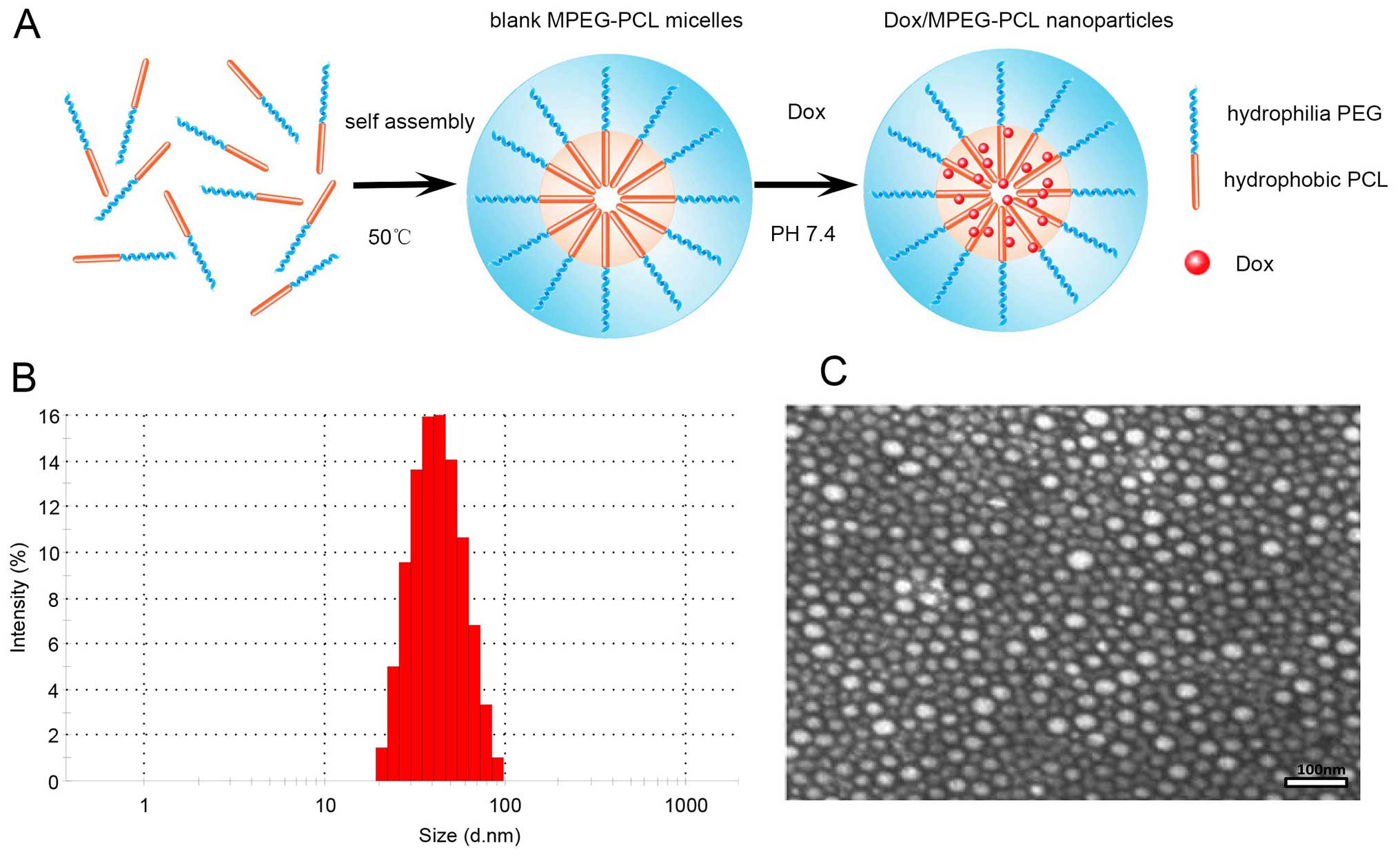
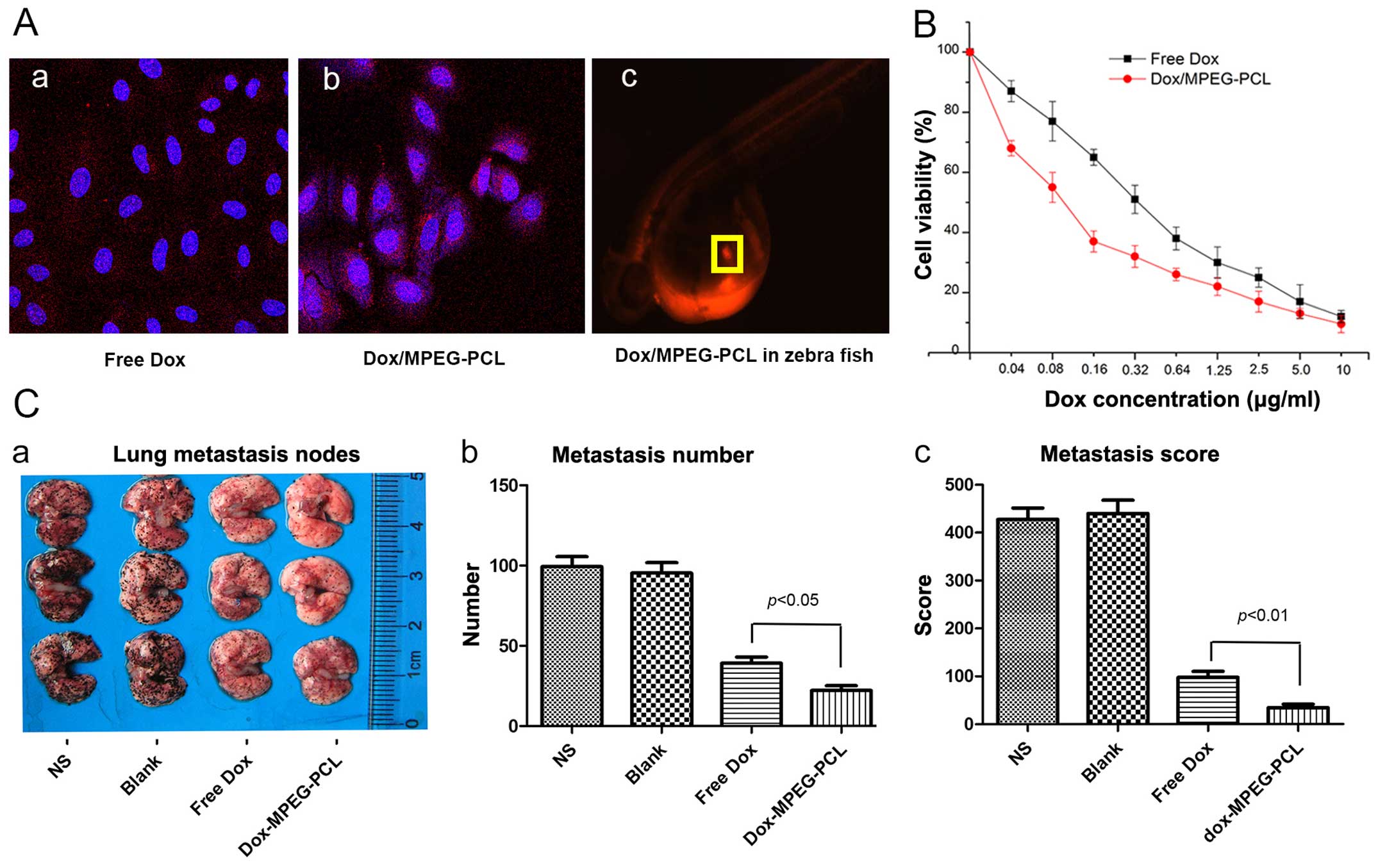
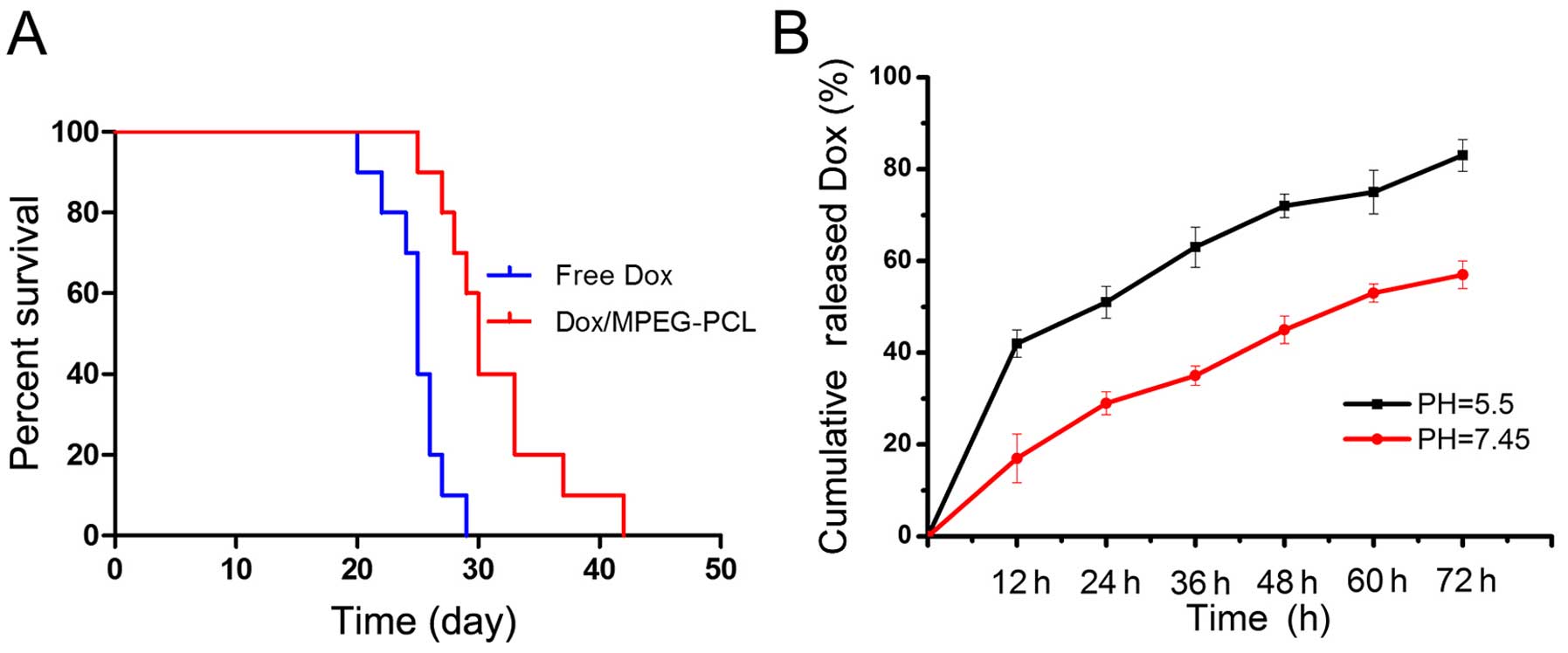
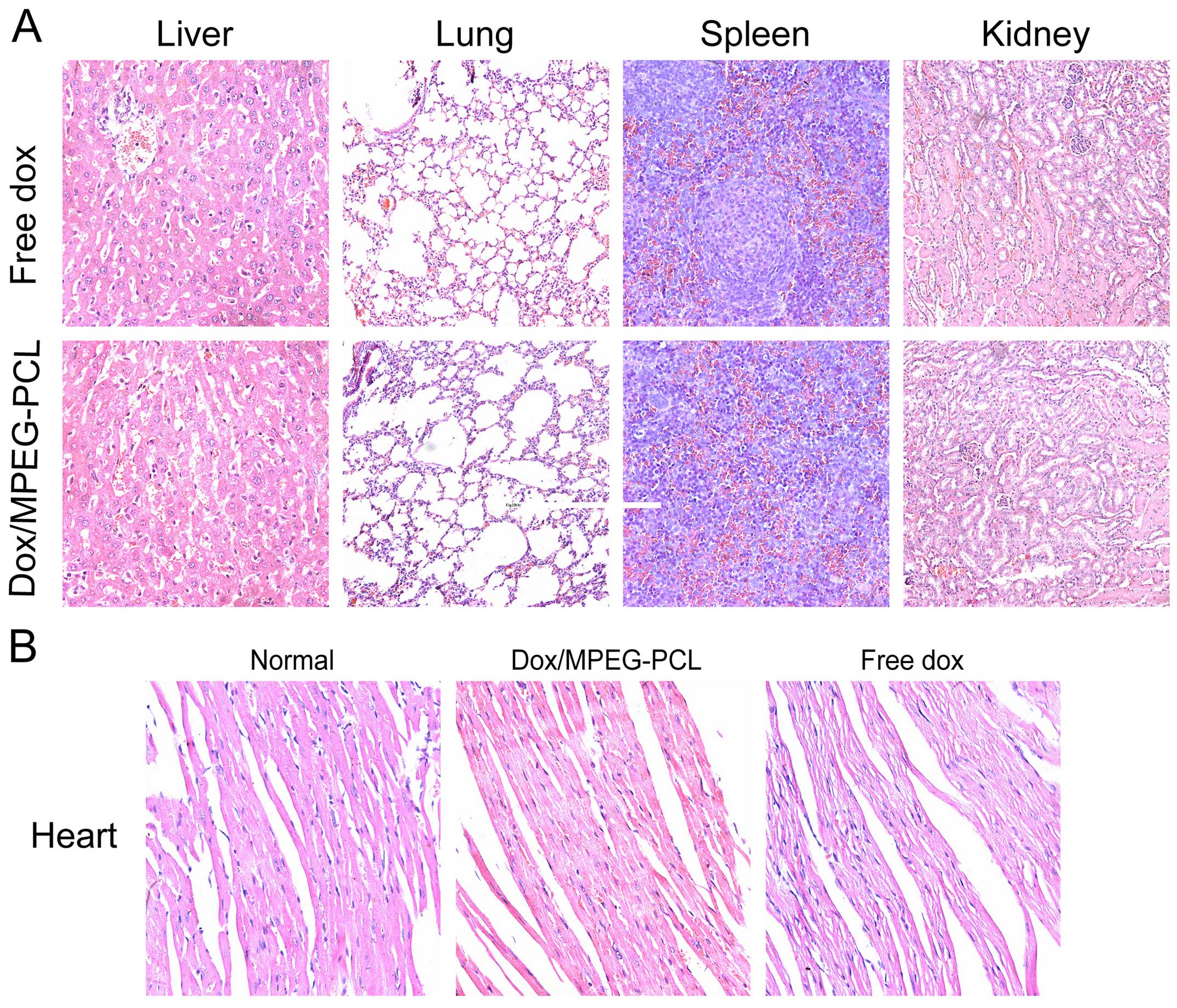
|
1
|
Azim HA, Santoro L, Bociek RG, Gandini S,
Malek RA and Azim HA Jr: High dose intensity doxorubicin in
aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: A literature-based
meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 21:1064–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sauter C: Doxorubicin adjuvant
combinations for breast cancer. Lancet. 342:1550–1551. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Staropoli N, Ciliberto D, Botta C,
Fiorillo L, Grimaldi A, Lama S, Caraglia M, Salvino A, Tassone P
and Tagliaferri P: Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in the
management of ovarian cancer: A systematic review and metaanalysis
of randomized trials. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:707–720. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grenader T, Goldberg A, Hadas-Halperin I
and Gabizon A: Long-term response to pegylated liposomal
doxorubicin in patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcomas.
Anticancer Drugs. 20:15–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heger Z, Cernei N, Kudr J, Gumulec J,
Blazkova I, Zitka O, Eckschlager T, Stiborova M, Adam V and Kizek
R: A novel insight into the cardiotoxicity of antineoplastic drug
doxorubicin. Int J Mol Sci. 14:21629–21646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chatterjee K, Zhang J, Honbo N and
Karliner JS: Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology. 115:155–162.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Wright J: Nanotechnology: Deliver on a
promise. Nature. 509:S58–S59. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gou M, Zheng X, Men K, Zhang J, Wang B, Lv
L, Wang X, Zhao Y, Luo F, Chen L, et al: Self-assembled hydrophobic
honokiol loaded MPEG-PCL diblock copolymer micelles. Pharm Res.
26:2164–2173. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng L, Gou M, Zhou S, Yi T, Zhong Q, Li
Z, He X, Chen X, Zhou L, Wei Y, et al: Antitumor activity of
monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)
micelle-encapsulated doxorubicin against mouse melanoma. Oncol Rep.
25:1557–1564. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Spriel AB, van Ojik HH, Bakker A,
Jansen MJ and van de Winkel JG: Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) is crucial for
effective Fc receptor-mediated immunity to melanoma. Blood.
101:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tsai NM, Chen BM, Wei SL, Wu CW and
Roffler SR: Anti-tumor immunoglobulin M increases lung metastasis
in an experimental model of malignant melanoma. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 20:103–109. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bourzac K: Nanotechnology: Carrying drugs.
Nature. 491:S58–S60. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aiken MJ, Suhag V, Garcia CA, Acio E,
Moreau S, Priebat DA, Chennupati SP and Van Nostrand D:
Doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity and cardiac rest gated blood
pool imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 34:762–767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Fang J, Kim YJ, Wong MK and Wang P:
Codelivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel by cross-linked
multilamellar liposome enables synergistic antitumor activity. Mol
Pharm. 11:1651–1661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Green AE and Rose PG: Pegylated liposomal
doxorubicin in ovarian cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 1:229–239.
2006.
|
|
16
|
Unsoy G, Khodadust R, Yalcin S, Mutlu P
and Gunduz U: Synthesis of Doxorubicin loaded magnetic chitosan
nanoparticles for pH responsive targeted drug delivery. Eur J Pharm
Sci. 62:243–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanyakamdhorn S, Agudelo D and
Tajmir-Riahi HA: Encapsulation of antitumor drug Doxorubicin and
its analogue by chitosan nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules.
14:557–563. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang X, Grailer JJ, Rowland IJ, Javadi A,
Hurley SA, Steeber DA and Gong S: Multifunctional SPIO/DOX-loaded
wormlike polymer vesicles for cancer therapy and MR imaging.
Biomaterials. 31:9065–9073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng H, Liong M, Xia T, Li Z, Ji Z, Zink
JI and Nel AE: Engineered design of mesoporous silica nanoparticles
to deliver doxorubicin and P-glycoprotein siRNA to overcome drug
resistance in a cancer cell line. ACS Nano. 4:4539–4550. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jia Y, Yuan M, Yuan H, Huang X, Sui X, Cui
X, Tang F, Peng J, Chen J, Lu S, et al: Co-encapsulation of
magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and doxorubicin
into biodegradable PLGA nanocarriers for intratumoral drug
delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:1697–1708. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Gaucher G, Dufresne MH, Sant VP, Kang N,
Maysinger D and Leroux JC: Block copolymer micelles: Preparation,
characterization and application in drug delivery. J Control
Release. 109:169–188. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Farokhzad OC, Jon S, Khademhosseini A,
Tran TN, Lavan DA and Langer R: Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates:
A new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
64:7668–7672. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hudson SP, Padera RF, Langer R and Kohane
DS: The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials.
29:4045–4055. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chow EK, Zhang XQ, Chen M, Lam R, Robinson
E, Huang H, Schaffer D, Osawa E, Goga A and Ho D: Nanodiamond
therapeutic delivery agents mediate enhanced chemoresistant tumor
treatment. Sci Transl Med. 3:73ra212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Canelas DA, Herlihy KP and DeSimone JM:
Top-down particle fabrication: Control of size and shape for
diagnostic imaging and drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed
Nanobiotechnol. 1:391–404. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gupta AK and Gupta M: Synthesis and
surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical
applications. Biomaterials. 26:3995–4021. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gupta AK and Wells S: Surface-modified
superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: Preparation,
characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. IEEE Trans
Nanobioscience. 3:66–73. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Agarwal A, Mackey MA, El-Sayed MA and
Bellamkonda RV: Remote triggered release of doxorubicin in tumors
by synergistic application of thermosensitive liposomes and gold
nanorods. ACS Nano. 5:4919–4926. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsumura Y and Maeda H: A new concept for
macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanism of
tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent
smancs. Cancer Res. 46:6387–6392. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sant S, Poulin S and Hildgen P: Effect of
polymer architecture on surface properties, plasma protein
adsorption, and cellular interactions of pegylated nanoparticles. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 87:885–895. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu J, Jia H, Guo L, Zhang G, Cao Y, Yan H
and Liu K: Zwitterionic polymeric micelles that undergo a
pH-triggered positive charge for enhanced cellular uptake. Eur
Polym J. 66:376–385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gou M, Zheng X, Men K, Zhang J, Zheng L,
Wang X, Luo F, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Wei Y, et al:
Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/poly(ethylene
glycol)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles: Preparation,
characterization, and application in doxorubicin delivery. J Phys
Chem B. 113:12928–12933. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|