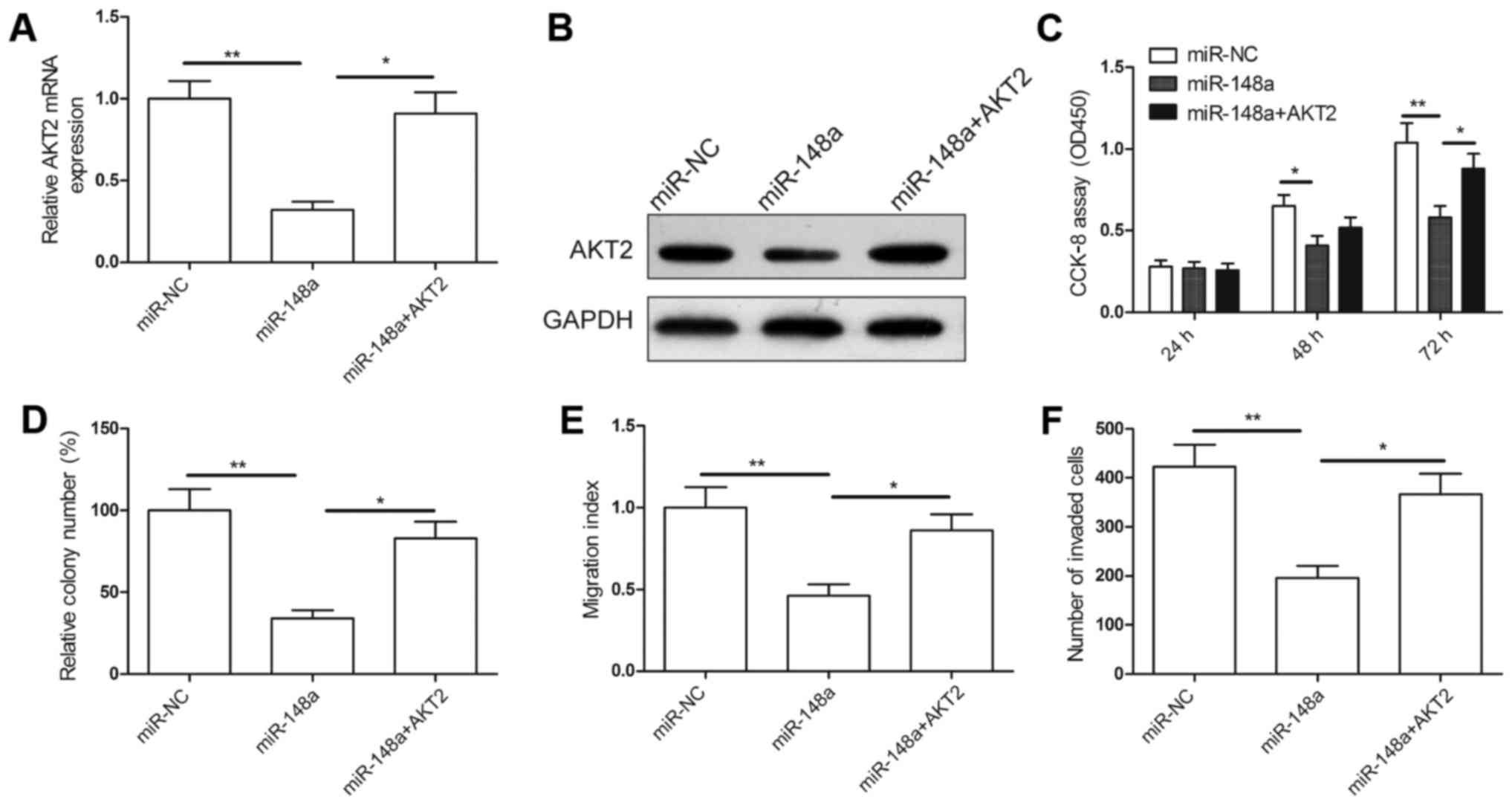
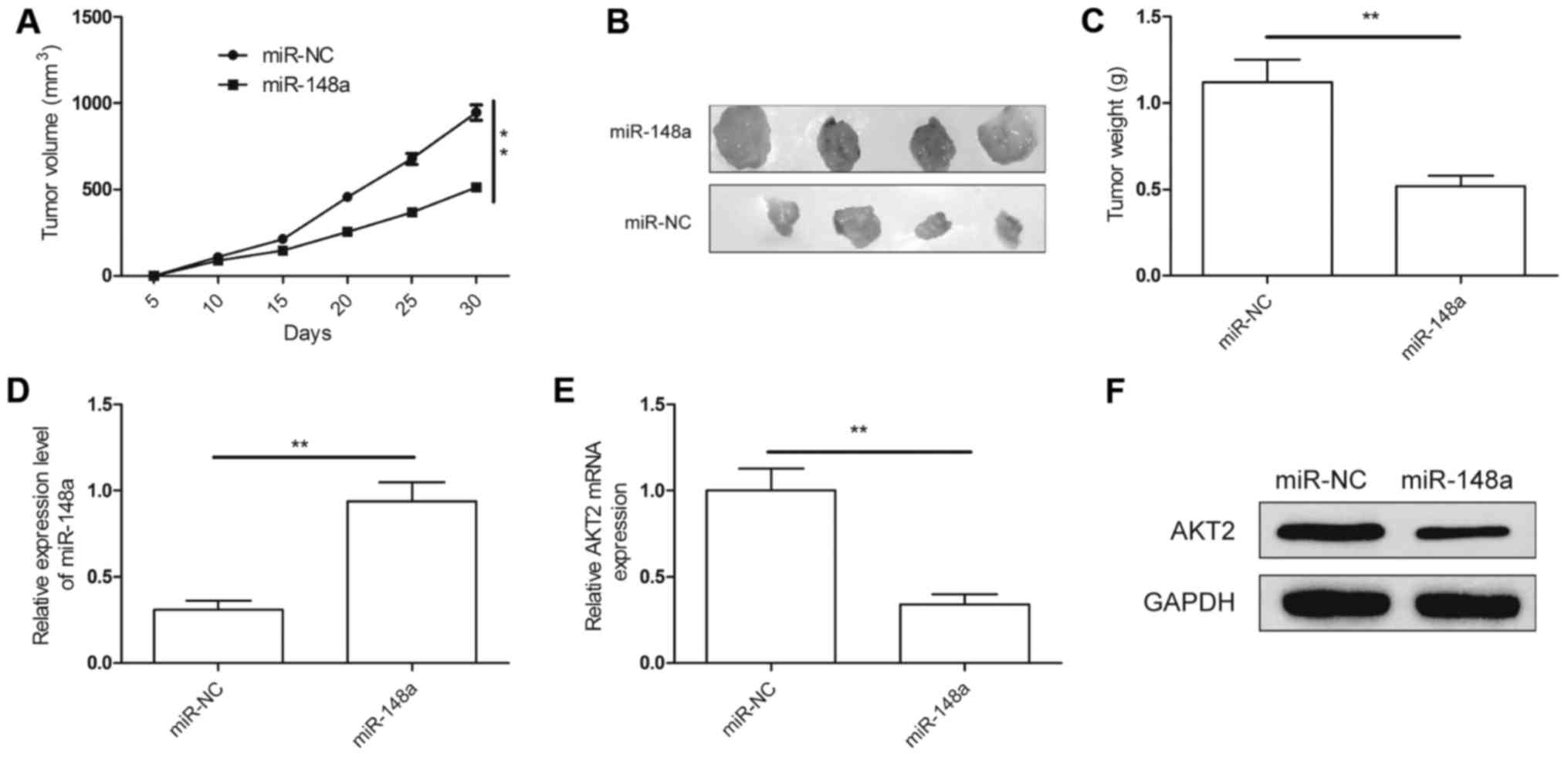
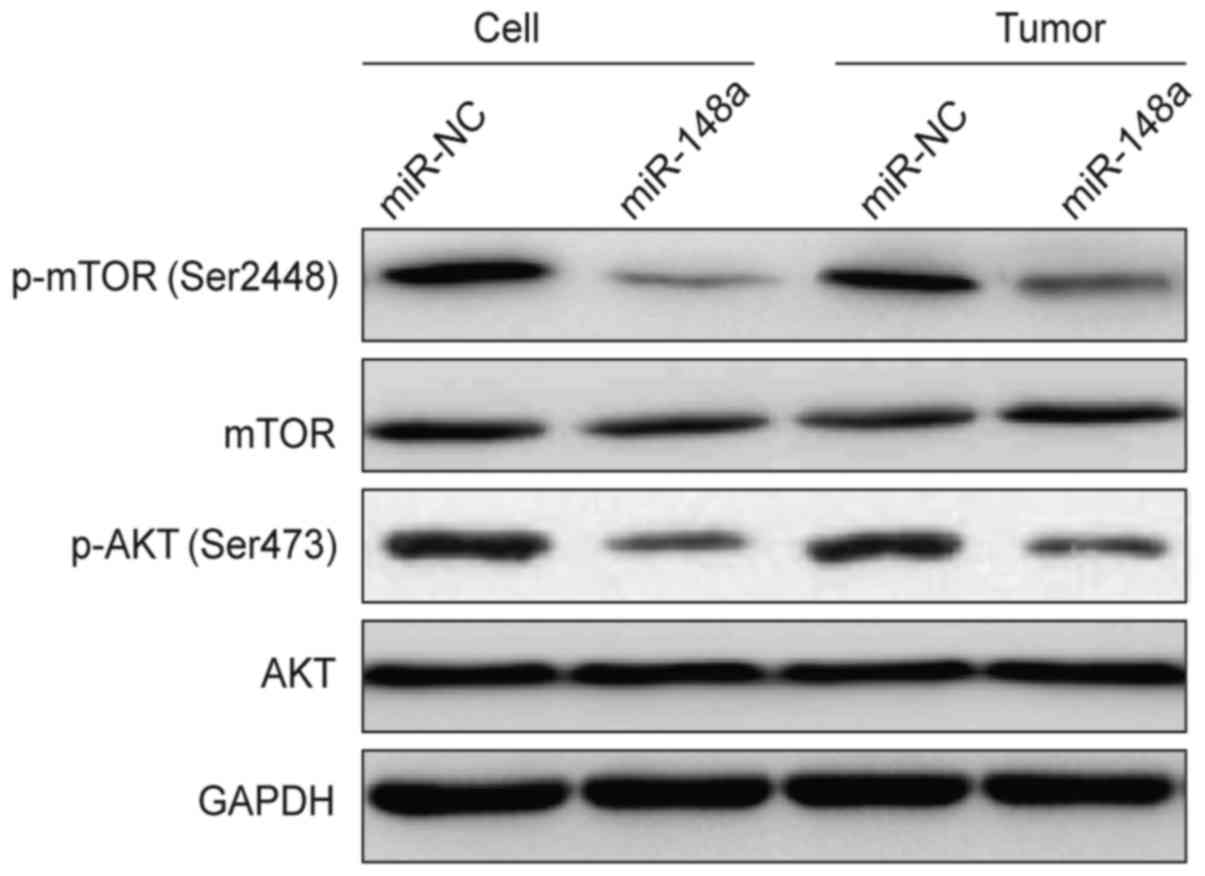
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Capitanio U and Montorsi F: Renal cancer.
Lancet. 387:894–906. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chow WH, Dong LM and Devesa SS:
Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
7:245–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pantuck AJ, Zisman A and Belldegrun AS:
The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
166:1611–1623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ying SY, Chang DC, Miller JD and Lin SL:
The microRNA: Overview of the RNA gene that modulates gene
functions. Methods Mol Biol. 342:1–18. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McManus MT: MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 13:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu L, Li H, Chen L, Ma X, Gao Y, Li X,
Zhang Y, Fan Y and Zhang X: MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular
signatures in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:32545–32560. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li JY, Yong TY, Michael MZ and Gleadle JM:
Review: The role of microRNAs in kidney disease. Nephrology
(Carlton). 15:599–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Jasper J, Lykken E,
Alexander PB, Markowitz GJ, McDonnell DP, Li QJ and Wang XF:
MiR-148a functions to suppress metastasis and serves as a
prognostic indicator in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:20381–20394. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pan L, Huang S, He R, Rong M, Dang Y and
Chen G: Decreased expression and clinical significance of miR-148a
in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Eur J Med Res. 19:682014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma W, Zhang X, Chai J, Chen P, Ren P and
Gong M: Circulating miR-148a is a significant diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
35:12467–12472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia J, Guo X, Yan J and Deng K: The role
of miR-148a in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1451–1456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hibino Y, Sakamoto N, Naito Y, Goto K, Oo
HZ, Sentani K, Hinoi T, Ohdan H, Oue N and Yasui W: Significance of
miR-148a in colorectal neoplasia: Downregulation of miR-148a
contributes to the carcinogenesis and cell invasion of colorectal
cancer. Pathobiology. 82:233–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yogi K, Sridhar E, Goel N, Jalali R, Goel
A, Moiyadi A, Thorat R, Panwalkar P, Khire A, Dasgupta A, et al:
MiR-148a, a microRNA upregulated in the WNT subgroup tumors,
inhibits invasion and tumorigenic potential of medulloblastoma
cells by targeting neuropilin 1. Oncoscience. 2:334–348. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lombard AP, Mooso BA, Libertini SJ, Lim
RM, Nakagawa RM, Vidallo KD, Costanzo NC, Ghosh PM and Mudryj M:
miR-148a dependent apoptosis of bladder cancer cells is mediated in
part by the epigenetic modifier DNMT1. Mol Carcinog. 55:757–767.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Joshi P, Jeon YJ, Laganà A, Middleton J,
Secchiero P, Garofalo M and Croce CM: MicroRNA-148a reduces
tumorigenesis and increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:8650–8655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, Li Q, He J, Jing Y,
Qi YT, Xu Q, Li W, Lu B, et al: A regulatory circuit of
miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation and tumor
angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:3–13.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li M, Li H, Liu X, Xu D and Wang F:
MicroRNA-29b regulates TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of retinal pigment epithelial cells by targeting AKT2.
Exp Cell Res. 345:115–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim J, Zhang Y, Skalski M, Hayes J, Kefas
B, Schiff D, Purow B, Parsons S, Lawler S and Abounader R:
microRNA-148a is a prognostic oncomiR that targets MIG6 and BIM to
regulate EGFR and apoptosis in glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
74:1541–1553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pereira L, Horta S, Mateus R and Videira
MA: Implications of Akt2/Twist crosstalk on breast cancer
metastatic outcome. Drug Discov Today. 20:1152–1158. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agarwal E, Brattain MG and Chowdhury S:
Cell survival and metastasis regulation by Akt signaling in
colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. 25:1711–1719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng GZ, Zhang W and Wang LH: Regulation
of cancer cell survival, migration, and invasion by Twist: AKT2
comes to interplay. Cancer Res. 68:957–960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toschi A, Lee E, Gadir N, Ohh M and Foster
DA: Differential dependence of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 alpha
and 2 alpha on mTORC1 and mTORC2. J Biol Chem. 283:34495–34499.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang CF, Li DM, Shi ZM, Wang L, Liu MM,
Ge X, Liu X, Qian YC, Wen YY, Zhen LL, et al: Estrogen regulates
miRNA expression: Implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2
in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 7:36940–36955.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sheng L, He P, Yang X, Zhou M and Feng Q:
miR-612 negatively regulates colorectal cancer growth and
metastasis by targeting AKT2. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18082015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu L, Chen J, Ding C, Wei S, Zhu Y, Yang
W, Zhang X, Wei X and Han D: MicroRNA-137 contributes to dampened
tumorigenesis in human gastric cancer by targeting AKT2. PLoS One.
10:e01301242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai Y, Li J, Li J, Liu Y and Zhang B:
MiR-615 inhibited cell proliferation and cell cycle of human breast
cancer cells by suppressing of AKT2 expression. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:3801–3808. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen H, Zhou L, Wu X, Li R, Wen J, Sha J
and Wen X: The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate
cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 21:1084–1091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang SX, Polley E and Lipkowitz S: New
insights on PI3K/AKT pathway alterations and clinical outcomes in
breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 45:87–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Robbins HL and Hague A: The PI3K/Akt
pathway in tumors of endocrine tissues. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 6:1882016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo H, German P, Bai S, Barnes S, Guo W,
Qi X, Lou H, Liang J, Jonasch E, Mills GB, et al: The PI3K/AKT
pathway and renal cell carcinoma. J Genet Genomics. 42:343–353.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee JJ, Loh K and Yap YS: PI3K/Akt/mTOR
inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Biol Med. 12:342–354.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hudes GR: Targeting mTOR in renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer 115 (Suppl 10). 2313–2320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|