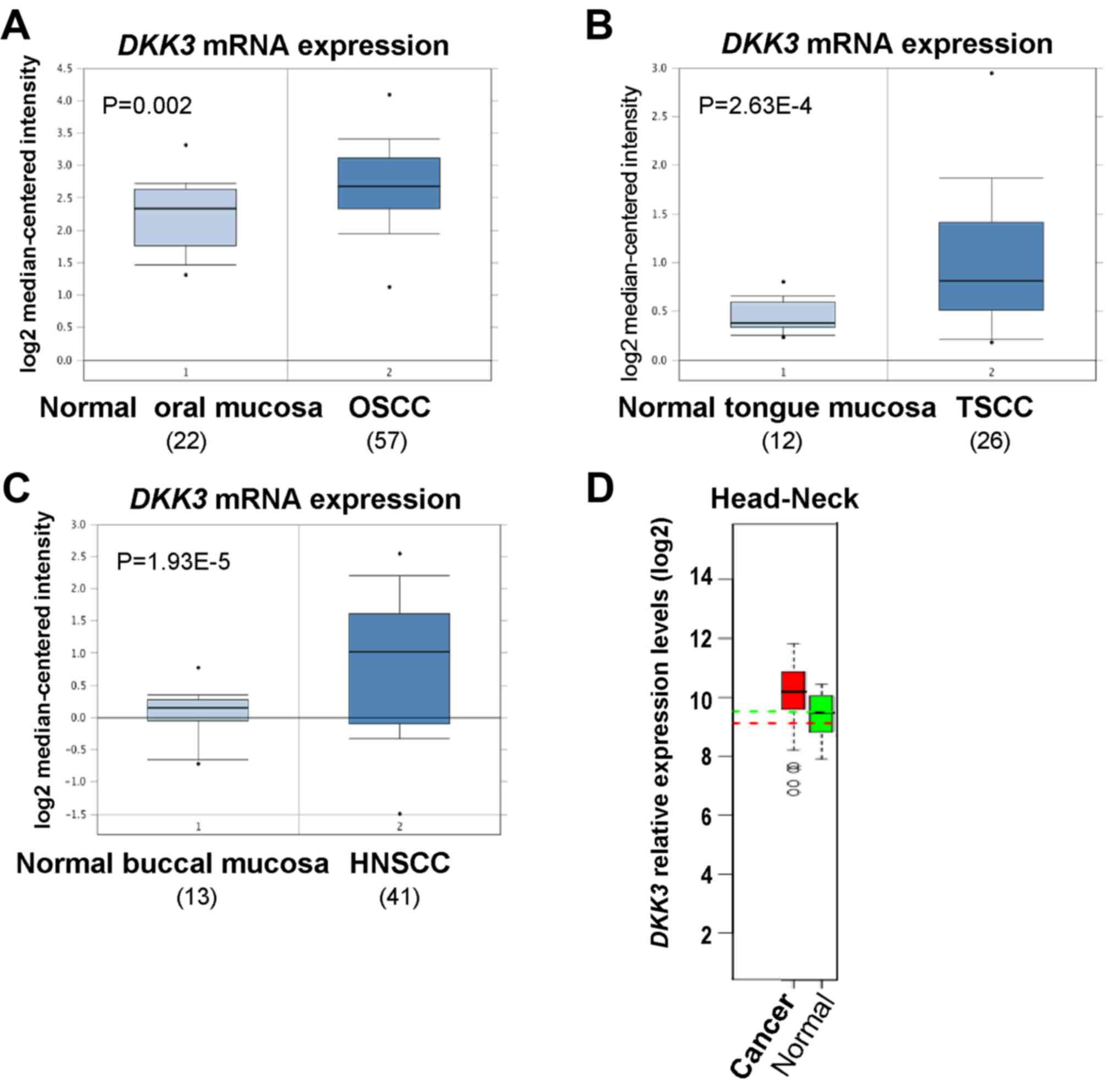
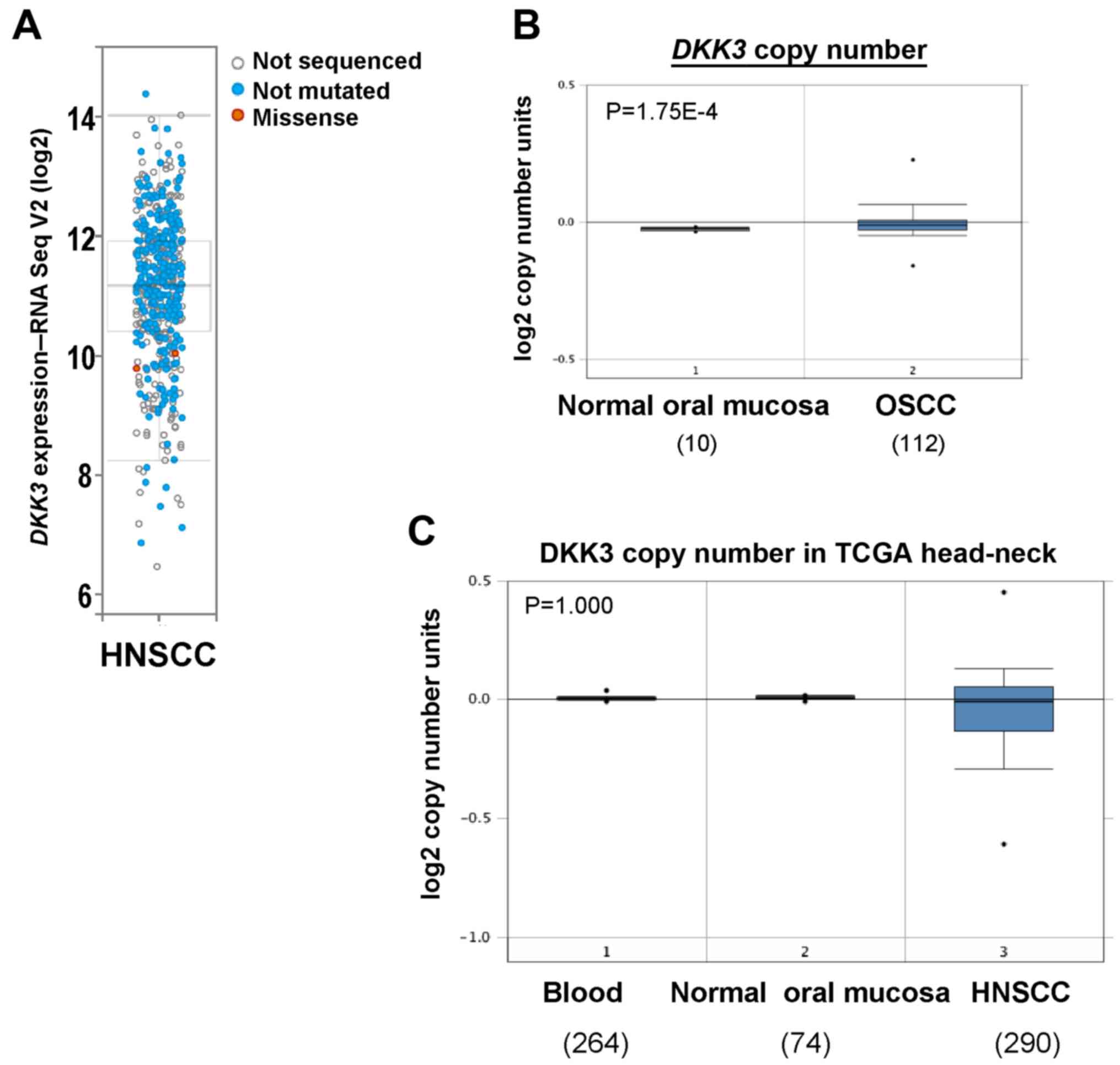
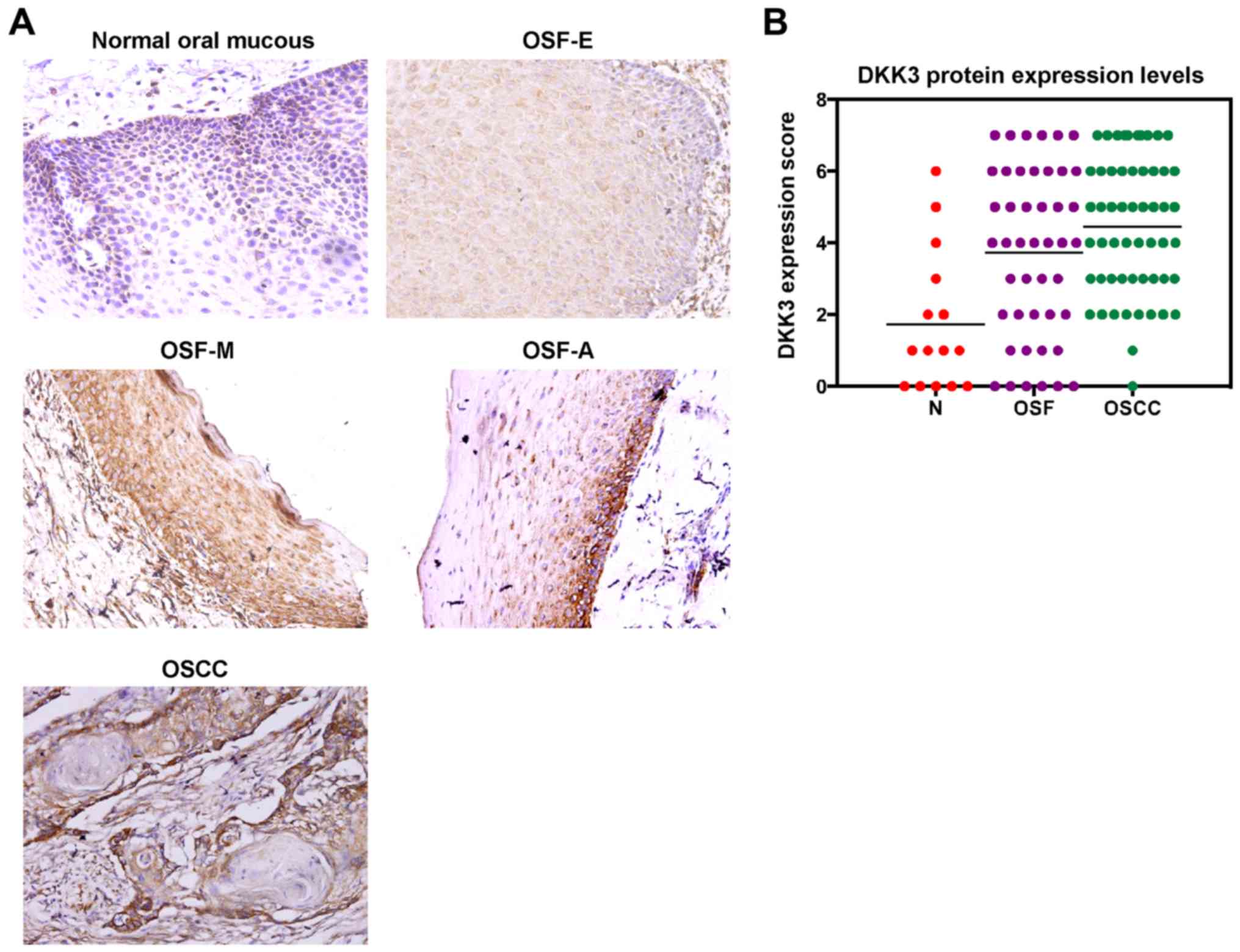
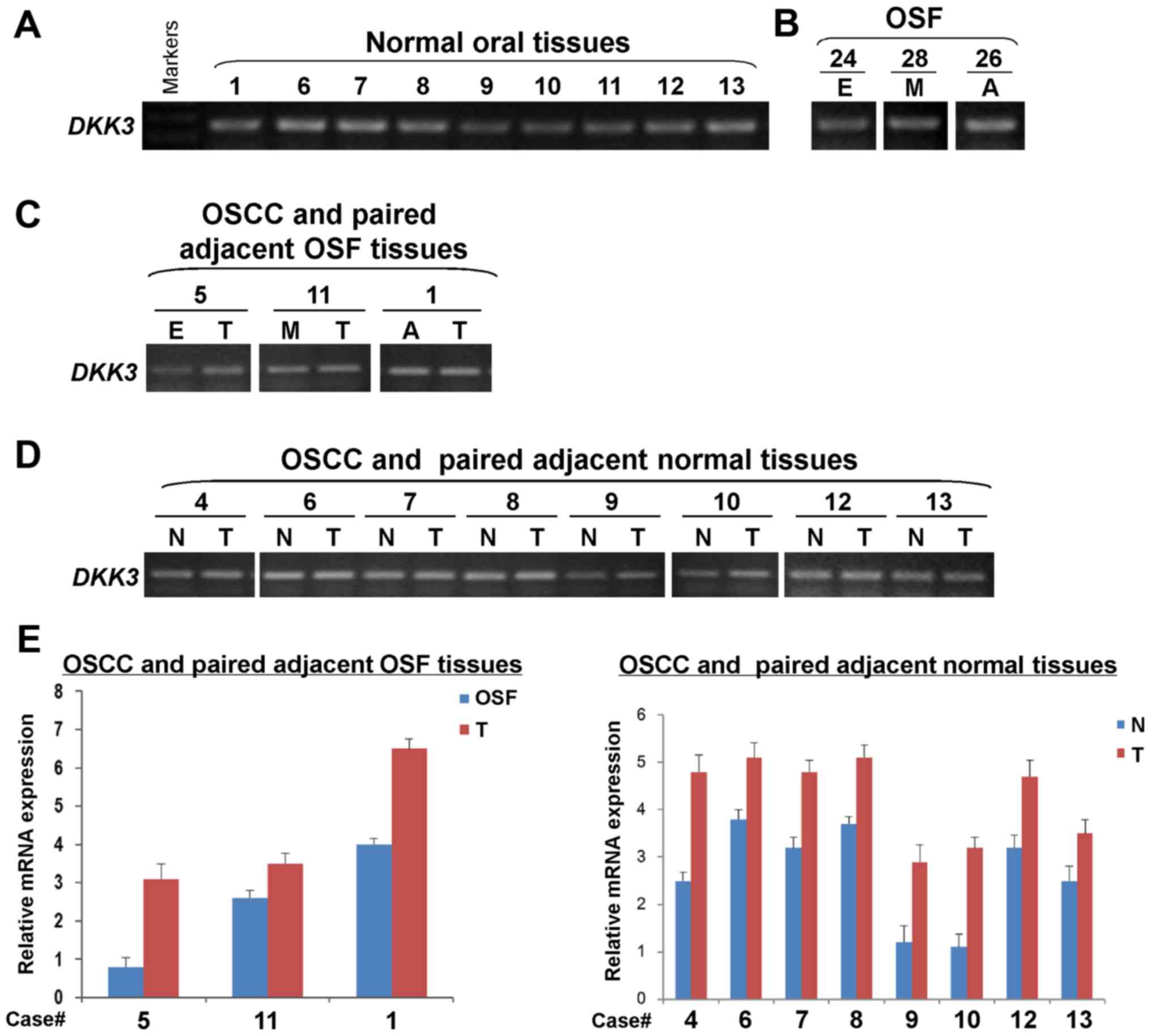
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH and Leemans
CR: Head and neck cancer: Molecular carcinogenesis. Ann Oncol.
16:(Suppl 2). ii249–ii250. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Choi S and Myers JN: Molecular
pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for
therapy. J Dent Res. 87:14–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pindborg JJ, Murti PR, Bhonsle RB, Gupta
PC, Daftary DK and Mehta FS: Oral submucous fibrosis as a
precancerous condition. Scand J Dent Res. 92:224–229.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tilakaratne WM, Klinikowski MF, Saku T,
Peters TJ and Warnakulasuriya S: Oral submucous fibrosis: Review on
aetiology and pathogenesis. Oral Oncol. 42:561–568. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wollina U, Verma SB, Ali FM and Patil K:
Oral submucous fibrosis: An update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol.
8:193–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling in cancer. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:42012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Veeck J and Dahl E: Targeting the Wnt
pathway in cancer: The emerging role of Dickkopf-3. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825:18–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Niehrs C: Function and biological roles of
the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene. 25:7469–7481.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katase N, Gunduz M, Beder L, Gunduz E,
Lefeuvre M, Hatipoglu OF, Borkosky SS, Tamamura R, Tominaga S,
Yamanaka N, et al: Deletion at Dickkopf (dkk)-3 locus (11p15.2) is
related with lower lymph node metastasis and better prognosis in
head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol Res. 17:273–282.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pannone G, Bufo P, Santoro A, Franco R,
Aquino G, Longo F, Botti G, Serpico R, Cafarelli B, Abbruzzese A,
et al: WNT pathway in oral cancer: Epigenetic inactivation of
WNT-inhibitors. Oncol Rep. 24:1035–1041. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujii M, Katase N, Lefeuvre M, Gunduz M,
Buery RR, Tamamura R, Tsujigiwa H and Nagatsuka H: Dickkopf (Dkk)-3
and β-catenin expressions increased in the transition from normal
oral mucosal to oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Histol.
42:499–504. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kataoka K, Du G, Maehara N, Murata H,
Sakaguchi M and Huh N: Expression pattern of REIC/Dkk-3 in mouse
squamous epithelia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 37:428–431. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katase N, Lefeuvre M, Tsujigiwa H, Fujii
M, Ito S, Tamamura R, Buery RR, Gunduz M and Nagatsuka H: Knockdown
of Dkk-3 decreases cancer cell migration and invasion independently
of the Wnt pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived cells.
Oncol Rep. 29:1349–1355. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta PC, Sinor PN, Bhonsle RB, Pawar VS
and Mehta HC: Oral submucous fibrosis in India: A new epidemic?
Natl Med J India. 11:113–116. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou S, Chen L, Mashrah M, Zhu Y, He Z, Hu
Y, Xiang T, Yao Z, Guo F and Zhang C: Expression and promoter
methylation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in the development of oral
submucous fibrosis. Oncol Rep. 34:2636–2642. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou S, Chen L, Mashrah M, Zhu Y, Liu J,
Yang X, He Z, Wang L, Xiang T, Yao Z, et al: Deregulation of
secreted frizzled-related proteins is associated with aberrant
β-catenin activation in the carcinogenesis of oral submucous
fibrosis. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2923–2931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng CH, Liao CT, Peng SC, Chen YJ, Cheng
AJ, Juang JL, Tsai CY, Chen TC, Chuang YJ, Tang CY, et al: A novel
molecular signature identified by systems genetics approach
predicts prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
6:e234522011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye H, Yu T, Temam S, Ziober BL, Wang J,
Schwartz JL, Mao L, Wong DT and Zhou X: Transcriptomic dissection
of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Genomics. 9:692008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ginos MA, Page GP, Michalowicz BS, Patel
KJ, Volker SE, Pambuccian SE, Ondrey FG, Adams GL and Gaffney PM:
Identification of a gene expression signature associated with
recurrent disease in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Cancer Res. 64:55–63. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Holmen SL, Robertson SA, Zylstra CR and
Williams BO: Wnt-independent activation of beta-catenin mediated by
a Dkk1-Fz5 fusion protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 328:533–539.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujii Y, Hoshino T and Kumon H: Molecular
simulation analysis of the structure complex of C2 domains of DKK
family members and β-propeller domains of LRP5/6: Explaining why
DKK3 does not bind to LRP5/6. Acta Med Okayama. 68:63–78.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yin DT, Wu W, Li M, Wang QE, Li H, Wang Y,
Tang Y and Xing M: DKK3 is a potential tumor suppressor gene in
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:507–514. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jung IL, Kang HJ, Kim KC and Kim IG:
Knockdown of the Dickkopf 3 gene induces apoptosis in a lung
adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 26:33–38. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kobayashi K, Ouchida M, Tsuji T, Hanafusa
H, Miyazaki M, Namba M, Shimizu N and Shimizu K: Reduced expression
of the REIC/Dkk-3 gene by promoter-hypermethylation in human tumor
cells. Gene. 282:151–158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sato H, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Nojima M,
Maruyama R, Sasaki S, Takagi H, Sogabe Y, Sasaki Y, Idogawa M, et
al: Frequent epigenetic inactivation of DICKKOPF family genes in
human gastrointestinal tumors. Carcinogenesis. 28:2459–2466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang L, He H, Lv R, Zhang M, Huang H, An
Z and Li S: Preliminary mechanism on the methylation modification
of Dkk-1 and Dkk-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
36:1245–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Veeck J, Bektas N, Hartmann A, Kristiansen
G, Heindrichs U, Knüchel R and Dahl E: Wnt signalling in human
breast cancer: Expression of the putative Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-3
(DKK3) is frequently suppressed by promoter hypermethylation in
mammary tumours. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R822008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiang T, Li L, Yin X, Zhong L, Peng W, Qiu
Z, Ren G and Tao Q: Epigenetic silencing of the WNT antagonist
Dickkopf 3 disrupts normal Wnt/β-catenin signalling and apoptosis
regulation in breast cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 17:1236–1246.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
You A, Fokas E, Wang LF, He H, Kleb B,
Niederacher D, Engenhart-Cabillic R and An HX: Expression of the
Wnt antagonist DKK3 is frequently suppressed in sporadic epithelial
ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:621–627. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee EJ, Jo M, Rho SB, Park K, Yoo YN, Park
J, Chae M, Zhang W and Lee JH: Dkk3, downregulated in cervical
cancer, functions as a negative regulator of beta-catenin. Int J
Cancer. 124:287–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kurose K, Sakaguchi M, Nasu Y, Ebara S,
Kaku H, Kariyama R, Arao Y, Miyazaki M, Tsushima T, Namba M, et al:
Decreased expression of REIC/Dkk-3 in human renal clear cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 171:1314–1318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Majid S, Chen Y, Zaman
MS, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R: Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-3
(Dkk-3) induces apoptosis in human renal cell carcinoma. Mol
Carcinog. 50:449–457. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Valencia A, Román-Gómez J, Cervera J, Such
E, Barragán E, Bolufer P, Moscardó F, Sanz GF and Sanz MA: Wnt
signaling pathway is epigenetically regulated by methylation of Wnt
antagonists in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 23:1658–1666.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mizobuchi Y, Matsuzaki K, Kuwayama K,
Kitazato K, Mure H, Kageji T and Nagahiro S: REIC/Dkk-3 induces
cell death in human malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 10:244–253.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carmon KS, Lin Q, Gong X, Thomas A and Liu
Q: LGR5 interacts and cointernalizes with Wnt receptors to modulate
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2054–2064. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
de Lau W, Barker N, Low TY, Koo BK, Li VS,
Teunissen H, Kujala P, Haegebarth A, Peters PJ, van de Wetering M,
et al: Lgr5 homologues associate with Wnt receptors and mediate
R-spondin signalling. Nature. 476:293–297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Epping MT, Meijer LA, Krijgsman O, Bos JL,
Pandolfi PP and Bernards R: TSPYL5 suppresses p53 levels and
function by physical interaction with USP7. Nat Cell Biol.
13:102–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheng Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Deng Y, Hu J, Mo X,
Li N, Li Y, Luo N, Yuan W, et al: A novel human gene ZNF415 with
five isoforms inhibits AP-1- and p53-mediated transcriptional
activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:33–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|