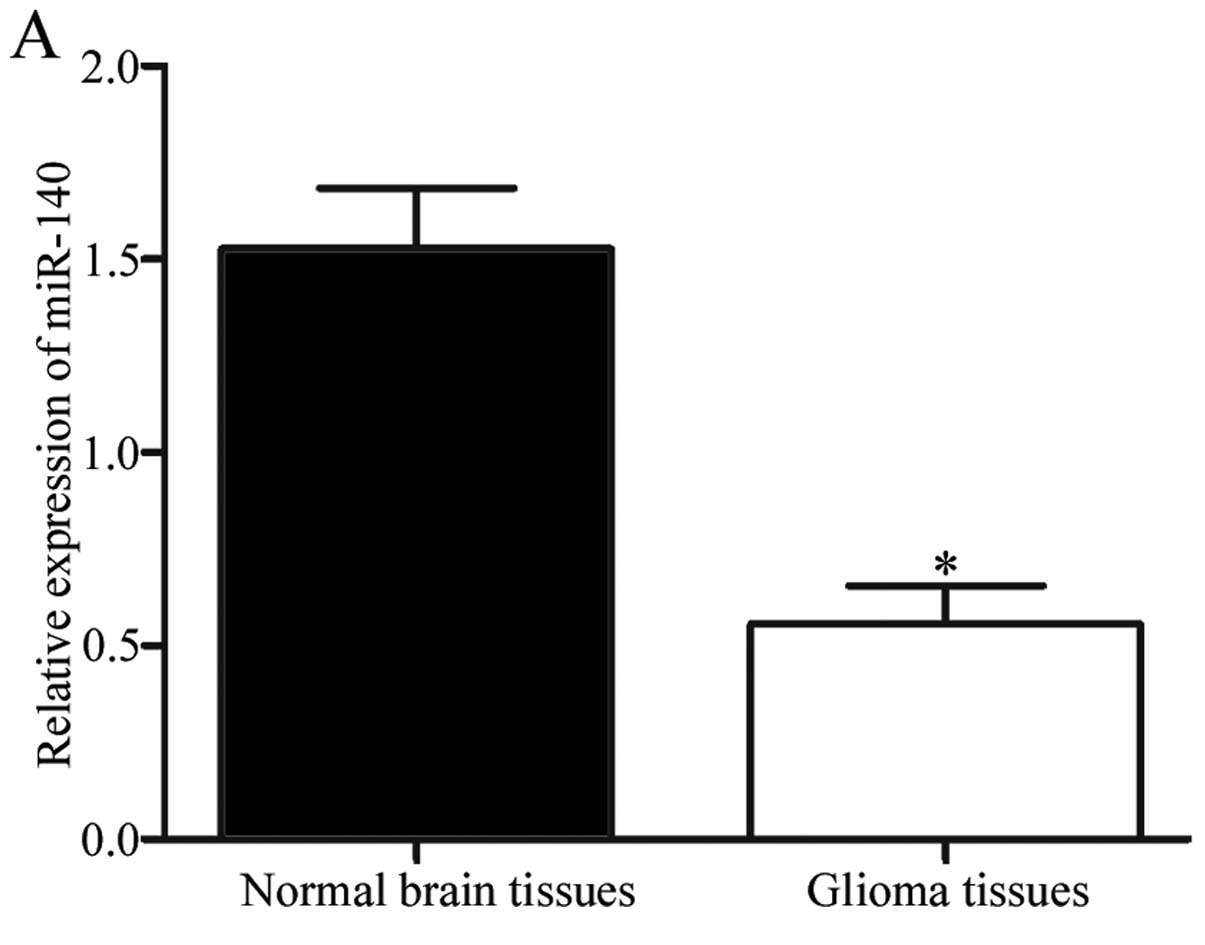
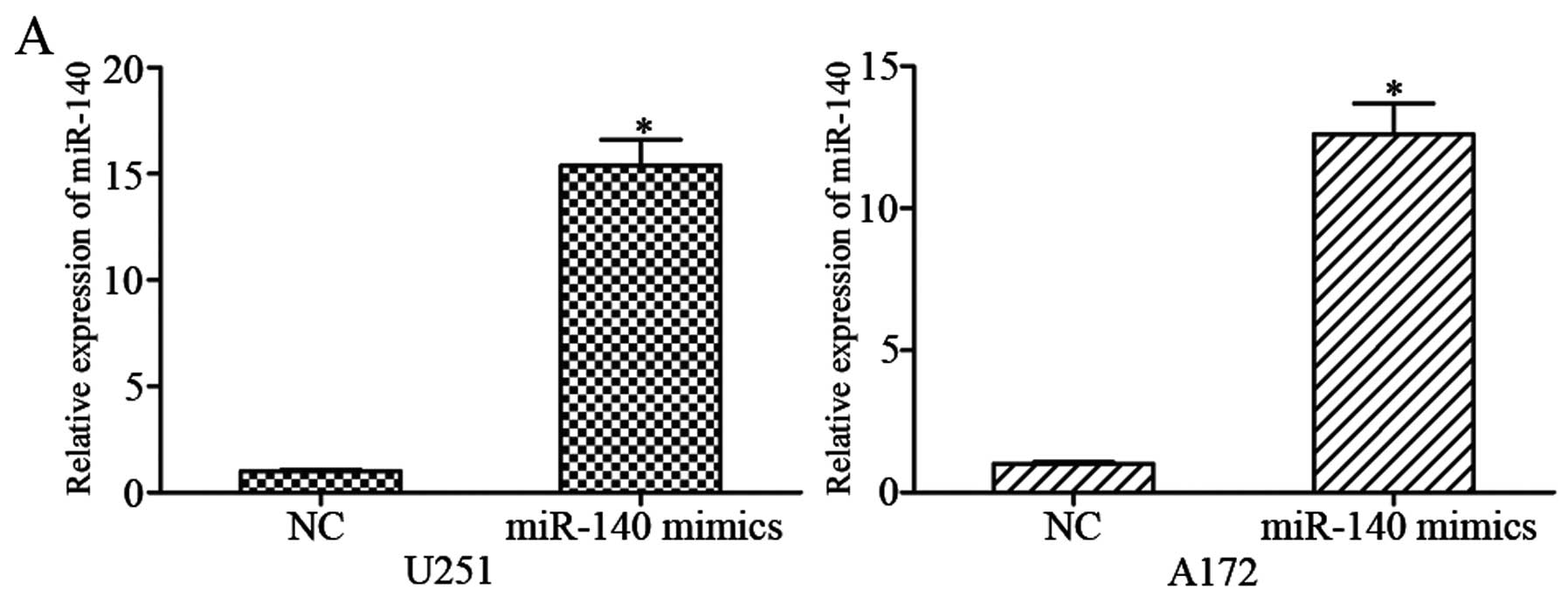
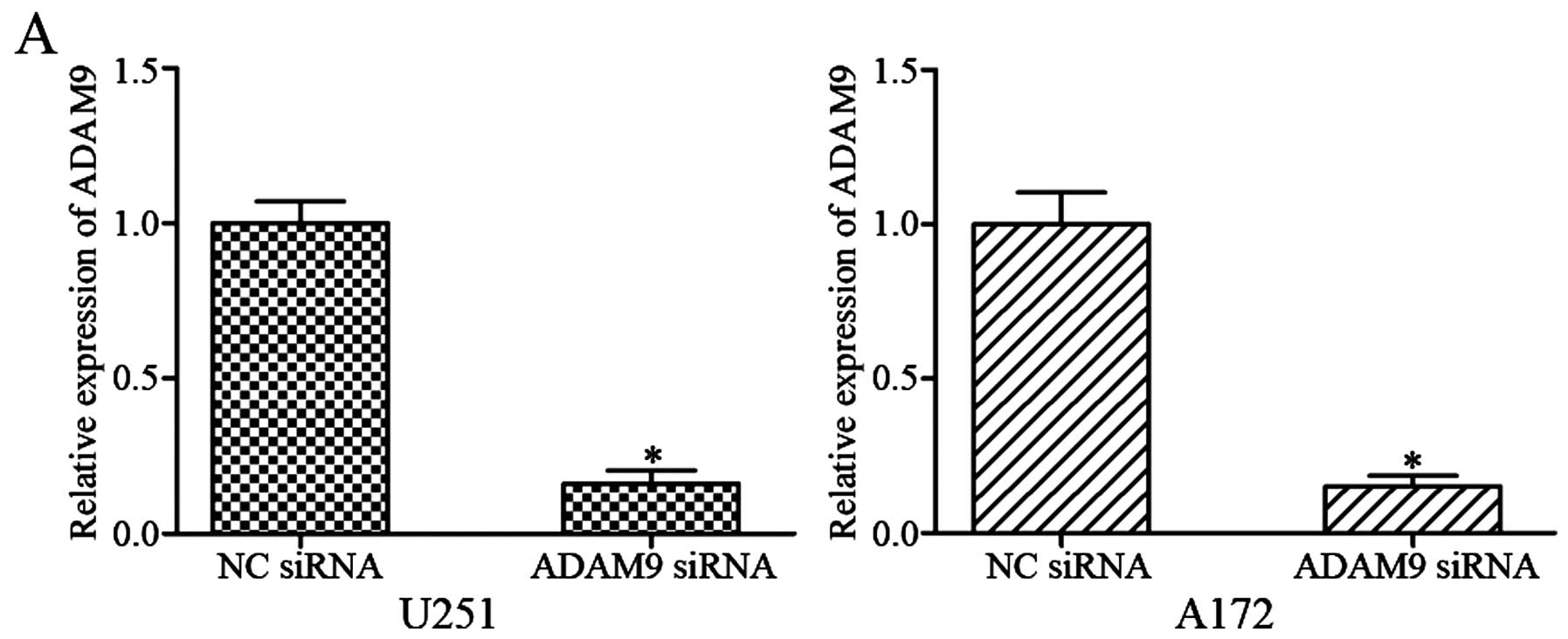
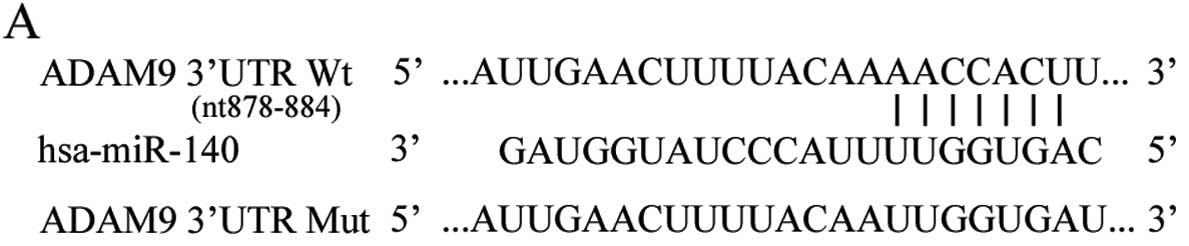|
1
|
Di Stefano AL, Enciso-Mora V, Marie Y,
Desestret V, Labussière M, Boisselier B, Mokhtari K, Idbaih A,
Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY, et al: Association between glioma
susceptibility loci and tumour pathology defines specific molecular
etiologies. Neuro Oncol. 15:542–547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu GY, Shi BZ and Li Y: FoxM1 regulates
Sirt1 expression in glioma cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:205–211. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M,
Hoang-Xuan K and Delattre JY: Primary brain tumours in adults.
Lancet. 379:1984–1996. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Waghmare I, Roebke A, Minata M,
Kango-Singh M and Nakano I: Intercellular cooperation and
competition in brain cancers: Lessons from Drosophila and human
studies. Stem Cells Transl Med. 3:1262–1268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li B, Wang Y, Li S, He H, Sun F, Wang C,
Lu Y, Wang X and Tao B: Decreased expression of miR-378 correlates
with tumor invasiveness and poor prognosis of patients with glioma.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7016–7021. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morgado AL, Rodrigues CM and Solá S:
MicroRNA-145 regulates neural stem cell differentiation through the
Sox2-Lin28/let-7 signaling pathway. Stem Cells. 34:1386–1395. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT,
Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe
SW, Hannon GJ, et al: A microRNA polycistron as a potential human
oncogene. Nature. 435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang JG, Shi Y, Hong DF, Song M, Huang D,
Wang CY and Zhao G: MiR-148b suppresses cell proliferation and
invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting WNT1/β-catenin
pathway. Sci Rep. 5:80872015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zheng B, Liang L, Wang C, Huang S, Cao X,
Zha R, Liu L, Jia D, Tian Q, Wu J, et al: MicroRNA-148a suppresses
tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in
gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7574–7583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pichler M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs in
cancer: From developmental genes in worms to their clinical
application in patients. Br J Cancer. 113:569–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Li Y, Ge P and Ma C: MiR-126
regulates the ERK pathway via targeting KRAS to inhibit the glioma
cell proliferation and invasion. Mol Neurobiol. Jan 5–2016.pub
ahead of print.
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Shi ZM, Jiang CF, Liu X, Chen QD,
Qian X, Li DM, Ge X, Wang XF, Liu LZ, et al: MiR-143 acts as a
tumor suppressor by targeting N-RAS and enhances
temozolomide-induced apoptosis in glioma. Oncotarget. 5:5416–5427.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi L, Wang Z, Sun G, Wan Y, Guo J and Fu
X: miR-145 inhibits migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by
targeting ABCG2. Neuromolecular Med. 16:517–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hong L, Ya-Wei L, Hai W, Qiang Z, Jun-Jie
L, Huang A, Song-Tao Q and Yun-Tao L: MiR-519a functions as a tumor
suppressor in glioma by targeting the oncogenic STAT3 pathway. J
Neurooncol. 128:35–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang ZY, Xiong J, Zhang SS, Wang JJ, Gong
ZJ and Dai MH: Up-regulation of microRNA-183 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion in glioma by directly targeting NEFL.
Cell Mol Neurobiol. Feb 15–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Dutta A and Abounader R: The role
of microRNAs in glioma initiation and progression. Front Biosci.
17:700–712. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Karsy M, Arslan E and Moy F: Current
progress on understanding microRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme.
Genes Cancer. 3:3–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang W, Shen Y, Wei J and Liu F:
MicroRNA-153/Nrf-2/GPx1 pathway regulates radiosensitivity and
stemness of glioma stem cells via reactive oxygen species.
Oncotarget. 6:22006–22027. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HK, Bier A, Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang
C, Twito H, Poisson LM, Mikkelsen T, Slavin S, Jacoby E, et al:
MicroRNA-145 is downregulated in glial tumors and regulates glioma
cell migration by targeting connective tissue growth factor. PLoS
One. 8:e546522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lai NS, Dong QS, Ding H, Miao ZL and Lin
YC: MicroRNA-210 overexpression predicts poorer prognosis in glioma
patients. J Clin Neurosci. 21:755–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng X, Chopp M, Lu Y, Buller B and Jiang
F: MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis
via NRP-2 and MMP-3. Cancer Lett. 329:146–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Chen L, Han L, Zhang K, Shi Z, Zhang J,
Zhang A, Wang Y, Song Y, Li Y, Jiang T, et al: VHL regulates the
effects of miR-23b on glioma survival and invasion via suppression
of HIF-1α/VEGF and β-catenin/Tcf-4 signaling. Neuro Oncol.
14:1026–1036. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang QQ, Xu H, Huang MB, Ma LM, Huang QJ,
Yao Q, Zhou H and Qu LH: MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role
in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways
involved in cellular proliferation and invasion. Neuro Oncol.
14:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang S, Gong X, Zhang G, Huang G, Lu Y
and Li Y: MicroRNA-140 regulates cell growth and invasion in
pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma by targeting iASPP. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin. 48:174–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kong XM, Zhang GH, Huo YK, Zhao XH, Cao
DW, Guo SF, Li AM and Zhang XR: MicroRNA-140-3p inhibits
proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells by
targeting ATP6AP2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12845–12852. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Dong W, Yao C, Teng X, Chai J, Yang X and
Li B: MiR-140-3p suppressed cell growth and invasion by
downregulating the expression of ATP8A1 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:2973–2985. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang W, Zou C, Pan L, Xu Y, Qi W, Ma G,
Hou Y and Jiang P: MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits the progression of
colorectal cancer by targeting VEGFA. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:1123–1133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lan H, Chen W, He G and Yang S: miR-140-5p
inhibits ovarian cancer growth partially by repression of PDGFRA.
Biomed Pharmacother. 75:117–122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li W, Jiang G, Zhou J, Wang H, Gong Z,
Zhang Z, Min K, Zhu H and Tan Y: Down-regulation of miR-140 induces
EMT and promotes invasion by targeting Slug in esophageal cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1466–1476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kai Y, Peng W, Ling W, Jiebing H and Zhuan
B: Reciprocal effects between microRNA-140-5p and ADAM10 suppress
migration and invasion of human tongue cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 448:308–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zou MX, Huang W, Wang XB, Lv GH, Li J and
Deng YW: Identification of miR-140-3p as a marker associated with
poor prognosis in spinal chordoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4877–4885. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Güllü G, Peker I, Haholu A, Eren F,
Küçükodaci Z, Güleç B, Baloglu H, Erzik C, Özer A and Akkiprik M:
Clinical significance of miR-140-5p and miR-193b expression in
patients with breast cancer and relationship to IGFBP5. Genet Mol
Biol. 38:21–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang H, Fang F, Chang R and Yang L:
MicroRNA-140-5p suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
transforming growth factor β receptor 1 and fibroblast growth
factor 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 58:205–217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yuan Y, Shen Y, Xue L and Fan H: miR-140
suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung
cancer by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. PLoS
One. 8:e736042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blobel CP: ADAMs: Key components in EGFR
signalling and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:32–43. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guaiquil V, Swendeman S, Yoshida T,
Chavala S, Campochiaro PA and Blobel CP: ADAM9 is involved in
pathological retinal neovascularization. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2694–2703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Duffy MJ, McKiernan E, O'Donovan N and
McGowan PM: Role of ADAMs in cancer formation and progression. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1140–1144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fritzsche FR, Wassermann K, Jung M, Tölle
A, Kristiansen I, Lein M, Johannsen M, Dietel M, Jung K and
Kristiansen G: ADAM9 is highly expressed in renal cell cancer and
is associated with tumour progression. BMC Cancer. 8:1792008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fritzsche FR, Jung M, Tölle A, Wild P,
Hartmann A, Wassermann K, Rabien A, Lein M, Dietel M, Pilarsky C,
et al: ADAM9 expression is a significant and independent prognostic
marker of PSA relapse in prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 54:1097–1106.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
O'Shea C, McKie N, Buggy Y, Duggan C, Hill
AD, McDermott E, O'Higgins N and Duffy MJ: Expression of ADAM-9
mRNA and protein in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 105:754–761.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tao K, Qian N, Tang Y, Ti Z, Song W, Cao D
and Dou K: Increased expression of a disintegrin and
metalloprotease-9 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for
tumor progression and prognosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:645–651.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Grützmann R, Lüttges J, Sipos B, Ammerpohl
O, Dobrowolski F, Alldinger I, Kersting S, Ockert D, Koch R,
Kalthoff H, et al: ADAM9 expression in pancreatic cancer is
associated with tumour type and is a prognostic factor in ductal
adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 90:1053–1058. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim YH, Shin EK, Kim DH, Lee HH, Park JH
and Kim JK: Antiangiogenic effect of licochalcone A. Biochem
Pharmacol. 80:1152–1159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen CM, Hsieh YH, Hwang JM, Jan HJ, Hsieh
SC, Lin SH and Lai CY: Fisetin suppresses ADAM9 expression and
inhibits invasion of glioma cancer cells through increased
phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Tumour Biol. 36:3407–3415. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|