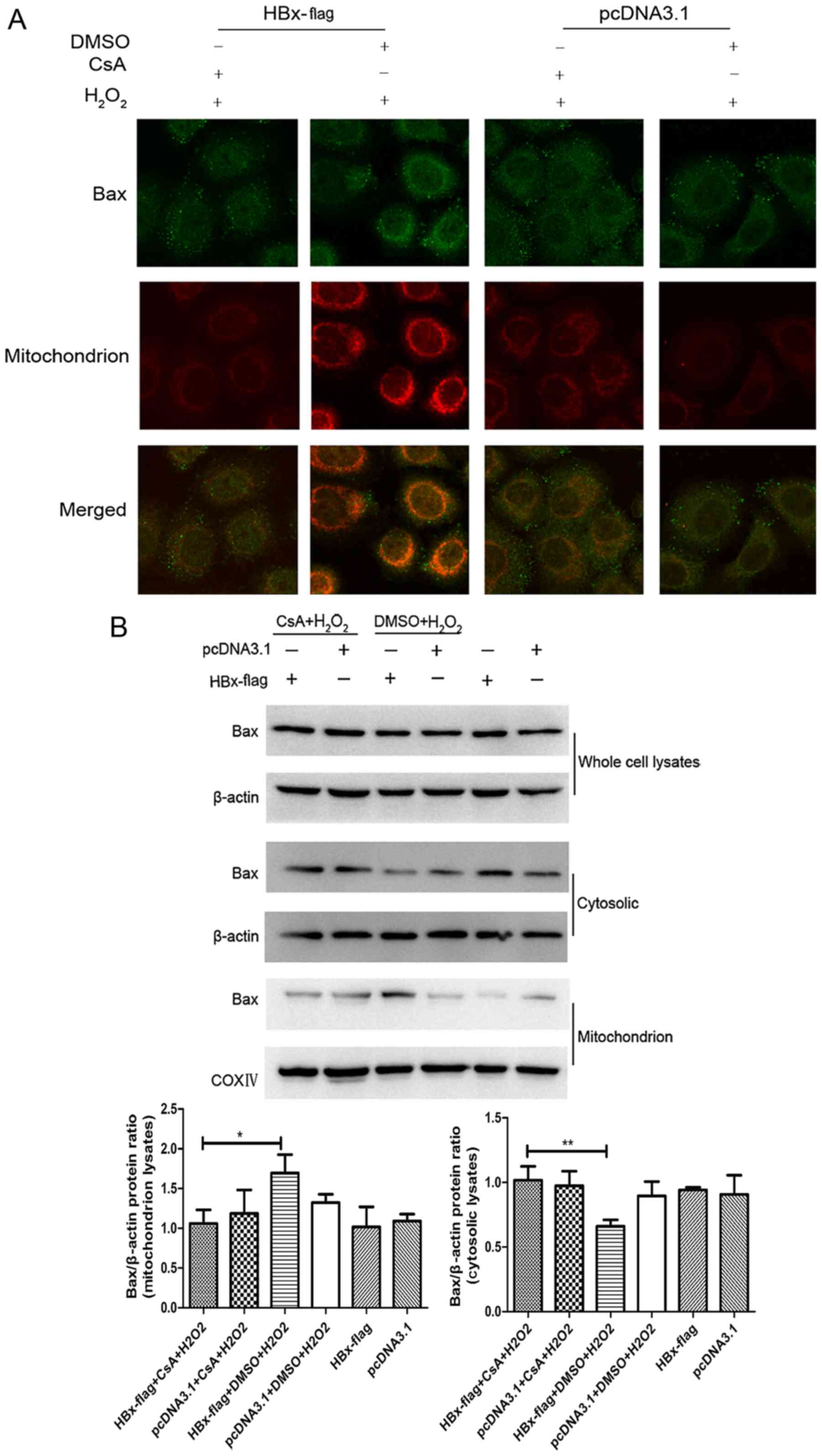
|
1
|
Feitelson MA and Lee J: Hepatitis B virus
integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
252:157–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Murakami S: Hepatitis B virus X protein: A
multifunctional viral regulator. J Gastroenterol. 36:651–660. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rawat S, Clippinger AJ and Bouchard MJ:
Modulation of apoptotic signaling by the hepatitis B virus X
protein. Viruses. 4:2945–2972. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma J, Sun T, Park S, Shen G and Liu J: The
role of hepatitis B virus X protein is related to its differential
intracellular localization. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 43:583–588.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huh KW and Siddiqui A: Characterization of
the mitochondrial association of hepatitis B virus X protein, HBx.
Mitochondrion. 1:349–359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rahmani Z, Huh KW, Lasher R and Siddiqui
A: Hepatitis B virus X protein colocalizes to mitochondria with a
human voltage-dependent anion channel, HVDAC3, and alters its
transmembrane potential. J Virol. 74:2840–2846. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shirakata Y and Koike K: Hepatitis B virus
X protein induces cell death by causing loss of mitochondrial
membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 278:22071–22078. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zou LY, Zheng BY, Fang XF, Li D, Huang YH,
Chen ZX, Zhou LY and Wang XZ: HBx co-localizes with COXIII in
HL-7702 cells to upregulate mitochondrial function and ROS
generation. Oncol Rep. 33:2461–2467. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng BY, Fang XF, Zou LY, Huang YH, Chen
ZX, Li D, Zhou LY, Chen H and Wang XZ: The co-localization of HBx
and COXIII upregulates COX-2 promoting HepG2 cell growth. Int J
Oncol. 45:1143–1150. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gearhart TL and Bouchard MJ: Replication
of the hepatitis B virus requires a calcium-dependent HBx-induced
G1 phase arrest of hepatocytes. Virology. 407:14–25. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McClain SL, Clippinger AJ, Lizzano R and
Bouchard MJ: Hepatitis B virus replication is associated with an
HBx-dependent mitochondrion-regulated increase in cytosolic calcium
levels. J Virol. 81:12061–12065. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takeyama N, Miki S, Hirakawa A and Tanaka
T: Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition and cytochrome
c release in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res.
274:16–24. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaeschke H: Reactive oxygen and mechanisms
of inflammatory liver injury: Present concepts. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 26:(Suppl 1). S173–S179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liang X, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Gao L, Han L, Ma
C, Zhang L, Chen YH and Sun W: Hepatitis B virus sensitizes
hepatocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through Bax. J Immunol.
178:503–510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miao J, Chen GG, Chun SY and Lai PPS:
Hepatitis B virus X protein induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells
through inhibiting Bcl-xL expression. Cancer Lett. 236:115–124.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rawat S and Bouchard MJ: The hepatitis B
virus (HBV) HBx protein activates AKT to simultaneously regulate
HBV replication and hepatocyte survival. J Virol. 89:999–1012.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen L, Zhang X, Hu D, Feng T, Li H, Lu Y
and Huang J: Hepatitis B virus X (HBx) play an anti-apoptosis role
in hepatic progenitor cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Mol Cell Biochem. 383:213–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Madden CRF, Finegold MJ and Slagle BL:
Expression of hepatitis B virus X protein does not alter the
accumulation of spontaneous mutations in transgenic mice. J Virol.
74:5266–5272. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu L, Chen L, Yang G, Li L, Sun H, Chang
Y, Tu Q, Wu M and Wang H: HBx sensitizes cells to oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis by accelerating the loss of Mcl-1 protein
via caspase-3 cascade. Mol Cancer. 10:432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim WH, Hong F, Jaruga B, Zhang ZS, Fan
SJ, Liang TJ and Gao B: Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes
primary mouse hepatocytes to ethanol- and TNF-alpha-induced
apoptosis by a caspase-3-dependent mechanism. Cell Mol Immunol.
2:40–48. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brady NR, Hamacher-Brady A, Westerhoff HV
and Gottlieb RA: A wave of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced
ROS release in a sea of excitable mitochondria. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 8:1651–1665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Breckenridge DG and Xue D: Regulation of
mitochondrial membrane permeabilization by BCL-2 family proteins
and caspases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 16:647–652. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Westphal D, Dewson G, Czabotar PE and
Kluck RM: Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:521–531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim J, Lee H, Choi M, Kim
JK and Ahn JK: Hepatitis B virus X protein induces apoptosis by
enhancing translocation of Bax to mitochondria. IUBMB Life.
60:473–480. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahmad KAIK, Iskandar KB, Hirpara JL,
Clement MV and Pervaiz S: Hydrogen peroxide-mediated cytosolic
acidification is a signal for mitochondrial translocation of Bax
during drug-induced apoptosis of tumor cells. Cancer Res.
64:7867–7878. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma SB, Nguyen TN, Tan I, Ninnis R, Iyer S,
Stroud DA, Menard M, Kluck RM, Ryan MT and Dewson G: Bax targets
mitochondria by distinct mechanisms before or during apoptotic cell
death: A requirement for VDAC2 or Bak for efficient Bax apoptotic
function. Cell Death Differ. 21:1925–1935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost
LC, Elmore SP, Nishimura Y, Crowe RA, Cascio WE, Bradham CA,
Brenner DA, et al: The mitochondrial permeability transition in
cell death: A common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and
autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1366:177–196. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Melegari M, Scaglioni P-P and Wands JR:
Cloning and characterization of a novel hepatitis B virus × binding
protein that inhibits viral replication. J Virol. 72:1737–1743.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scaglioni PP, Melegari M and Wands JR:
Posttranscriptional regulation of hepatitis B virus replication by
the precore protein. J Virol. 71:345–353. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siletsky SA and Konstantinov AA:
Cytochrome c oxidase: Charge translocation coupled to
single-electron partial steps of the catalytic cycle. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1817:476–488. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Wang B, Zhu C, Feng Y, Wang S,
Shahzad M, Hu C, Mo M, Du F and Yu X: 17β-estradiol impedes
Bax-involved mitochondrial apoptosis of retinal nerve cells induced
by oxidative damage via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
signal pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 50:482–493. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schellenberg B, Wang P, Keeble JA,
Rodriguez-Enriquez R, Walker S, Owens TW, Foster F, Tanianis-Hughes
J, Brennan K, Streuli CH, et al: Bax exists in a dynamic
equilibrium between the cytosol and mitochondria to control
apoptotic priming. Mol Cell. 49:959–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang JC and Cortopassi GA: Induction of
the mitochondrial permeability transition causes release of the
apoptogenic factor cytochrome c. Free Radic Biol Med. 24:624–631.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Clippinger AJ, Gearhart TL and Bouchard
MJ: Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates apoptosis in primary rat
hepatocytes by regulating both NF-kappaB and the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. J Virol. 83:4718–4731. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li D, Wang XZ, Yu JP, Chen ZX, Huang YH
and Tao QM: Cytochrome c oxidase III interacts with hepatitis B
virus X protein in vivo by yeast two-hybrid system. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:2805–2808. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang XZ, Li D, Tao QM, Lin N and Chen ZX:
A novel hepatitis B virus X-interactive protein: Cytochrome c
oxidase III. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:711–715. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mkaouar-Rebai E, Ellouze E, Chamkha I,
Kammoun F, Triki C and Fakhfakh F: Molecular-clinical correlation
in a family with a novel heteroplasmic Leigh syndrome missense
mutation in the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase III gene. J
Child Neurol. 26:12–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tsujimoto Y, Nakagawa T and Shimizu S:
Mitochondrial membrane permeability transition and cell death.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1297–1300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang JH, Yun C, Kim S, Lee JH, Yoon G, Lee
MO and Cho H: Reactive oxygen species modulates the intracellular
level of HBx viral oncoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
310:32–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sugano N, Ito K and Murai S: Cyclosporin A
inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis of human
fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 447:274–276. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Harris MH and Thompson CB: The role of the
Bcl-2 family in the regulation of outer mitochondrial membrane
permeability. Cell Death Differ. 7:1182–1191. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|