|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Cho H,
Lee DH and Lee KH: Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence,
mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2012. Cancer Res Treat.
47:127–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shin A, Kim KZ, Jung KW, Park S, Won YJ,
Kim J, Kim DY and Oh JH: Increasing trend of colorectal cancer
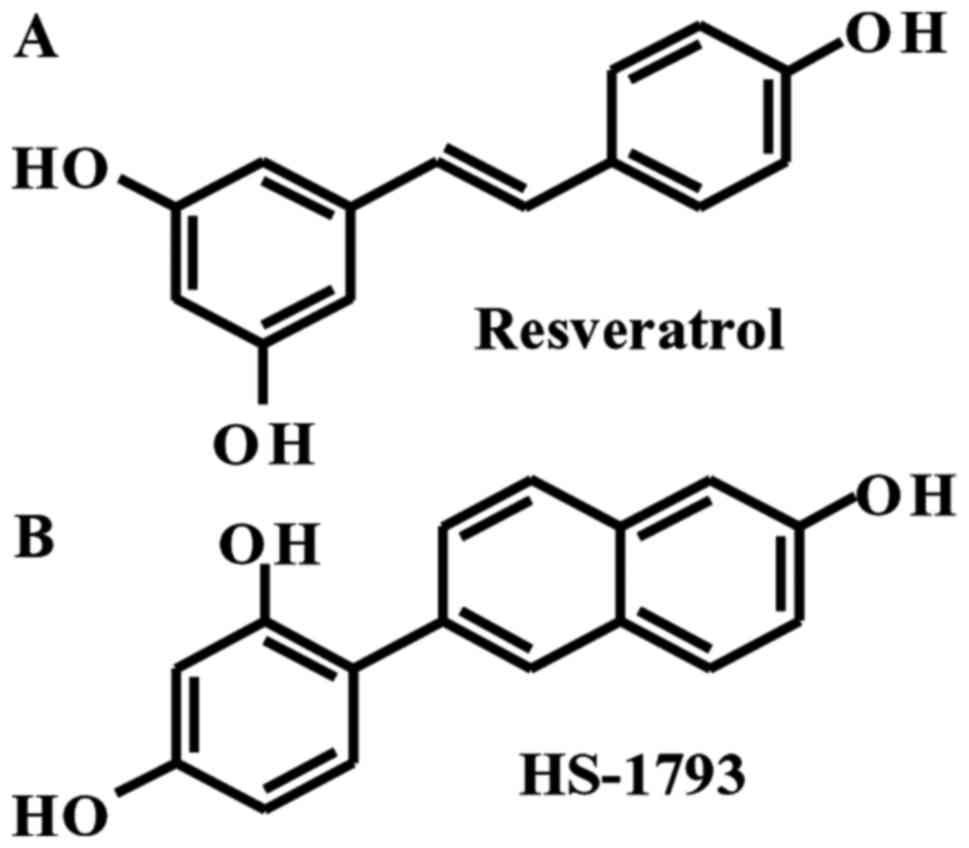
incidence in Korea, 1999–2009. Cancer Res Treat. 44:219–226. 2012.
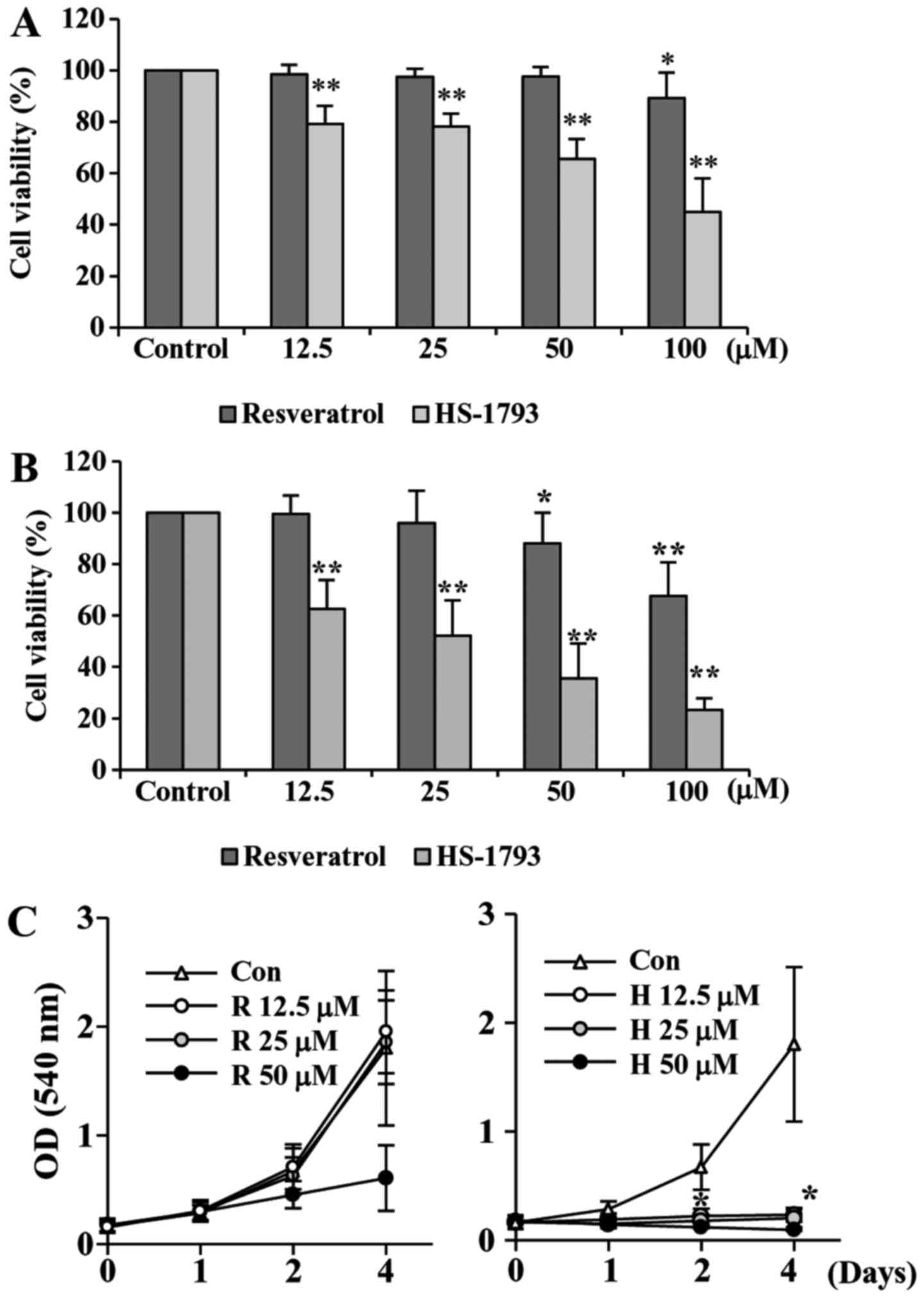
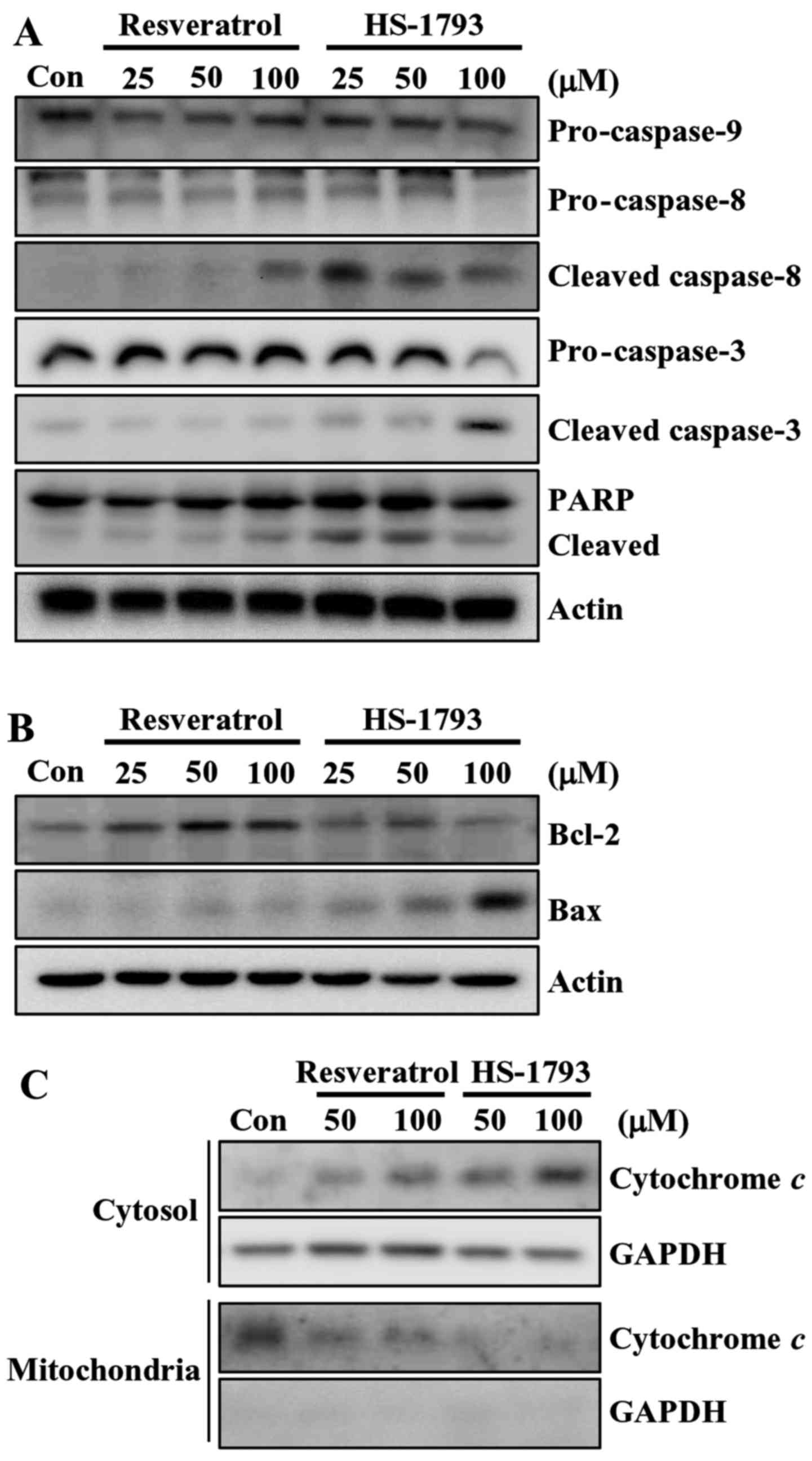
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
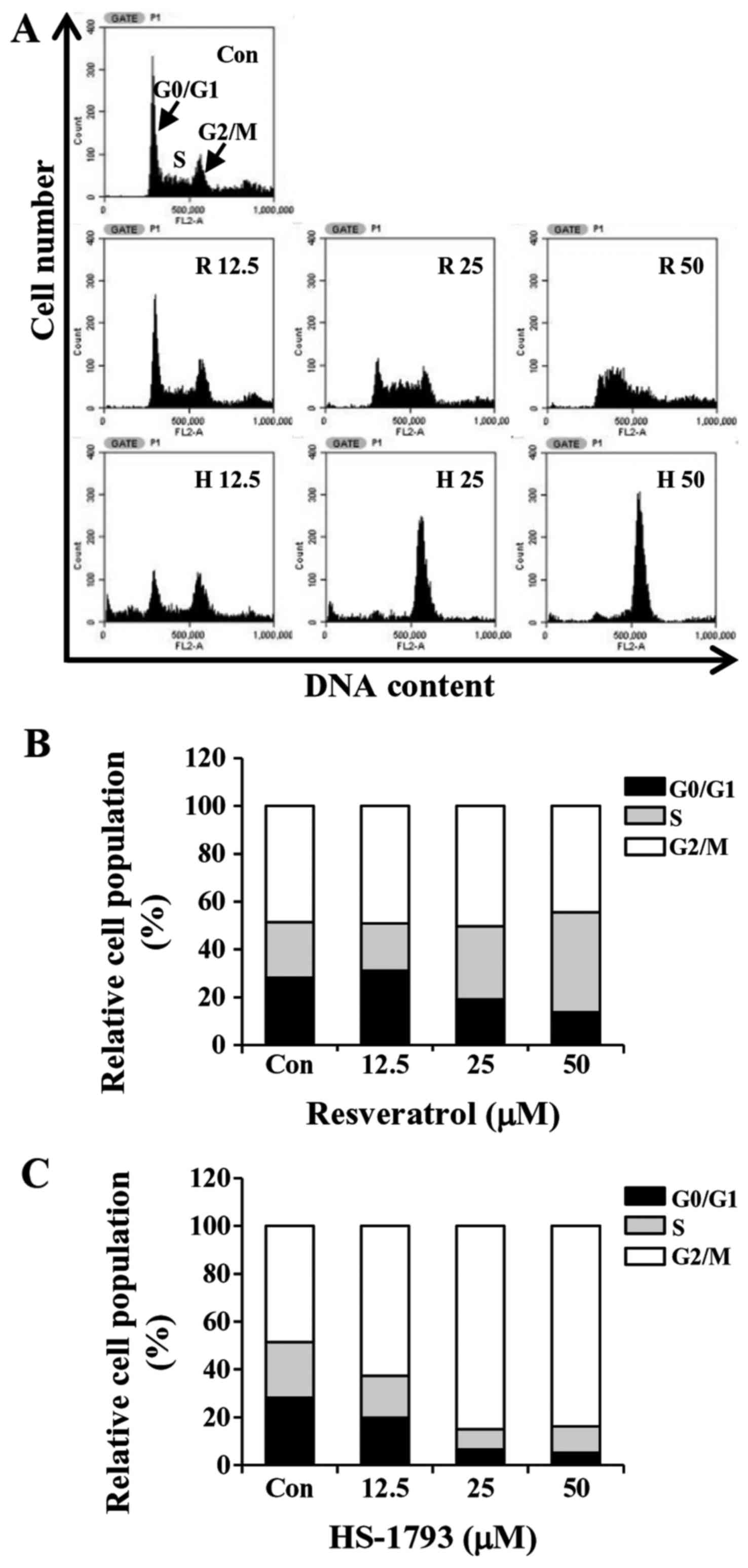
4
|
Li YH, Niu YB, Sun Y, Zhang F, Liu CX, Fan
L and Mei QB: Role of phytochemicals in colorectal cancer
prevention. World J Gastroenterol. 21:9262–9272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhat KP, Lantvit D, Christov K, Mehta RG,
Moon RC and Pezzuto JM: Estrogenic and antiestrogenic properties of
resveratrol in mammary tumor models. Cancer Res. 61:7456–7463.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schneider Y, Duranton B, Gossé F,
Schleiffer R, Seiler N and Raul F: Resveratrol inhibits intestinal
tumorigenesis and modulates host-defense-related gene expression in
an animal model of human familial adenomatous polyposis. Nutr
Cancer. 39:102–107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li ZG, Hong T, Shimada Y, Komoto I, Kawabe
A, Ding Y, Kaganoi J, Hashimoto Y and Imamura M: Suppression of
N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine (NMBA)-induced esophageal tumorigenesis
in F344 rats by resveratrol. Carcinogenesis. 23:1531–1536. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sale S, Tunstall RG, Ruparelia KC, Potter
GA, Steward WP and Gescher AJ: Comparison of the effects of the
chemopreventive agent resveratrol and its synthetic analog
trans-3,4,5,4-tetramethoxystilbene (DMU-212) on adenoma development
in the Apc(Min+) mouse and cyclooxygenase-2 in
human-derived colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 115:194–201. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu HS, Pan CE, Yang W and Liu XM:
Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of resveratrol on
experimentally implanted tumor of H22 in Balb/c mice. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:1474–1476. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Tseng SH, Lai HS and Chen WJ:
Resveratrol-induced cellular apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
neuroblastoma cells and antitumor effects on neuroblastoma in mice.
Surgery. 136:57–66. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pan MH, Gao JH, Lai CS, Wang YJ, Chen WM,
Lo CY, Wang M, Dushenkov S and Ho CT: Antitumor activity of
3,5,4-trimethoxystilbene in COLO 205 cells and xenografts in SCID
mice. Mol Carcinog. 47:184–196. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JC, Chen Y, Lin JH, Wu JM and Tseng
SH: Resveratrol suppresses angiogenesis in gliomas: Evaluation by
color Doppler ultrasound. Anticancer Res. 26:1237–1245.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Busquets S, Ametller E, Fuster G, Olivan
M, Raab V, Argilés JM and López-Soriano FJ: Resveratrol, a natural
diphenol, reduces metastatic growth in an experimental cancer
model. Cancer Lett. 245:144–148. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kosmeder JW II, Pezzuto JM, Pezzuto JM and
Bhat KP: Biological effects of resveratrol. Antioxid Redox Signal.
3:1041–1064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harikumar KB and Aggarwal BB: Resveratrol:
A multitargeted agent for age-associated chronic diseases. Cell
Cycle. 7:1020–1035. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai YJ, Wei QY, Fang JG, Yang L, Liu ZL,
Wyche JH and Han Z: The 3,4-dihydroxyl groups are important for
trans-resveratrol analogs to exhibit enhanced antioxidant and
apoptotic activities. Anticancer Res. 24:999–1002. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szekeres T, Fritzer-Szekeres M, Saiko P
and Jäger W: Resveratrol and resveratrol analogues -
structure-activity relationship. Pharm Res. 27:1042–1048. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song S, Lee H, Jin Y, Ha YM, Bae S, Chung
HY and Suh H: Syntheses of hydroxy substituted
2-phenyl-naphthalenes as inhibitors of tyrosinase. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 17:461–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jeong SH, Lee JS, Jeong NY, Kim TH, Yoo
KS, Song S, Suh H, Kwon TK, Park BS and Yoo YH: A novel resveratrol
analogue HS-1793 treatment overcomes the resistance conferred by
Bcl-2 and is associated with the formation of mature PML nuclear
bodies in renal clear cell carcinoma Caki-1 cells. Int J Oncol.
35:1353–1360. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeong SH, Jo WS, Song S, Suh H, Seol SY,
Leem SH, Kwon TK and Yoo YH: A novel resveratrol derivative,
HS1793, overcomes the resistance conferred by Bcl-2 in human
leukemic U937 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1337–1347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Um HJ, Bae JH, Park JW, Suh H, Jeong NY,
Yoo YH and Kwon TK: Differential effects of resveratrol and novel
resveratrol derivative, HS-1793, on endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis and Akt inactivation. Int J Oncol.
36:1007–1013. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JA, Kim DH, Hossain MA, Kim MY, Sung
B, Yoon JH, Suh H, Jeong TC, Chung HY and Kim ND: HS-1793, a
resveratrol analogue, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell
death in human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 44:473–480.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim DH, Hossain MA, Kim MY, Kim JA, Yoon
JH, Suh HS, Kim GY, Choi YH, Chung HY and Kim ND: A novel
resveratrol analogue, HS-1793, inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α and
VEGF expression, and migration in human prostate cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 43:1915–1924. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang C and Youle RJ: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 43:95–118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Perry JA and Kornbluth S: Cdc25 and Wee1:
Analogous opposites? Cell Div. 2:122007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu B, Zhou Z, Zhou W, Liu J, Zhang Q, Xia
J, Liu J, Chen N, Li M and Zhu R: Resveratrol inhibits
proliferation in human colorectal carcinoma cells by inducing G1/S
phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through caspase/cyclin CDK
pathways. Mol Med Rep. 10:1697–1702. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: Implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 94:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong NY, Yoon YG, Rho JH, Lee JS, Lee SY,
Yoo KS, Song S, Suh H, Choi YH and Yoo YH: The novel resveratrol
analog HS-1793-induced polyploid LNCaP prostate cancer cells are
vulnerable to downregulation of Bcl-xL. Int J Oncol. 38:1597–1604.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeong SH, Song IS, Kim HK, Lee SR, Song S,
Suh H, Yoon YG, Yoo YH, Kim N, Rhee BD, et al: An analogue of
resveratrol HS-1793 exhibits anticancer activity against MCF-7
cells via inhibition of mitochondrial biogenesis gene expression.
Mol Cells. 34:357–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HJ, Yang KM, Park YS, Choi YJ, Yun JH,
Son CH, Suh HS, Jeong MH and Jo WS: The novel resveratrol analogue
HS-1793 induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in murine
breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1628–1634. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D,
Holder A, Dickson C and Peters G: CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3)
are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that
associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 9:71–79. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Malinowsky K, Nitsche U, Janssen KP, Bader
FG, Späth C, Drecoll E, Keller G, Höfler H, Slotta-Huspenina J and
Becker KF: Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway correlates with
prognosis in stage II colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:2081–2089.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rychahou PG, Kang J, Gulhati P, Doan HQ,
Chen LA, Xiao SY, Chung DH and Evers BM: Akt2 overexpression plays
a critical role in the establishment of colorectal cancer
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:20315–20320. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Crowell JA, Steele VE and Fay JR:
Targeting the AKT protein kinase for cancer chemoprevention. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:2139–2148. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|