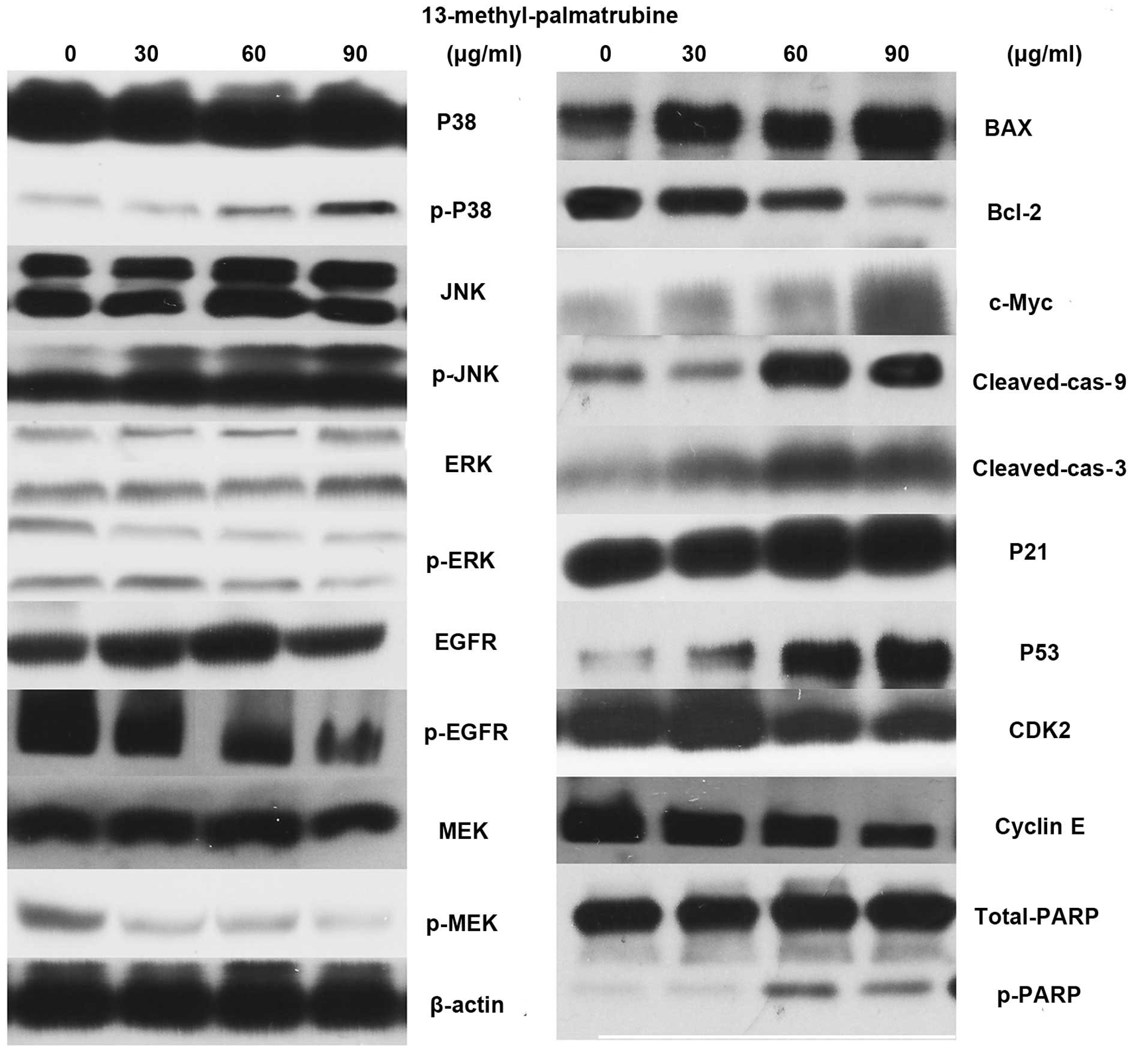
|
1
|
Saika K and Sobue T: Cancer statistics in
the world. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 40:2475–2480. 2013.In Japanese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis C, Naishadham D and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics for African Americans, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin.
63:151–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Safarzadeh E, Sandoghchian Shotorbani S
and Baradaran B: Herbal medicine as inducers of apoptosis in cancer
treatment. Adv Pharm Bull. 4(Suppl 1): S421–S427. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Hiruma W, Suruga K, Kadokura K, Tomita T,
Sekino Y, Komatsu Y, Kimura M and Ono N: Antitumor effects of a
plant extract mixture. Yakugaku Zasshi. 133:487–491. 2013.In
Japanese. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lu Y, Li CS and Dong Q: Chinese herb
related molecules of cancer-cell-apoptosis: A minireview of
progress between Kanglaite injection and related genes. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 27:312008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng S, Yang H, Zhang S, Wang X, Yu L, Lu
J and Li J: Initial study on naturally occurring products from
traditional Chinese herbs and vegetables for chemoprevention. J
Cell Biochem Suppl. 27:106–112. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leung WC, Zheng H, Huen M, Law SL and Xue
H: Anxiolytic-like action of orally administered
dl-tetrahydropalmatine in elevated plus-maze. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 27:775–779. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sagare AP, Lee YL, Lin TC, Chen CC and
Tsay HS: Cytokinin-induced somatic embryogenesis and plant
regeneration in Corydalis yanhusuo (Fumariaceae) - a medicinal
plant. Plant Sci. 160:139–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu G, Qian Z, Guo J, Hu D, Bao J, Xie J,
Xu W, Lu J, Chen X and Wang Y: Ganoderma lucidum extract induces G1
cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Am J
Chin Med. 40:631–642. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng XY, Shi Y, Zheng SL, Jin W and Sun
H: Two new protoberberine quaternary alkaloids from Corydalis
yanhusuo. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 10:1117–1121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ikekawa T and Ikeda Y: Antitumor activity
of 13-methyl-berberrubine derivatives. J Pharmacobiodyn. 5:469–474.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lurje G and Lenz HJ: EGFR signaling and
drug discovery. Oncology. 77:400–410. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Uribe P and Gonzalez S: Epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy. Pathol Res Pract.
207:337–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hynes NE and Lane HA: ERBB receptors and
cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:341–354. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Normanno N, Campiglio M, Maiello MR, De
Luca A, Mancino M, Gallo M, D'Alessio A and Menard S: Breast cancer
cells with acquired resistance to the EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitor gefitinib show persistent activation of MAPK signaling.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 112:25–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
LaBonte MJ, Wilson PM, Fazzone W, Russell
J, Louie SG, El-Khoueiry A, Lenz HJ and Ladner RD: The dual
EGFR/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib synergistically enhances the
antitumor activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor
panobinostat in colorectal cancer models. Cancer Res. 71:3635–3648.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kandala PK, Wright SE and Srivastava SK:
Blocking epidermal growth factor receptor activation by
3,3′-diindolylmethane suppresses ovarian tumor growth in vitro and
in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 341:24–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Zhen Y, Guanghui L and Xiefu Z: Knockdown
of EGFR inhibits growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells.
Cancer Gene Ther. 21:491–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gadgeel SM, Ali S, Philip PA, Ahmed F,
Wozniak A and Sarkar FH: Response to dual blockade of epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cycloxygenase-2 in nonsmall cell
lung cancer may be dependent on the EGFR mutational status of the
tumor. Cancer. 110:2775–2784. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne
PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG and Halmos
B: EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huguet F, Fernet M, Giocanti N, Favaudon V
and Larsen AK: Afatinib, an irreversible EGFR family inhibitor,
shows activity toward pancreatic cancer cells, alone and in
combination with radiotherapy, independent of KRAS status. Target
Oncol. 11:371–381. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Yan G, Song X, Wu K, Li Z, Yang C,
Deng T, Sun Y, Hu X, Yang C, et al: STIP overexpression confers
oncogenic potential to human non-small cell lung cancer cells by
regulating cell cycle and apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2806–2817.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang G, Tang B, Tang K, Dong X, Deng J,
Liao L, Liao Z, Yang H and He S: Isoquercitrin inhibits the
progression of liver cancer in vivo and in vitro via the MAPK
signalling pathway. Oncol Rep. 31:2377–2384. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kasahara A and Scorrano L: Mitochondria:
From cell death executioners to regulators of cell differentiation.
Trends Cell Biol. 24:761–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ly JD, Grubb DR and Lawen A: The
mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; An
update. Apoptosis. 8:115–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li L, Gao Y, Zhang L, Zeng J, He D and Sun
Y: Silibinin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis by caspase
activation, downregulating survivin and blocking EGFR-ERK
activation in renal cell carcinoma.
|
|
29
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seifrtová M, Cochlarová T, Havelek R and
Řezáčová M: Benfluron induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and
activation of p53 pathway in MOLT-4 leukemic cells. Folia Biol.
61:147–155. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Malumbres M: Cyclin-dependent kinases.
Genome Biol. 15:1222014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhuo Z, Hu J, Yang X, Chen M, Lei X, Deng
L, Yao N, Peng Q, Chen Z, Ye W, et al: Ailanthone inhibits Huh7
cancer cell growth via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vitro and
in vivo. Sci Rep. 5:161852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chien CC, Wu MS, Shen SC, Ko CH, Chen CH,
Yang LL and Chen YC: Activation of JNK contributes to
evodiamine-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human
colorectal carcinoma cells: A structure-activity study of
evodiamine. PLoS One. 9:e997292014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ondrouskova E and Vojtesek B: Programmed
cell death in cancer cells. Klin Onkol. 27(Suppl 1): S7–S14.
2014.In Czech. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lai CY, Tsai AC, Chen MC, Chang LH, Sun
HL, Chang YL, Chen CC, Teng CM and Pan SL: Aciculatin induces
p53-dependent apoptosis via MDM2 depletion in human cancer cells in
vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e421922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|