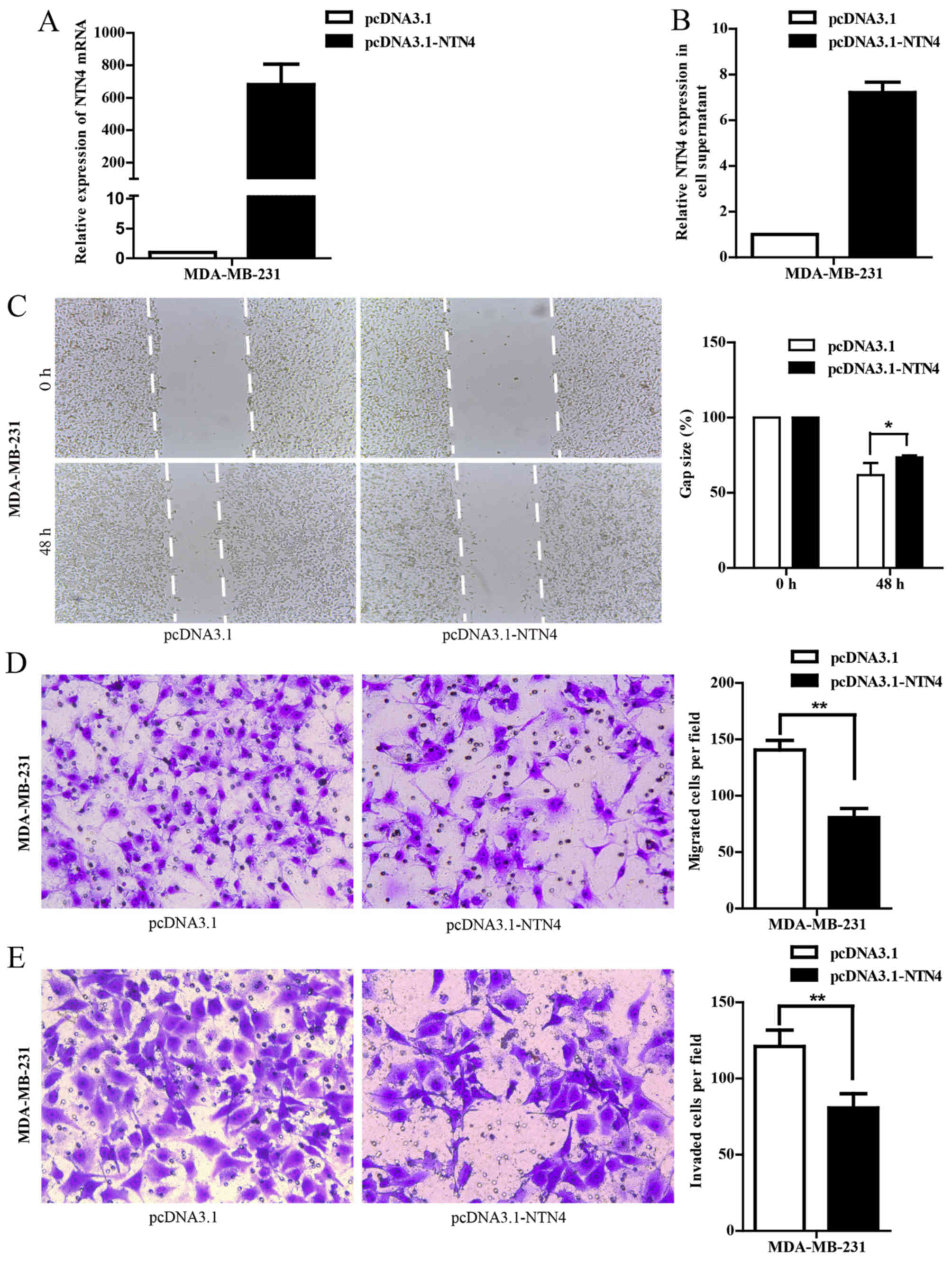
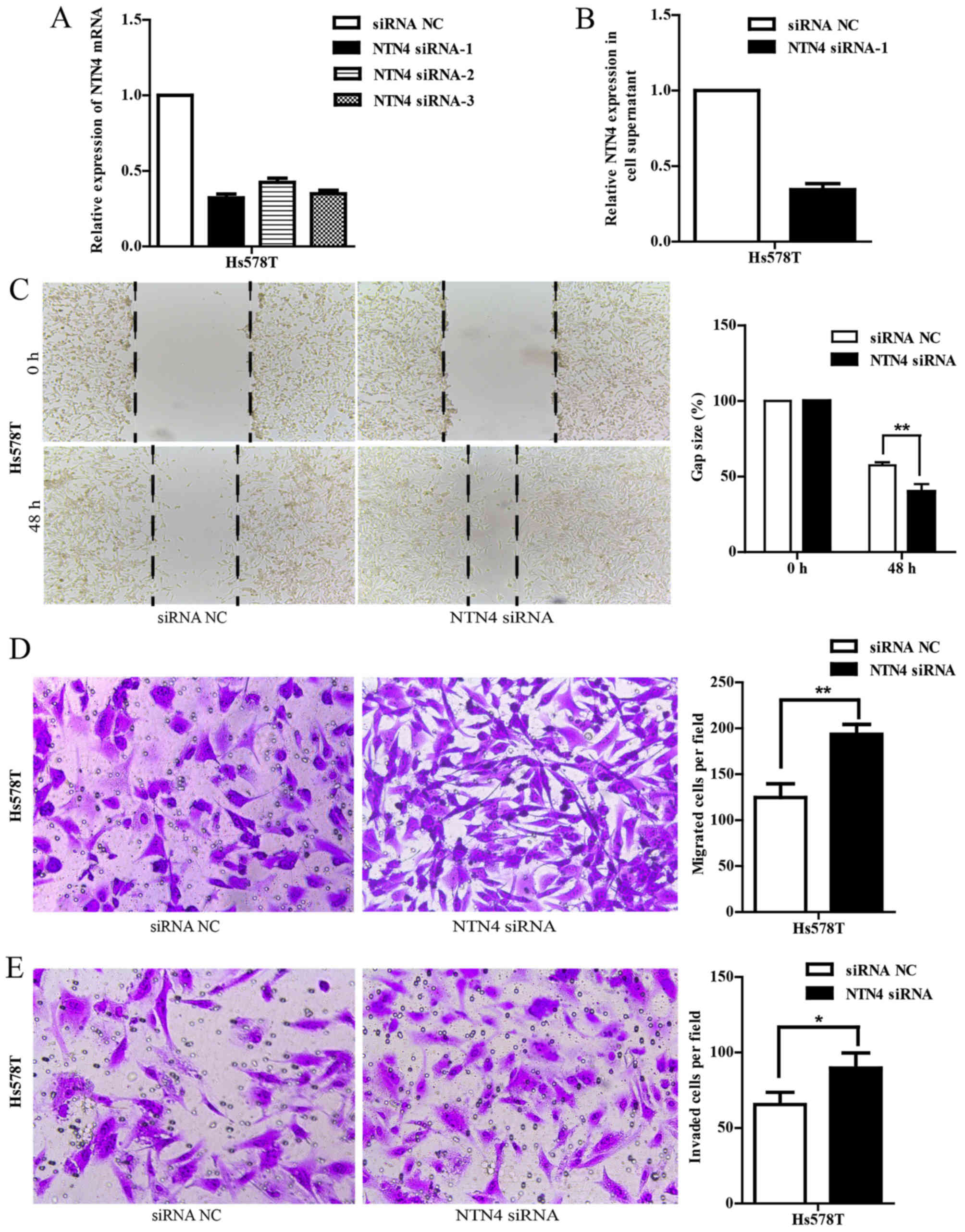
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zou X and Chen
W: Female breast cancer statistics of 2010 in China: Estimates
based on data from 145 population-based cancer registries. J Thorac
Dis. 6:466–470. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yin Y, Sanes JR and Miner JH:
Identification and expression of mouse netrin-4. Mech Dev.
96:115–119. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu Y, Stein E, Oliver T, Li Y, Brunken
WJ, Koch M, Tessier-Lavigne M and Hogan BL: Novel role for Netrins
in regulating epithelial behavior during lung branching
morphogenesis. Curr Biol. 14:897–905. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoang S, Liauw J, Choi M, Choi M, Guzman
RG and Steinberg GK: Netrin-4 enhances angiogenesis and neurologic
outcome after cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
29:385–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han Y, Shao Y, Liu T, Qu YL, Li W and Liu
Z: Therapeutic effects of topical netrin-4 inhibits corneal
neovascularization in alkali-burn rats. PLoS One. 10:e01229512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang YH, Szabat M, Bragagnini C, Kott K,
Helgason CD, Hoffman BG and Johnson JD: Paracrine signalling loops
in adult human and mouse pancreatic islets: Netrins modulate beta
cell apoptosis signalling via dependence receptors. Diabetologia.
54:828–842. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv B, Song C, Wu L, Zhang Q, Hou D, Chen
P, Yu S, Wang Z, Chu Y, Zhang J, et al: Netrin-4 as a biomarker
promotes cell proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:9794–9806. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lambert E, Coissieux MM, Laudet V and
Mehlen P: Netrin-4 acts as a pro-angiogenic factor during zebrafish
development. J Biol Chem. 287:3987–3999. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esseghir S, Kennedy A, Seedhar P, Nerurkar
A, Poulsom R, Reis-Filho JS and Isacke CM: Identification of NTN4,
TRA1, and STC2 as prognostic markers in breast cancer in a screen
for signal sequence encoding proteins. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3164–3173. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eveno C, Broqueres-You D, Feron JG,
Rampanou A, Tijeras-Raballand A, Ropert S, Leconte L, Levy BI and
Pocard M: Netrin-4 delays colorectal cancer carcinomatosis by
inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 178:1861–1869. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eveno C, Contreres JO, Hainaud P, Nemeth
J, Dupuy E and Pocard M: Netrin-4 overexpression suppresses primary
and metastatic colorectal tumor progression. Oncol Rep. 29:73–78.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nacht M, St Martin TB, Byrne A, Klinger
KW, Teicher BA, Madden SL and Jiang Y: Netrin-4 regulates
angiogenic responses and tumor cell growth. Exp Cell Res.
315:784–794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fujikane T, Nishikawa N, Toyota M, Suzuki
H, Nojima M, Maruyama R, Ashida M, Ohe-Toyota M, Kai M, Nishidate
T, et al: Genomic screening for genes upregulated by demethylation
revealed novel targets of epigenetic silencing in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 122:699–710. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Latil A, Chêne L, Cochant-Priollet B,
Mangin P, Fournier G, Berthon P and Cussenot O: Quantification of
expression of netrins, slits and their receptors in human prostate
tumors. Int J Cancer. 103:306–315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Hu Y, Ylivinkka I, Li H, Chen P,
Keski-Oja J and Hyytiäinen M: NETRIN-4 protects glioblastoma cells
FROM temozolomide induced senescence. PLoS One. 8:e803632013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu Y, Ylivinkka I, Chen P, Li L,
Hautaniemi S, Nyman TA, Keski-Oja J and Hyytiäinen M: Netrin-4
promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation through integrin β4
signaling. Neoplasia. 14:219–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Larrieu-Lahargue F, Welm AL, Thomas KR and
Li DY: Netrin-4 induces lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Blood.
115:5418–5426. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan Y, Leszczynska M, Konstantinovsky S,
Tropé CG, Reich R and Davidson B: Netrin-4 is upregulated in breast
carcinoma effusions compared to corresponding solid tumors. Diagn
Cytopathol. 39:562–566. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Amith SR, Wilkinson JM and Fliegel L:
Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 regulation modulates
metastatic potential and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:21091–21113.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ho JN, Jun W, Choue R and Lee J: I3C and
ICZ inhibit migration by suppressing the EMT process and FAK
expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:384–388.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng HL, Lin CW, Yang JS, Hsieh MJ, Yang
SF and Lu KH: Zoledronate blocks geranylgeranylation not
farnesylation to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells metastasis
by EMT via Rho A activation and FAK-inhibited JNK and p38 pathways.
Oncotarget. 7:9742–9758. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taliaferro-Smith L, Oberlick E, Liu T,
McGlothen T, Alcaide T, Tobin R, Donnelly S, Commander R, Kline E,
Nagaraju GP, et al: FAK activation is required for IGF1R-mediated
regulation of EMT, migration, and invasion in mesenchymal triple
negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:4757–4772. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei J, Li Z, Chen W, Ma C, Zhan F, Wu W
and Peng Y: AEG-1 participates in TGF-beta1-induced EMT through p38
MAPK activation. Cell Biol Int. 37:1016–1021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koch M, Murrell JR, Hunter DD, Olson PF,
Jin W, Keene DR, Brunken WJ and Burgeson RE: A novel member of the
netrin family, beta-netrin, shares homology with the beta chain of
laminin: Identification, expression, and functional
characterization. J Cell Biol. 151:221–234. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rajasekharan S and Kennedy TE: The netrin
protein family. Genome Biol. 10:2392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lejmi E, Leconte L, Pédron-Mazoyer S,
Ropert S, Raoul W, Lavalette S, Bouras I, Feron JG, Maitre-Boube M,
Assayag F, et al: Netrin-4 inhibits angiogenesis via binding to
neogenin and recruitment of Unc5B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:12491–12496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao J and Guan JL: Signal transduction by
focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:35–49.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Micalizzi DS, Christensen KL, Jedlicka P,
Coletta RD, Barón AE, Harrell JC, Horwitz KB, Billheimer D,
Heichman KA, Welm AL, et al: The Six1 homeoprotein induces human
mammary carcinoma cells to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in mice through increasing TGF-beta
signaling. J Clin Invest. 119:2678–2690. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bock C, Kuhn C, Ditsch N, Krebold R,
Heublein S, Mayr D, Doisneau-Sixou S and Jeschke U: Strong
correlation between N-cadherin and CD133 in breast cancer: Role of
both markers in metastatic events. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1873–1881. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakagawa M, Bando Y, Nagao T, Morimoto M,
Takai C, Ohnishi T, Honda J, Moriya T, Izumi K, Takahashi M, et al:
Expression of p53, Ki-67, E-cadherin, N-cadherin and TOP2A in
triple-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:2389–2394.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Whipple RA, Balzer EM, Cho EH, Matrone MA,
Yoon JR and Martin SS: Vimentin filaments support extension of
tubulin-based microtentacles in detached breast tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 68:5678–5688. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF, Norton L
and Aaronson SA: Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast
cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J
Cell Biol. 148:779–790. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nieman MT, Prudoff RS, Johnson KR and
Wheelock MJ: N-cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer
cells regardless of their E-cadherin expression. J Cell Biol.
147:631–644. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zajchowski DA, Bartholdi MF, Gong Y,
Webster L, Liu HL, Munishkin A, Beauheim C, Harvey S, Ethier SP and
Johnson PH: Identification of gene expression profiles that predict
the aggressive. Cancer Res. 61:5168–5178. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|