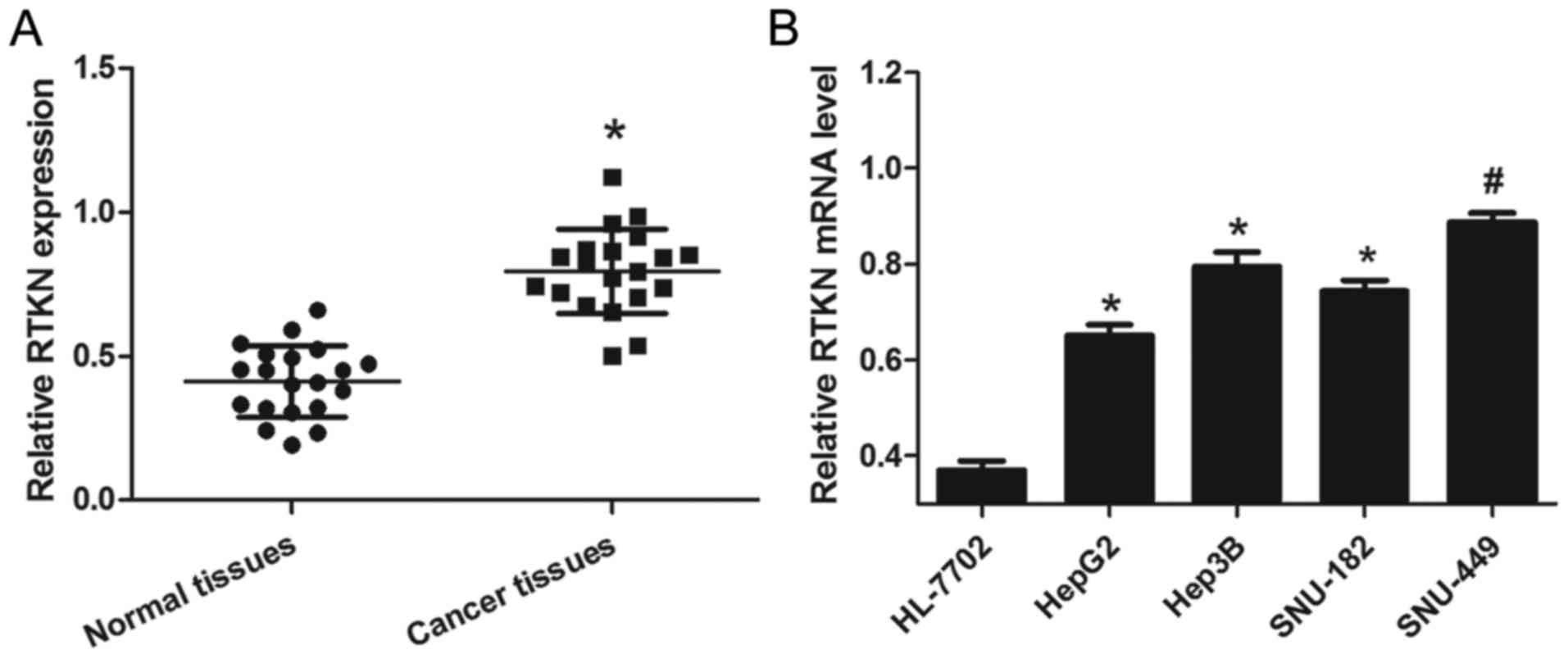
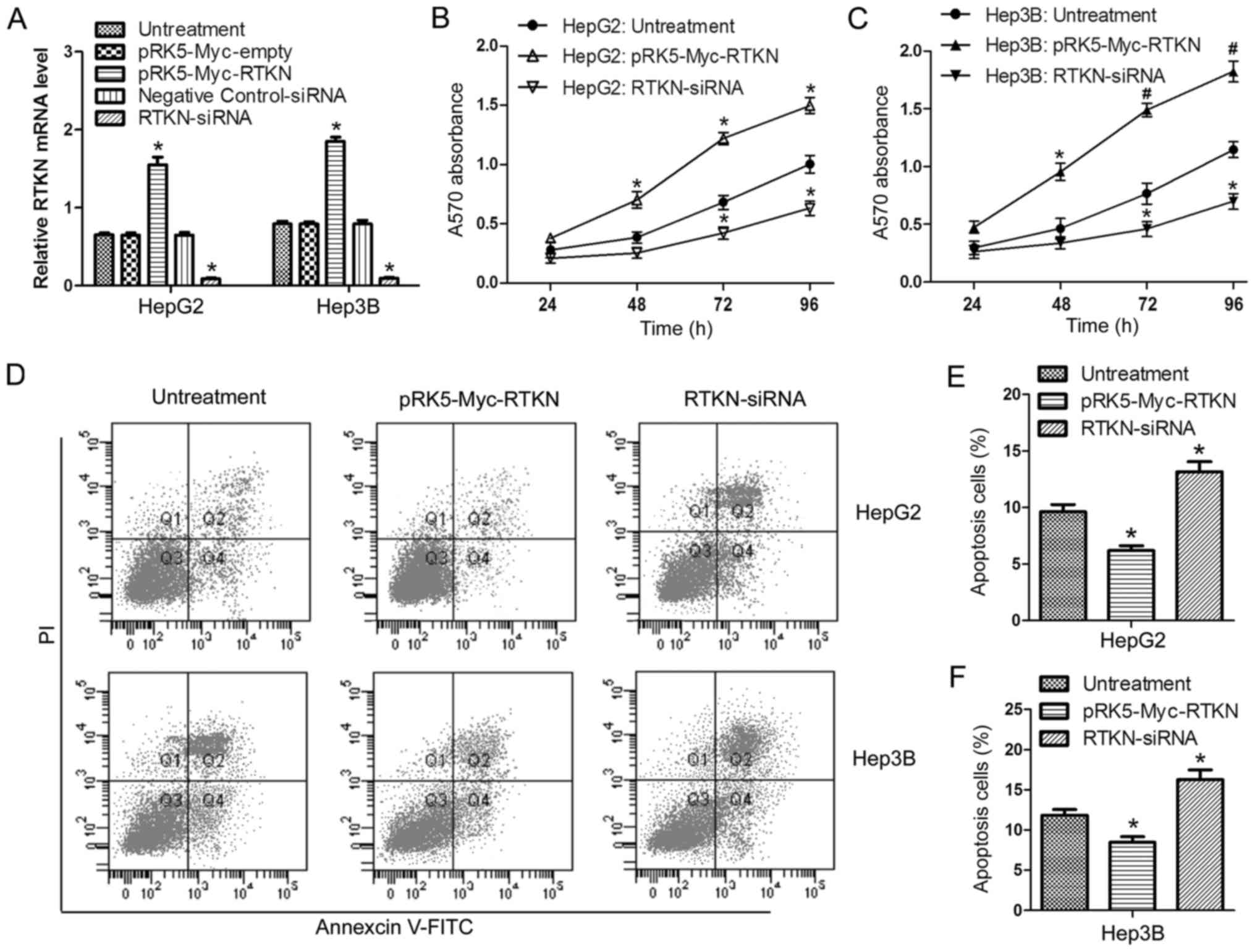
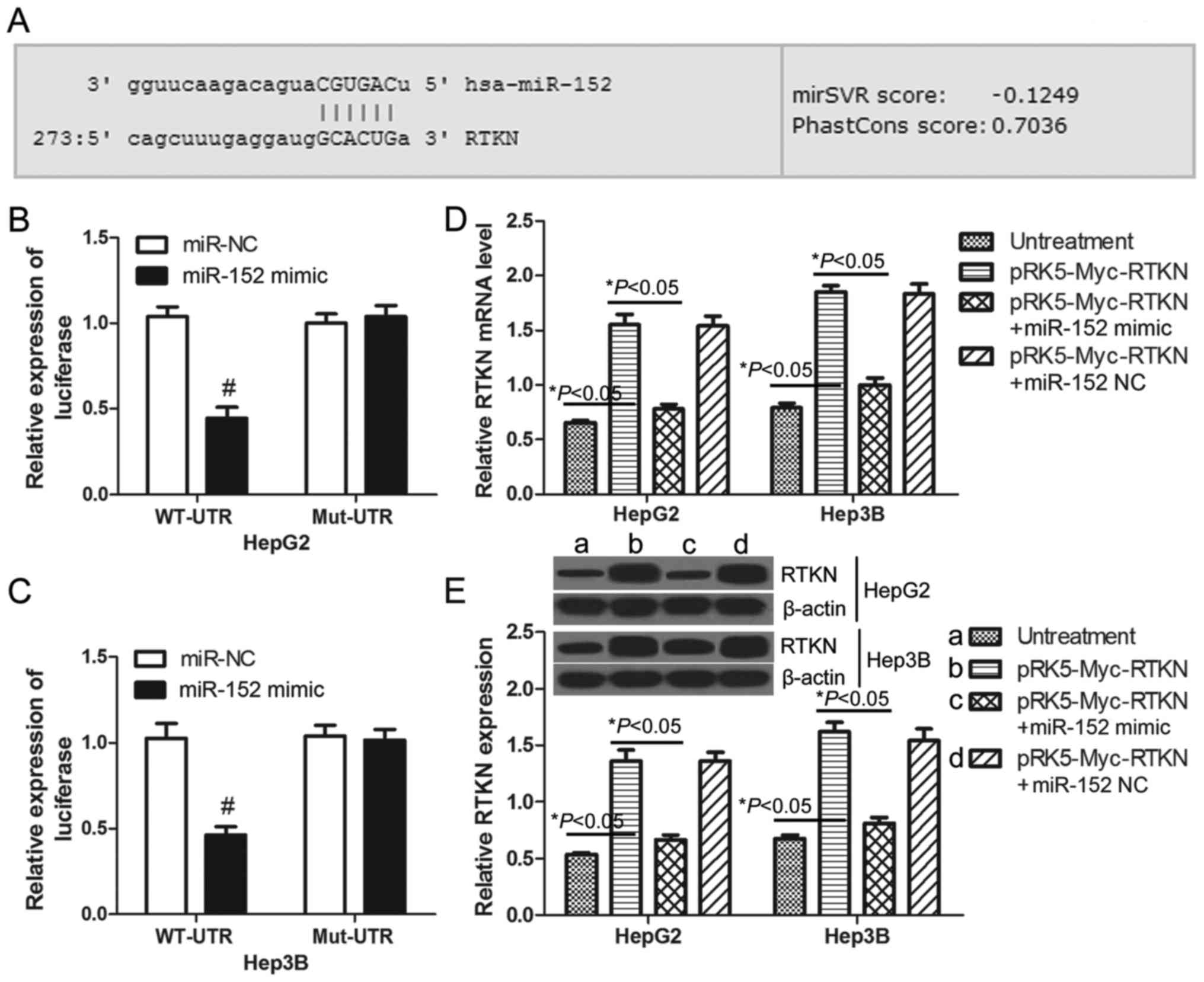
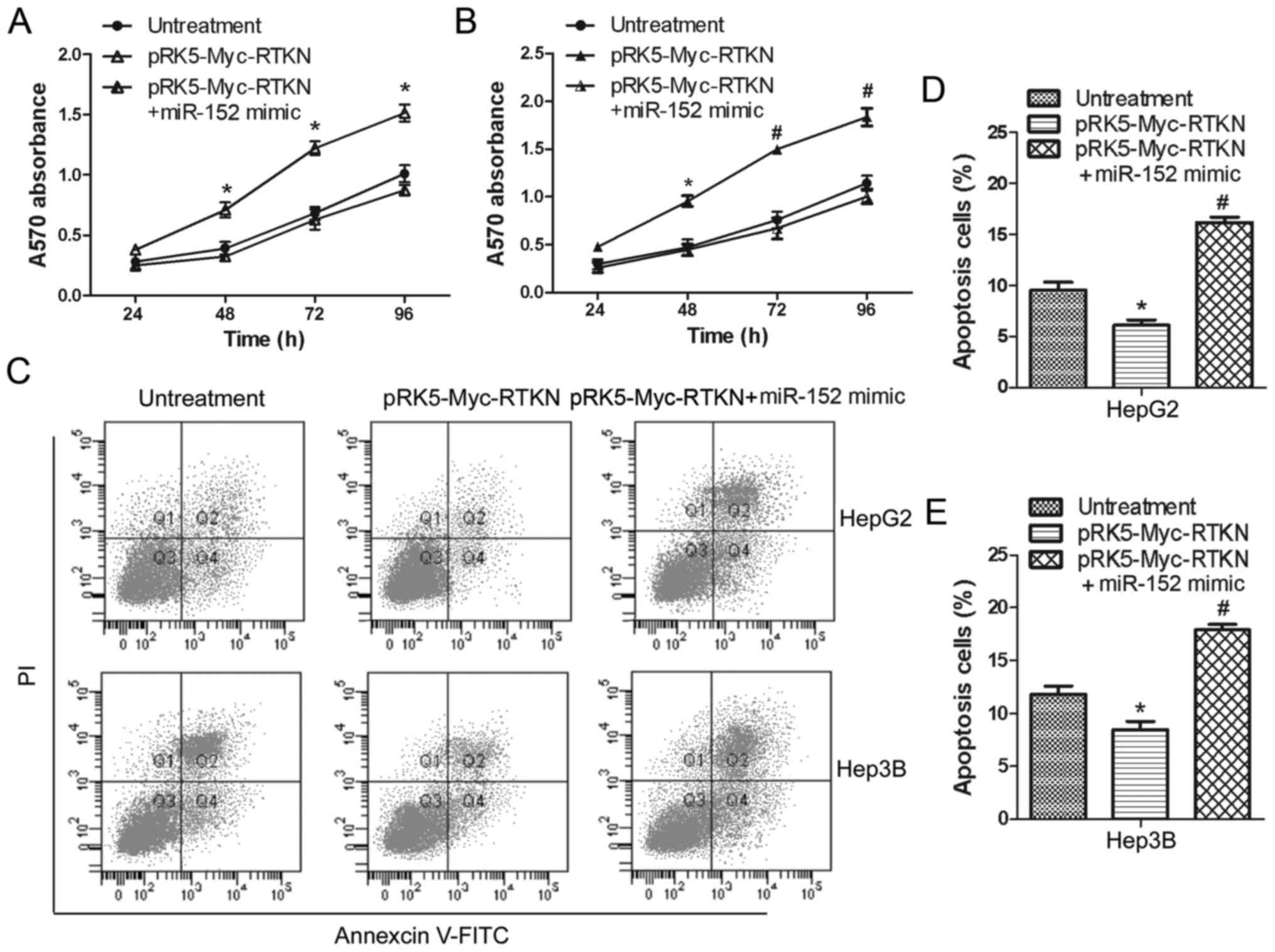
|
1
|
Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M,
Nicolosi D, Raiti F, Travali S, Spandidos DA and Libra M: The tumor
microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Int J Oncol.
40:1733–1747. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yuen MF, Hou JL and Chutaputti A: Asia
Pacific Working Party on Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma:
Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:346–353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pang RW, Joh JW, Johnson PJ, Monden M,
Pawlik TM and Poon RT: Biology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann
Surg Oncol. 15:962–971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reid T, Furuyashiki T, Ishizaki T,
Watanabe G, Watanabe N, Fujisawa K, Morii N, Madaule P and Narumiya
S: Rhotekin, a new putative target for Rho bearing homology to a
serine/threonine kinase, PKN, and rhophilin in the rho-binding
domain. J Biol Chem. 271:13556–13560. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ren XD, Kiosses WB and Schwartz MA:
Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion
and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 18:578–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu C-A, Wang M-J, Chi C-W, Wu C-W and
Chen J-Y: Overexpression of rho effector rhotekin confers increased
survival in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Biomed Sci. 11:661–670. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C-A, Wang M-J, Chi C-W, Wu C-W and
Chen J-Y: Rho/Rhotekin-mediated NF-kappaB activation confers
resistance to apoptosis. Oncogene. 23:8731–8742. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ying-Tao Z, Yi-Ping G, Lu-Sheng S and
Yi-Li W: Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins
between metastatic and non-metastatic human colorectal carcinoma
cell lines. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:725–732. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan J, Ma L-J, Xia S-J, Yu L, Fu Q, Wu CQ,
Huang XH, Jiang JM and Tang XD: Association between clinical
characteristics and expression abundance of RTKN gene in human
bladder carcinoma tissues from Chinese patients. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 131:157–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mallory AC and Vaucheret H: MicroRNAs:
Something important between the genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol.
7:120–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H-H, Wang X-J, Li G-X, Yang E and
Yang N-M: Detection of let-7a microRNA by real-time PCR in gastric
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 13:2883–2888. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Catto JW, Alcaraz A, Bjartell AS, De Vere
White R, Evans CP, Fussel S, Hamdy FC, Kallioniemi O, Mengual L,
Schlomm T, et al: MicroRNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer:
A systematic review. Eur Urol. 59:671–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Calin GA,
Fassan M, Bassi P, Sevignani C, Byrne D, Negrini M, Pagano F, et
al: Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol.
25:387–392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I,
Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G and Voros D: Expression of
microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c,
miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic
significance. Mol Carcinog. 52:297–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sato F, Hatano E, Kitamura K, Myomoto A,
Fujiwara T, Takizawa S, Tsuchiya S, Tsujimoto G, Uemoto S and
Shimizu K: MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan Criteria.
PLoS One. 6:e164352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Zhao F, Wang Z-N, Song YX, Chang
H, Chiang Y and Xu HM: Altered expression of miR-152 and miR-148a
in ovarian cancer is related to cell proliferation. Oncol Rep.
27:447–454. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Song Y, Wang Z, Yue Z, Xu H, Xing
C and Liu Z: Altered expression of MiR-148a and MiR-152 in
gastrointestinal cancers and its clinical significance. J
Gastrointest Surg. 14:1170–1179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, Li Q, He J, Jing Y,
Qi YT, Xu Q, Li W, Lu B, et al: A regulatory circuit of
miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation and tumor
angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:3–13.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu C, Li J, Ding Q, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao
L, Cai H, Li P, Cao Q, Ju X, et al: miR-152 controls migration and
invasive potential by targeting TGFα in prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 73:1082–1089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma J, Yao Y, Wang P, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li Z,
Li Z and Xue Y: MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in
glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4. Cancer
Lett. 355:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Woo H-H, László CF, Greco S and Chambers
SK: Regulation of colony stimulating factor-1 expression and
ovarian cancer cell behavior in vitro by miR-128 and miR-152. Mol
Cancer. 11:582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Song Y-X and Wang Z-N: The
microRNA-148/152 family: Multi-faceted players. Mol Cancer.
12:432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dang Y-W, Zeng J, He R-Q, Rong M-H, Luo
D-Z and Chen G: Effects of miR-152 on cell growth inhibition,
motility suppression and apoptosis induction in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4969–4976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ito H, Iwamoto I, Morishita R, Nozawa Y,
Narumiya S, Asano T and Nagata K: Possible role of Rho/Rhotekin
signaling in mammalian septin organization. Oncogene. 24:7064–7072.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai SD, Chen JS, Xi ZW, Zhang LJ, Niu ML
and Gao ZY: MicroRNA144 inhibits migration and proliferation in
rectal cancer by downregulating ROCK1. Mol Med Rep. 12:7396–7402.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li Z-W:
NF-kappaB in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:301–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qu GQ, Lu YM, Liu YF, Liu Y, Chen WX, Liao
XH and Kong WM: Effect of RTKN on progression and metastasis of
colon cancer in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:117–123. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oxford G and Theodorescu D: The role of
Ras superfamily proteins in bladder cancer progression. J Urol.
170:1987–1993. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|