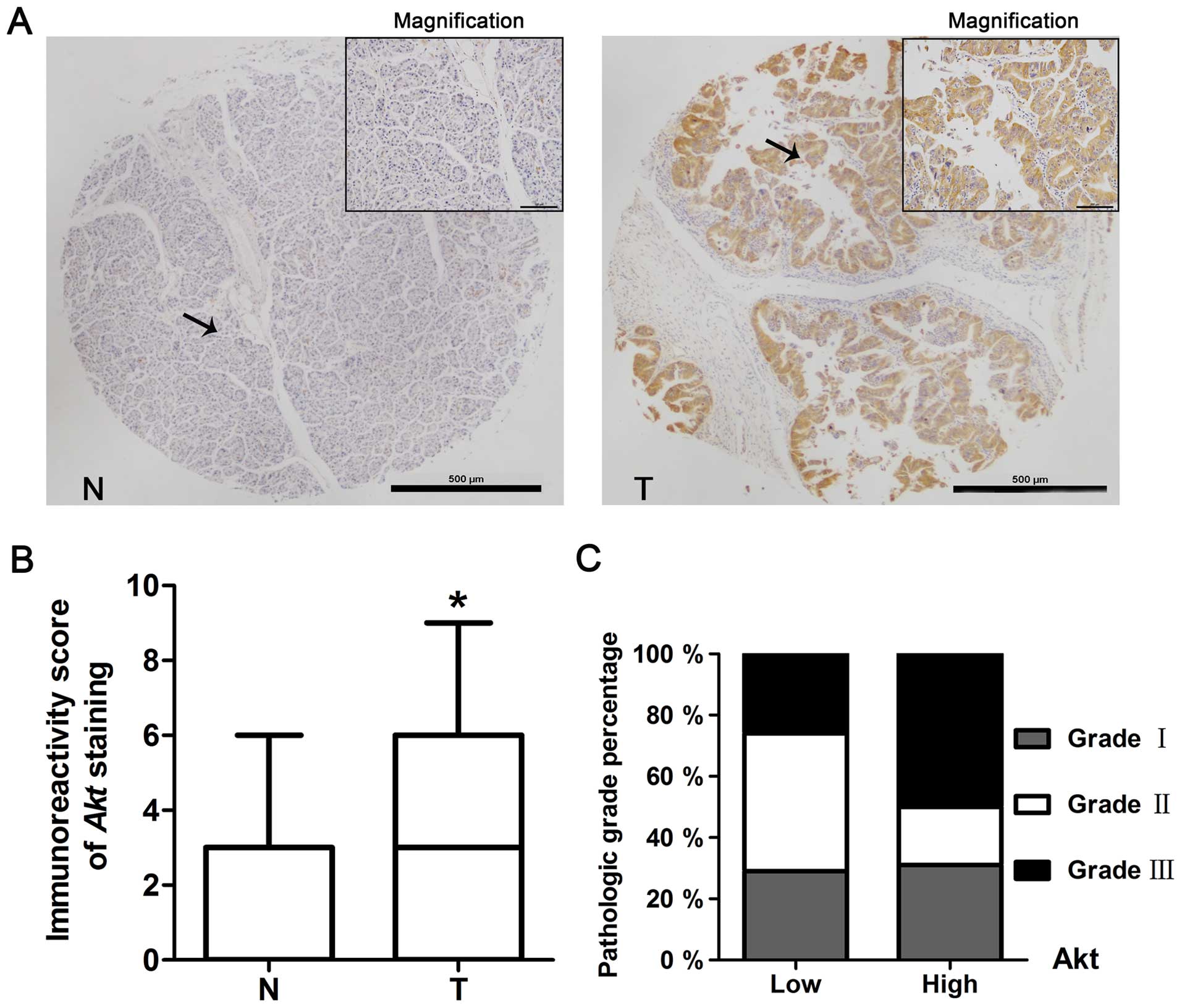
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Ko CY, Stewart
AK, Winchester DP and Talamonti MS: National failure to operate on
early stage pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 246:173–180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Duong HQ, Kim HJ, Kang HJ, Seong YS and
Bae I: ZSTK474, a PI3K inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and
sensitizes human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to gemcitabine.
Oncol Rep. 27:182–188. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Yuan TL and Cantley LC: PI3K pathway
alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene.
27:5497–5510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: Implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 94:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Michl P and Downward J: Mechanisms of
disease: PI3K/AKT signaling in gastrointestinal cancers. Z
Gastroenterol. 43:1133–1139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Falasca M, Selvaggi F, Buus R, Sulpizio S
and Edling CE: Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathways in
pancreatic cancer - from molecular signalling to clinical trials.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:455–463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Edling CE, Selvaggi F, Buus R, Maffucci T,
Di Sebastiano P, Friess H, Innocenti P, Kocher HM and Falasca M:
Key role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase class IB in pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:4928–4937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, Morooka
T, Nagano H, Dono K, Umeshita K, Sakon M, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H,
et al: Prognostic significance of activated Akt expression in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2846–2850.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schlieman MG, Fahy BN, Ramsamooj R,
Beckett L and Bold RJ: Incidence, mechanism and prognostic value of
activated AKT in pancreas cancer. Br J Cancer. 89:2110–2115. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elghazi L, Weiss AJ, Barker DJ, Callaghan
J, Staloch L, Sandgren EP, Gannon M, Adsay VN and Bernal-Mizrachi
E: Regulation of pancreas plasticity and malignant transformation
by Akt signaling. Gastroenterology. 136:1091–1103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Strebhardt K: Multifaceted polo-like
kinases: Drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 9:643–660. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Holtrich U, Wolf G, Bräuninger A, Karn T,
Böhme B, Rübsamen-Waigmann H and Strebhardt K: Induction and
down-regulation of PLK, a human serine/threonine kinase expressed
in proliferating cells and tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:1736–1740. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weichert W, Schmidt M, Jacob J, Gekeler V,
Langrehr J, Neuhaus P, Bahra M, Denkert C, Dietel M and Kristiansen
G: Overexpression of Polo-like kinase 1 is a common and early event
in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 5:259–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song B, Liu XS, Rice SJ, Kuang S, Elzey
BD, Konieczny SF, Ratliff TL, Hazbun T, Chiorean EG and Liu X: Plk1
phosphorylation of orc2 and hbo1 contributes to gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:58–68. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Lo ACY, Woo TTY, Wong RL and Wong D:
Apoptosis and other cell death mechanisms after retinal detachment:
Implications for photoreceptor rescue. Ophthalmologica. 226(Suppl
1): 10–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Christensen ME, Jansen ES, Sanchez W and
Waterhouse NJ: Flow cytometry based assays for the measurement of
apoptosis-associated mitochondrial membrane depolarisation and
cytochrome c release. Methods. 61:138–145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fulda S, Galluzzi L and Kroemer G:
Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
9:447–464. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kasahara K, Goto H, Izawa I, Kiyono T,
Watanabe N, Elowe S, Nigg EA and Inagaki M: PI 3-kinase-dependent
phosphorylation of Plk1-Ser99 promotes association with 14-3-3
gamma and is required for metaphase-anaphase transition. Nat
Commun. 4:18822013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Li Z, Ahmad N and Liu X: Plk1
phosphorylation of IRS2 prevents premature mitotic exit via AKT
inactivation. Biochemistry. 54:2473–2480. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang S, Wu X, Zhang J, Chen Y, Xu J, Xia
X, He S, Qiang F, Li A, Shu Y, et al: CHIP functions as a novel
suppressor of tumour angiogenesis with prognostic significance in
human gastric cancer. Gut. 62:496–508. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Weichert W, Röske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T,
Ebert MP, Pross M, Dietel M, Denkert C and Röcken C: Association of
patterns of class I histone deacetylase expression with patient
prognosis in gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 9:139–148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jia L, Xing J, Ding Y, Shen Y, Shi X, Ren
W, Wan M, Guo J, Zheng S, Liu Y, et al: Hyperuricemia causes
pancreatic β-cell death and dysfunction through NF-κB signaling
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e782842013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yu C, Zhang X, Sun G, Guo X, Li H, You Y,
Jacobs JL, Gardner K, Yuan D, Xu Z, et al: RNA
interference-mediated silencing of the polo-like kinase 1 gene
enhances chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Mol Med. 12A:2334–2349. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ng SS, Tsao MS, Nicklee T and Hedley DW:
Wortmannin inhibits pkb/akt phosphorylation and promotes
gemcitabine antitumor activity in orthotopic human pancreatic
cancer xenografts in immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res.
7:3269–3275. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ng SSW, Tsao MS, Chow S and Hedley DW:
Inhibition of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase enhances
gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 60:5451–5455. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Costello E, Greenhalf W and Neoptolemos
JP: New biomarkers and targets in pancreatic cancer and their
application to treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:435–444.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
di Magliano MP and Logsdon CD: Roles for
KRAS in pancreatic tumor development and progression.
Gastroenterology. 144:1220–1229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stephen AG, Esposito D, Bagni RK and
McCormick F: Dragging ras back in the ring. Cancer Cell.
25:272–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hofmann I, Weiss A, Elain G, Schwaederle
M, Sterker D, Romanet V, Schmelzle T, Lai A, Brachmann SM,
Bentires-Alj M, et al: K-RAS mutant pancreatic tumors show higher
sensitivity to MEK than to PI3K inhibition in vivo. PloS One.
7:e441462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim R, Yamauchi T, Husain K, Sebti S and
Malafa M: Triciribine phosphate monohydrate, an AKT inhibitor,
enhances gemcitabine activity in pancreatic cancer cells.
Anticancer Res. 35:4599–4604. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bondar VM, Sweeney-Gotsch B, Andreeff M,
Mills GB and McConkey DJ: Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol
3′-kinase-AKT pathway induces apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma
cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:989–997.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arlt A, Müerköster SS and Schäfer H:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett.
332:346–358. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ivey R, Desai M, Green K, Sinha-Hikim I,
Friedman TC and Sinha-Hikim AP: Additive effects of nicotine and
high-fat diet on hepatocellular apoptosis in mice: Involvement of
caspase 2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase-mediated intrinsic
pathway signaling. Horm Metab Res. 46:568–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dan HC, Sun M, Kaneko S, Feldman RI,
Nicosia SV, Wang HG, Tsang BK and Cheng JQ: Akt phosphorylation and
stabilization of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). J
Biol Chem. 279:5405–5412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|