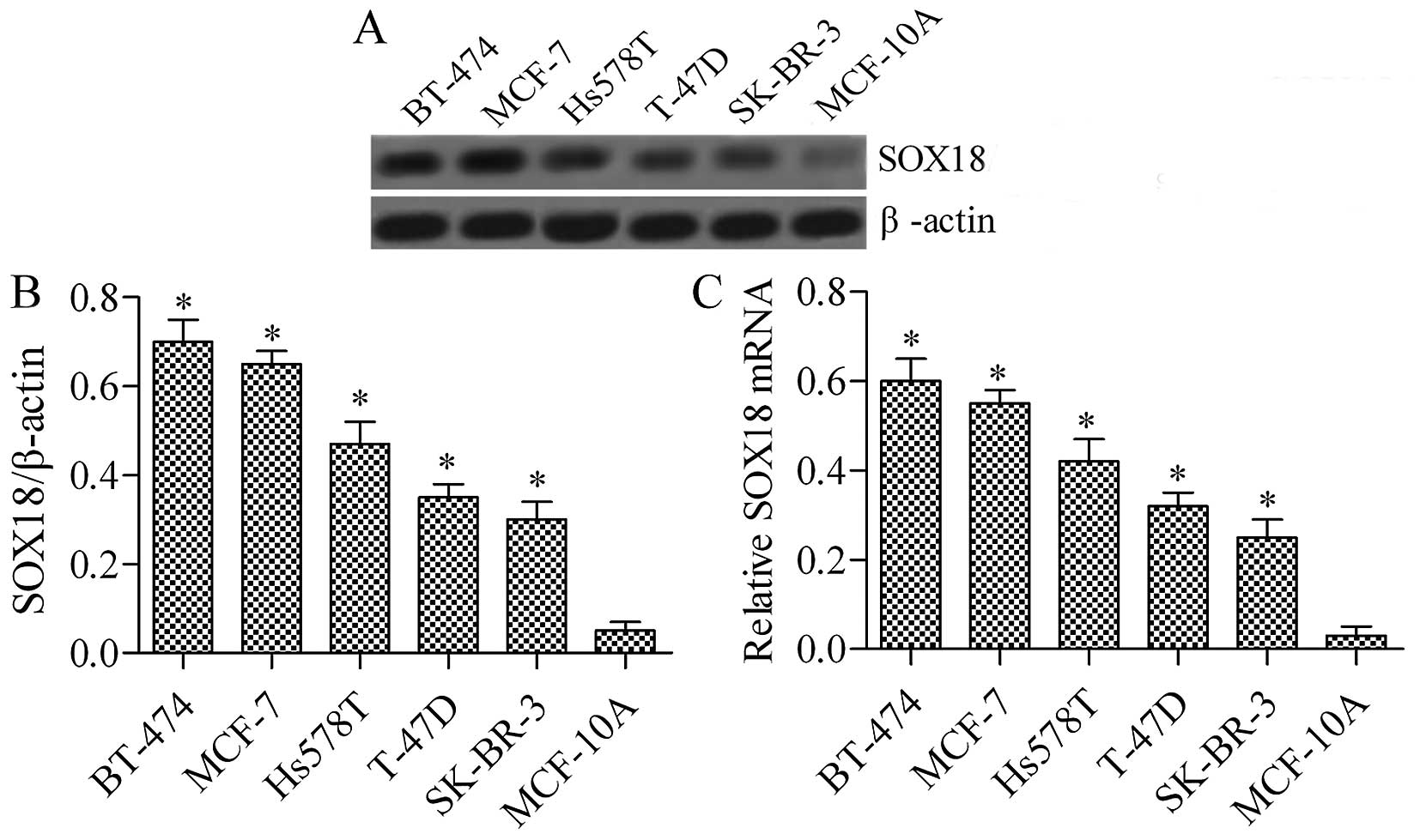
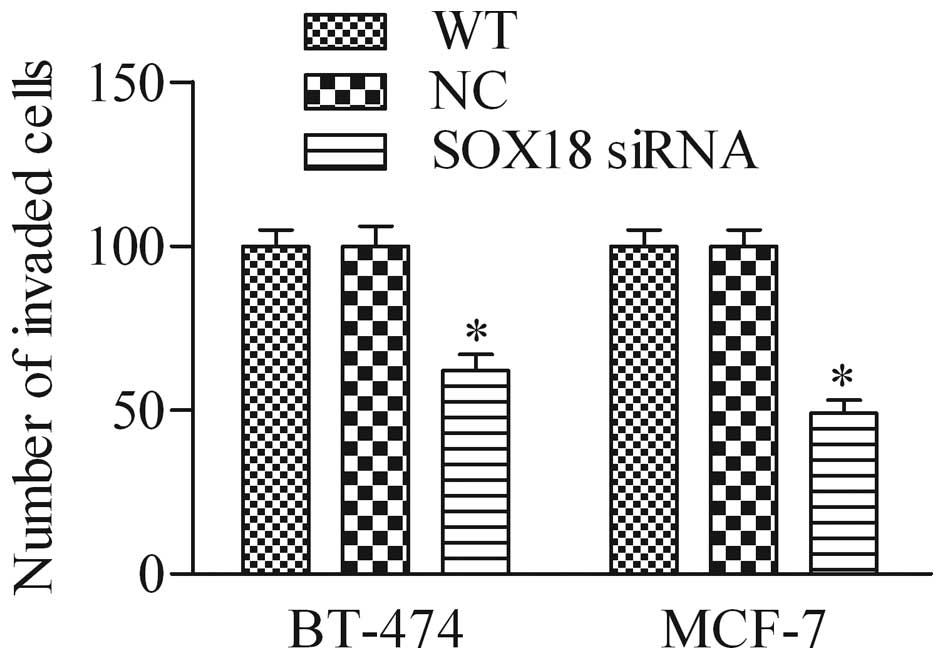
|
1
|
Anaya-Ruiz M and Perez-Santos M:
Innovation status of gene therapy for breast cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:4133–4136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang GQ, He C, Tao L and Liu F: Role of
DJ-1 siRNA in reverse sensitivity of breast cancer cells to
chemotherapy and its possible mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:6944–6951. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harley VR, Lovell-Badge R and Goodfellow
PN: Definition of a consensus DNA binding site for SRY. Nucleic
Acids Res. 22:1500–1501. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wegner M: From head to toes: The multiple
facets of Sox proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 27:1409–1420. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dunn TL, Mynett-Johnson L, Wright EM,
Hosking BM, Koopman PA and Muscat GE: Sequence and expression of
Sox-18 encoding a new HMG-box transcription factor. Gene.
161:223–225. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanai Y, Kanai-Azuma M, Noce T, Saido TC,
Shiroishi T, Hayashi Y and Yazaki K: Identification of two Sox17
messenger RNA isoforms, with and without the high mobility group
box region, and their differential expression in mouse
spermatogenesis. J Cell Biol. 133:667–681. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Taniguchi K, Hiraoka Y, Ogawa M, Sakai Y,
Kido S and Aiso S: Isolation and characterization of a mouse
SRY-related cDNA, mSox7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1445:225–231. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Downes M, François M, Ferguson C, Parton
RG and Koopman P: Vascular defects in a mouse model of
hypotrichosis-lymphedematelangiectasia syndrome indicate a role for
SOX18 in blood vessel maturation. Hum Mol Genet. 18:2839–2850.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
François M, Caprini A, Hosking B, Orsenigo
F, Wilhelm D, Browne C, Paavonen K, Karnezis T, Shayan R, Downes M,
et al: Sox18 induces development of the lymphatic vasculature in
mice. Nature. 456:643–647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Irrthum A, Devriendt K, Chitayat D,
Matthijs G, Glade C, Steijlen PM, Fryns JP, Van Steensel MA and
Vikkula M: Mutations in the transcription factor gene SOX18
underlie recessive and dominant forms of
hypotrichosis-lymphedematelangiectasia. Am J Hum Genet.
72:1470–1478. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pennisi D, Gardner J, Chambers D, Hosking
B, Peters J, Muscat G, Abbott C and Koopman P: Mutations in Sox18
underlie cardiovascular and hair follicle defects in ragged mice.
Nat Genet. 24:434–437. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jethon A, Pula B, Olbromski M, Werynska B,
Muszczynska-Bernhard B, Witkiewicz W, Dziegiel P and
Podhorska-Okolow M: Prognostic significance of SOX18 expression in
non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 46:123–132. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Saitoh T and Katoh M: Expression of human
SOX18 in normal tissues and tumors. Int J Mol Med. 10:339–344.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang G, Wei Z, Jia H, Zhao W, Yang G and
Zhao H: Knockdown of SOX18 inhibits the proliferation, migration
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
34:1121–1128. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Young N, Hahn CN, Poh A, Dong C, Wilhelm
D, Olsson J, Muscat GE, Parsons P, Gamble JR and Koopman P: Effect
of disrupted SOX18 transcription factor function on tumor growth,
vascularization, and endothelial development. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1060–1067. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Di J, Huang H, Qu D, Tang J, Cao W, Lu Z,
Cheng Q, Yang J, Bai J, Zhang Y, et al: Rap2B promotes
proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer
through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Sci Rep.
5:123632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
McGarry T, Veale DJ, Gao W, Orr C, Fearon
U and Connolly M: Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) induces migration and
invasive mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
17:1532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Castillo SD and Sanchez-Cespedes M: The
SOX family of genes in cancer development: Biological relevance and
opportunities for therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:903–919.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pula B, Kobierzycki C, Solinski D,
Olbromski M, Nowak-Markwitz E, Spaczynski M, Kedzia W, Zabel M and
Dziegiel P: SOX18 expression predicts response to platinum-based
chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 34:4029–4037.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pula B, Olbromski M, Wojnar A,
Gomulkiewicz A, Witkiewicz W, Ugorski M, Dziegiel P and
Podhorska-Okolow M: Impact of SOX18 expression in cancer cells and
vessels on the outcome of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 36:469–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
García-Ramírez M, Martínez-González J,
Juan-Babot JO, Rodríguez C and Badimon L: Transcription factor
SOX18 is expressed in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions and
regulates DNA synthesis and vascular cell growth. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:2398–2403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Azhikina T, Kozlova A, Skvortsov T and
Sverdlov E: Heterogeneity and degree of TIMP4, GATA4, SOX18, and
EGFL7 gene promoter methylation in non-small cell lung cancer and
surrounding tissues. Cancer Genet. 204:492–500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma LJ, Wang J, Deng L and Yu S: Expression
of SOX18, VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 and their clinical significance in
gastric carcinoma. J Clin Exp Pathol. 29:1310–1316. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Huang KH, Lan YT, Chen MH, Chao Y, Lo SS,
Li AF, Wu CW, Chiou SH, Yang MH, Shyr YM, et al: The Correlation
Between RhoA Expression and Clinicopathological Characteristics in
Gastric Cancer Patients After Curative Surgery. World J Surg.
39:2289–2299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li XR, Ji F, Ouyang J, Wu W, Qian LY and
Yang KY: Overexpression of RhoA is associated with poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 32:1130–1134. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang M, Wang XJ and Liu BR: Effect of
shRNA targeted against RhoA on proliferation and migration of human
colonic cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7040–7044.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kuzmanov A, Hopfer U, Marti P,
Meyer-Schaller N, Yilmaz M and Christofori G: LIM-homeobox gene 2
promotes tumor growth and metastasis by inducing autocrine and
paracrine PDGF-B signaling. Mol Oncol. 8:401–416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kryza T, Achard C, Parent C, Marchand-Adam
S, Guillon-Munos A, Iochmann S, Korkmaz B, Respaud R, Courty Y and
Heuzé-Vourc'h N: Angiogenesis stimulated by human
kallikrein-related peptidase 12 acting via a platelet-derived
growth factor B-dependent paracrine pathway. FASEB J. 28:740–751.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pietras K, Sjöblom T, Rubin K, Heldin CH
and Ostman A: PDGF receptors as cancer drug targets. Cancer Cell.
3:439–443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deng WY, Li N, Wan XB, Luo SX and Zhang
YW: Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression
predicts poor prognosis of Chinese patients with gastric cancer.
Med Oncol. 31:1412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Farabaugh SM, Boone DN and Lee AV: Role of
IGF1R in breast cancer subtypes, stemness, and lineage
differentiation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:592015.
|
|
33
|
Furukawa J, Wraight CJ, Freier SM, Peralta
E, Atley LM, Monia BP, Gleave ME and Cox ME: Antisense
oligonucleotide targeting of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
(IGF-1R) in prostate cancer. Prostate. 70:206–218. 2010.
|
|
34
|
Hirano H, Lopes MB, Laws ER Jr, Asakura T,
Goto M, Carpenter JE, Karns LR and VandenBerg SR: Insulin-like
growth factor-1 content and pattern of expression correlates with
histopathologic grade in diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. Neuro
Oncol. 1:109–119. 1999.
|
|
35
|
Ning XH, Wang YZ, Bai CM and Li J:
Clinical significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in
platinum-based chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 32:366–370. 2010.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao S, Qiu Z, He J, Li L and Li W:
Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and
survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A meta-analysis.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6694–6704. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pollak M: The insulin and insulin-like
growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:159–169. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patterson BC and Sang QA:
Angiostatin-converting enzyme activities of human matrilysin
(MMP-7) and gelatinase B/type IV collagenase (MMP-9). J Biol Chem.
272:28823–28825. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hoeth M, Niederleithner H, Hofer-Warbinek
R, Bilban M, Mayer H, Resch U, Lemberger C, Wagner O, Hofer E,
Petzelbauer P, et al: The transcription factor SOX18 regulates the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and guidance molecules in
human endothelial cells. PLoS One. 7:e309822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cermenati S, Moleri S, Neyt C, Bresciani
E, Carra S, Grassini DR, Omini A, Goi M, Cotelli F, François M, et
al: Sox18 genetically interacts with VegfC to regulate
lymphangiogenesis in zebrafish. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:1238–1247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duong T, Proulx ST, Luciani P, Leroux JC,
Detmar M, Koopman P and Francois M: Genetic ablation of SOX18
function suppresses tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis of
melanoma in mice. Cancer Res. 72:3105–3114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|