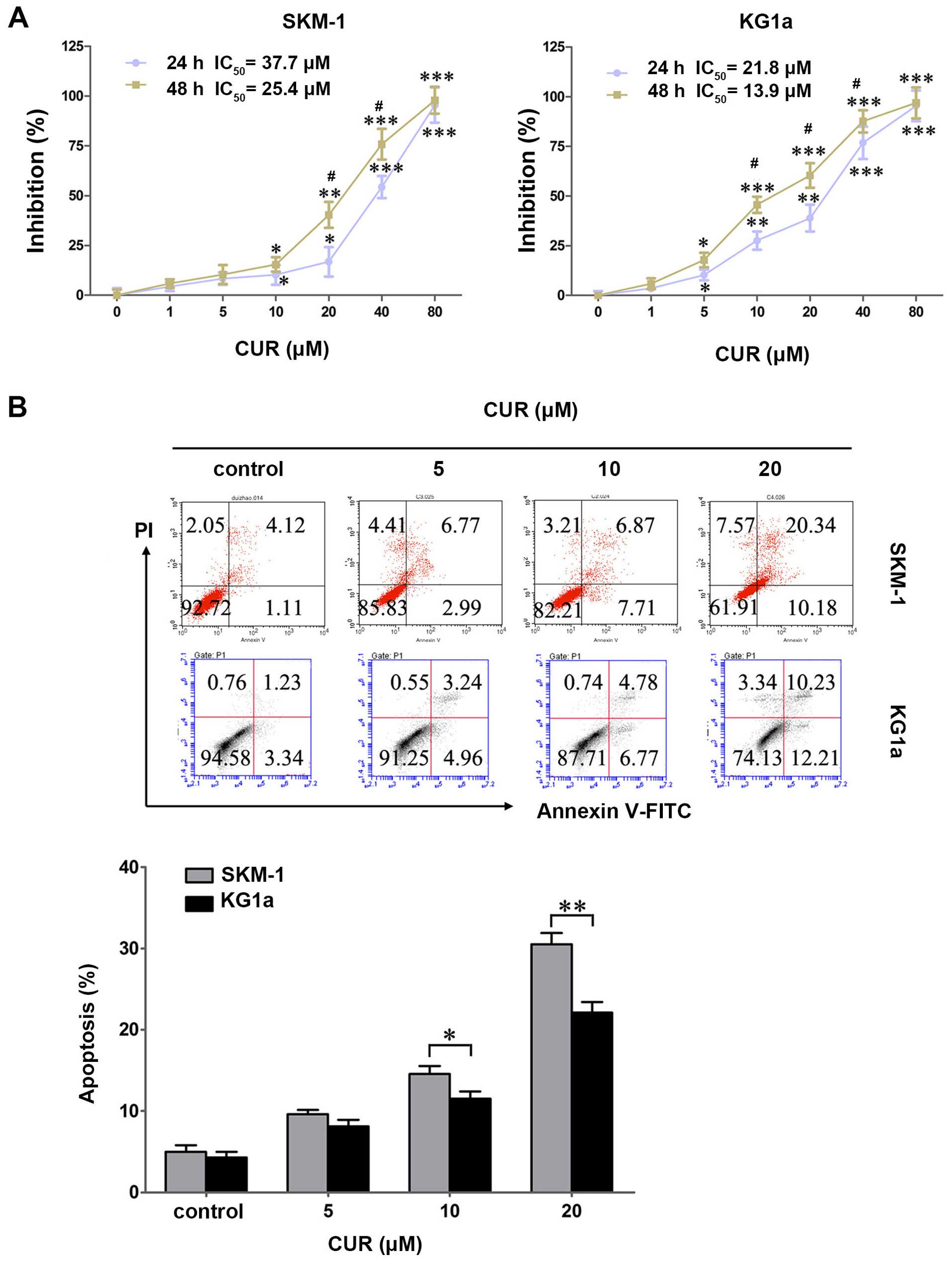
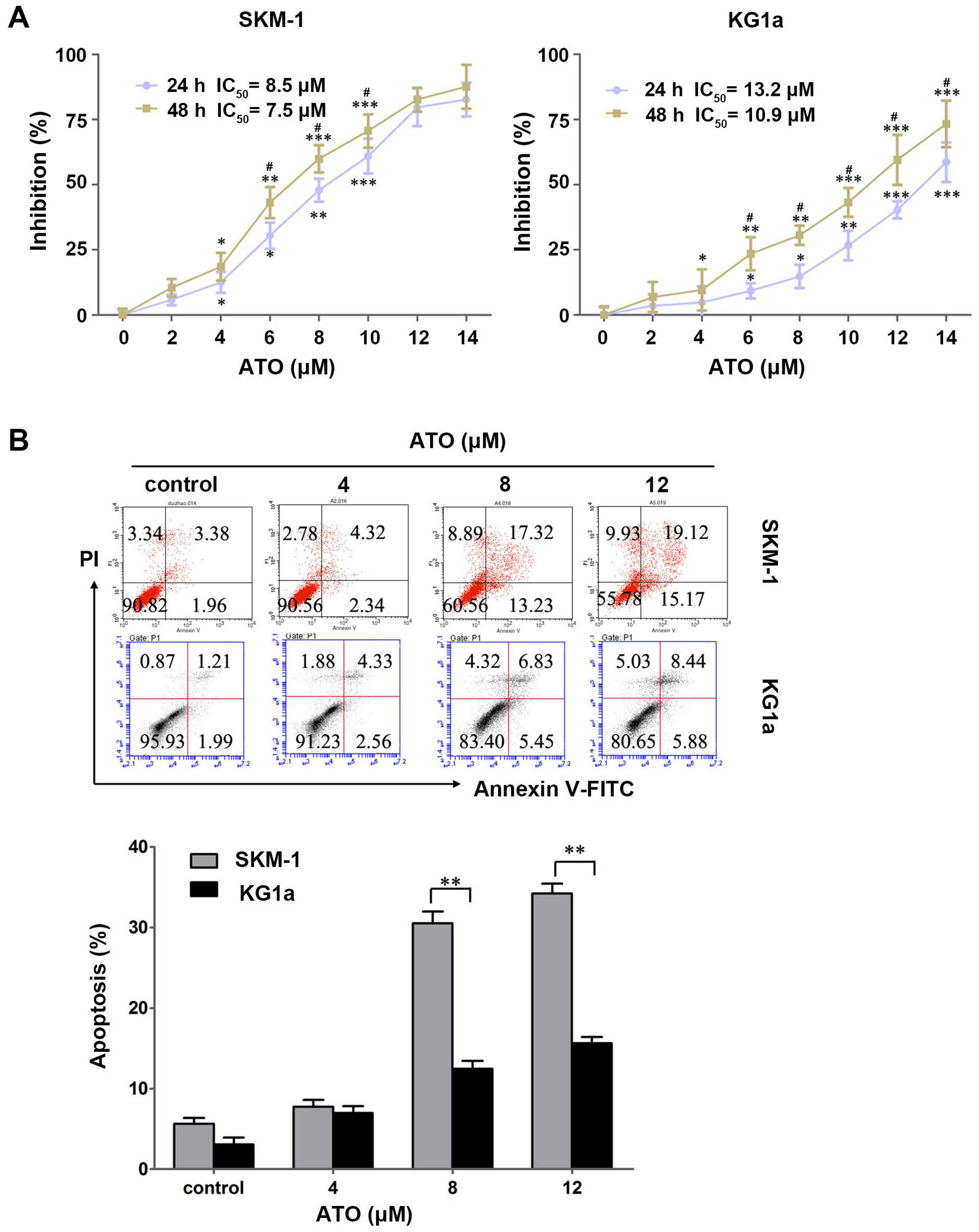
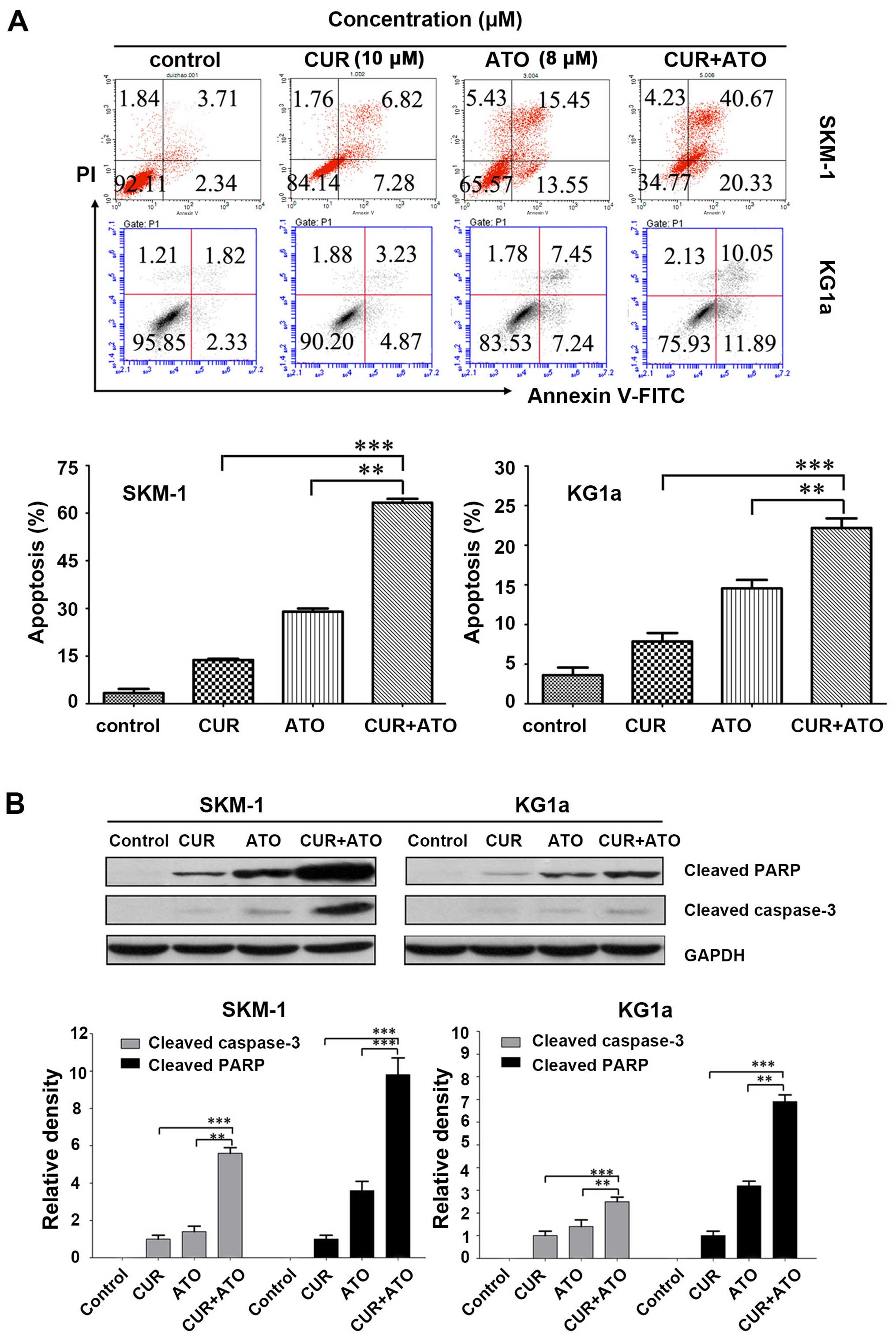
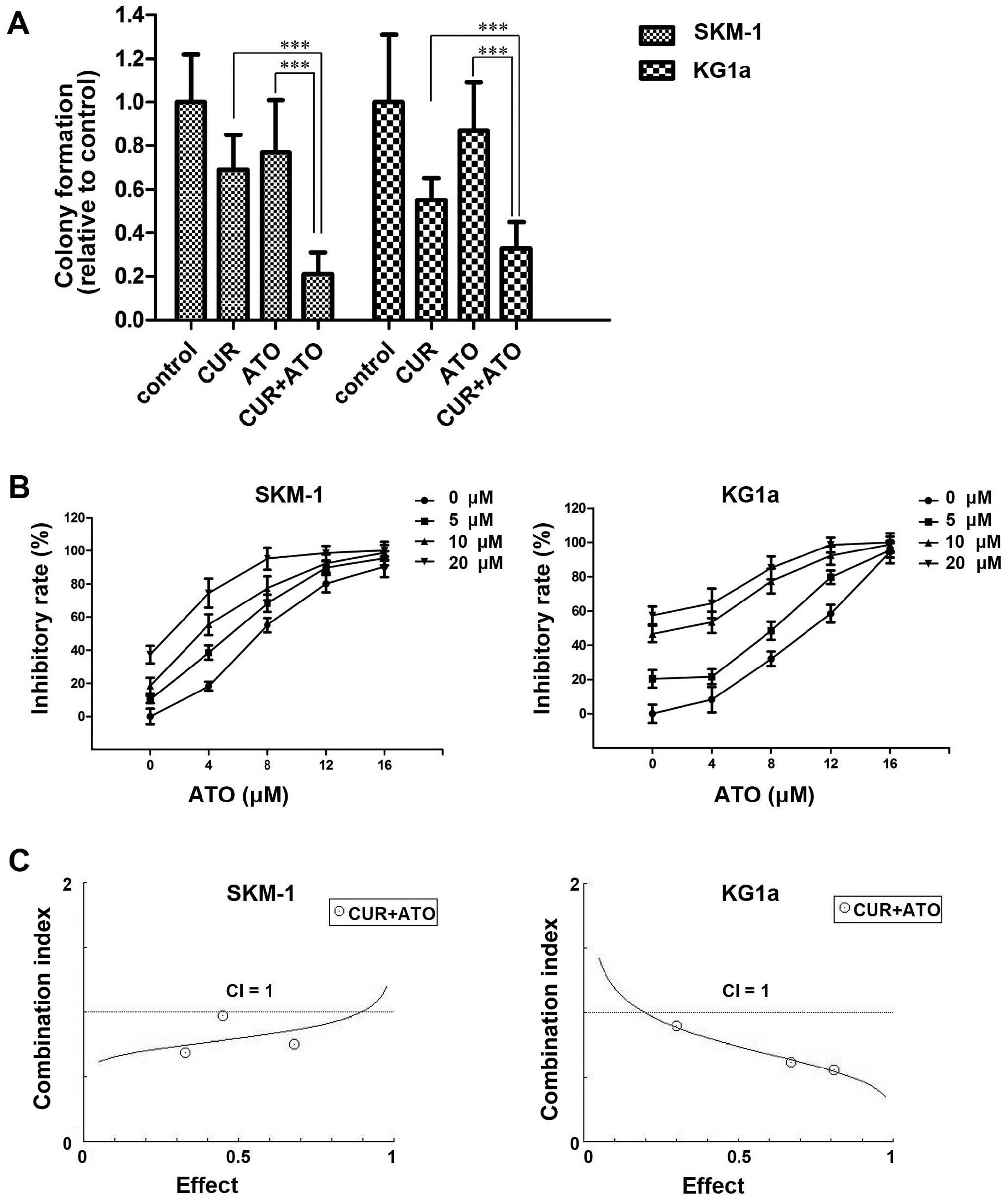
|
1
|
Nimer SD: Myelodysplastic syndromes.
Blood. 111:4841–4851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cogle CR, Craig BM, Rollison DE and List
AF: Incidence of the myelodysplastic syndromes using a novel
claims-based algorithm: High number of uncaptured cases by cancer
registries. Blood. 117:7121–7125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sekeres MA, Schoonen WM, Kantarjian H,
List A, Fryzek J, Paquette R and Maciejewski JP: Characteristics of
US patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: Results of six
cross-sectional physician surveys. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:1542–1551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma X, Does M, Raza A and Mayne ST:
Myelodysplastic syndromes: Incidence and survival in the United
States. Cancer. 109:1536–1542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeidan AM, Linhares Y and Gore SD: Current
therapy of myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Rev. 27:243–259. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lengfelder E, Hofmann WK and Nowak D:
Impact of arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Leukemia. 26:433–442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mayorga J, Richardson-Hardin C and Dicke
KA: Arsenic trioxide as effective therapy for relapsed acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 6:341–346. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vey N, Bosly A, Guerci A, Feremans W,
Dombret H, Dreyfus F, Bowen D, Burnett A, Dennis M, Ribrag V, et
al: Arsenic trioxide in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: A
phase II multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 24:2465–2471. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schiller GJ, Slack J, Hainsworth JD, Mason
J, Saleh M, Rizzieri D, Douer D and List AF: Phase II multicenter
study of arsenic trioxide in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 24:2456–2464. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei W, Zhou F, Zhang Y, Guo L, Shi H and
Hou J: A combination of thalidomide and arsenic trioxide is
effective and well tolerated in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. Leuk Res. 36:715–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Galimberti S, Guerrini F, Salvi F, Petrini
I, Gioia D, Messa E, Palumbo GA, Cilloni D, Petrini M and Levis A:
Arsenic trioxide and ascorbic acid interfere with the BCL2 family
genes in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: An ex-vivo study.
J Hematol Oncol. 5:532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo Q, Li Y, Deng J and Zhang Z: PARP-1
inhibitor sensitizes arsenic trioxide in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via abrogation of G2/M checkpoint and suppression of DNA
damage repair. Chem Biol Interact. 226:12–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tao JL, Li LJ, Fu R, Wang HQ, Jiang HJ,
Yue LZ, Zhang W, Liu H, Ruan EB, Qu W, et al: Elevated TIM3+
hematopoietic stem cells in untreated myelodysplastic syndrome
displayed aberrant differentiation, overproliferation and decreased
apoptosis. Leuk Res. 38:714–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pandolfi A, Barreyro L and Steidl U:
Concise review: Preleukemic stem cells: Molecular biology and
clinical implications of the precursors to leukemia stem cells.
Stem Cells Transl Med. 2:143–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roboz GJ, Ritchie EK, Curcio T, Samuel M,
Provenzano J, Segovia J, Christos PJ, Mathew S, Allen-Bard S and
Feldman EJ: Arsenic trioxide and low-dose cytarabine for patients
with intermediate-2 and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk
Res. 35:522–525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zheng WL, Zhang GS, Xu YX, Shen JK, Dai CW
and Pei MF: Arsenic trioxide, thalidomide and retinoid acid
combination therapy in higher risk myelodysplastic syndrome
patients. Leuk Res. 32:251–254. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Goel A and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin, the
golden spice from Indian saffron, is a chemosensitizer and
radiosensitizer for tumors and chemoprotector and radioprotector
for normal organs. Nutr Cancer. 62:919–930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du B, Jiang L, Xia Q and Zhong L:
Synergistic inhibitory effects of curcumin and 5-fluorouracil on
the growth of the human colon cancer cell line HT-29. Chemotherapy.
52:23–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Everett PC, Meyers JA, Makkinje A, Rabbi M
and Lerner A: Preclinical assessment of curcumin as a potential
therapy for B-CLL. Am J Hematol. 82:23–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kamat AM, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin potentiates the apoptotic effects of chemotherapeutic
agents and cytokines through down-regulation of nuclear
factor-kappaB and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products in
IFN-alpha-sensitive and IFN-alpha-resistant human bladder cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1022–1030. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bharti AC, Donato N, Singh S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates the constitutive
activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and IkappaBalpha kinase in
human multiple myeloma cells, leading to suppression of
proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Blood. 101:1053–1062.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li L, Ahmed B, Mehta K and Kurzrock R:
Liposomal curcumin with and without oxaliplatin: Effects on cell
growth, apoptosis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:1276–1282. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anand P, Sundaram C, Jhurani S,
Kunnumakkara AB and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin and cancer: An ̔old-age̓
disease with an ̔age-old̓ solution. Cancer Lett. 267:133–164. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matozaki S, Nakagawa T, Kawaguchi R,
Aozaki R, Tsutsumi M, Murayama T, Koizumi T, Nishimura R, Isobe T
and Chihara K: Establishment of a myeloid leukaemic cell line
(SKNO-1) from a patient with t(8;21) who acquired monosomy 17
during disease progression. Br J Haematol. 89:805–811. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakagawa T, Matozaki S, Murayama T,
Nishimura R, Tsutsumi M, Kawaguchi R, Yokoyama Y, Hikiji K, Isobe T
and Chihara K: Establishment of a leukaemic cell line from a
patient with acquisition of chromosomal abnormalities during
disease progression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol.
85:469–476. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou J, Hong Y, Tong Y, Wei J, Qin Y, Shao
S, Wang C and Zhou K: Sonic hedgehog produced by bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells supports cell survival in
myelodysplastic syndrome. Stem Cells Int. 2015:9575022015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fuchs D, Daniel V, Sadeghi M, Opelz G and
Naujokat C: Salinomycin overcomes ABC transporter-mediated
multidrug and apoptosis resistance in human leukemia stem cell-like
KG-1a cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:1098–1104. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
She M, Niu X, Chen X, Li J, Zhou M, He Y,
Le Y and Guo K: Resistance of leukemic stem-like cells in AML cell
line KG1a to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer
Lett. 318:173–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Uchida H, Tanaka T, Sasaki K, Kato K,
Dehari H, Ito Y, Kobune M, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Tahara H, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against survivin induced
apoptosis and attenuated tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
Mol Ther. 10:162–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tefferi A and Vardiman JW: Myelodysplastic
syndromes. N Engl J Med. 361:1872–1885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue LZ, Fu R, Wang HQ, Li LJ, Hu HR, Fu L
and Shao ZH: Expression of CD123 and CD114 on the bone marrow cells
of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Chin Med J.
123:2034–2037. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Becker MW and Jordan CT: Leukemia stem
cells in 2010: Current understanding and future directions. Blood
Rev. 25:75–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rojewski MT, Körper S and Schrezenmeier H:
Arsenic trioxide therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia and
beyond: From bench to bedside. Leuk Lymphoma. 45:2387–2401. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian W, Liu J, Jin J, Ni W and Xu W:
Arsenic trioxide induces not only apoptosis but also autophagic
cell death in leukemia cell lines via up-regulation of Beclin-1.
Leuk Res. 31:329–339. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Emadi A and Gore SD: Arsenic trioxide - An
old drug rediscovered. Blood Rev. 24:191–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sánchez Y, Simón GP, Calviño E, de Blas E
and Aller P: Curcumin stimulates reactive oxygen species production
and potentiates apoptosis induction by the antitumor drugs arsenic
trioxide and lonidamine in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 335:114–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fulda S: Targeting extrinsic apoptosis in
cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
39:20–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Waligórska-Stachura J, Jankowska A, Waśko
R, Liebert W, Biczysko M, Czarnywojtek A, Baszko-Błaszyk D, Shimek
V and Ruchała M: Survivin - prognostic tumor biomarker in human
neoplasms - review. Ginekol Pol. 83:537–540. 2012.
|
|
40
|
Yu DD, Wang CT, Shi HS, Li ZY, Pan L, Yuan
QZ, Leng F, Wen Y, Chen X and Wei YQ: Enhancement of cisplatin
sensitivity in Lewis lung carcinoma by liposome-mediated delivery
of a survivin mutant. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:462010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu Y, Zheng W, Wang T, Wang P, Zhu L and
Ma X: Genetic protein TmSm(T34A) enhances sensitivity of
chemotherapy to breast cancer cell lines as a synergistic drug to
doxorubicin. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:368–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Athanasoula KC, Gogas H, Polonifi K,
Vaiopoulos AG, Polyzos A and Mantzourani M: Survivin beyond
physiology: Orchestration of multistep carcinogenesis and
therapeutic potentials. Cancer Lett. 347:175–182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|