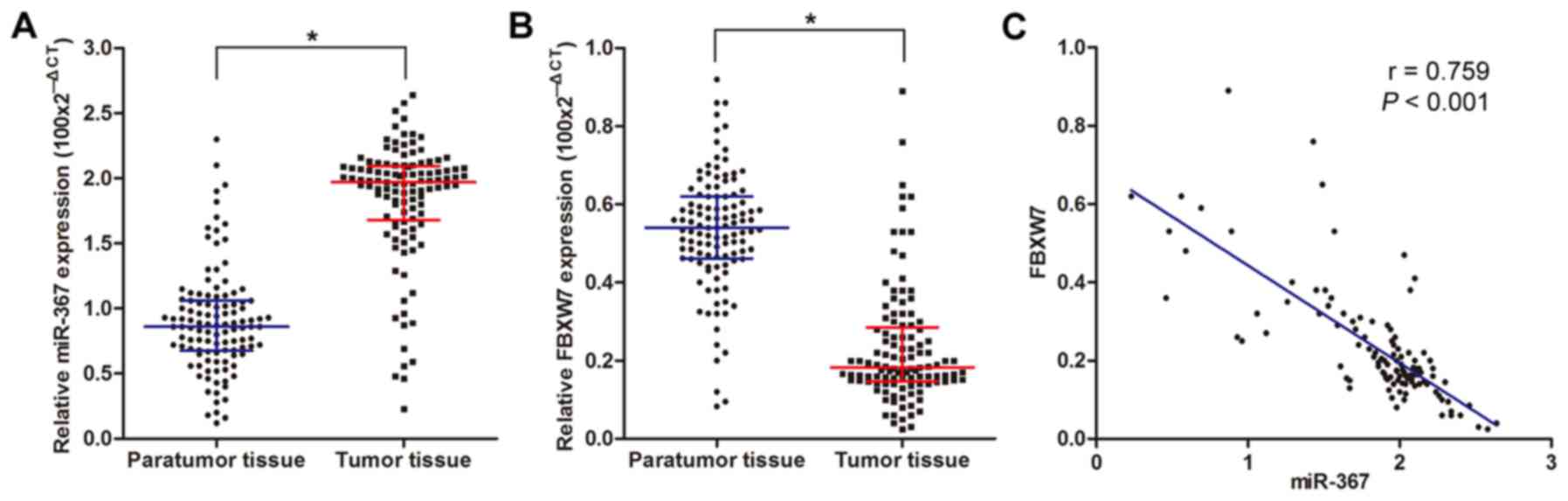
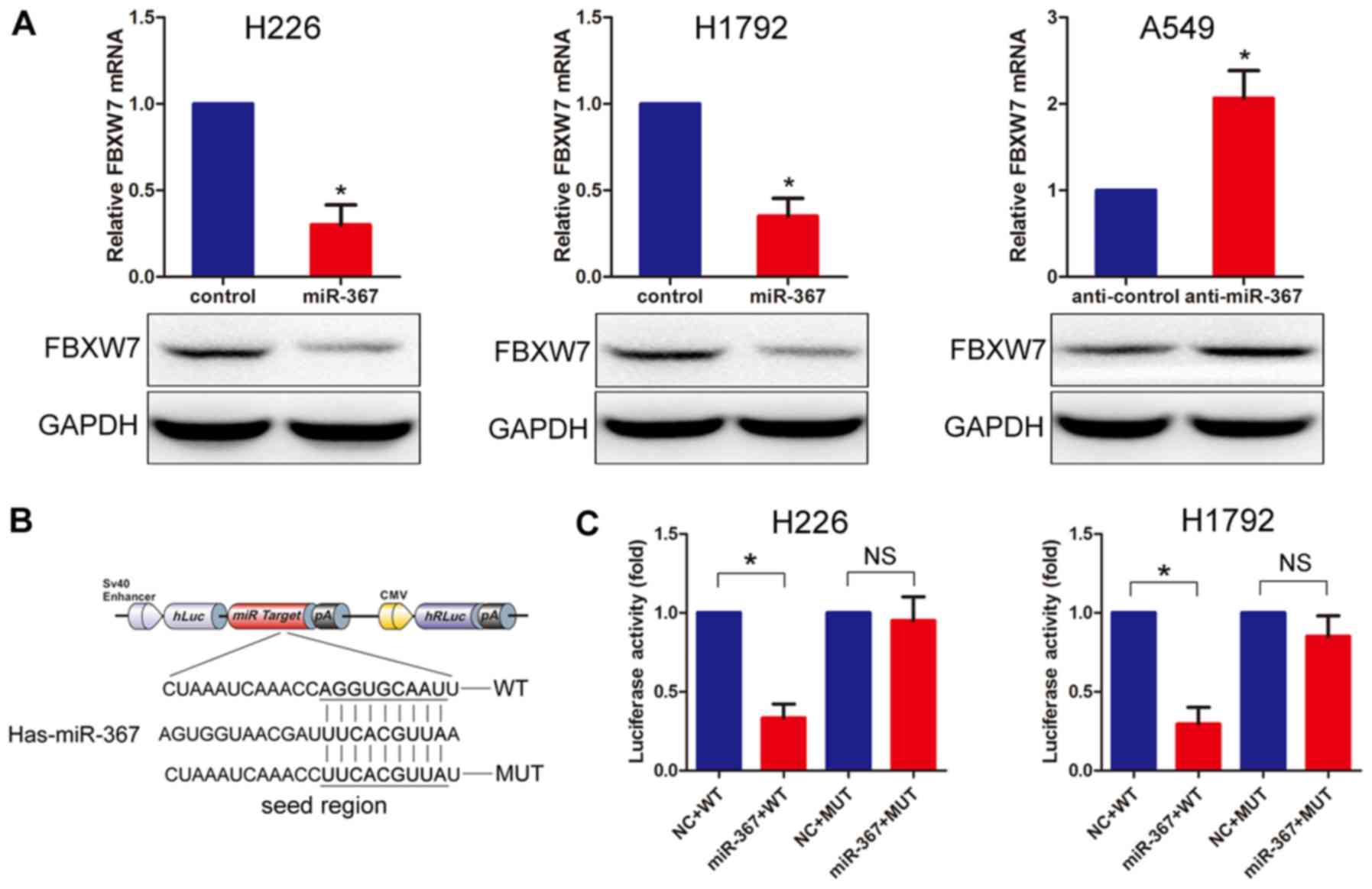
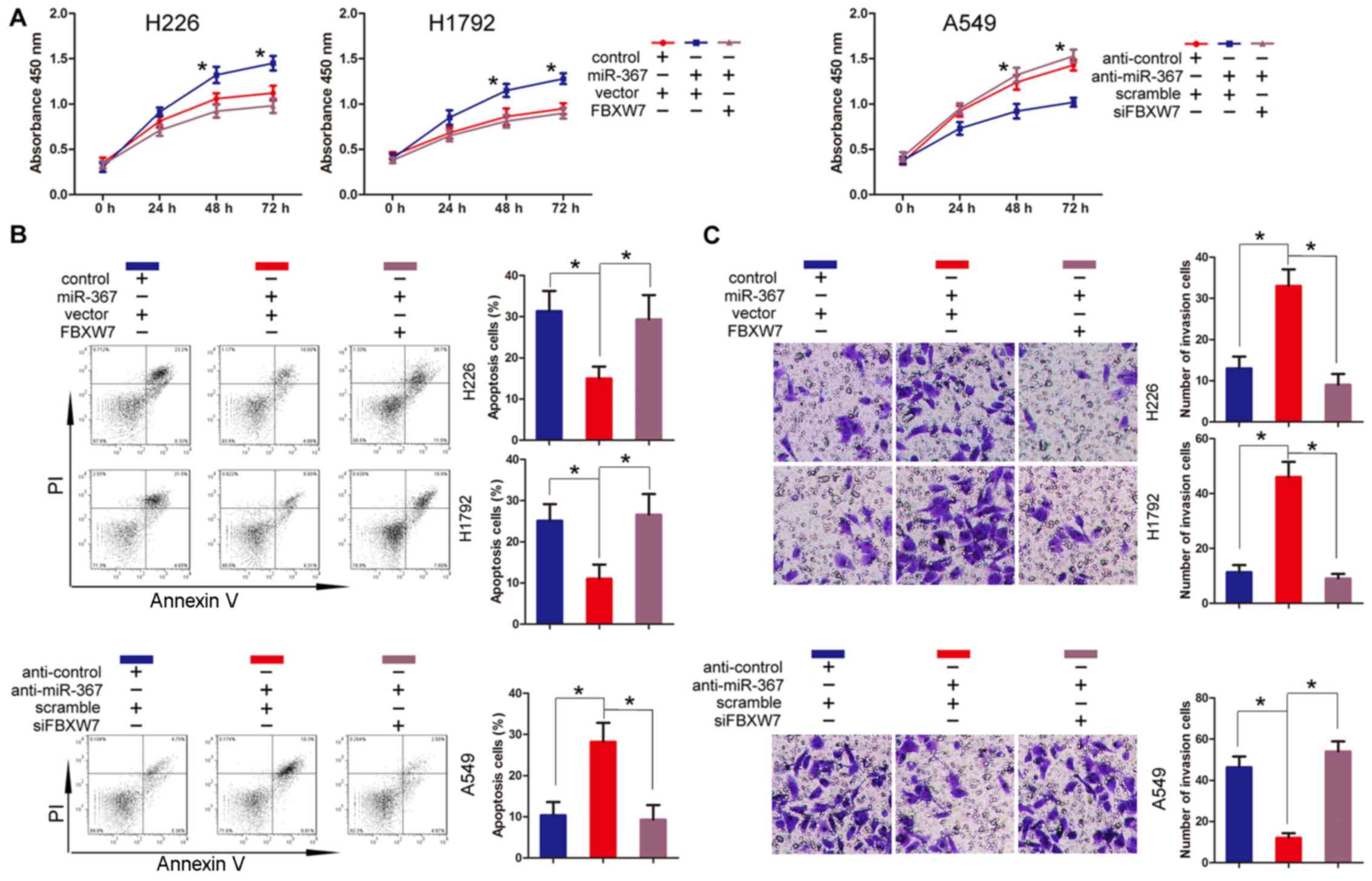
|
1
|
Villaruz LC, Kalyan A, Zarour H and
Socinski MA: Immunotherapy in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
3:2–14. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ricciuti B, Mecca C, Crinò L, Baglivo S,
Cenci M and Metro G: Non-coding RNAs in lung cancer. Oncoscience.
1:674–705. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Landi L and Cappuzzo F: Management of
NSCLC: Focus on crizotinib. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15:2587–2597.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gridelli C, Peters S, Sgambato A, Casaluce
F, Adjei AA and Ciardiello F: ALK inhibitors in the treatment of
advanced NSCLC. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:300–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uramoto H and Tanaka F: Recurrence after
surgery in patients with NSCLC. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:242–249.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vallières E: Oligometastatic NSCLC: The
changing role of surgery. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:192–194.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McElnay P and Lim E: Adjuvant or
neoadjuvant chemotherapy for NSCLC. J Thorac Dis. 6:(Suppl 2).
S224–S227. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shcherba M, Liang Y, Fernandes D,
Perez-Soler R and Cheng H: Cell cycle inhibitors for the treatment
of NSCLC. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15:991–1004. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gentzler RD, Yentz SE, Johnson ML,
Rademaker AW and Patel JD: The changing landscape of phase II/III
metastatic NSCLC clinical trials and the importance of biomarker
selection criteria. Cancer. 120:3853–3858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gómez AM, Sarceda JR Jarabo, García-Asenjo
JA, Fernandez C, Hernandez S, Sanz J, Fernandez E, Calatayud J,
Torres A and Hernando F: Relationship of immunohistochemical
biomarker expression and lymph node involvement in patients
undergoing surgical treatment of NSCLC with long-term follow-up.
Tumour Biol. 35:4551–4559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grim JE: Fbxw7 hotspot mutations and human
colon cancer: Mechanistic insights from new mouse models. Gut.
63:707–709. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Zan X, Han S, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with the
expression of c-Myc, cyclin E and p53 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo Z, Zhou Y, Evers BM and Wang Q: Rictor
regulates FBXW7-dependent c-Myc and cyclin E degradation in
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 418:426–432.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Izumi N, Helker C, Ehling M, Behrens A,
Herzog W and Adams RH: Fbxw7 controls angiogenesis by regulating
endothelial Notch activity. PLoS One. 7:e411162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Babaei-Jadidi R, Li N, Saadeddin A,
Spencer-Dene B, Jandke A, Muhammad B, Ibrahim EE, Muraleedharan R,
Abuzinadah M, Davis H, et al: FBXW7 influences murine intestinal
homeostasis and cancer, targeting Notch, Jun, and DEK for
degradation. J Exp Med. 208:295–312. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ren H, Koo J, Guan B, Yue P, Deng X, Chen
M, Khuri FR and Sun SY: The E3 ubiquitin ligases β-TrCP and FBXW7
cooperatively mediates GSK3-dependent Mcl-1 degradation induced by
the Akt inhibitor API-1, resulting in apoptosis. Mol Cancer.
12:1462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren H, Zhao L, Li Y, Yue P, Deng X,
Owonikoko TK, Chen M, Khuri FR and Sun SY: The PI3 kinase inhibitor
NVP-BKM120 induces GSK3/FBXW7-dependent Mcl-1 degradation,
contributing to induction of apoptosis and enhancement of
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 338:229–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li N, Lorenzi F, Kalakouti E, Normatova M,
Babaei-Jadidi R, Tomlinson I and Nateri AS: FBXW7-mutated
colorectal cancer cells exhibit aberrant expression of
phosphorylated-p53 at Serine-15. Oncotarget. 6:9240–9256. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Shen L, Mao L, Wang B, Li Y and Yu
H: miR-92a is upregulated in cervical cancer and promotes cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting FBXW7. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 458:63–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calcagno DQ, Freitas VM, Leal MF, de Souza
CR, Demachki S, Montenegro R, Assumpção PP, Khayat AS, Smith MA,
dos Santos AK, et al: MYC, FBXW7 and TP53 copy number variation and
expression in gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 13:1412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ibusuki M, Yamamoto Y, Shinriki S, Ando Y
and Iwase H: Reduced expression of ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 mRNA is
associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Cancer
Sci. 102:439–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan Y, Sangfelt O and Spruck C: The
Fbxw7/hCdc4 tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Lett.
271:1–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kuiper RP, Vreede L, Venkatachalam R,
Ricketts C, Kamping E, Verwiel E, Govaerts L, Debiec-Rychter M,
Lerut E, van Erp F, et al: The tumor suppressor gene FBXW7 is
disrupted by a constitutional t(3;4)(q21;q31) in a patient with
renal cell cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 195:105–111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park MJ, Taki T, Oda M, Watanabe T,
Yumura-Yagi K, Kobayashi R, Suzuki N, Hara J, Horibe K and Hayashi
Y: FBXW7 and NOTCH1 mutations in childhood T cell acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia and T cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J
Haematol. 145:198–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morra F, Luise C, Merolla F, Poser I,
Visconti R, Ilardi G, Paladino S, Inuzuka H, Guggino G, Monaco R,
et al: FBXW7 and USP7 regulate CCDC6 turnover during the cell cycle
and affect cancer drugs susceptibility in NSCLC. Oncotarget.
6:12697–12709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qin C, Huang RY and Wang ZX: Potential
role of miR-100 in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Tumour
Biol. 36:1403–1409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bennett PE, Bemis L, Norris DA and
Shellman YG: miR in melanoma development: miRNAs and acquired
hallmarks of cancer in melanoma. Physiol Genomics. 45:1049–1059.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yokobori T, Yokoyama Y, Mogi A, Endoh H,
Altan B, Kosaka T, Yamaki E, Yajima T, Tomizawa K, Azuma Y, et al:
FBXW7 mediates chemotherapeutic sensitivity and prognosis in
NSCLCs. Mol Cancer Res. 12:32–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Sun XX, Ma X and Chen
ZN: microRNA-146a inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating VEGF
through dual pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
14:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Natarajan V, Bandapalli OR, Rajkumar T,
Sagar TG and Karunakaran N: NOTCH1 and FBXW7 mutations favor better
outcome in pediatric South Indian T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 37:e23–e30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Naganawa Y, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitsui A, Katada T, Tanaka T, Shiozaki M, Fujii Y and Takeyama
H: Decreased expression of FBXW7 is correlated with poor prognosis
in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med.
1:841–846. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Milne AN, Leguit R, Corver WE, Morsink FH,
Polak M, de Leng WW, Carvalho R and Offerhaus GJ: Loss of
CDC4/FBXW7 in gastric carcinoma. Cell Oncol. 32:347–359.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsunematsu R, Nakayama K, Oike Y,
Nishiyama M, Ishida N, Hatakeyama S, Bessho Y, Kageyama R, Suda T
and Nakayama KI: Mouse Fbw7/Sel-10/Cdc4 is required for notch
degradation during vascular development. J Biol Chem.
279:9417–9423. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mao JH, Perez-Losada J, Wu D, Delrosario
R, Tsunematsu R, Nakayama KI, Brown K, Bryson S and Balmain A:
Fbxw7/Cdc4 is a p53-dependent, haploinsufficient tumour suppressor
gene. Nature. 432:775–779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang H, Lu X, Liu Z, Chen L, Xu Y, Wang Y,
Wei G and Chen Y: FBXW7 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, stemness and metastatic potential of cholangiocarcinoma
cells. Oncotarget. 6:6310–6325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sato M, Rodriguez-Barrueco R, Yu J, Do C,
Silva JM and Gautier J: MYC is a critical target of FBXW7.
Oncotarget. 6:3292–3305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Sun Y, Chen X, Squires J,
Nowroozizadeh B, Liang C and Huang J: p53 mutation directs AURKA
overexpression via miR-25 and FBXW7 in prostatic small cell
neuroendocrine carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 13:584–591. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH and Pfeffer LM: The
role of miR-21 in Cancer. Drug Dev Res. 76:270–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Xie YJ, Xu Q, Chen JX, Shan NC and
Zhang Y: Down-regulation of miR-1246 in cervical cancer tissues and
its clinical significance. Gynecol Oncol. 138:683–688. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ye H, Pang L, Wu Q, Zhu Y, Guo C, Deng Y
and Zheng X: A critical role of mir-199a in the cell biological
behaviors of colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol. 10:652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han S, Yang S, Cai Z, Pan D, Li Z, Huang
Z, Zhang P, Zhu H, Lei L and Wang W: Anti-Warburg effect of
rosmarinic acid via miR-155 in gastric cancer cells. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 9:2695–2703. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liang J, Li X, Li Y, Wei J, Daniels G,
Zhong X, Wang J, Sfanos K, Melamed J, Zhao J, et al: LEF1 targeting
EMT in prostate cancer invasion is mediated by miR-181a. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:1124–1132. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang N, Wei X and Xu L: miR-150 promotes
the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting P53. FEBS Lett.
587:2346–2351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang Z, Qiao Q, Chen M, Li X, Wang Z, Liu
C and Xie Z: miR-625 down-regulation promotes proliferation and
invasion in esophageal cancer by targeting Sox2. FEBS Lett.
588:915–921. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|