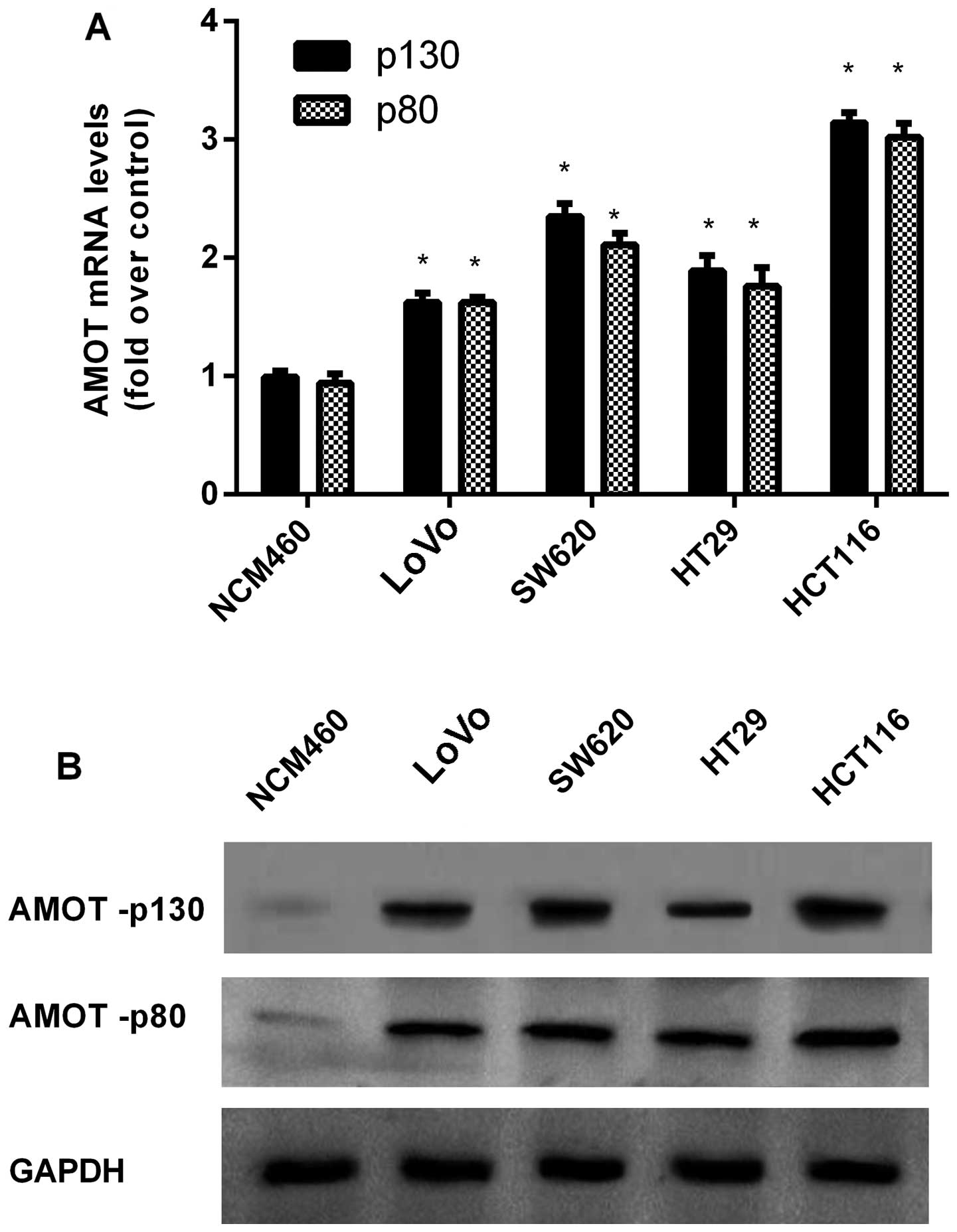
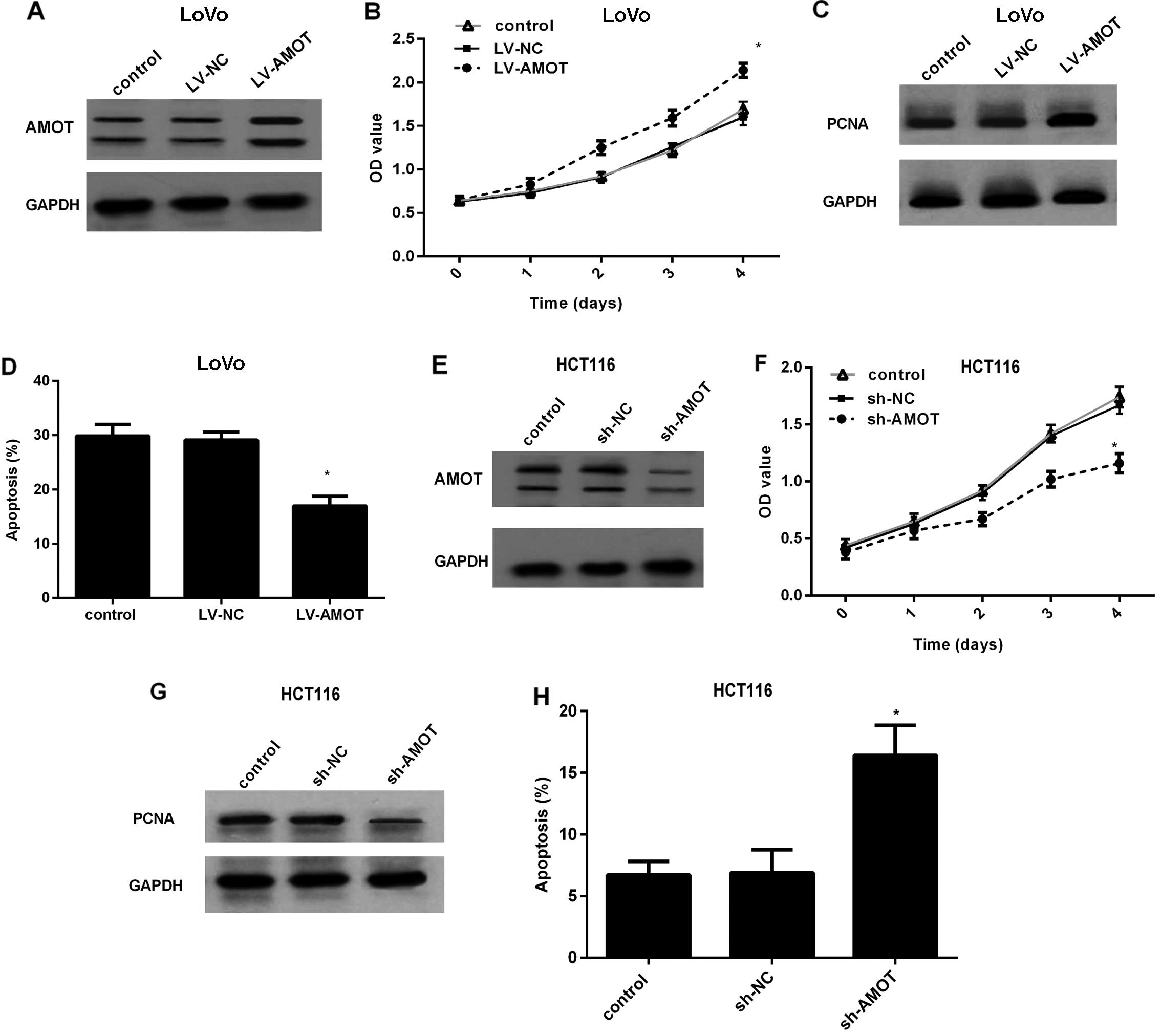
|
1
|
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle
PR and Büchler MW: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 365:153–165. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu F, Li D, Wang Y, Yao X, Zhang W, Liang
J, Lin C, Ren J, Zhu L, Wu Z, et al: Novel DNA variants and
mutation frequencies of hMLH1 and hMSH2 genes in colorectal cancer
in the Northeast China population. PLoS One. 8:e602332013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Troyanovsky B, Levchenko T, Månsson G,
Matvijenko O and Holmgren L: Angiomotin: An angiostatin binding
protein that regulates endothelial cell migration and tube
formation. J Cell Biol. 152:1247–1254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ernkvist M, Aase K, Ukomadu C,
Wohlschlegel J, Blackman R, Veitonmäki N, Bratt A, Dutta A and
Holmgren L: p130-angiomotin associates to actin and controls
endothelial cell shape. FEBS J. 273:2000–2011. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bratt A, Birot O, Sinha I, Veitonmäki N,
Aase K, Ernkvist M and Holmgren L: Angiomotin regulates endothelial
cell-cell junctions and cell motility. J Biol Chem.
280:34859–34869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moleirinho S, Guerrant W and Kissil JL:
The angiomotins - from discovery to function. FEBS Lett.
588:2693–2703. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lv M, Li S, Luo C, Zhang X, Shen Y, Sui
YX, Wang F, Wang X, Yang J, Liu P, et al: Angiomotin promotes renal
epithelial and carcinoma cell proliferation by retaining the
nuclear YAP. Oncotarget. 7:12393–12403. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv M, Lv M, Chen L, Qin T, Zhang X, Liu P
and Yang J: Angiomotin promotes breast cancer cell proliferation
and invasion. Oncol Rep. 33:1938–1946. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Chou SH, Huang MS, Tsai
MJ, Lin YS, Chiang SY, Ho YW, Wu CY and Kuo PL: Angiomotin
decreases lung cancer progression by sequestering oncogenic YAP/TAZ
and decreasing Cyr61 expression. Oncogene. 34:4056–4068. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi C, Shen Z, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Dawany
N, Troutman S, Showe LC, Liu Q, Shimono A, Sudol M, Holmgren L, et
al: The p130 isoform of angiomotin is required for Yap-mediated
hepatic epithelial cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Sci
Signal. 6:ra772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang H and Fan Q: MicroRNA-205 inhibits
the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer by regulating AMOT
expression. Oncol Rep. 34:2163–2170. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia J, Li C, Luo S, Liu-Smith F, Yang J,
Wang X, Wang N, Lai B, Lei T, Wang Q, et al: Yes-associated protein
contributes to the development of human cutaneous squamous cell
carcinoma via activation of RAS. J Invest Dermatol. 136:1267–1277.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ye Q, Cai W, Zheng Y, Evers BM and She QB:
ERK and AKT signaling cooperate to translationally regulate
survivin expression for metastatic progression of colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 33:1828–1839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huynh N, Liu KH, Baldwin GS and He H:
P21-activated kinase 1 stimulates colon cancer cell growth and
migration/invasion via ERK- and AKT-dependent pathways. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1803:1106–1113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao D, Sui Y and Zheng X: MiR-331-3p
inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting HER2
through the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways in colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep. 35:1075–1082. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang J, Che MI, Lin NY, Hung JS, Huang
YT, Lin WC, Huang HC, Lee PH, Liang JT and Huang MC: The molecular
chaperone cosmc enhances malignant behaviors of colon cancer cells
via activation of Akt and ERK. Mol Carcinog. 53:(Suppl 1). E62–E71.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin L, Sabnis AJ, Chan E, Olivas V, Cade
L, Pazarentzos E, Asthana S, Neel D, Yan JJ, Lu X, et al: The Hippo
effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer
therapies. Nat Genet. 47:250–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li H, Wang S, Wang G, Zhang Z, Wu X, Zhang
T, Fu B and Chen G: Yes-associated protein expression is a
predictive marker for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
liver transplantation. Dig Surg. 31:468–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao B, Lei QY and Guan KL: The Hippo-YAP
pathway: New connections between regulation of organ size and
cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 20:638–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dai XY, Zhuang LH, Wang DD, Zhou TY, Chang
LL, Gai RH, Zhu DF, Yang B, Zhu H and He QJ: Nuclear translocation
and activation of YAP by hypoxia contributes to the chemoresistance
of SN38 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:6933–6947.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao B, Li L, Lu Q, Wang LH, Liu CY, Lei Q
and Guan KL: Angiomotin is a novel Hippo pathway component that
inhibits YAP oncoprotein. Genes Dev. 25:51–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Shi S, Guo Z, Zhang X, Han S, Yang
A, Wen W and Zhu Q: Overexpression of YAP and TAZ is an independent
predictor of prognosis in colorectal cancer and related to the
proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e655392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ranahan WP, Han Z, Smith-Kinnaman W,
Nabinger SC, Heller B, Herbert BS, Chan R and Wells CD: The adaptor
protein AMOT promotes the proliferation of mammary epithelial cells
via the prolonged activation of the extracellular signal-regulated
kinases. Cancer Res. 71:2203–2211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuan Y, Li D, Li H, Wang L, Tian G and
Dong Y: YAP overexpression promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Med
Rep. 13:237–242. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|