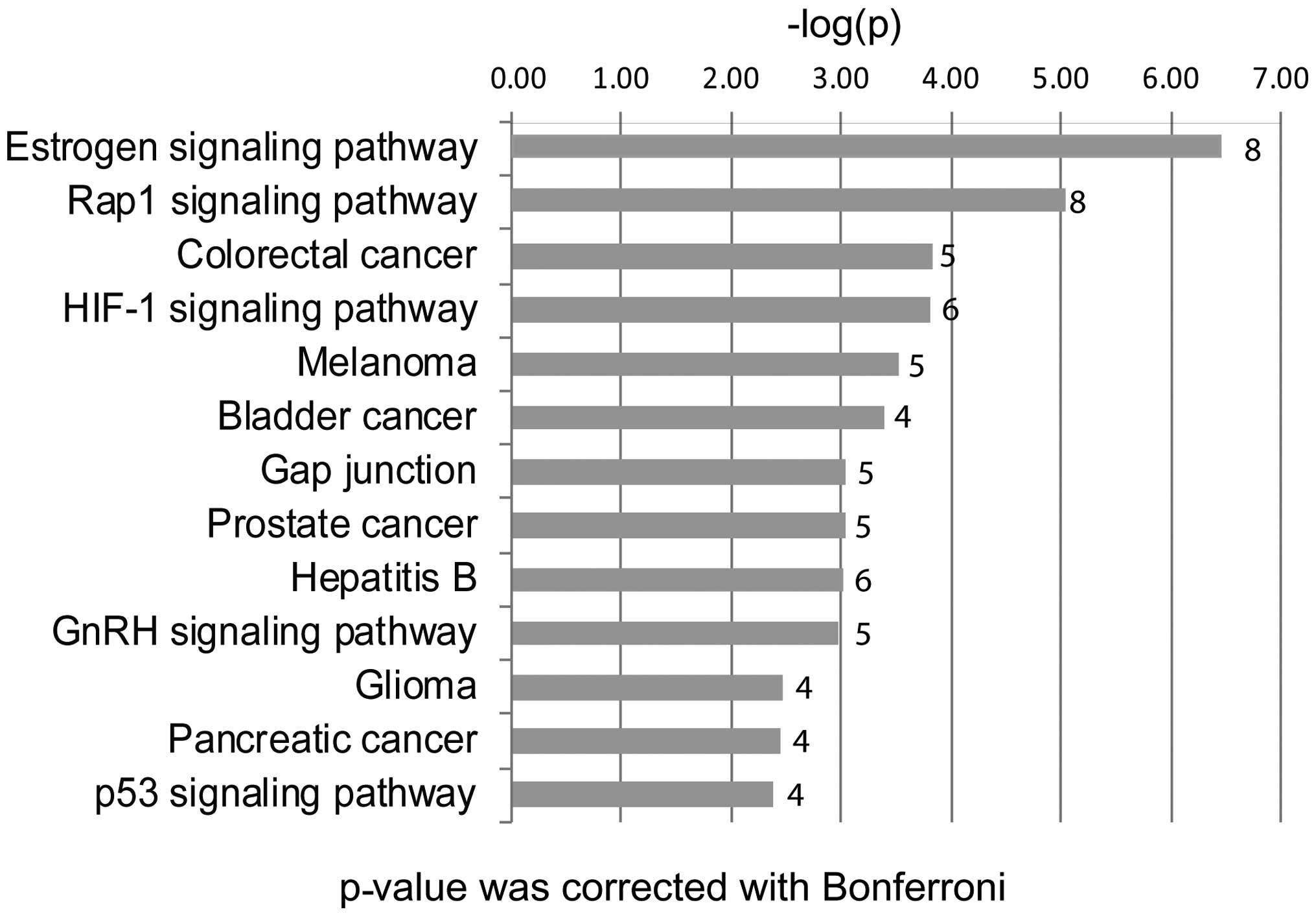
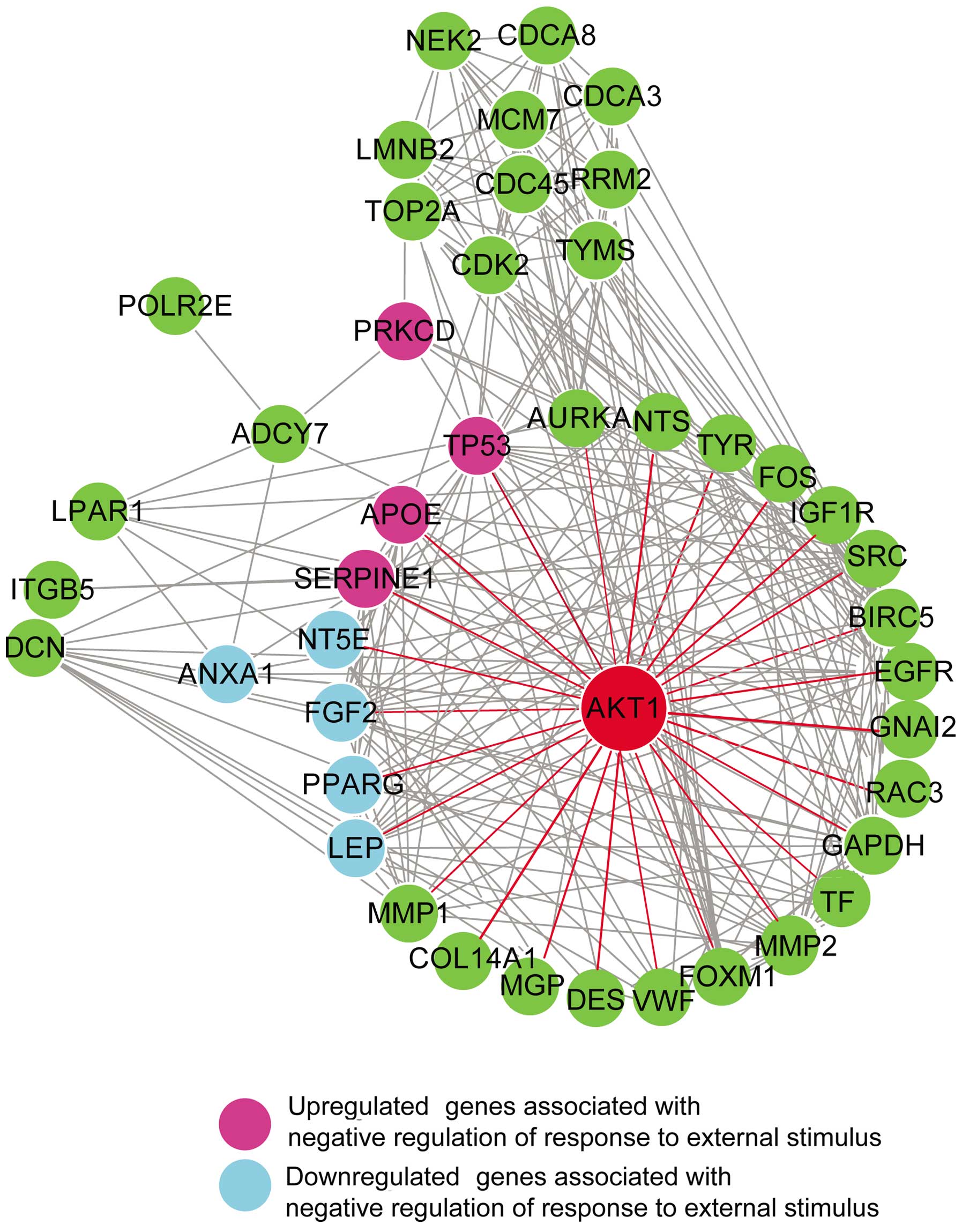
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maes H, Martin S, Verfaillie T and
Agostinis P: Dynamic interplay between autophagic flux and Akt
during melanoma progression in vitro. Exp Dermatol. 23:101–106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shi H, Hong A, Kong X, Koya RC, Song C,
Moriceau G, Hugo W, Yu CC, Ng C, Chodon T, et al: A novel AKT1
mutant amplifies an adaptive melanoma response to BRAF inhibition.
Cancer Discov. 4:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Holtan SG, Creedon DJ, Haluska P and
Markovic SN: Cancer and pregnancy: parallels in growth, invasion,
and immune modulation and implications for cancer therapeutic
agents. Mayo Clin Proc. 84:985–1000. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller JG and Mac Neil S: Gender and
cutaneous melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 136:657–665. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Enninga EA, Holtan SG, Creedon DJ, Dronca
RS, Nevala WK, Ognjanovic S and Markovic SN: Immunomodulatory
effects of sex hormones: requirements for pregnancy and relevance
in melanoma. Mayo Clin Proc. 89:520–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Janik ME, Bełkot K and Przybyło M: Is
oestrogen an important player in melanoma progression? Contemp
Oncol (Pozn). 18:302–306. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Stevenson S and Thornton J: Effect of
estrogens on skin aging and the potential role of SERMs. Clin
Interv Aging. 2:283–297. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bredow L, Stutzel L, Bohringer D, Gundlach
E, Reinhard T and Auw-Haedrich C: Progesterone and estrogen
receptors in conjunctival melanoma and nevi. Graefes Arch Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 252:359–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Roy S, Reddy BS, Sudhakar G, Kumar JM and
Banerjee R: 17β-estradiol-linked nitro-L-arginine as simultaneous
inducer of apoptosis in melanoma and tumor-angiogenic vascular
endothelial cells. Mol Pharm. 8:350–359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Talantov D, Mazumder A, Yu JX, Briggs T,
Jiang Y, Backus J, Atkins D and Wang Y: Novel genes associated with
malignant melanoma but not benign melanocytic lesions. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:7234–7242. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hipfel R, Garbe C and Schittek B: RNA
isolation from human skin tissues for colorimetric differential
display. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 37:131–135. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kerr MK: Linear models for microarray data
analysis: hidden similarities and differences. J Comput Biol.
10:891–901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N
and Golani I: Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior
genetics research. Behav Brain Res. 125:279–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reiner A, Yekutieli D and Benjamini Y:
Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery
rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics. 19:368–375. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Assenov Y, Ramírez F, Schelhorn SE,
Lengauer T and Albrecht M: Computing topological parameters of
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 24:282–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: a
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Page L, Brin S, Motwani R and Winograd T:
The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web. Technical
Report. Stanford InfoLab; 1999, http://ilpubs.stanford.edu:8090/422/.
|
|
20
|
Griffiths TL, Steyvers M and Firl A:
Google and the mind: predicting fluency with PageRank. Psychol Sci.
18:1069–1076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwan HY, Fu X, Liu B, Chao X, Chan CL, Cao
H, Su T, Tse AK, Fong WF and Yu ZL: Subcutaneous adipocytes promote
melanoma cell growth by activating the Akt signaling pathway: role
of palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 289:30525–30537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P,
Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W,
et al: Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature.
417:949–954. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Calipel A, Mouriaux F, Glotin AL, Malecaze
F, Faussat AM and Mascarelli F: Extracellular signal-regulated
kinase-dependent proliferation is mediated through the protein
kinase A/B-Raf pathway in human uveal melanoma cells. J Biol Chem.
281:9238–9250. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen
JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et
al: Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E
mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lo RS: Combinatorial therapies to overcome
B-RAF inhibitor resistance in melanomas. Pharmacogenomics.
13:125–128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zang YC, Halder JB, Hong J, Rivera VM and
Zhang JZ: Regulatory effects of estriol on T cell migration and
cytokine profile: inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappa B. J
Neuroimmunol. 124:106–114. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ribeiro MP, Silva FS, Paixão J, Santos AE
and Custódio JB: The combination of the antiestrogen endoxifen with
all-trans-retinoic acid has anti-proliferative and anti-migration
effects on melanoma cells without inducing significant toxicity in
non-neoplasic cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 715:354–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shifren JL, Tseng JF, Zaloudek CJ, Ryan
IP, Meng YG, Ferrara N, Jaffe RB and Taylor RN: Ovarian steroid
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in the human
endometrium: implications for angiogenesis during the menstrual
cycle and in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 81:3112–3118. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsuoka H, Tsubaki M, Yamazoe Y, Ogaki M,
Satou T, Itoh T, Kusunoki T and Nishida S: Tamoxifen inhibits tumor
cell invasion and metastasis in mouse melanoma through suppression
of PKC/MEK/ERK and PKC/PI3K/Akt pathways. Exp Cell Res.
315:2022–2032. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Coló GP, Hernández-Varas P, Lock J,
Bartolomé RA, Arellano-Sánchez N, Strömblad S and Teixidó J: Focal
adhesion disassembly is regulated by a RIAM to MEK-1 pathway. J
Cell Sci. 125:5338–5352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|