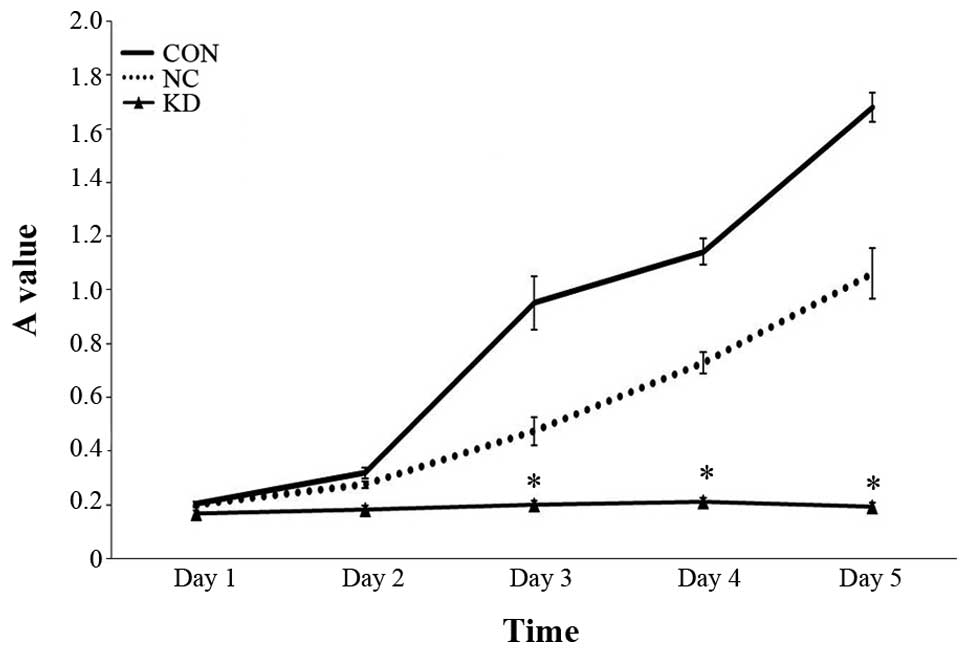
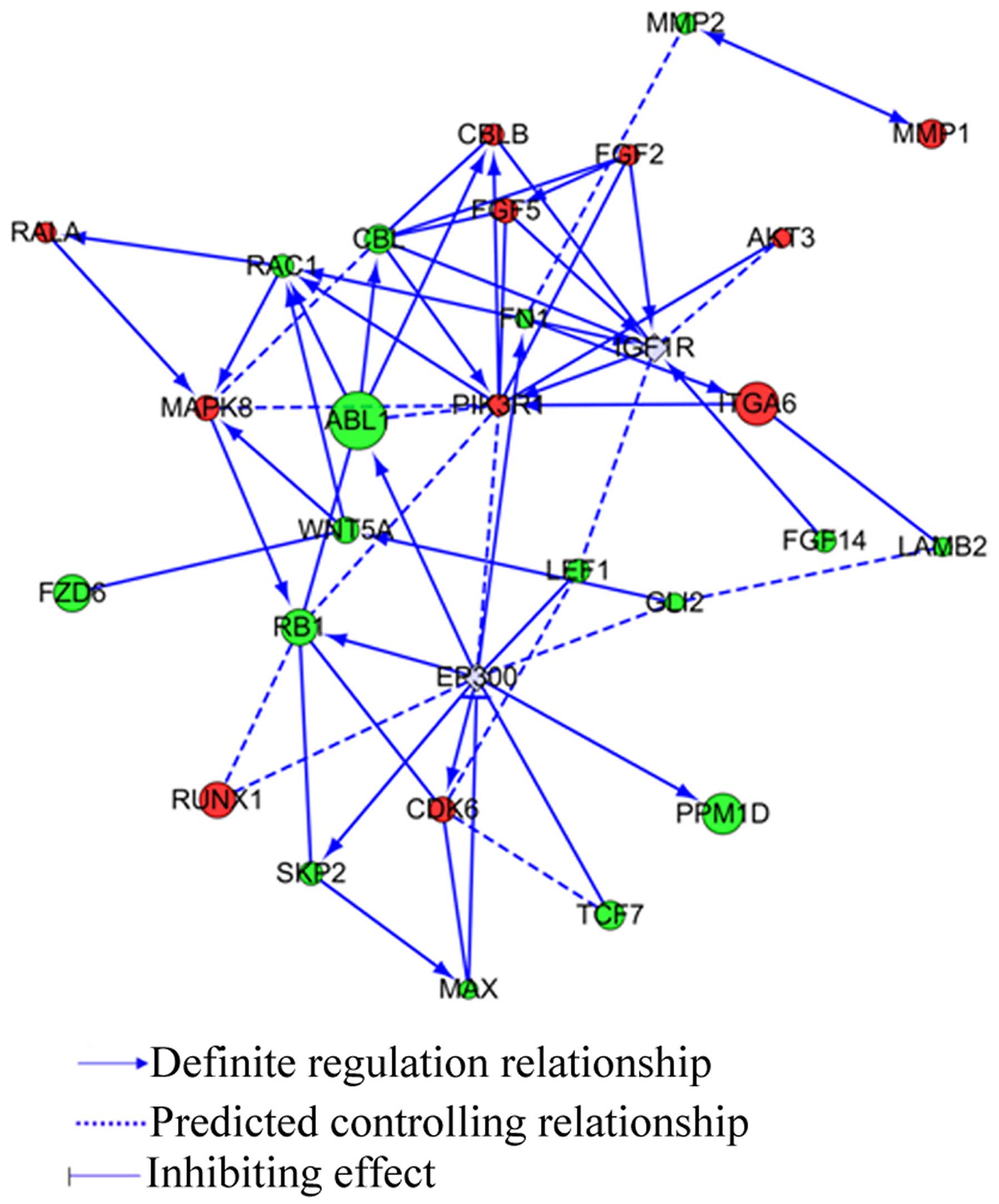
|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of
Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chamberlain MC: Temozolomide: Therapeutic
limitations in the treatment of adult high-grade gliomas. Expert
Rev Neurother. 10:1537–1544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marchesi F, Turriziani M, Tortorelli G,
Avvisati G, Torino F and De Vecchis L: Triazene compounds:
Mechanism of action and related DNA repair systems. Pharmacol Res.
56:275–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miao W, Liu X, Wang H, Fan Y, Lian S, Yang
X, Wang X, Guo G, Li Q and Wang S: p53 upregulated modulator of
apoptosis sensitizes drug-resistant U251 glioblastoma stem cells to
temozolomide through enhanced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 11:4165–4173.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martinez-Rivera M and Siddik ZH:
Resistance and gain-of-resistance phenotypes in cancers harboring
wild-type p53. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1049–1062. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li S, Jiang T, Li G and Wang Z: Impact of
p53 status to response of temozolomide in low MGMT expression
glioblastomas: Preliminary results. Neurol Res. 30:567–570. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K,
Shen S, Mercer WE, Vande Woude GF, O'Connor PM and Appella E: Wip1,
a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to
ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:6048–6053. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang P, Rao J, Yang H, Zhao H and Yang L:
Wip1 overexpression correlated with TP53/p14(ARF) pathway
disruption in human astrocytomas. J Surg oncol. 104:679–684. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bulavin DV, Demidov ON, Saito S,
Kauraniemi P, Phillips C, Amundson SA, Ambrosino C, Sauter G,
Nebreda AR, Anderson CW, et al: Amplification of PPM1D in human
tumors abrogates p53 tumor-suppressor activity. Nat Genet.
31:210–215. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Yang Y, Peng Y, Austin RJ, van
Eyndhoven WG, Nguyen KC, Gabriele T, McCurrach ME, Marks JR, Hoey
T, et al: Oncogenic properties of PPM1D located within a breast
cancer amplification epicenter at 17q23. Nat Genet. 31:133–134.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saito-Ohara F, Imoto I, Inoue J, Hosoi H,
Nakagawara A, Sugimoto T and Inazawa J: PPM1D is a potential target
for 17q gain in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 63:1876–1883.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang C, Guo E, Lu S, Wang S, Kang C,
Chang L, Liu L, Zhang G, Wu Z, Zhao Z, et al: Over-expression of
wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 confers poor prognosis of
patients with gliomas. Brain Res. 1444:65–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hirasawa A, Saito-Ohara F, Inoue J, Aoki
D, Susumu N, Yokoyama T, Nozawa S, Inazawa J and Imoto I:
Association of 17q21-q24 gain in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinomas
with poor prognosis and identification of PPM1D and APPBP2 as
likely amplification targets. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1995–2004.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang P, Rao J, Yang H, Zhao H and Yang L:
PPM1D silencing by lentiviral-mediated RNA interference inhibits
proliferation and invasion of human glioma cells. J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 31:94–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spiro T, Liu L and Gerson S: New cytotoxic
agents for the treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma:
Temozolomide and related alkylating agents in combination with
guanine analogues to abrogate drug resistance. Forum (Genova).
10:274–285. 2000.
|
|
16
|
Shen W, Hu JA and Zheng JS: Mechanism of
temozolomideinduced antitumour effects on glioma cells. J Int Med
Res. 42:164–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO: p53
effects both the duration of G2/M arrest and the fate of
temozolomide-treated human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res.
61:1957–1963. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Batista LF, Roos WP, Kaina B and Menck CF:
p53 mutant human glioma cells are sensitive to UV-C-induced
apoptosis due to impaired cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer removal. Mol
Cancer Res. 7:237–246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tivnan A, Zakaria Z, O'leary C, Kögel D,
Pokorny JL, Sarkaria JN and Prehn JH: Inhibition of multidrug
resistance protein 1 (MRP1) improves chemotherapy drug response in
primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Front Neurosci.
9:2182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu YH, Zhang CW, Lu L, Demidov ON, Sun L,
Yang L, Bulavin DV and Xiao ZC: Wipl regulates the generation of
new neural cells in the adult olfactory bulb through p53-dependent
cell cycle control. Stem Cells. 27:1433–1442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang YL, Liu X, Gao SY, Feng H, Jiang YP,
Wang SS, Yang J, Jiang J, Ma XR, Tang YJ, et al: WIP1 stimulates
migration and invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by
inducing MMP-9 and VEGF-C. Oncotarget. 6:9031–9044. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gilmartin AG, Faitg TH, Richter M, Groy A,
Seefeld MA, Darcy MG, Peng X, Federowicz K, Yang J, Zhang SY, et
al: Allosteric Wip1 phosphatase inhibition through flap-subdomain
interaction. Nat Chem Biol. 10:181–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hirose Y, Katayama M, Mirzoeva OK, Berger
MS and Pieper RO: Akt activation suppresses Chk2-mediated,
methylating agent-induced G2 arrest and protects from
temozolomide-induced mitotic catastrophe and cellular senescence.
Cancer Res. 65:4861–4869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Molina JR, Hayashi Y, Stephens C and
Georgescu MM: Invasive glioblastoma cells acquire stemness and
increased Akt activation. Neoplasia. 12:453–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caporali S, Levati L, Starace G, Ragone G,
Bonmassar E, Alvino E and D'Atri S: AKT is activated in an
ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related-dependent manner in response
to temozolomide and confers protection against drug-induced cell
growth inhibition. Mol Pharmacol. 74:173–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Salvo M, Maresca G, D'agnano I,
Marchese R, Stigliano A, Gagliassi R, Brunetti E, Raza GH, De Paula
U and Bucci B: Temozolomide induced c-Myc-mediated apoptosis via
Akt signalling in MGMT expressing glioblastoma cells. Int J Radiat
Biol. 87:518–533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Signore M, Pelacchi F, di Martino S, Runci
D, Biffoni M, Giannetti S, Morgante L, De Majo M, Petricoin EF,
Stancato L, et al: Combined PDK1 and CHK1 inhibition is required to
kill glioblastoma stem-like cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e12232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang Y, Liu L, Sheng M, Xiong K, Huang L,
Gao Q, Wei J, Wu T, Yang S, Liu H, et al: Wip1 knockout inhibits
the proliferation and enhances the migration of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 334:310–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao N, Zhang Z, Jiang BH and Shi X: Role
of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human
prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:1124–1132. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bao JM, He MY, Liu YW, Lu YJ, Hong YQ, Luo
HH, Ren ZL, Zhao SC and Jiang Y: AGE/RAGE/Akt pathway contributes
to prostate cancer cell proliferation by promoting Rb
phosphorylation and degradation. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1741–1750.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Westhoff MA, Faham N, Marx D, Nonnenmacher
L, Jennewein C, Enzenmüller S, Gonzalez P, Fulda S and Debatin KM:
Sequential dosing in chemosensitization: Targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in neuroblastoma. PLoS one. 8:e831282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fu Y, Zhang Q, Kang C, Zhang K, Zhang J,
Pu P, Wang G and Wang T: Inhibitory effects of adenovirus mediated
COX-2, Akt1 and PIK3R1 shRNA on the growth of malignant tumor cells
in vitro and in vivo. Int J oncol. 35:583–591. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|