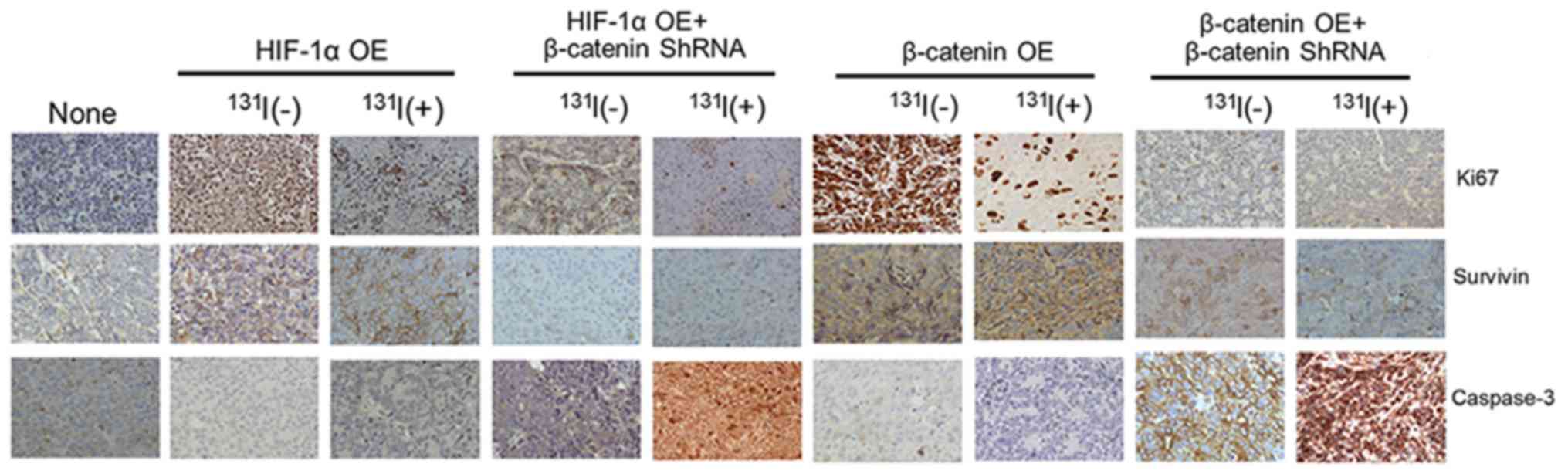
|
1
|
Giannoula E, Iakovou I and Chatzipavlidou
V: Risk factors and the progression of thyroid malignancies. Hell J
Nucl Med. 18:275–284. 2015.(In Greek). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mohamed AF, González JM and Fairchild A:
Patient benefit-risk tradeoffs for radioactive iodine-refractory
differentiated thyroid cancer treatments. J Thyroid Res.
2015:4382352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, Politti U,
Materazzi G, Baldini E, Ulisse S, Miccoli P and Antonelli A:
Molecular targeted therapies of aggressive thyroid cancer. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:1762015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo Y, He DL, Ning L, Shen SL, Li L, Li X,
Zhau HE and Chung LW: Over-expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha increases the invasive potency of LNCaP cells in
vitro. BJU Int. 98:1315–1319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steinert HC and Aberle S: CME: Radioactive
iodine therapy in thyroid cancer. Praxis (Bern 1994).
104:1235–1243; quiz 1244–1235. 2015.[(In German)]. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai G, Levy O and Carrasco N: Cloning and
characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature.
379:458–460. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smanik PA, Liu Q, Furminger TL, Ryu K,
Xing S, Mazzaferri EL and Jhiang SM: Cloning of the human sodium
lodide symporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 226:339–345. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsuno A, Murakami M, Hoya K, Yamada SM,
Miyamoto S, Yamada S, Son JH, Nishido H, Ide F, Nagashima H, et al:
Clinicopathological and molecular histochemical review of skull
base metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Acta
Histochem Cytochem. 46:129–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bauer AJ: Thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr Dev. 26:183–201.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dadu R and Cabanillas ME: Optimizing
therapy for radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid
cancer: Current state of the art and future directions. Minerva
Endocrinol. 37:335–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rahmani N, Hashemi S Abbas, Fazli M and
Raisian M: Clinical management and outcomes of papillary,
follicular and medullary thyroid cancer surgery. Med Glas (Zenica).
10:164–167. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Phay JE and Ringel MD: Metastatic
mechanisms in follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 20:R307–R319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dohán O, Baloch Z, Bánrévi Z, Livolsi V
and Carrasco N: Rapid communication: Predominant intracellular
overexpression of the Na+/I− symporter (NIS)
in a large sampling of thyroid cancer cases. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 86:2697–2700. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saito T, Endo T, Kawaguchi A, Ikeda M,
Katoh R, Kawaoi A, Muramatsu A and Onaya T: Increased expression of
the sodium/iodide symporter in papillary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin
Invest. 101:1296–1300. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wapnir IL, van de Rijn M, Nowels K, Amenta
PS, Walton K, Montgomery K, Greco RS, Dohán O and Carrasco N:
Immunohistochemical profile of the sodium/iodide symporter in
thyroid, breast, and other carcinomas using high density tissue
microarrays and conventional sections. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
88:1880–1888. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Venkataraman GM, Yatin M, Marcinek R and
Ain KB: Restoration of iodide uptake in dedifferentiated thyroid
carcinoma: Relationship to human Na+/I-symporter gene
methylation status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:2449–2457. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arturi F, Russo D, Schlumberger M, du
Villard JA, Caillou B, Vigneri P, Wicker R, Chiefari E, Suarez HG
and Filetti S: Iodide symporter gene expression in human thyroid
tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 83:2493–2496. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dohán O, De la Vieja A, Paroder V, Riedel
C, Artani M, Reed M, Ginter CS and Carrasco N: The sodium/iodide
Symporter (NIS): Characterization, regulation, and medical
significance. Endocr Rev. 24:48–77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arturi F, Russo D, Giuffrida D,
Schlumberger M and Filetti S: Sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) gene
expression in lymph-node metastases of papillary thyroid
carcinomas. Eur J Endocrinol. 143:623–627. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boelaert K and Franklyn JA: Sodium iodide
symporter: A novel strategy to target breast, prostate, and other
cancers? Lancet. 361:796–797. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xing M: Molecular pathogenesis and
mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:184–199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Liu D, Murugan AK, Liu Z and Xing
M: Histone deacetylation of NIS promoter underlies BRAF
V600E-promoted NIS silencing in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 21:161–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo H, Xing Y, Liu Y, Luo Y, Deng F, Yang
T, Yang K and Li Y: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activates
melanocyte stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J Dermatol Sci.
83:45–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sastre-Perona A and Santisteban P:
Wnt-independent role of β-catenin in thyroid cell proliferation and
differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 28:681–695. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lan L, Deng W, Chen HL, Huo LL, Deng LL,
Zhang GY and Luo Y: All-trans retinoic acid improves iodine uptake
of thyroid cancer cells via repressing transcriptional activity of
β-catenin. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:553–558. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rossi ED, Straccia P, Palumbo M, Stigliano
E, Revelli L, Lombardi CP, Santeusanio G, Pontecorvi A and Fadda G:
Diagnostic and prognostic role of HBME-1, galectin-3, and β-catenin
in poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 21:237–241. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lan L, Luo Y, Cui D, Shi BY, Deng W, Huo
LL, Chen HL, Zhang GY and Deng LL: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition induces cancer stem cell generation in human thyroid
cancer cells in vitro. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 93:1261–1265.
2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pagni F, Manzoni M, Buscone S and Leone
BE: β-catenin as a morpho-immunohistochemical marker for the
diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
139:572–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lan L, Deng W, Chen H, Huo L, Deng L,
Zhang G and Luo Y: Nuclear translocation of β-catenin represses
membrane localization of NIS in human thyroid cancer cells.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:891–896. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin S, Borkhuu O, Bao W and Yang YT:
Signaling pathways in thyroid cancer and their therapeutic
implications. J Clin Med Res. 8:284–296. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Höckel M and Vaupel P: Tumor hypoxia:
Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:266–276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, Ma T, Hu Q, Liang
C, Xie S, Chen C, Hu L, Xu S, et al: Wnt/β-catenin signaling
enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with hif-1α signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 34:962–973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Burrows N, Babur M, Resch J, Williams KJ
and Brabant G: Hypoxia-inducible factor in thyroid carcinoma. J
Thyroid Res. 2011:7629052011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Burrows N, Resch J, Cowen RL, von
Wasielewski R, Hoang-Vu C, West CM, Williams KJ and Brabant G:
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in thyroid
carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:61–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goretzki PE, Frilling A, Simon D and
Roeher HD: Growth regulation of normal thyroids and thyroid tumors
in man. Recent Results Cancer Res. 118:48–63. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao JH, Luo Y, Jiang YG, He DL and Wu CT:
Knockdown of β-catenin through shRNA cause a reversal of EMT and
metastatic phenotypes induced by HIF-1α. Cancer Invest. 29:377–382.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kraiem Z, Sadeh O and Yosef M: Iodide
uptake and organification, tri-iodothyronine secretion, cyclic AMP
accumulation and cell proliferation in an optimized system of human
thyroid follicles cultured in collagen gel suspended in serum-free
medium. J Endocrinol. 131:499–506. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin H, Jiang X, Zhu H, Jiang W, Dong X,
Qiao H, Sun X and Jiang H: 2ME2 inhibits the activated
hypoxia-inducible pathways by cabozantinib and enhances its
efficacy against medullary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:381–391. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang R, Wang H, Zhao J, Yao J, Shang H,
Zhu H, Liao L and Dong J: Association between sodium iodide
symporter and differentiated thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis of 9
studies. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:17986–17994. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Riedel C, Levy O and Carrasco N:
Post-transcriptional regulation of the sodium/iodide symporter by
thyrotropin. J Biol Chem. 276:21458–21463. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|