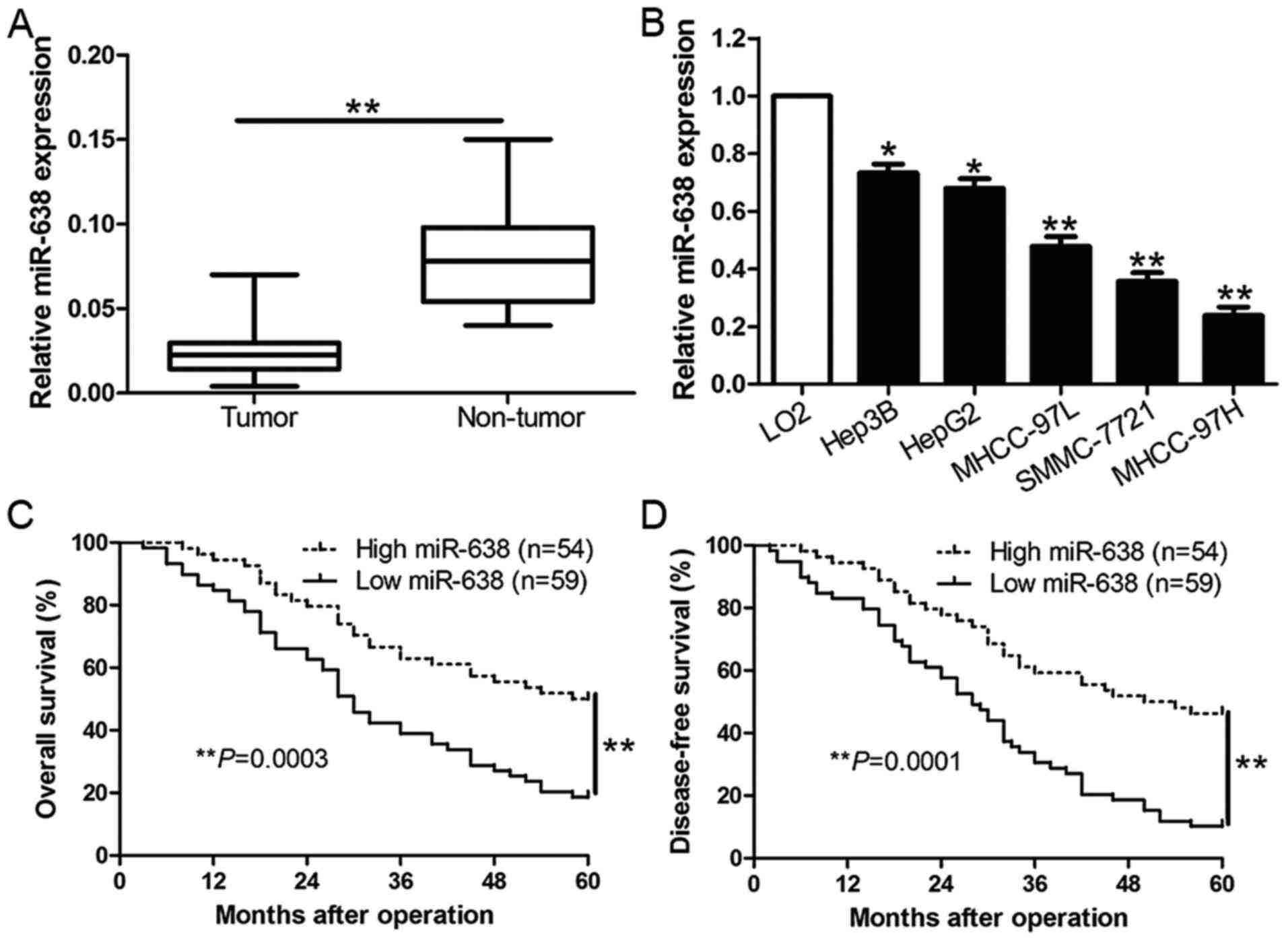
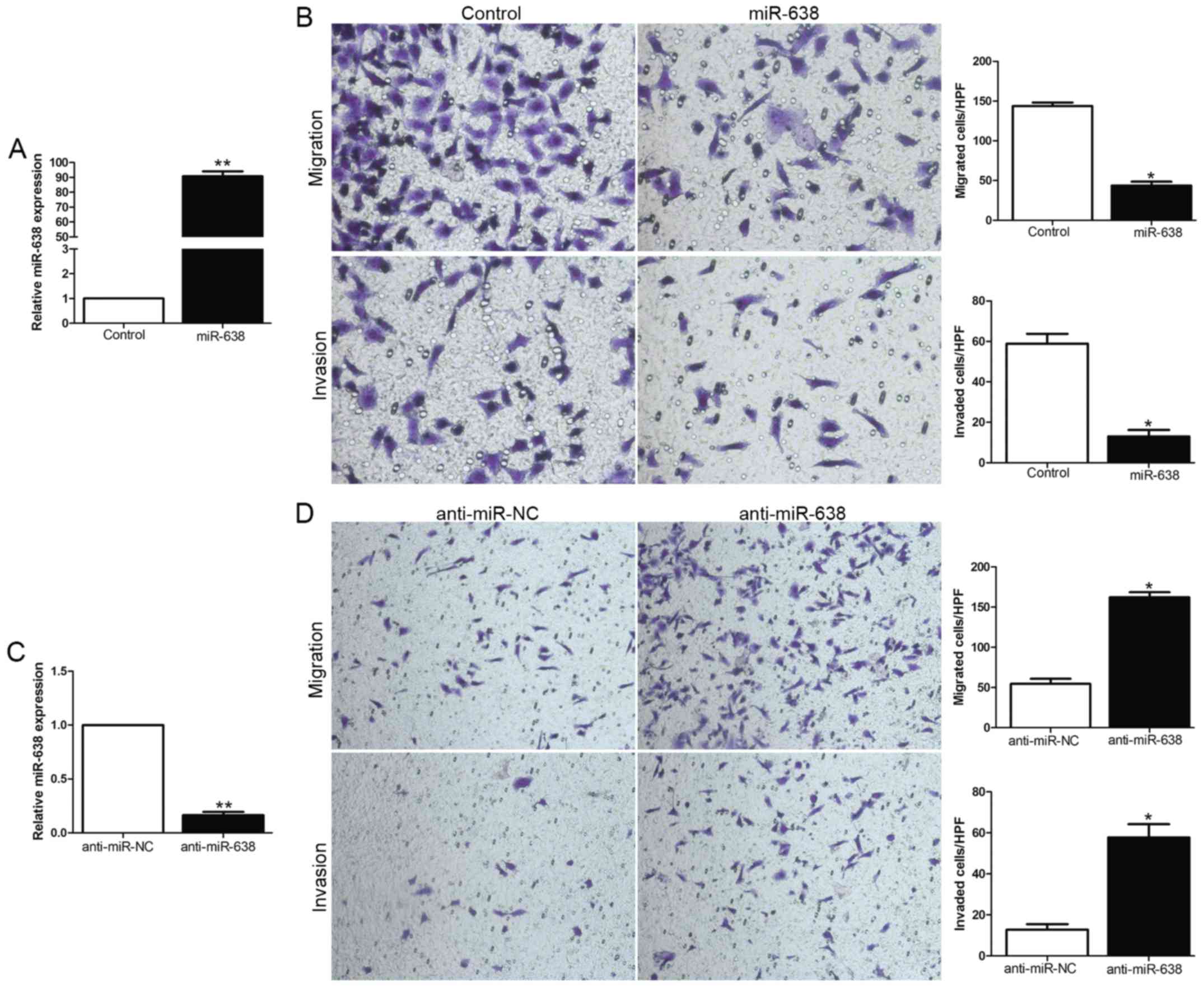
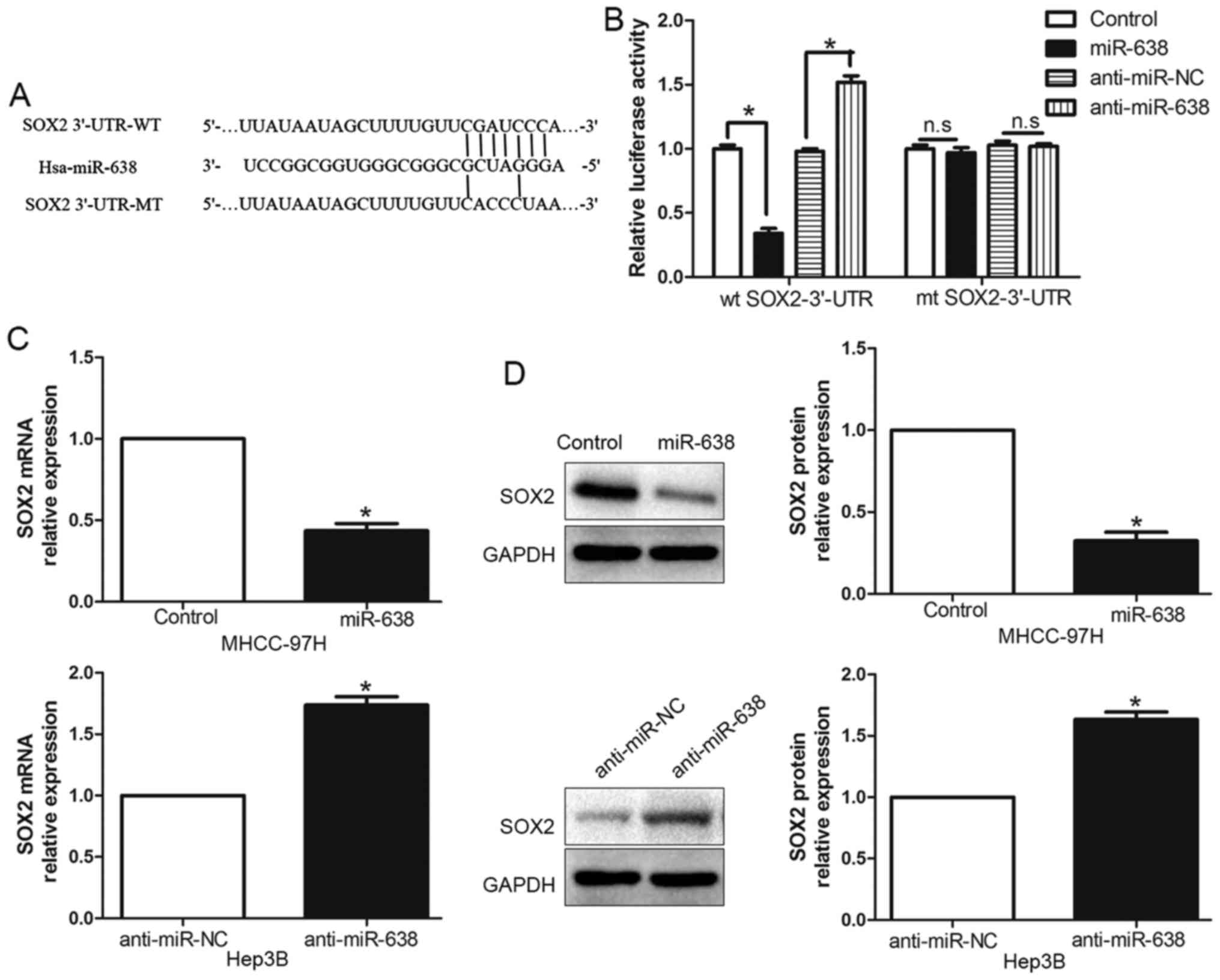
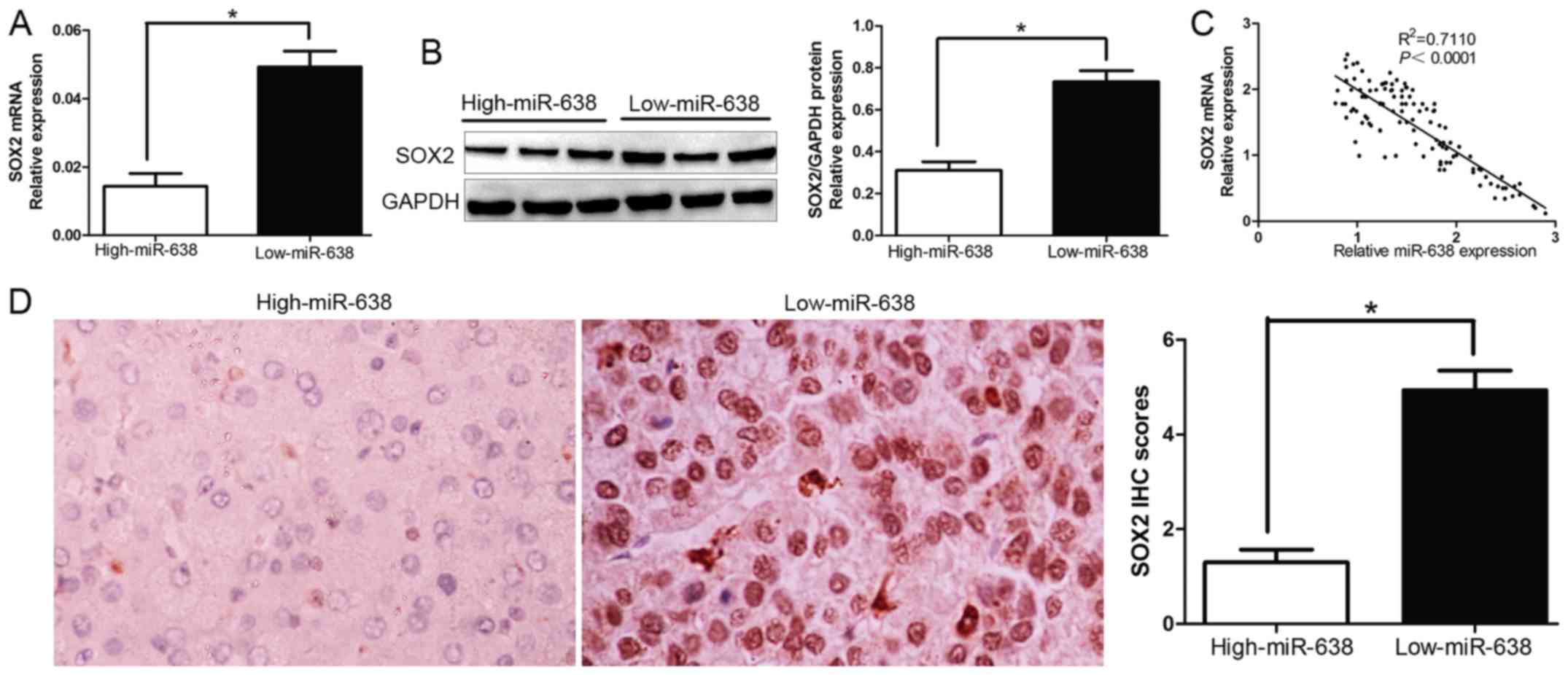
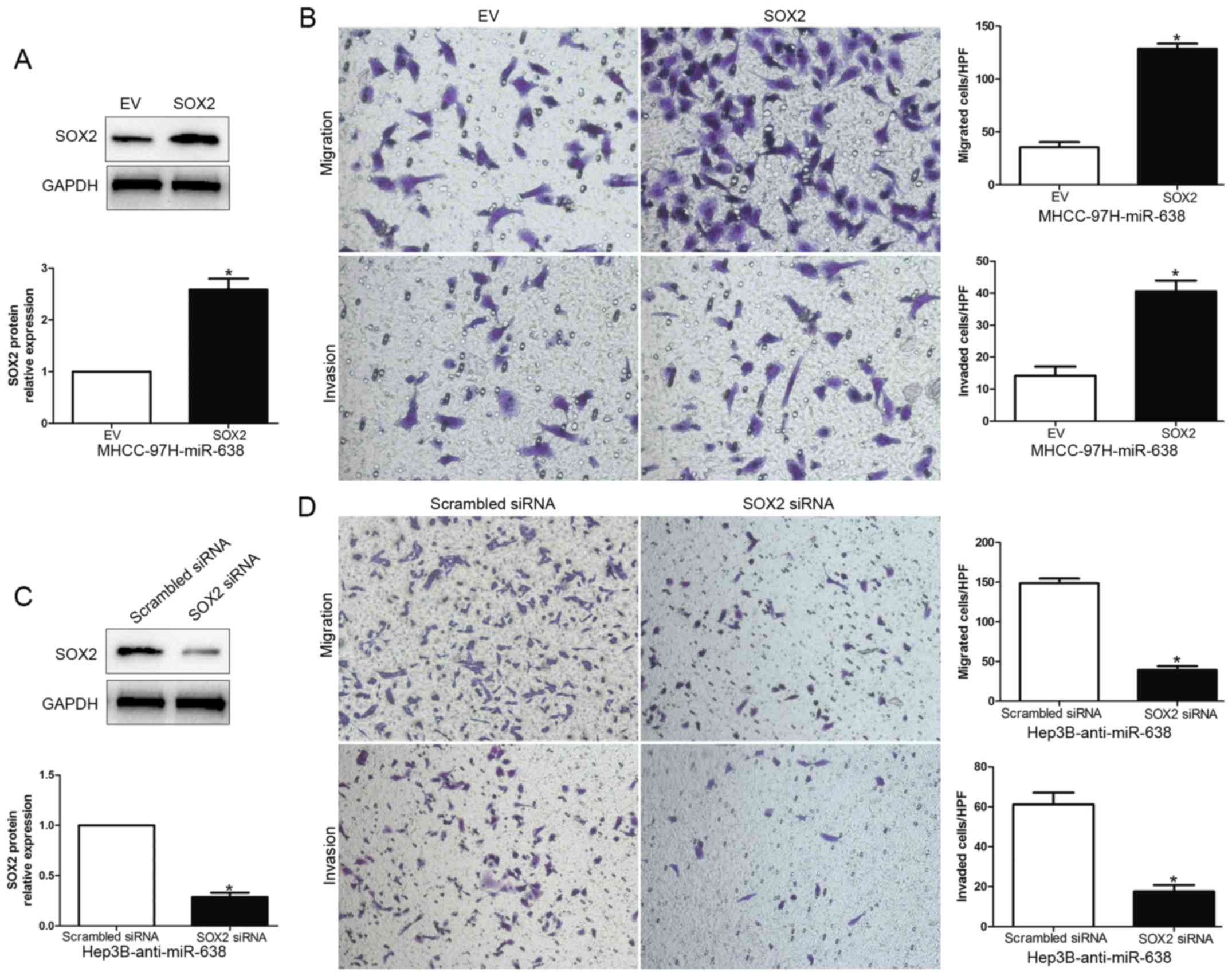
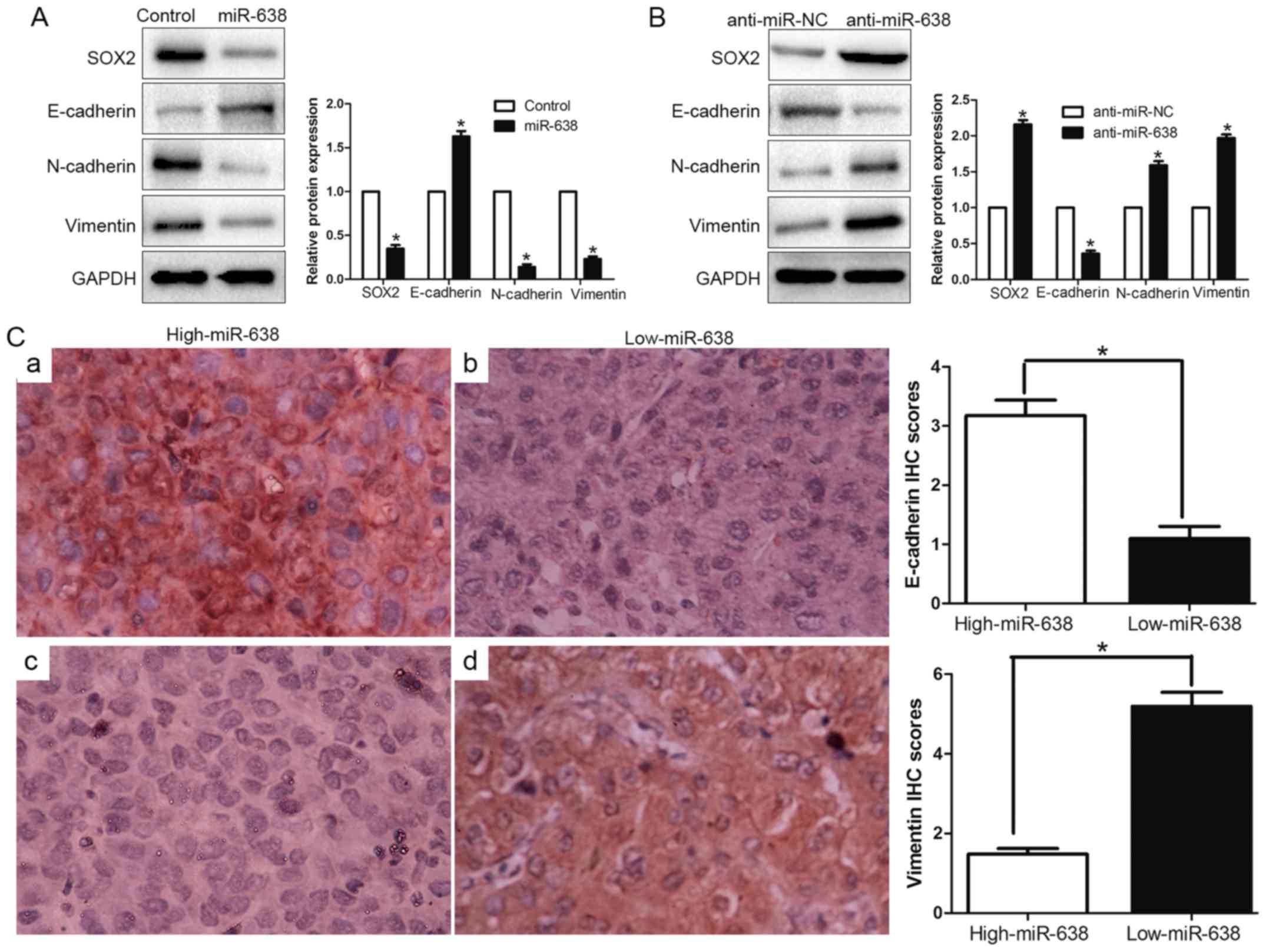
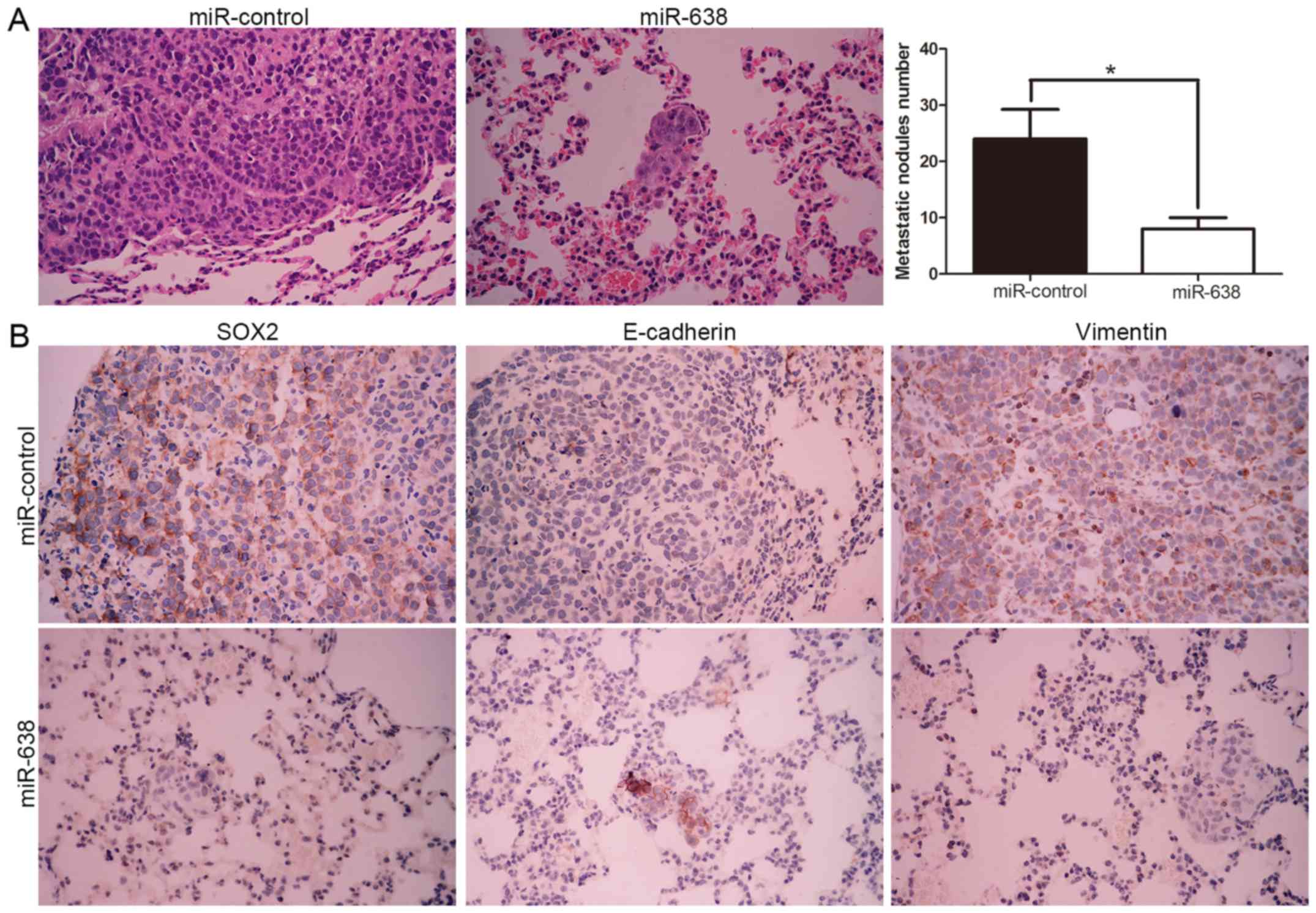
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosa A and Brivanlou AH: MicroRNAs in
early vertebrate development. Cell Cycle. 8:3513–3520. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu Z, Dou C, Yao B, Xu M, Ding L, Wang Y,
Jia Y, Li Q, Zhang H, Tu K, et al: Ftx non coding RNA-derived
miR-545 promotes cell proliferation by targeting RIG-I in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:25350–25365.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Dou C, Li C, Yang W, Yao Y
and Liu Q: MicroRNA-130b promotes cell aggressiveness by inhibiting
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20486–20499. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan X, Peng J, Fu Y, An S, Rezaei K,
Tabbara S, Teal CB, Man YG, Brem RF and Fu SW: miR-638 mediated
regulation of BRCA1 affects DNA repair and sensitivity to UV and
cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
16:4352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang F, Lou JF, Cao Y, Shi XH, Wang P, Xu
J, Xie EF, Xu T, Sun RH, Rao JY, et al: miR-638 is a new biomarker
for outcome prediction of non-small cell lung cancer patients
receiving chemotherapy. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Wang P and Chen Y:
Downregulation of miR-638 promotes invasion and proliferation by
regulating SOX2 and induces EMT in NSCLC. FEBS Lett. 588:2238–2245.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Li D, Liang Q, Liu S, Zuo X, Li L,
Sun X, Li W, Guo M and Huang Z: miR-638 regulates differentiation
and proliferation in leukemic cells by targeting cyclin-dependent
kinase 2. J Biol Chem. 290:1818–1828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, Georgas D, Hahn
SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Expression of
microRNAs in basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 167:847–855.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Fei B, Wang Q, Song M, Yin Y,
Zhang B, Ni S, Guo W, Bian Z, Quan C, et al: MicroRNA-638 inhibits
cell proliferation, invasion and regulates cell cycle by targeting
tetraspanin 1 in human colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
5:12083–12096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao LY, Yao Y, Han J, Yang J, Wang XF,
Tong DD, Song TS, Huang C and Shao Y: miR-638 suppresses cell
proliferation in gastric cancer by targeting Sp2. Dig Dis Sci.
59:1743–1753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bhattacharya A, Schmitz U, Raatz Y,
Schönherr M, Kottek T, Schauer M, Franz S, Saalbach A, Anderegg U,
Wolkenhauer O, et al: miR-638 promotes melanoma metastasis and
protects melanoma cells from apoptosis and autophagy. Oncotarget.
6:2966–2980. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li P, Liu Y, Yi B, Wang G, You X, Zhao X,
Summer R, Qin Y and Sun J: MicroRNA-638 is highly expressed in
human vascular smooth muscle cells and inhibits PDGF-BB-induced
cell proliferation and migration through targeting orphan nuclear
receptor NOR1. Cardiovasc Res. 99:185–193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng J, Chen Y, Zhao P, Liu X, Dong J, Li
J, Huang C, Wu R and Lv Y: Downregulation of miRNA-638 promotes
angiogenesis and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting
VEGF. Oncotarget. 7:30702–30711. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hlubek F, Berx
G, Eger A, Merkel S, Jung A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: A
transient, EMT-linked loss of basement membranes indicates
metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 131:830–840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye J, Wu D, Shen J, Wu P, Ni C, Chen J,
Zhao J, Zhang T, Wang X and Huang J: Enrichment of colorectal
cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
CDH1 knockdown. Mol Med Rep. 6:507–512. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma K, Pan X, Fan P, He Y, Gu J, Wang W,
Zhang T, Li Z and Luo X: Loss of miR-638 in vitro promotes cell
invasion and a mesenchymal-like transition by influencing SOX2
expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1182014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127:(Suppl 1). S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang J, Bian Z, Zhou J, Song M, Liu Z,
Feng Y, Zhe L, Zhang B, Yin Y and Huang Z: MicroRNA-638 inhibits
cell proliferation by targeting phospholipase D1 in human gastric
carcinoma. Protein Cell. 6:680–688. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang P, Qiu J, Li B, Hong J, Lu C, Wang
L, Wang J, Hu Y, Jia W and Yuan Y: Role of Sox2 and Oct4 in
predicting survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after
hepatectomy. Clin Biochem. 44:582–589. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun C, Sun L, Li Y, Kang X, Zhang S and
Liu Y: Sox2 expression predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients and it promotes liver cancer cell invasion by
activating Slug. Med Oncol. 30:5032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao X, Sun B, Sun D, Liu T, Che N, Gu Q,
Dong X, Li R, Liu Y and Li J: Slug promotes hepatocellular cancer
cell progression by increasing sox2 and nanog expression. Oncol
Rep. 33:149–156. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wen W, Han T, Chen C, Huang L, Sun W, Wang
X, Chen SZ, Xiang DM, Tang L, Cao D, et al: Cyclin G1 expands liver
tumor-initiating cells by Sox2 induction via Akt/mTOR signaling.
Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1796–1804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao C, Li Y, Zhang M, Yang Y and Chang L:
miR-126 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells partially by targeting Sox2. Hum
Cell. 28:91–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Velpula KK, Dasari VR, Tsung AJ, Dinh DH
and Rao JS: Cord blood stem cells revert glioma stem cell EMT by
down regulating transcriptional activation of Sox2 and Twist1.
Oncotarget. 2:1028–1042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wuebben EL, Wilder PJ, Cox JL, Grunkemeyer
JA, Caffrey T, Hollingsworth MA and Rizzino A: SOX2 functions as a
molecular rheostat to control the growth, tumorigenicity and drug
responses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget.
7:34890–34906. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Xu Y, Chen Y, Chen S, Jia X, Sun T,
Liu Y, Li X, Xiang R and Li N: SOX2 promotes tumor metastasis by
stimulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via regulation of
WNT/β-catenin signal network. Cancer Lett. 336:379–389. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|