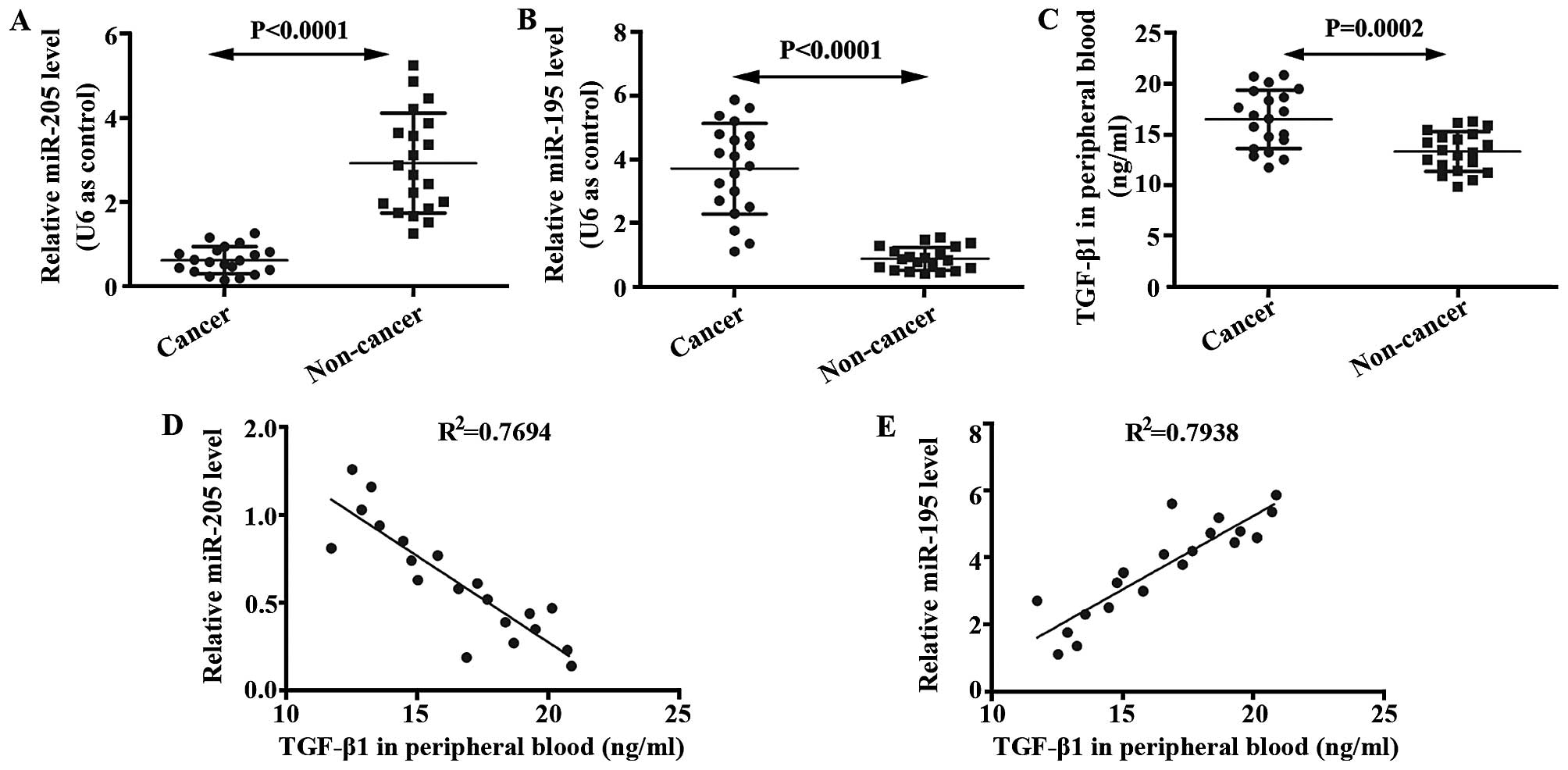
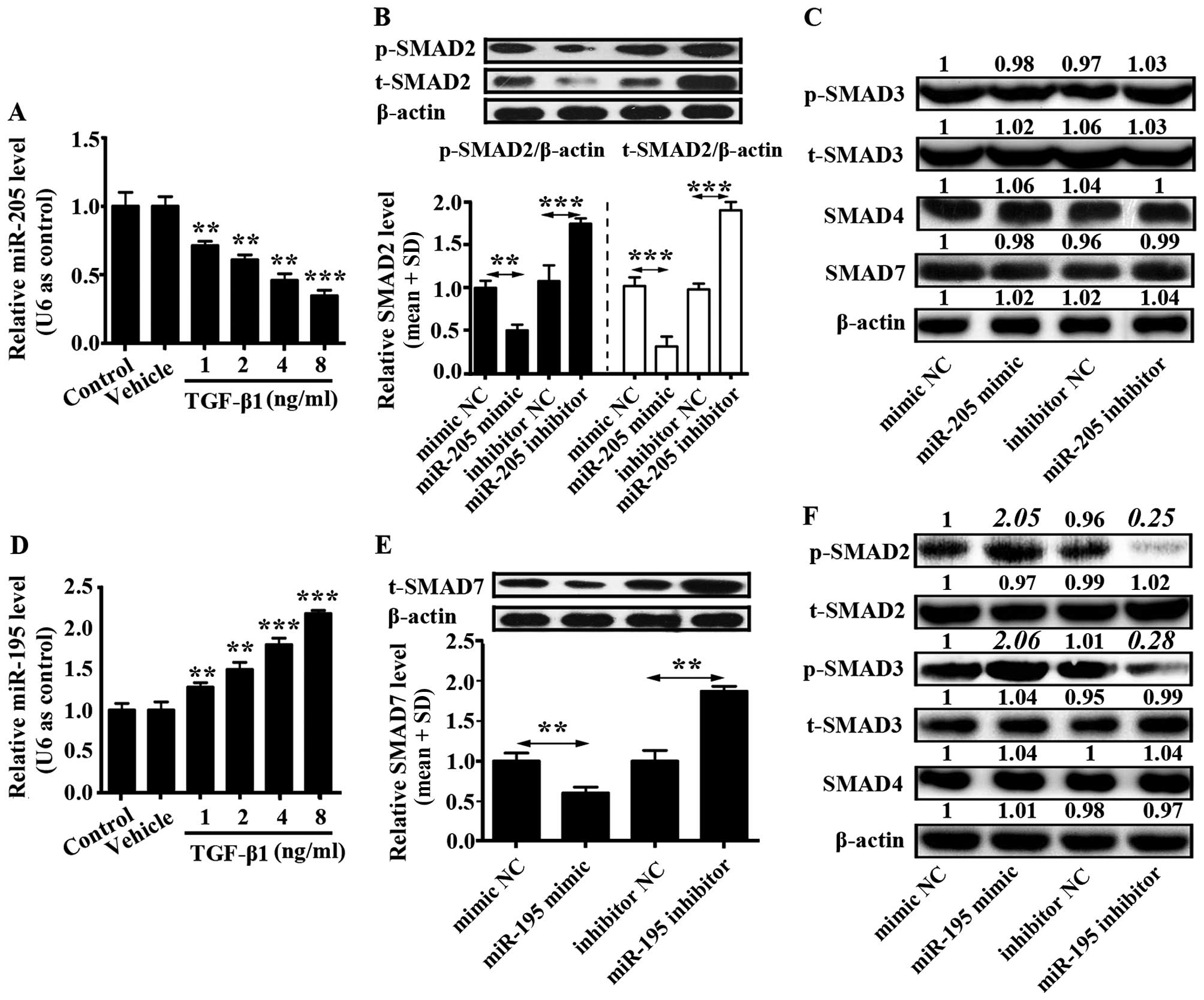
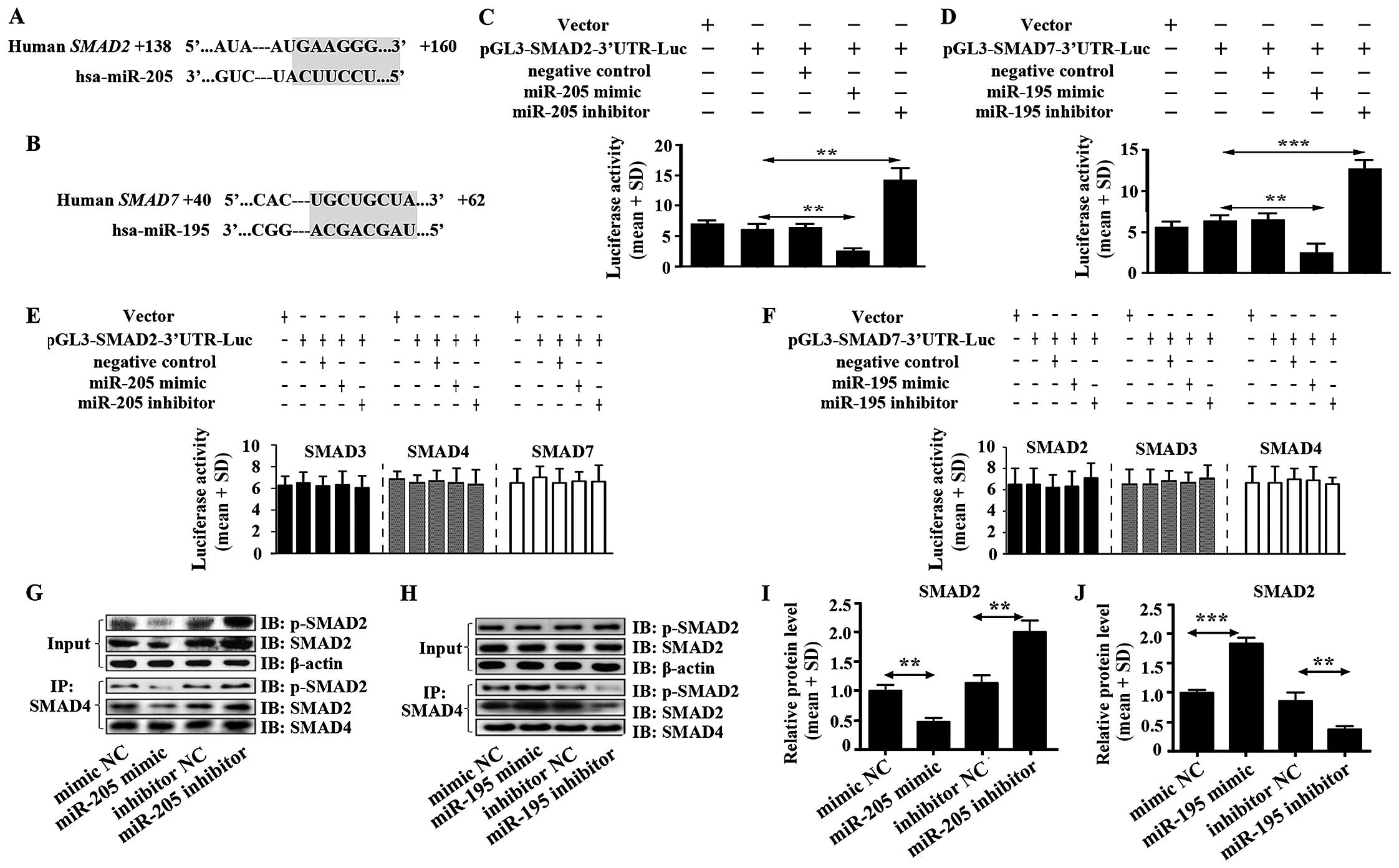
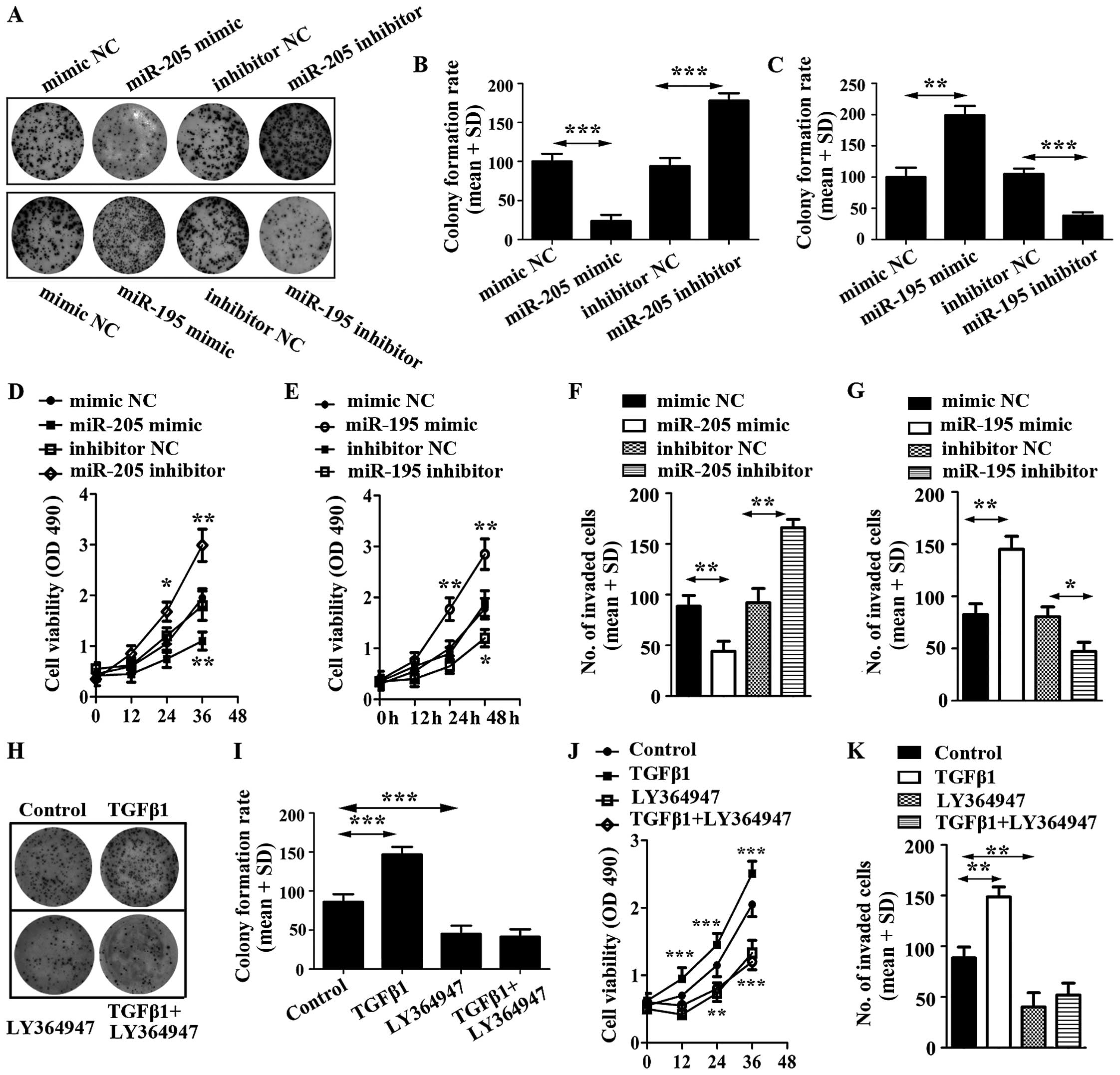
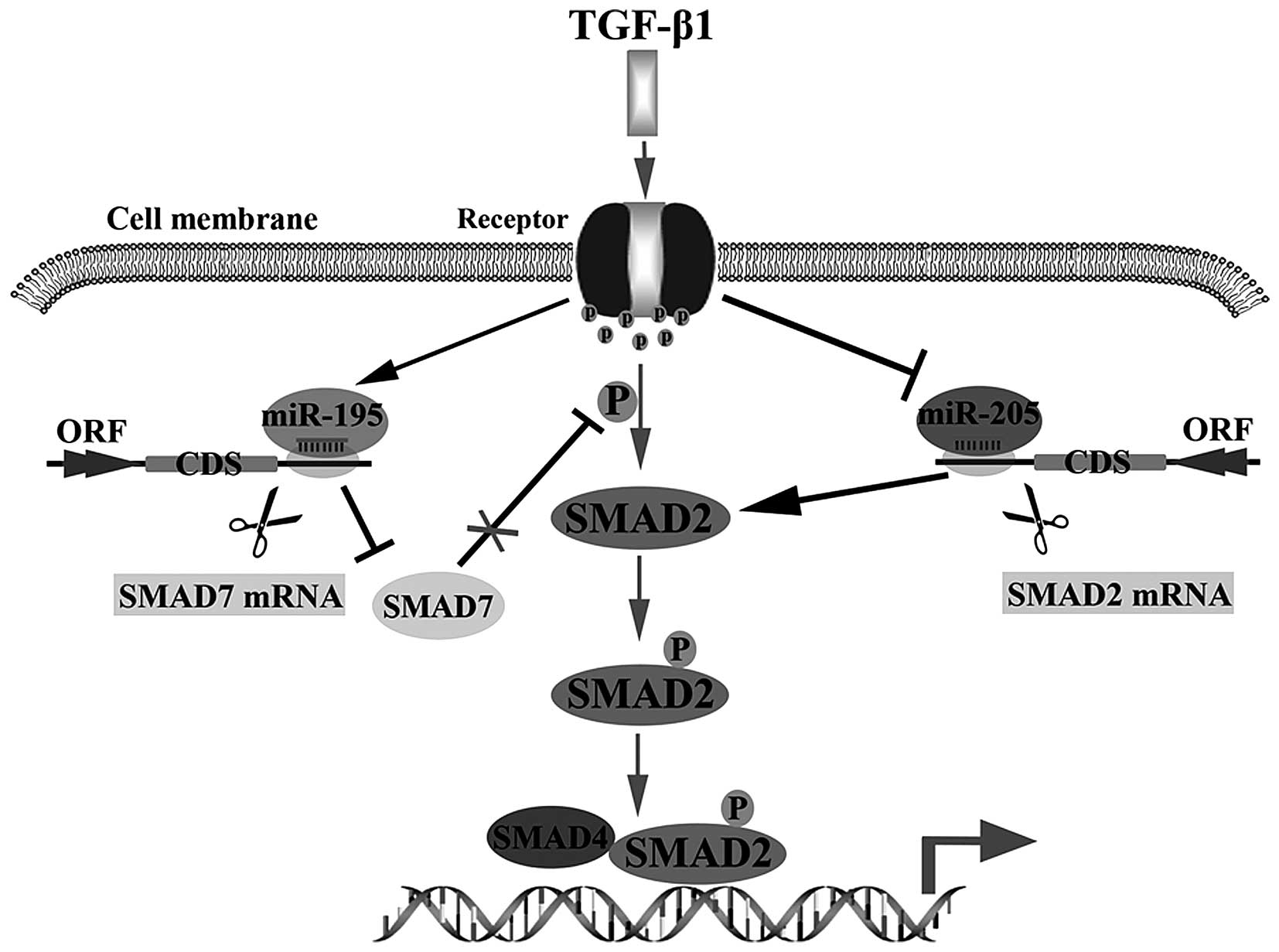
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lawrence DA: Transforming growth
factor-beta: A general review. Eur Cytokine Netw. 7:363–374.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meulmeester E and Ten Dijke P: The dynamic
roles of TGF-β in cancer. J Pathol. 223:205–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M,
Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA and Massagué J: A multigenic
program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell.
3:537–549. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Flavell RA, Sanjabi S, Wrzesinski SH and
Licona-Limón P: The polarization of immune cells in the tumour
environment by TGFbeta. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:554–567. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Connolly EC, Freimuth J and Akhurst RJ:
Complexities of TGF-β targeted cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci.
8:964–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Alexandrow MG and Moses HL: Transforming
growth factor beta and cell cycle regulation. Cancer Res.
55:1452–1457. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wesolowska A, Kwiatkowska A, Slomnicki L,
Dembinski M, Master A, Sliwa M, Franciszkiewicz K, Chouaib S and
Kaminska B: Microglia-derived TGF-beta as an important regulator of
glioblastoma invasion - an inhibition of TGF-beta-dependent effects
by shRNA against human TGF-beta type II receptor. Oncogene.
27:918–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Brabletz S and Brabletz T: The ZEB/miR-200
feedback loop - a motor of cellular plasticity in development and
cancer? EMBO Rep. 11:670–677. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cottonham CL, Kaneko S and Xu L: miR-21
and miR-31 converge on TIAM1 to regulate migration and invasion of
colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 285:35293–35302. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saito A, Suzuki HI, Horie M, Ohshima M,
Morishita Y, Abiko Y and Nagase T: An integrated expression
profiling reveals target genes of TGF-β and TNF-α possibly mediated
by microRNAs in lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e565872013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Katz LH, Li Y, Chen JS, Muñoz NM, Majumdar
A, Chen J and Mishra L: Targeting TGF-β signaling in cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 17:743–760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA and
Massagué J: Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the
control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation.
Cell. 117:211–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Louafi F, Martinez-Nunez RT and
Sanchez-Elsner T: MicroRNA-155 targets SMAD2 and modulates the
response of macrophages to transforming growth factor-β. J Biol
Chem. 285:41328–41336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brower JV, Clark PA, Lyon W and Kuo JS:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Glioblastoma and glioblastoma cancer stem
cells. Neurochem Int. 77:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leeper NJ, Raiesdana A, Kojima Y, Chun HJ,
Azuma J, Maegdefessel L, Kundu RK, Quertermous T, Tsao PS and Spin
JM: MicroRNA-26a is a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle
cell function. J Cell Physiol. 226:1035–1043. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L,
Fotinou M, Georgoulias V and Lianidou ES: Prognostic value of
mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small
cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem.
54:1696–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Li L, Li Z, Gong G, Chen P, Liu H,
Wang J, Liu Y and Wu X: The role of miR-205 in the VEGF-mediated
promotion of human ovarian cancer cell invasion. Gynecol Oncol.
137:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao P, Zhou L, Zhang J, Zheng F, Wang H,
Ma D and Tian J: Comprehensive expression profiling of microRNAs in
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 35:720–728. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nam EJ, Lee M, Yim GW, Kim JH, Kim S, Kim
SW and Kim YT: MicroRNA profiling of a CD133+
spheroid-forming subpopulation of the OVCAR3 human ovarian cancer
cell line. BMC Med Genomics. 5:182012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Greene SB, Herschkowitz JI and Rosen JM:
The ups and downs of miR-205: Identifying the roles of miR-205 in
mammary gland development and breast cancer. RNA Biol. 7:300–304.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu J, Ryan DG, Getsios S,
Oliveira-Fernandes M, Fatima A and Lavker RM: MicroRNA-184
antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19300–19305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu H, Zhu S and Mo YY: Suppression of cell
growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res.
19:439–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dar AA, Majid S, de Semir D, Nosrati M,
Bezrookove V and Kashani-Sabet M: miRNA-205 suppresses melanoma
cell proliferation and induces senescence via regulation of E2F1
protein. J Biol Chem. 286:16606–16614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Majid S, Saini S, Dar AA, Hirata H,
Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, Yamamura S, Ueno K, Zaman MS, Singh K, et
al: MicroRNA-205 inhibits Src-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:2611–2621. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia LF, Wei SB, Gong K, Gan YH and Yu GY:
Prognostic implications of micoRNA miR-195 expression in human
tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e566342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu J and Li Y: Trichostatin A and
Tamoxifen inhibit breast cancer cell growth by miR-204 and ERα
reducing AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:242–247.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bai J, Zhu X, Ma J and Wang W: miR-205
regulates A549 cells proliferation by targeting PTEN. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:1175–1183. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Chen H, Fu Y, Ai A, Xue S, Lyu Q
and Kuang Y: MiR-195 inhibits proliferation and growth and induces
apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells by targeting FKN. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 6:2824–2834. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liao Y, Zhang M and Lönnerdal B: Growth
factor TGF-β induces intestinal epithelial cell (IEC-6)
differentiation: miR-146b as a regulatory component in the negative
feedback loop. Genes Nutr. 8:69–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gratchev A: TGF-β signalling in tumour
associated macrophages. Immunobiology. S0171–2985:30096. 2016.
|
|
32
|
Wang ZH, Zhang QS, Duan YL, Zhang JL, Li
GF and Zheng DL: TGF-β induced miR-132 enhances the activation of
TGF-β signaling through inhibiting SMAD7 expression in glioma
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:187–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song L, Liu L, Wu Z, Li Y, Ying Z, Lin C,
Wu J, Hu B, Cheng SY, Li M, et al: TGF-β induces miR-182 to sustain
NF-κB activation in glioma subsets. J Clin Invest. 122:3563–3578.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sempere LF, Christensen M, Silahtaroglu A,
Bak M, Heath CV, Schwartz G, Wells W, Kauppinen S and Cole CN:
Altered MicroRNA expression confined to specific epithelial cell
subpopulations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 67:11612–11620. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dou L, Li J, Zheng D, Li Y, Gao X, Xu C,
Gao L, Wang L and Yu L: MicroRNA-205 downregulates
mixed-lineage-AF4 oncogene expression in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Onco Targets Ther. 6:1153–1160. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie H, Zhao Y, Caramuta S, Larsson C and
Lui WO: miR-205 expression promotes cell proliferation and
migration of human cervical cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e469902012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Amer M, Elhefnawi M, El-Ahwany E, Awad AF,
Gawad NA, Zada S and Tawab FM: Hsa-miR-195 targets PCMT1 in
hepa-tocellular carcinoma that increases tumor life span. Tumour
Biol. 35:11301–11309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bhattacharya A, Schmitz U, Wolkenhauer O,
Schönherr M, Raatz Y and Kunz M: Regulation of cell cycle
checkpoint kinase WEE1 by miR-195 in malignant melanoma. Oncogene.
32:3175–3183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen G, Cao S, Liu F and Liu Y: miR-195
plays a role in steroid resistance of ulcerative colitis by
targeting Smad7. Biochem J. 471:357–367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yan X and Chen YG: Smad7: Not only a
regulator, but also a cross-talk mediator of TGF-β signalling.
Biochem J. 434:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nicklas D and Saiz L: Computational
modelling of Smad-mediated negative feedback and crosstalk in the
TGF-β superfamily network. J R Soc Interface. 10:201303632013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lin CX, Rhaleb NE, Yang XP, Liao TD,
D'Ambrosio MA and Carretero OA: Prevention of aortic fibrosis by
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline in angiotensin II-induced
hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1253–H1261.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tang LX, He RH, Yang G, Tan JJ, Zhou L,
Meng XM, Huang XR and Lan HY: Asiatic acid inhibits liver fibrosis
by blocking TGF-beta/Smad signaling in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One.
7:e313502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|