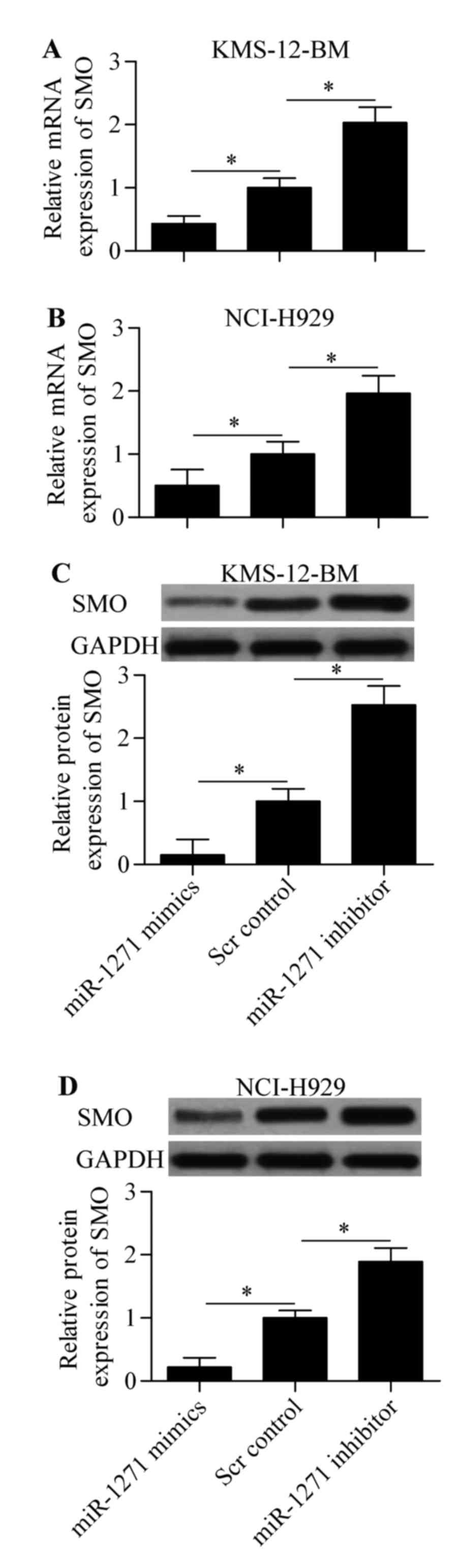
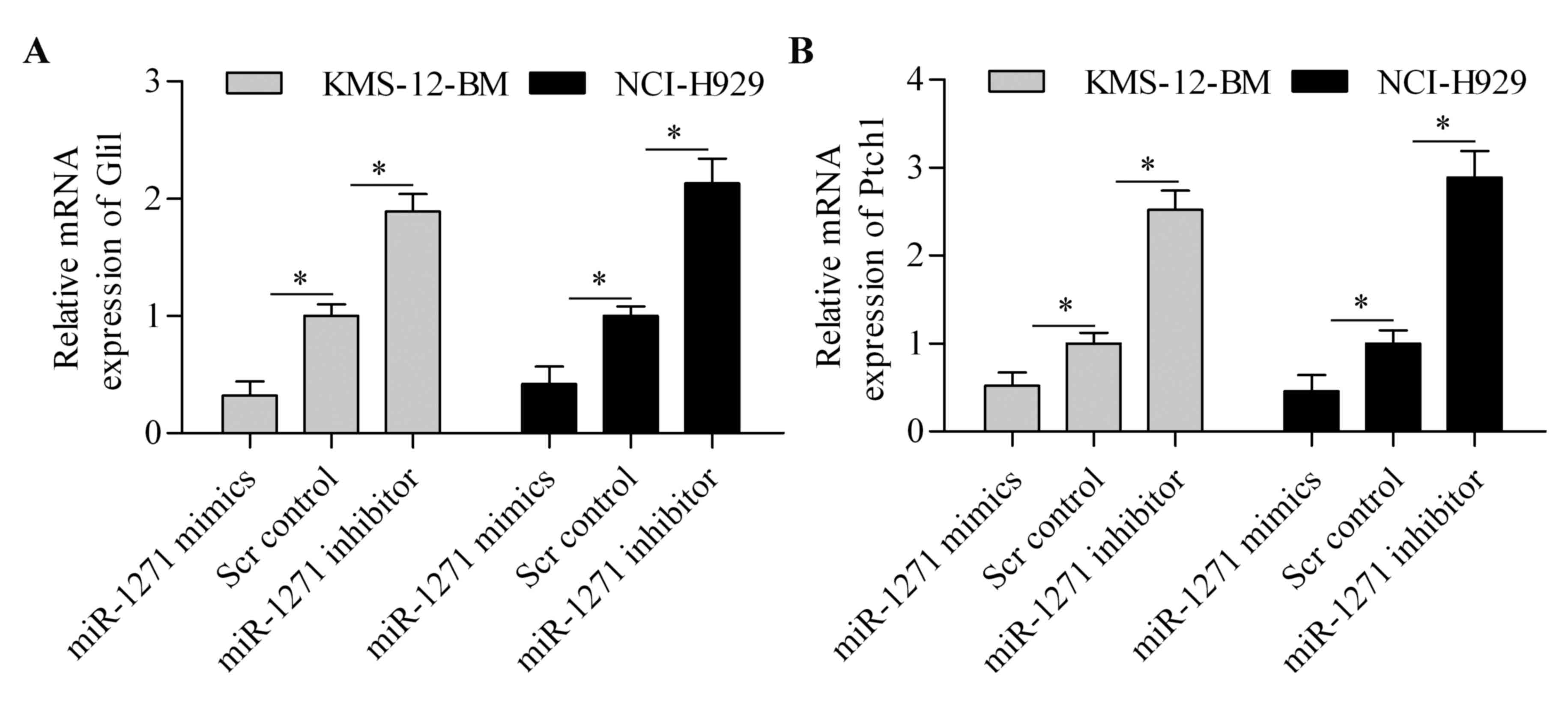
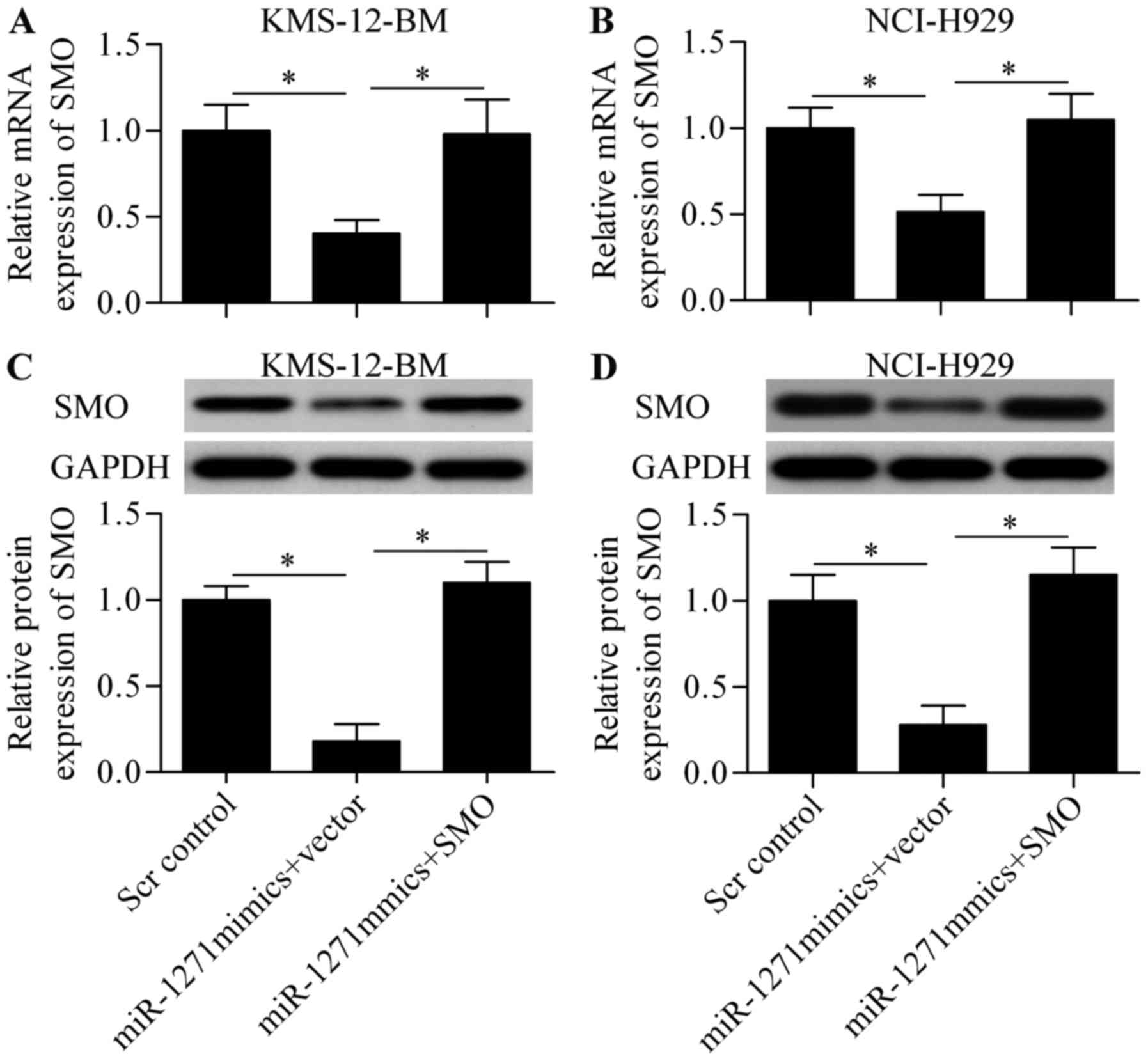
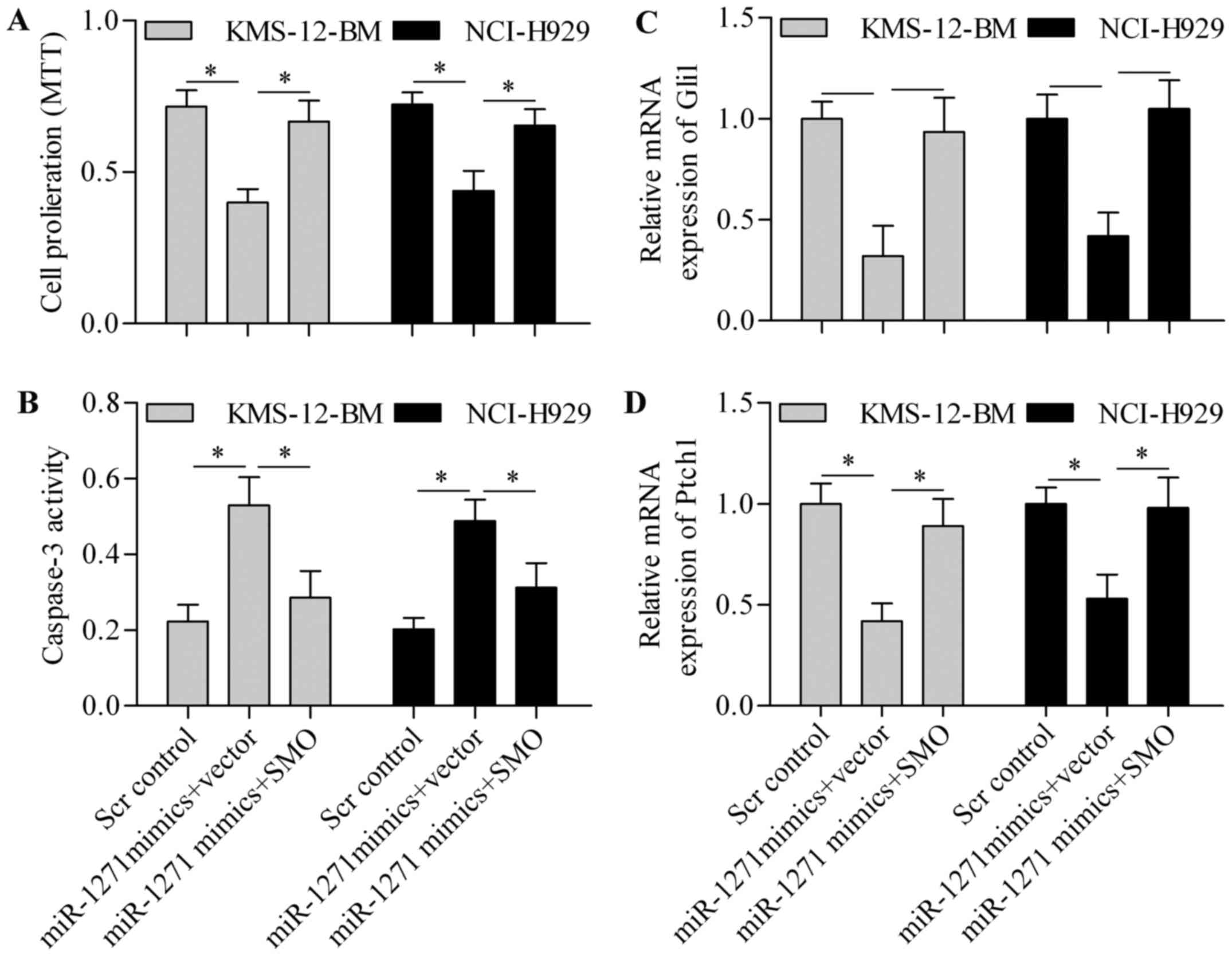
|
1
|
Hatzimichael E, Dasoula A, Benetatos L,
Syed N, Dranitsaris G, Crook T and Bourantas K: Study of specific
genetic and epigenetic variables in multiple myeloma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 51:2270–2274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kyle RA and Rajkumar SV: Multiple myeloma.
Blood. 111:2962–2972. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Agarwal A and Mahadevan D: Novel targeted
therapies and combinations for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 13:2–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rossi M, Tagliaferri P and Tassone P:
MicroRNAs in multiple myeloma and related bone disease. Ann Transl
Med. 3:3342015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Z, Zhang G, Yu W, Gao N and Peng J:
miR-186 inhibits cell proliferation in multiple myeloma by
repressing Jagged1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:692–697. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang B, Yin JJ and Zhan XR: MiR-301a
promotes cell proliferation by directly targeting TIMP2 in multiple
myeloma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:9168–9174. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu Y, Wu D, Wang J, Li Y, Chai X and Kang
Q: miR-320a regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in multiple
myeloma by targeting pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 3.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:1315–1320. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saha MN, Abdi J, Yang Y and Chang H:
MiRNA-29a as a tumor suppressor mediates PRIMA-1Met-induced
anti-myeloma activity by targeting c-Myc. Oncotarget. 7:7149–7160.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Li F, Saha MN, Abdi J, Qiu L and
Chang H: miR-137 and miR-197 induce apoptosis and suppress
tumorigenicity by targeting MCL-1 in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:2399–2411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Zhu D, Wang X, Brooks D,
Chen M, Chu ZB, Takada K, Ciccarelli B, Admin S, et al: miR-30-5p
functions as a tumor suppressor and novel therapeutic tool by
targeting the oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin/BCL9 pathway. Cancer Res.
74:1801–1813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Yan W, Bai Y, Xu H, Fu C, Zheng
W, Zhu Y and Ma J: Synthetic miR-145 mimic inhibits multiple
myeloma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 33:448–456.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seckinger A, Meißner T, Moreaux J, Benes
V, Hillengass J, Castoldi M, Zimmermann J, Ho AD, Jauch A,
Goldschmidt H, et al: miRNAs in multiple myeloma - a survival
relevant complex regulator of gene expression. Oncotarget.
6:39165–39183. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sedlaříková L, Bešše L, Novosadová S,
Kubaczková V, Radová L, Staník M, Krejčí M, Hájek R and Ševčíková
S: MicroRNAs in urine are not biomarkers of multiple myeloma. J
Negat Results Biomed. 14:162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Besse L, Sedlarikova L, Kryukov F,
Nekvindova J, Radova L, Slaby O, Kuglik P, Almasi M, Penka M,
Krejci M, et al: Circulating serum MicroRNA-130a as a novel
putative marker of extramedullary myeloma. PLoS One.
10:e01372942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hooper JE and Scott MP: Communicating with
Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:306–317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mann RK and Beachy PA: Novel lipid
modifications of secreted protein signals. Annu Rev Biochem.
73:891–923. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taipale J, Cooper MK, Maiti T and Beachy
PA: Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of
Smoothened. Nature. 418:892–897. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lum L and Beachy PA: The Hedgehog response
network: Sensors, switches, and routers. Science. 304:1755–1759.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS and Berman DM:
Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature.
432:324–331. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kinzler KW, Bigner SH, Bigner DD, Trent
JM, Law ML, OBrien SJ, Wong AJ and Vogelstein B: Identification of
an amplified, highly expressed gene in a human glioma. Science.
236:70–73. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee Y, Miller HL, Jensen P, Hernan R,
Connelly M, Wetmore C, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Curran T, Gilbertson
RJ, et al: A molecular fingerprint for medulloblastoma. Cancer Res.
63:5428–5437. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog target
genes: Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog
signaling activation. Curr Mol Med. 9:873–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suzman DL and Antonarakis ES: Clinical
implications of Hedgehog pathway signaling in prostate cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 7:1983–1993. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang L, Walter V, Hayes DN and Onaitis M:
Hedgehog-GLI signaling inhibition suppresses tumor growth in
squamous lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1566–1575. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Onishi H and Katano M: Hedgehog signaling
pathway as a new therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:2335–2342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lindemann RK: Stroma-initiated hedgehog
signaling takes center stage in B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res.
68:961–964. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tam M, Lin P, Hu P and Lennon PA:
Examining Hedgehog pathway genes GLI3, SHH, and PTCH1 and the p53
target GLIPR1/GLIPR1L1/GLIPR1L2 gene cluster using fluorescence in
situ hybridization uncovers GLIPR1/GLIPR1L1/GLIPR1L2 deletion in 9%
of patients with multiple myeloma. J Assoc Genet Technol.
36:111–114. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peacock CD, Wang Q, Gesell GS,
Corcoran-Schwartz IM, Jones E, Kim J, Devereux WL, Rhodes JT, Huff
CA, Beachy PA, et al: Hedgehog signaling maintains a tumor stem
cell compartment in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:4048–4053. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Xu J, He J, Zheng Y, Li H, Lu Y,
Qian J, Lin P, Weber DM, Yang J, et al: A critical role of
autocrine sonic hedgehog signaling in human CD138+
myeloma cell survival and drug resistance. Blood. 124:2061–2071.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
de la Puente P, Muz B, Azab F, Luderer M
and Azab AK: Molecularly targeted therapies in multiple myeloma.
Leukemia Res Treat. 2014:9765672014.
|
|
36
|
Agarwal JR, Wang Q, Tanno T, Rasheed Z,
Merchant A, Ghosh N, Borrello I, Huff CA, Parhami F and Matsui W:
Activation of liver X receptors inhibits hedgehog signaling,
clonogenic growth, and self-renewal in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer
Ther. 13:1873–1881. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu H, Wang H, Liu X and Yu T: miR-1271
inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by targeting ZEB1 and TWIST1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 472:346–352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Z, Niu X, Li C, Sheng S and Lu S:
Inhibition of the growth of non-small cell lung cancer by
miRNA-1271. Am J Transl Res. 7:1917–1924. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu X, Ma L, Rao Q, Mao Y, Xin Y, Xu H, Li
C and Wang X: MiR-1271 inhibits ovarian cancer growth by targeting
cyclin G1. Med Sci Monit. 21:3152–3158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiang XJ, Deng J, Liu YW, Wan LY, Feng M,
Chen J and Xiong JP: MiR-1271 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion
and EMT in gastric cancer by targeting FOXQ1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1382–1394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hönemann D, Chatterjee M, Savino R,
Bommert K, Burger R, Gramatzki M, Dörken B and Bargou RC: The IL-6
receptor antagonist SANT-7 overcomes bone marrow stromal
cell-mediated drug resistance of multiple myeloma cells. Int J
Cancer. 93:674–680. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M
and Lo HW: Targeting the sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway: Review
of smoothened and GLI inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 8:82016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chira P, Vareli K, Sainis I, Papandreou C
and Briasoulis E: Alterations of MicroRNAs in solid cancers and
their prognostic value. Cancers (Basel). 2:1328–1353. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Maurel M, Jalvy S, Ladeiro Y, Combe C,
Vachet L, Sagliocco F, Bioulac-Sage P, Pitard V, Jacquemin-Sablon
H, Zucman-Rossi J, et al: A functional screening identifies five
microRNAs controlling glypican-3: Role of miR-1271 down-regulation
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:195–204. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang M, Shan X, Zhou X, Qiu T, Zhu W, Ding
Y, Shu Y and Liu P: miR-1271 regulates cisplatin resistance of
human gastric cancer cell lines by targeting IGF1R, IRS1, mTOR, and
BCL2. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:884–891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kong D, Zhang G, Ma H and Jiang G:
miR-1271 inhibits OSCC cell growth and metastasis by targeting ALK.
Neoplasma. 62:559–566. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Y, Xu L and Jiang L: miR-1271
promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion
via targeting HOXA5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:714–719. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Blotta S, Jakubikova J, Calimeri T,
Roccaro AM, Amodio N, Azab AK, Foresta U, Mitsiades CS, Rossi M,
Todoerti K, et al: Canonical and noncanonical Hedgehog pathway in
the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Blood. 120:5002–5013. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sandhiya S, Melvin G, Kumar SS and Dkhar
SA: The dawn of hedgehog inhibitors: Vismodegib. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 4:4–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang XH, Chen JS, Wang Q, Chen XL, Wen L,
Chen LZ, Bi J, Zhang LJ, Su Q and Zeng WT: miR-338-3p suppresses
invasion of liver cancer cell by targeting smoothened. J Pathol.
225:463–472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sun K, Deng HJ, Lei ST, Dong JQ and Li GX:
miRNA-338-3p suppresses cell growth of human colorectal carcinoma
by targeting smoothened. World J Gastroenterol. 19:2197–2207. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xue Q, Sun K, Deng HJ, Lei ST, Dong JQ and
Li GX: MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits colorectal carcinoma cell invasion
and migration by targeting smoothened. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 44:13–21.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Hajifathali A,
Tavirani MR, Zomorod MS, Ghadiani M and Soleimani M: Targeting of
the signal transducer Smo links microRNA-326 to the oncogenic
Hedgehog pathway in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells. Int
J Cancer. 133:579–589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Du W, Liu X, Chen L, Dou Z, Lei X, Chang
L, Cai J, Cui Y, Yang D, Sun Y, et al: Targeting the SMO oncogene
by miR-326 inhibits glioma biological behaviors and stemness. Neuro
Oncol. 17:243–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|