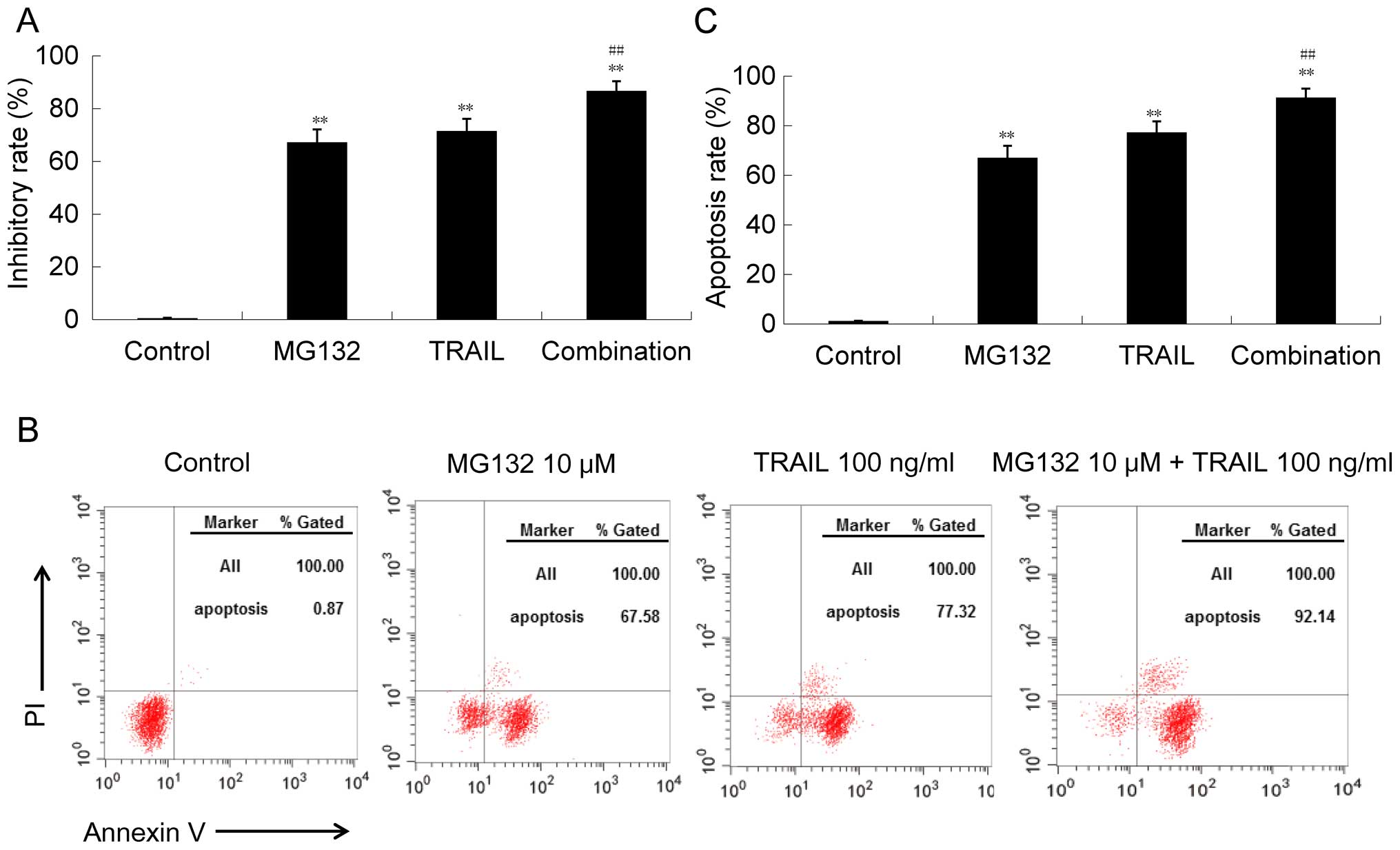
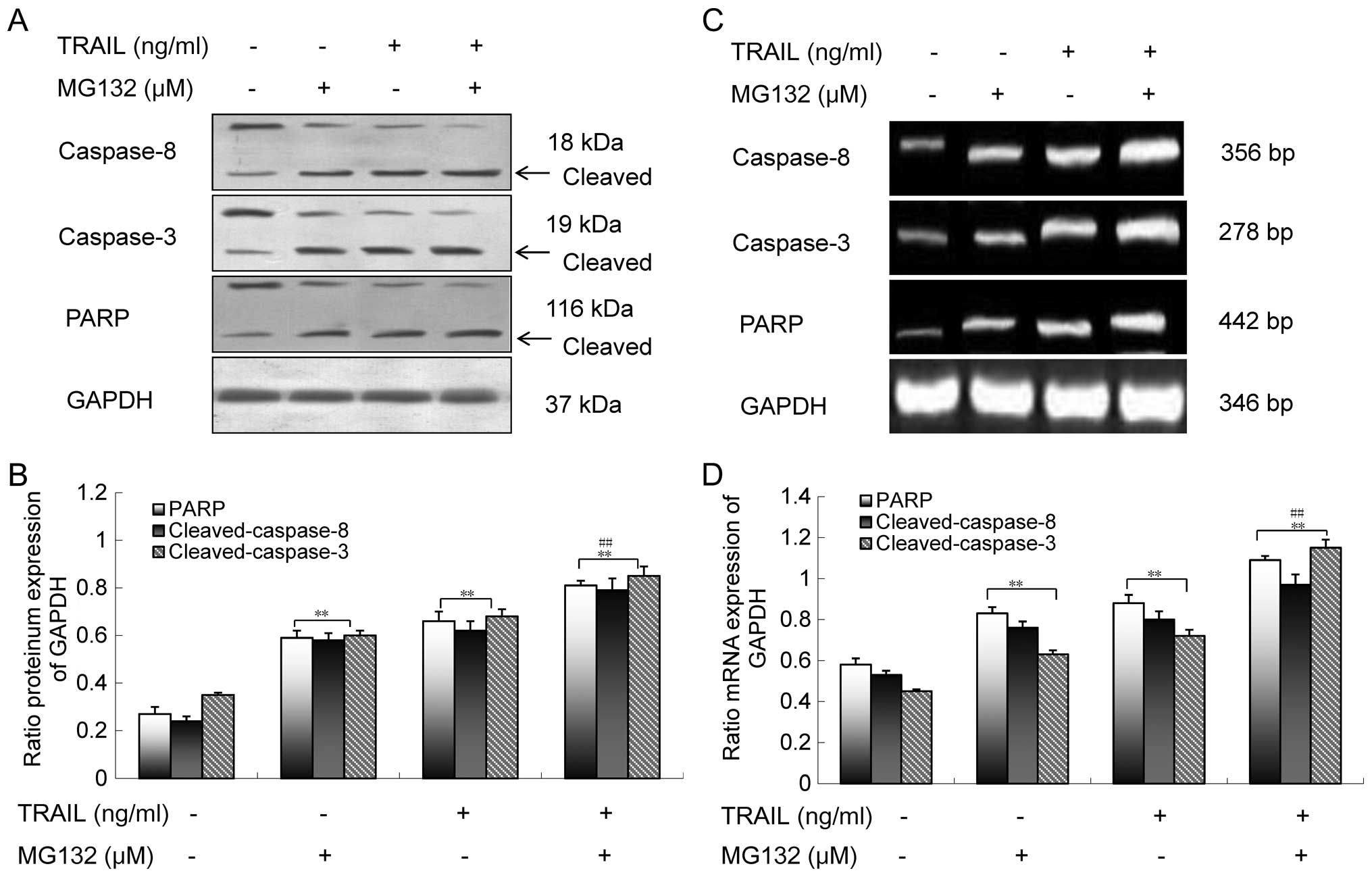
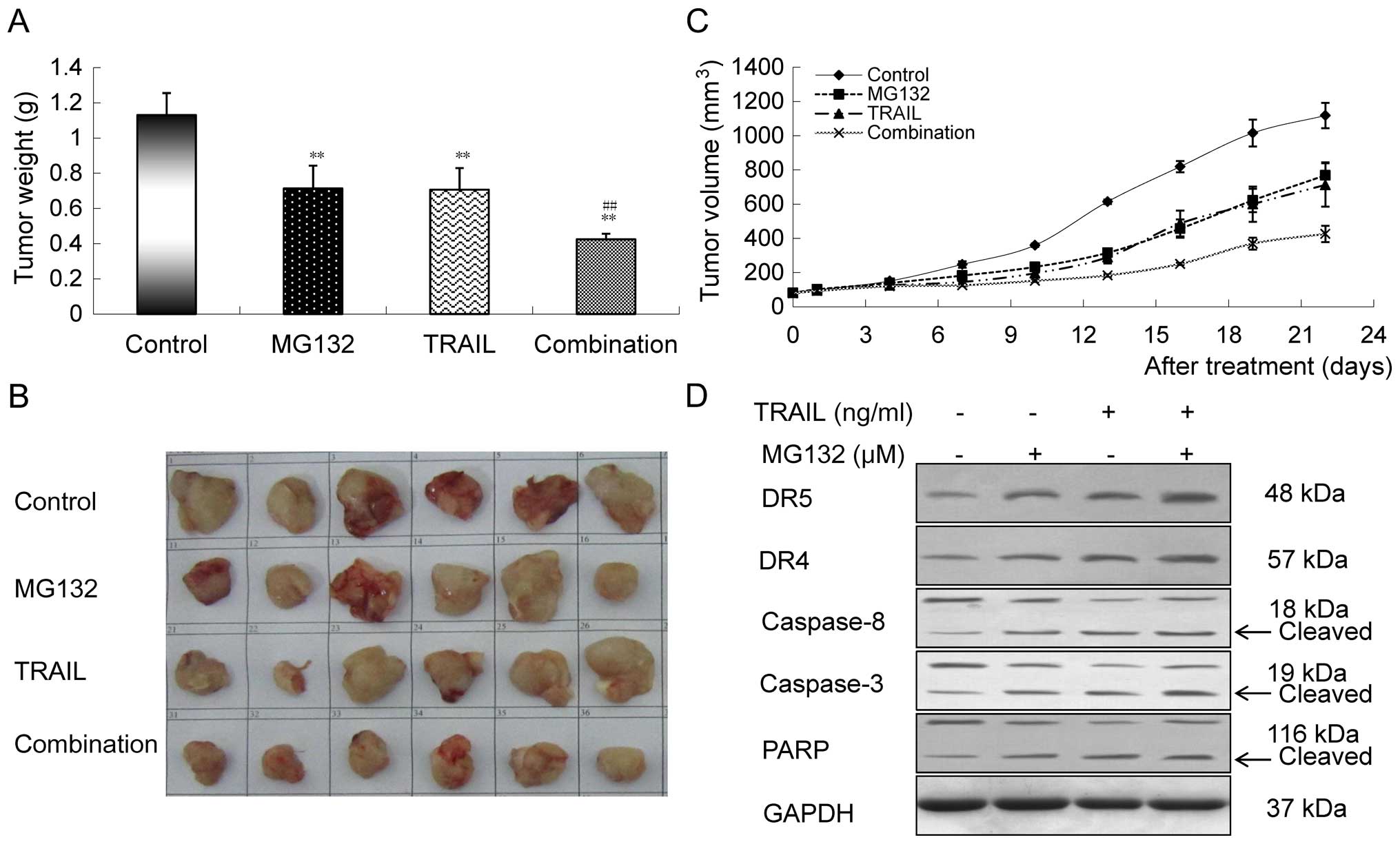
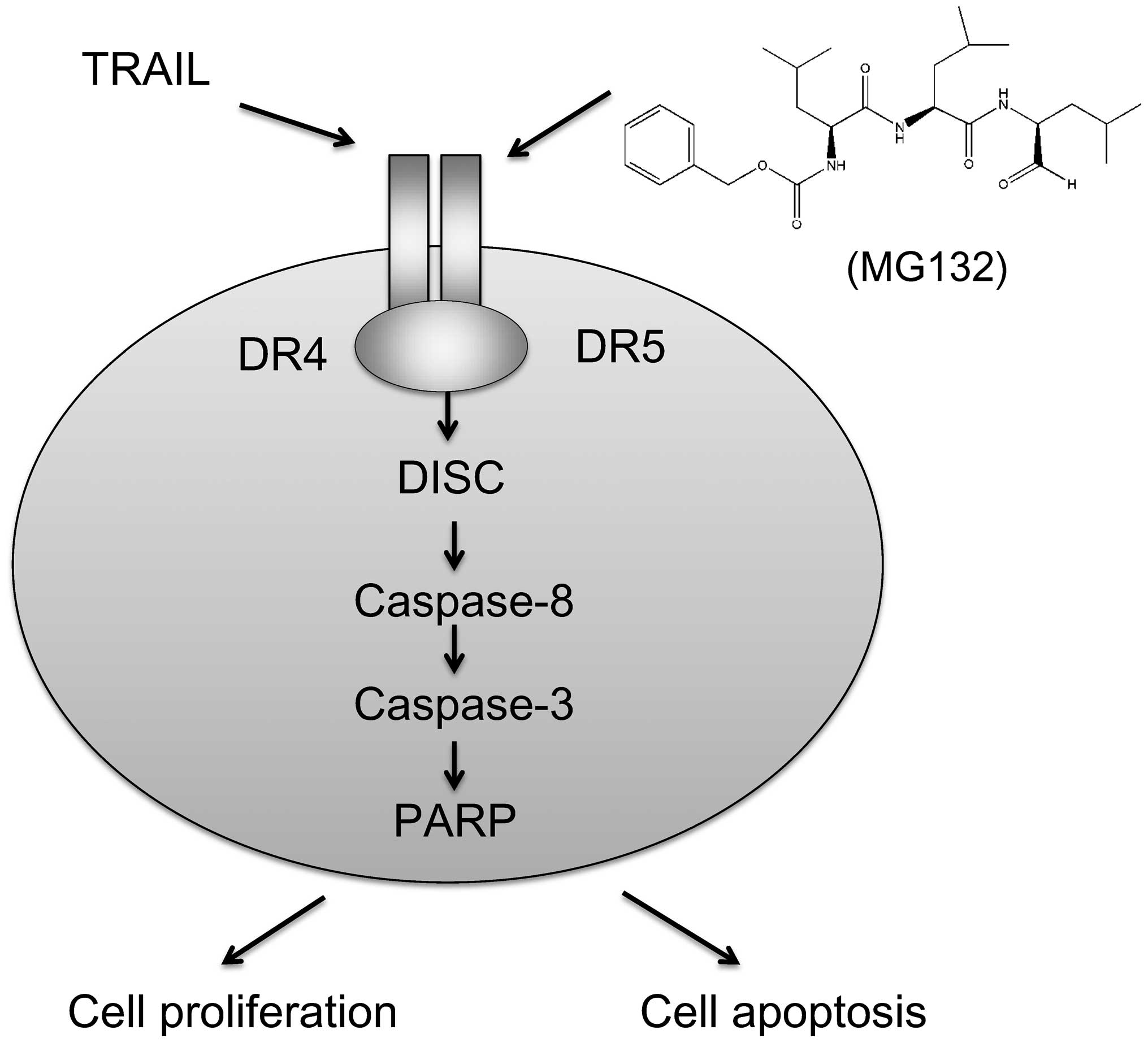
|
1
|
Bizama C, García P, Espinoza JA, Weber H,
Leal P, Nervi B and Roa JC: Targeting specific molecular pathways
holds promise for advanced gallbladder cancer therapy. Cancer Treat
Rev. 41:222–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC and Sharma
ID: Carcinoma of the gallbladder. Lancet Oncol. 4:167–176. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Henley SJ, Weir HK, Jim MA, Watson M and
Richardson LC: Gallbladder cancer incidence and mortality, United
States 1999–2011. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 24:1319–1326.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan E and Berlin J: Biliary tract
cancers: Understudied and poorly understood. J Clin Oncol.
33:1845–1848. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nesterov A, Nikrad M, Johnson T and Kraft
AS: Oncogenic Ras sensitizes normal human cells to tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis.
Cancer Res. 64:3922–3927. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R,
Ebner R, Ni J and Dixit VM: The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand
TRAIL. Science. 276:111–113. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bellail AC, Tse MC, Song JH, Phuphanich S,
Olson JJ, Sun SY and Hao C: DR5-mediated DISC controls caspase-8
cleavage and initiation of apoptosis in human glioblastomas. J Cell
Mol Med. 14A:1303–1317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fernald K and Kurokawa M: Evading
apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 23:620–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Enhancement
of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and
irradiation: mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:139–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin EA, Sohn EJ, Won G, Choi JU, Jeong M,
Kim B, Kim MJ and Kim SH: Upregulation of microRNA135a-3p and death
receptor 5 plays a critical role in Tanshinone I sensitized
prostate cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis. Oncotarget.
5:5624–5636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stuckey DW and Shah K: TRAIL on trial:
Preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 19:685–694.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sarhan D, Wennerberg E, D'Arcy P, Gurajada
D, Linder S and Lundqvist A: A novel inhibitor of proteasome
deubiquitinating activity renders tumor cells sensitive to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by natural killer cells and T cells.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:1359–1368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dokouhaki P, Schuh NW, Joe B, Allen CA,
Der SD, Tsao MS and Zhang L: NKG2D regulates production of soluble
TRAIL by ex vivo expanded human γδ T cells. Eur J Immunol.
43:3175–3182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nalepa G, Rolfe M and Harper JW: Drug
discovery in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
5:596–613. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adams J: The proteasome: A suitable
antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnson DE: The ubiquitin-proteasome
system: Opportunities for therapeutic intervention in solid tumors.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:T1–T17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
He Q, Huang Y and Sheikh MS: Proteasome
inhibitor MG132 upregulates death receptor 5 and cooperates with
Apo2L/TRAIL to induce apoptosis in Bax-proficient and -deficient
cells. Oncogene. 23:2554–2558. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pandit B and Gartel AL: Proteasome
inhibitors induce p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cells.
Am J Pathol. 178:355–360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ustundag Y, Bronk SF and Gores GJ:
Proteasome inhibition-induces endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction and
cell death of human cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:851–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim OH, Lim JH, Woo KJ, Kim YH, Jin IN,
Han ST, Park JW and Kwon TK: Influence of p53 and p21Waf1
expression on G2/M phase arrest of colorectal carcinoma HCT116
cells to proteasome inhibitors. Int J Oncol. 24:935–941.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Watts TH: TNF/TNFR family members in
costimulation of T cell responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:23–68.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vucic D, Dixit VM and Wertz IE:
Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: A post-translational modification at
the edge of life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:439–452.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song JJ, Szczepanski MJ, Kim SY, Kim JH,
An JY, Kwon YT, Alcala MA Jr, Bartlett DL and Lee YJ:
c-Cbl-mediated degradation of TRAIL receptors is responsible for
the development of the early phase of TRAIL resistance. Cell
Signal. 22:553–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Li X, Huang T, Jiang G, Gong W, Qian H and
Zou C: Proteasome inhibitor MG132 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis
and inhibits invasion of human osteosarcoma OS732 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 439:179–186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han B, Yao W, Oh YT, Tong JS, Li S, Deng
J, Yue P, Khuri FR and Sun SY: The novel proteasome inhibitor
carfilzomib activates and enhances extrinsic apoptosis involving
stabilization of death receptor 5. Oncotarget. 6:17532–17542. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ko H, Jeong MH, Jeon H, Sung GJ, So Y, Kim
I, Son J, Lee SW, Yoon HG and Choi KC: Delphinidin sensitizes
prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, by inducing DR5
and causing caspase-mediated HDAC3 cleavage. Oncotarget.
6:9970–9984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kelley SK and Ashkenazi A: Targeting death
receptors in cancer with Apo2L/TRAIL. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
4:333–339. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Merchant MS, Geller JI, Baird K, Chou AJ,
Galli S, Charles A, Amaoko M, Rhee EH, Price A, Wexler LH, et al:
Phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in pediatric
patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 30:4141–4147. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jazirehi AR, Kurdistani SK and Economou
JS: Histone deacetylase inhibitor sensitizes apoptosis-resistant
melanomas to cytotoxic human T lymphocytes through regulation of
TRAIL/DR5 pathway. J Immunol. 192:3981–3989. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee YJ, Seol JW, Jeong JK, Moon MH and
Park SY: Inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system sensitizes
TRAIL-resistant prostate cancer cells by up-regulation of death
receptor 5. Mol Med Rep. 4:1255–1259. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Wilt LH, Kroon J, Jansen G, de Jong S,
Peters GJ and Kruyt FA: Bortezomib and TRAIL: A perfect match for
apoptotic elimination of tumour cells? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
85:363–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|