significance of microRNAs in cervical cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 31:131–139. 2016.
|
|
22
|
Han Y, Xu GX, Lu H, Yu DH, Ren Y, Wang L,
Huang XH, Hou WJ, Wei ZH, Chen YP, et al: Dysregulation of miRNA-21
and their potential as biomarkers for the diagnosis of cervical
cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7131–7139. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Y, Xie YJ, Xu Q, Chen JX, Shan NC and
Zhang Y: Down-regulation of miR-1246 in cervical cancer tissues and
its clinical significance. Gynecol Oncol. 138:683–688. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Q, Zhai YX, Liu HQ, Shi YA and Li XB:
MicroRNA-491-5p suppresses cervical cancer cell growth by targeting
hTERT. Oncol Rep. 34:979–986. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song X, Shi B, Huang K and Zhang W:
miR-133a inhibits cervical cancer growth by targeting EGFR. Oncol
Rep. 34:1573–1580. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, Yuan S, Wang R,
Pan Z, Yang Y, Huang G, Gu F, Jiang B, et al: Double-negative
feedback loop between microRNA-422a and forkhead box (FOX)G1/Q1/E1
regulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth and metastasis.
Hepatology. 61:561–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Peng XH, Huang HR, Lu J, Liu X, Zhao FP,
Zhang B, Lin SX, Wang L, Chen HH, Xu X, et al: miR-124 suppresses
tumor growth and metastasis by targeting Foxq1 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Lin C, Liao G, Liu S, Ding J,
Tang F, Wang Z, Liang X, Li B, Wei Y, et al: MicroRNA-506
suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis in colon cancer by
directly targeting the oncogene EZH2. Oncotarget. 6:32586–32601.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun G, Liu Y, Wang K and Xu Z: miR-506
regulates breast cancer cell metastasis by targeting IQGAP1. Int J
Oncol. 47:1963–1970. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang W, He S, Ji J, Huang J, Zhang S and
Zhang Y: The prognostic significance of FOXQ1 oncogene
overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
209:353–358. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan DM, Feng XS, Qi PW and Chen YW:
Forkhead factor FOXQ1 promotes TGF-β1 expression and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell Biochem. 397:179–186.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu Z, Zhu Z, Pang Z, Xing Y, Wan F, Lan D
and Wang H: Short hairpin RNA targeting FOXQ1 inhibits invasion and
metastasis via the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 42:1271–1278. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Z, Ma J, Luan G, Kang L, Su Y, He Y
and Luan F: miR-506 suppresses tumor proliferation and invasion by
targeting FOXQ1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01228512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiang XJ, Deng J, Liu YW, Wan LY, Feng M,
Chen J and Xiong JP: miR-1271 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion
and EMT in gastric cancer by targeting FOXQ1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1382–1394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arora H, Qureshi R and Park WY: miR-506
regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell
lines. PLoS One. 8:e642732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu F, Lv M, Li D, Cai H, Ma L, Luo Q, Yuan
X and Lv Z: miR-506 over-expression inhibits proliferation and
metastasis of breast cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 21:1687–1692.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Liu Z, Dong S, Zhang J, Tan J, Wang
Y, Ge C, Li R, Xue Y, Li M, et al: miR-506 inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in gastric
cancer. Am J Pathol. 185:2412–2420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sakimura S, Sugimachi K, Kurashige J, Ueda
M, Hirata H, Nambara S, Komatsu H, Saito T, Takano Y, Uchi R, et
al: The miR-506-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition is
involved in poor prognosis for patients with gastric cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 22(Suppl 3): 1436–1443. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deng J, Lei W, Xiang X, Zhang L, Yu F,
Chen J, Feng M and Xiong J: MicroRNA-506 inhibits gastric cancer
proliferation and invasion by directly targeting Yap1. Tumour Biol.
36:6823–6831. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deng Q, Xie L and Li H: miR-506 suppresses
cell proliferation and tumor growth by targeting Rho-associated
protein kinase 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 467:921–927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng L and Liu H: MicroRNA-506 suppresses
growth and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting
GATA6. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:1862–1870. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wen SY, Lin Y, Yu YQ, Cao SJ, Zhang R,
Yang XM, Li J, Zhang YL, Wang YH, Ma MZ, et al: miR-506 acts as a
tumor suppressor by directly targeting the hedgehog pathway
transcription factor Gli3 in human cervical cancer. Oncogene.
34:717–725. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|