|
1
|
Friedman RJ and Heilman ER: The pathology
of malignant melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 20:659–676. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lens MB and Dawes M: Global perspectives
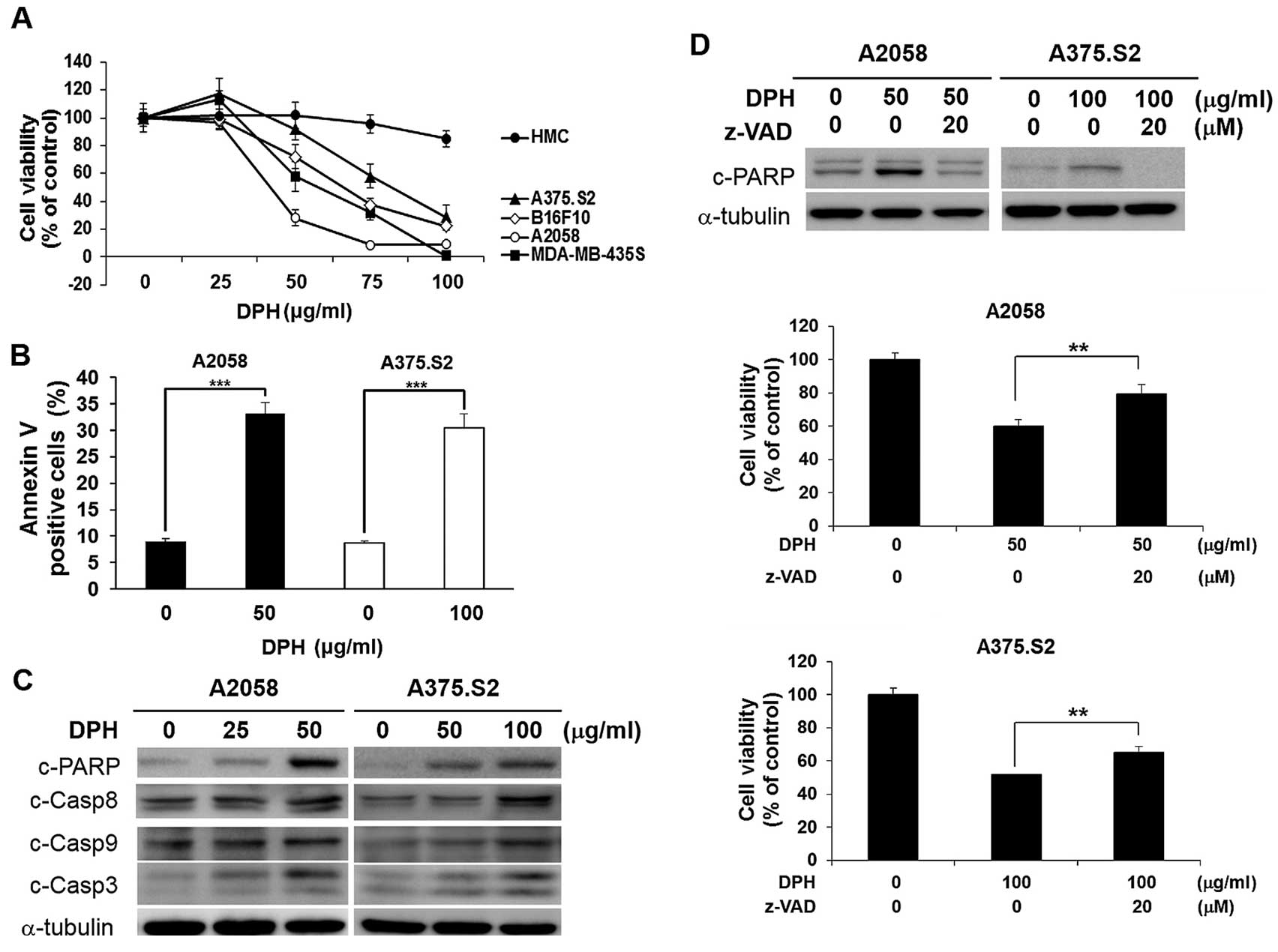
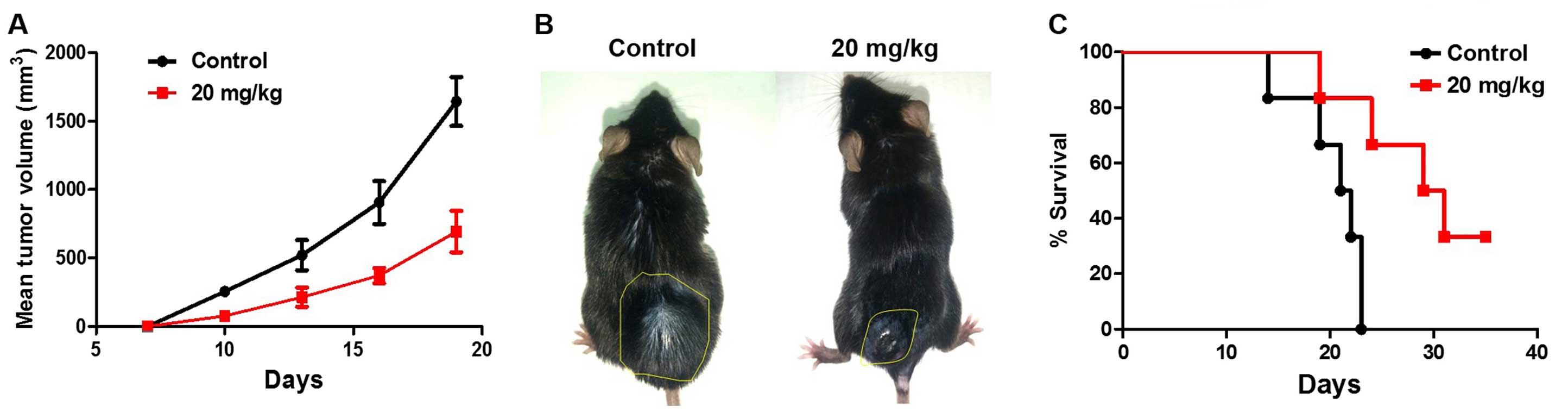
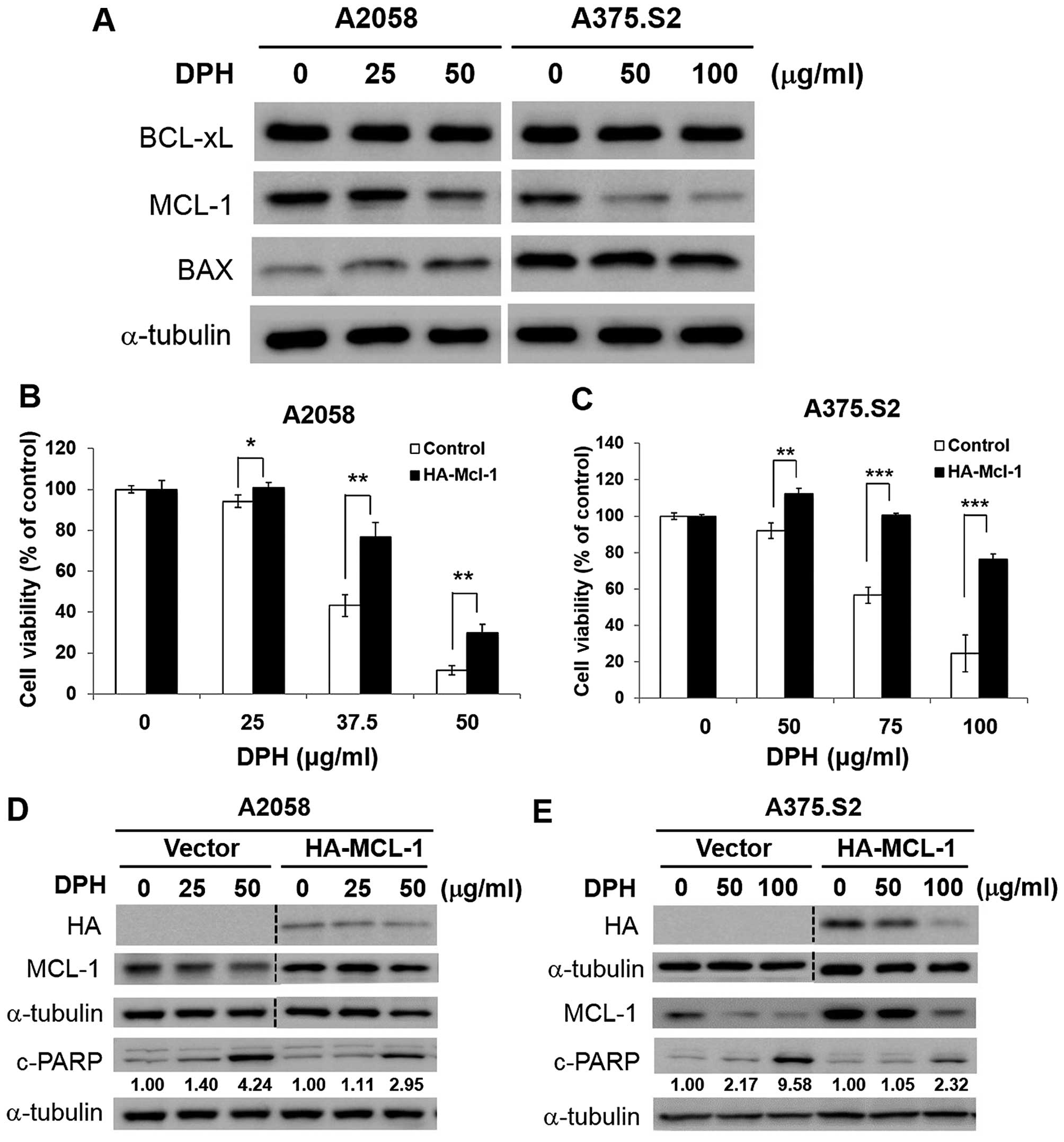
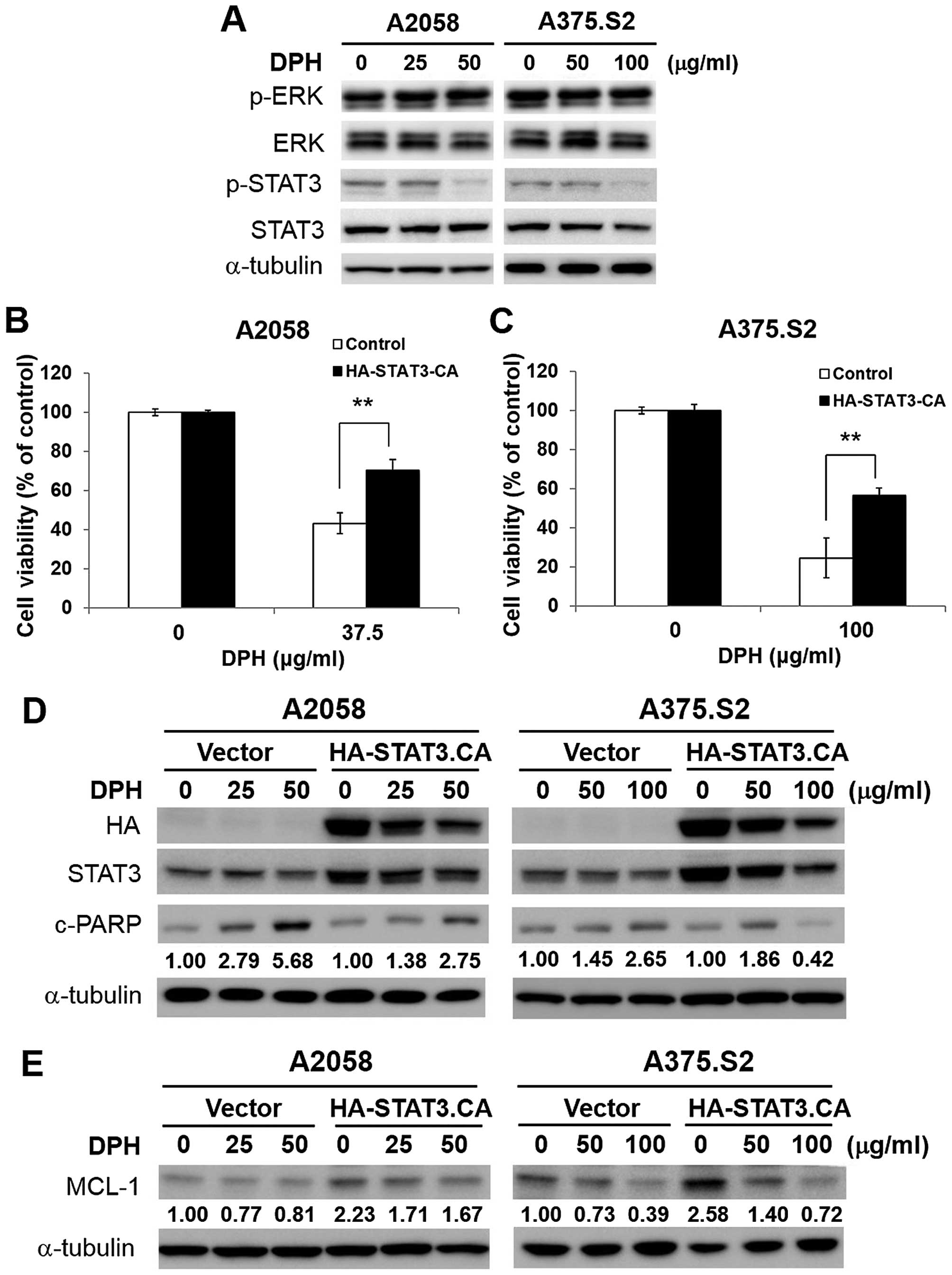
of contemporary epidemiological trends of cutaneous malignant
melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 150:179–185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Houghton AN and Polsky D: Focus on
melanoma. Cancer Cell. 2:275–278. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diepgen TL and Mahler V: The epidemiology
of skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 146:(Suppl 61). 1–6. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Linos E, Swetter SM, Cockburn MG, Colditz
GA and Clarke CA: Increasing burden of melanoma in the United
States. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1666–1674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Antihistamine Drugs, . Drug information.
85. American Society of Hospital Pharmacists; Bethesda, MD:
1985
|
|
7
|
Dupuis LL and Nathan PC: Optimizing emetic
control in children receiving antineoplastic therapy: Beyond the
guidelines. Paediatr Drugs. 12:51–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuo CC, Huang RC and Lou BS: Inhibition of
Na+ current by diphenhydramine and other diphenyl
compounds: Molecular determinants of selective binding to the
inactivated channels. Mol Pharmacol. 57:135–143. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Green SM, Rothrock SG and Gorchynski J:
Validation of diphenhydramine as a dermal local anesthetic. Ann
Emerg Med. 23:1284–1289. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jangi SM, Díaz-Pérez JL, Ochoa-Lizarralde
B, Martín-Ruiz I, Asumendi A, Pérez-Yarza G, Gardeazabal J,
Díaz-Ramón JL and Boyano MD: H1 histamine receptor antagonists
induce genotoxic and caspase-2-dependent apoptosis in human
melanoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:1787–1796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsieh HY, Shieh JJ, Chen CJ, Pan MY, Yang
SY, Lin SC, Chang JS, Lee AYL and Chang CC: Prodigiosin
down-regulates SKP2 to induce p27KIP1 stabilization and
antiproliferation in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 166:2095–2108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhuang L, Lee CS, Scolyer RA, McCarthy SW,
Zhang XD, Thompson JF and Hersey P: Mcl-1, Bcl-XL and Stat3
expression are associated with progression of melanoma whereas
Bcl-2, AP-2 and MITF levels decrease during progression of
melanoma. Mod Pathol. 20:416–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perciavalle RM and Opferman JT: Delving
deeper: MCL-1s contributions to normal and cancer biology. Trends
Cell Biol. 23:22–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Belmar J and Fesik SW: Small molecule
Mcl-1 inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
145:76–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Becker TM, Boyd SC, Mijatov B,
Gowrishankar K, Snoyman S, Pupo GM, Scolyer RA, Mann GJ, Kefford
RF, Zhang XD, et al: Mutant B-RAF-Mcl-1 survival signaling depends
on the STAT3 transcription factor. Oncogene. 33:1158–1166. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Niu G, Bowman T, Huang M, Shivers S,
Reintgen D, Daud A, Chang A, Kraker A, Jove R and Yu H: Roles of
activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth.
Oncogene. 21:7001–7010. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang
J, Kumar AP, Tan BKH, Sethi G and Bishayee A: Targeting the STAT3
signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural
inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:136–154. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao C, Li H, Lin HJ, Yang S, Lin J and
Liang G: Feedback activation of STAT3 as a cancer drug-resistance
mechanism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 37:47–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mukherjee N, Lu Y, Almeida A, Lambert K,
Shiau CW, Su JC, Luo Y, Fujita M, Robinson WA, Robinson SE, et al:
Use of a MCL-1 inhibitor alone to de-bulk melanoma and in
combination to kill melanoma initiating cells. Oncotarget. Apr
12–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
20
|
Jangi SM, Asumendi A, Arlucea J, Nieto N,
Perez-Yarza G, Morales MC, de la Fuente-Pinedo M and Boyano MD:
Apoptosis of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by
diphenhydramine, an H1 histamine receptor antagonist. Oncol Res.
14:363–372. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jangi SM, Ruiz-Larrea MB, Nicolau-Galmés
F, Andollo Y, Arroyo-Berdugo N, Ortega-Martínez I, Díaz-Pérez JL
and Boyano MD: Terfenadine-induced apoptosis in human melanoma
cells is mediated through Ca+2 homeostasis modulation
and tyrosine kinase activity, independently of H1 histamine
receptors. Carcinogenesis. 29:500–509. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
García-Quiroz J and Camacho J: Astemizole:
An old anti- histamine as a new promising anti-cancer drug.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:307–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roger S, Gillet L, Le Guennec JY and
Besson P: Voltage-gated sodium channels and cancer: Is excitability
their primary role? Front Pharmacol. 6:1522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fofaria NM, Frederick DT, Sullivan RJ,
Flaherty KT and Srivastava SK: Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers
resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in
combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma. Oncotarget.
6:40535–40556. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu F, Cao J, Wu J, Sullivan K, Shen J,
Ryu B, Xu Z, Wei W and Cui R: Stat3-targeted therapies overcome the
acquired resistance to vemurafenib in melanomas. J Invest Dermatol.
133:2041–2049. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|