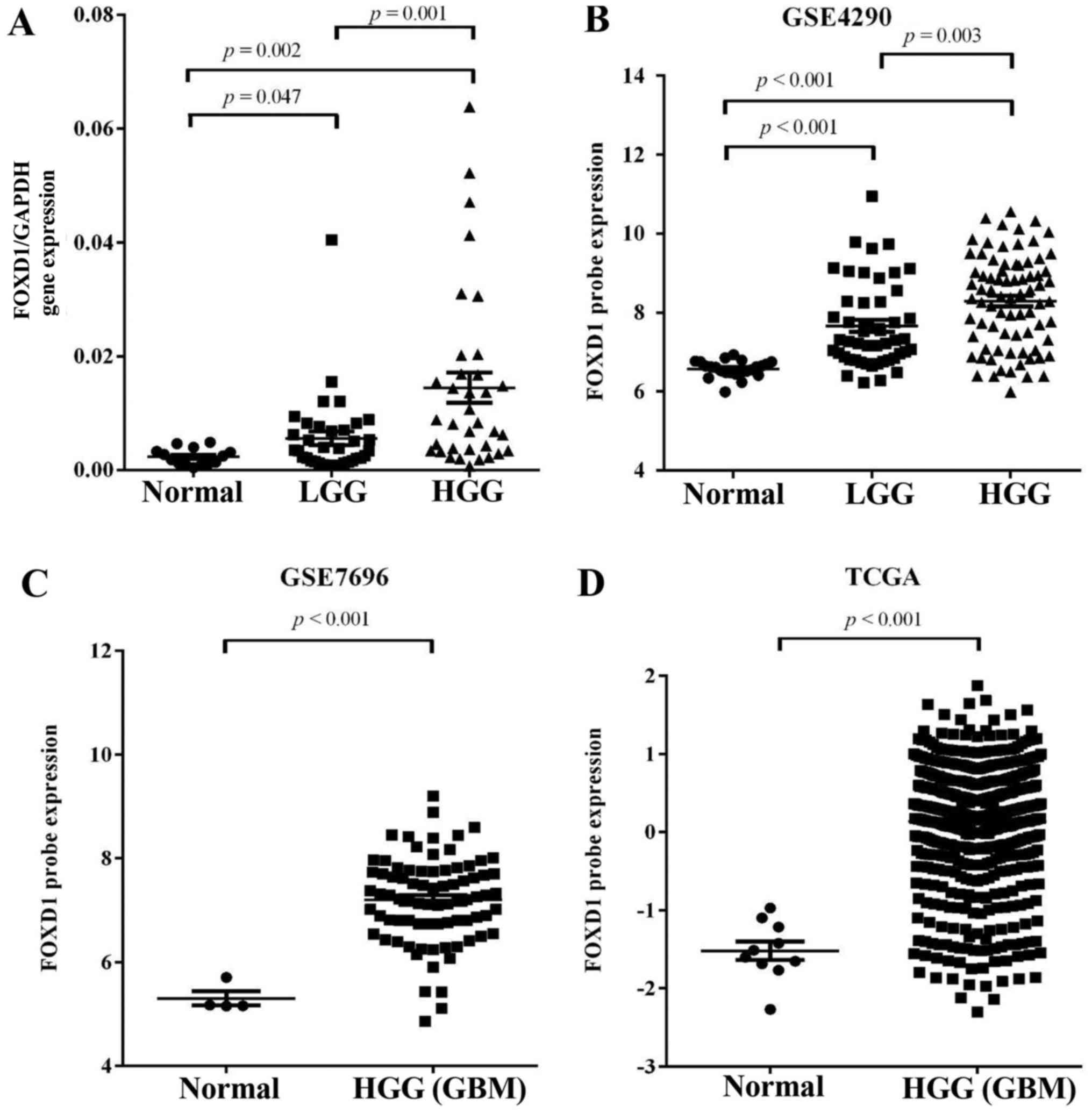
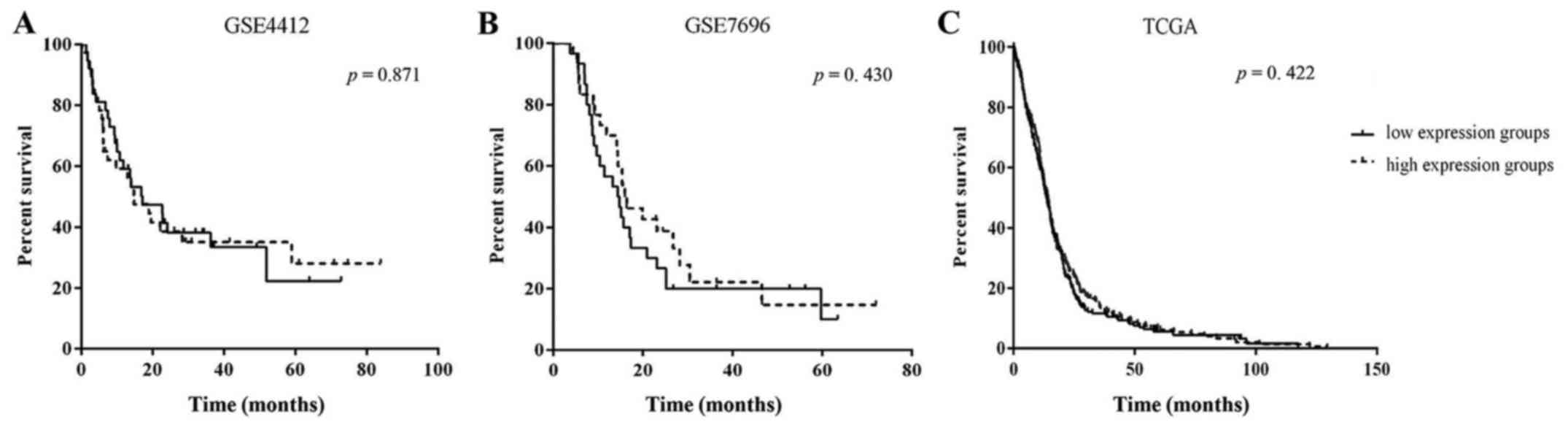
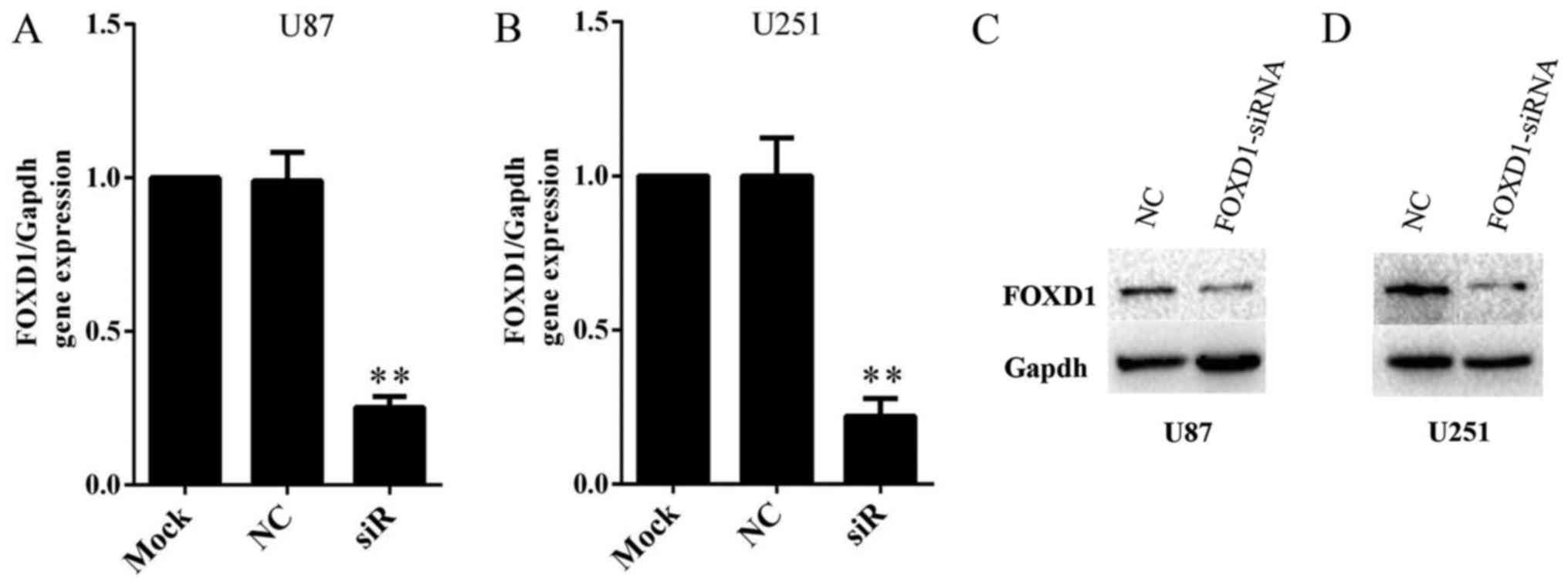
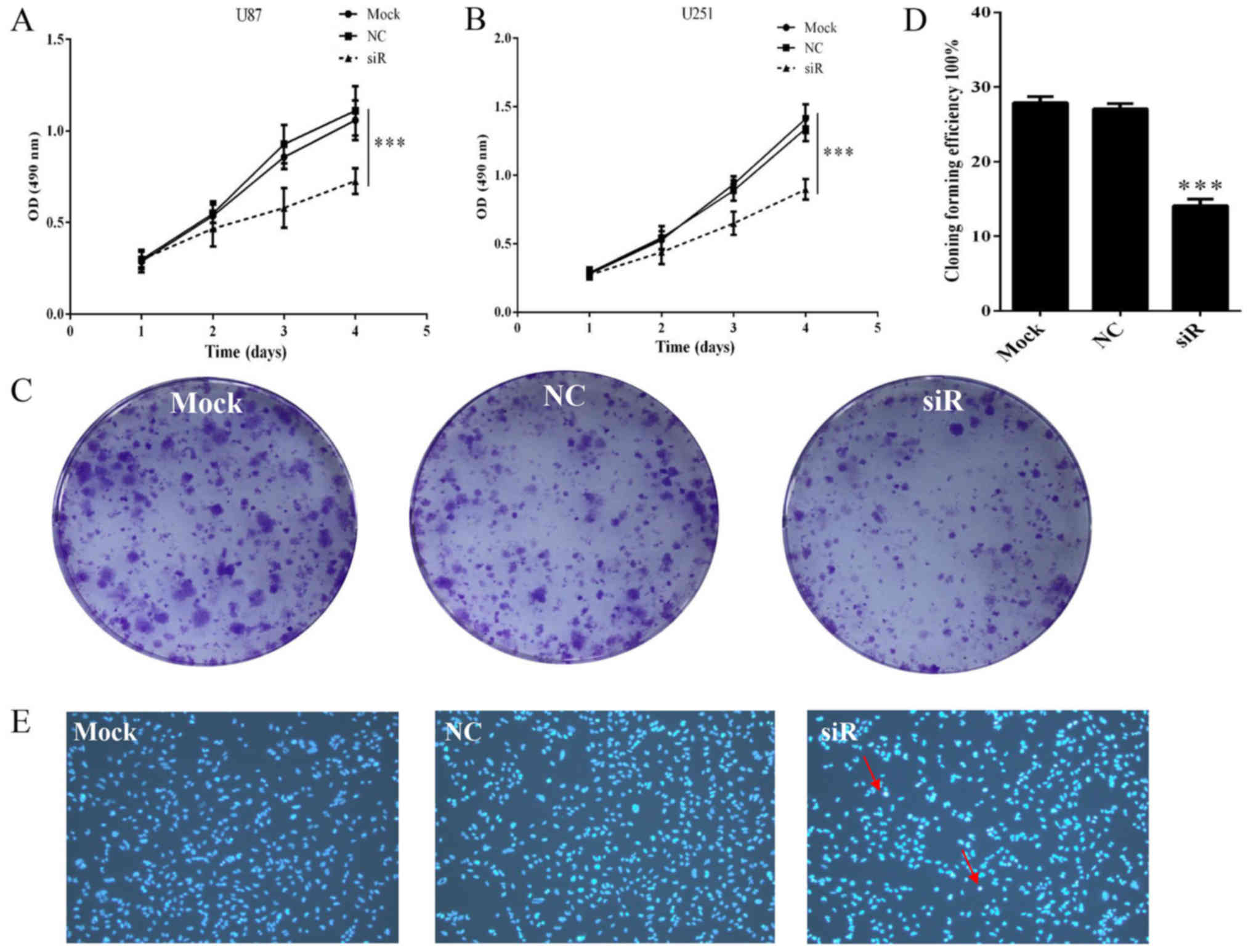
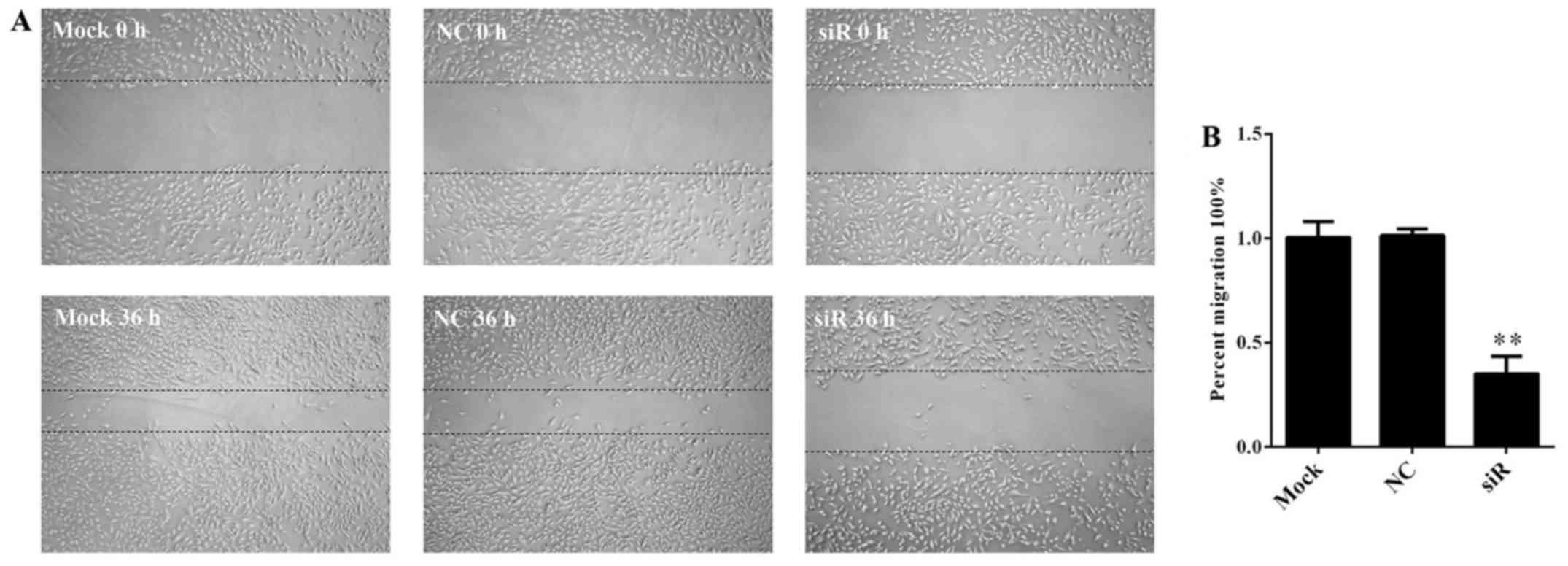
|
1
|
Schucht P, Beck J, Seidel K and Raabe A:
Extending resection and preserving function: Modern concepts of
glioma surgery. Swiss Med Wkly. 145:w140822015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haque A, Banik NL and Ray SK: Emerging
role of combination of all-trans retinoic acid and interferon-gamma
as chemoimmunotherapy in the management of human glioblastoma.
Neurochem Res. 32:2203–2209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ohgaki H: Epidemiology of brain tumors.
Methods Mol Biol. 472:323–342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of
Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pulkkanen KJ and Yla-Herttuala S: Gene
therapy for malignant glioma: Current clinical status. Mol Ther.
12:585–598. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weigel D, Jürgens G, Küttner F, Seifert E
and Jäckle H: The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein
and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo.
Cell. 57:645–658. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai E, Prezioso VR, Smith E, Litvin O,
Costa RH and Darnell JE Jr: HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched
transcription factor of novel structure is regulated
transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 4:1427–1436. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lai E, Prezioso VR, Tao WF, Chen WS and
Darnell JE Jr: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene
family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic
gene fork head. Genes Dev. 5:416–427. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaestner KH, Knochel W and Martinez DE:
Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription
factors. Genes Dev. 14:142–146. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Human FOX gene family
(Review). Int J Oncol. 25:1495–1500. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin L, Miller CT, Contreras JI, Prescott
MS, Dagenais SL, Wu R, Yee J, Orringer MB, Misek DE, Hanash SM, et
al: The hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha gene, HNF3alpha (FOXA1),
on chromosome band 14q13 is amplified and overexpressed in
esophageal and lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 62:5273–5279.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sorensen PH, Lynch JC, Qualman SJ,
Tirabosco R, Lim JF, Maurer HM, Bridge JA, Crist WM, Triche TJ and
Barr FG: PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic
indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the
children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 20:2672–2679. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hillion J, Le Coniat M, Jonveaux P, Berger
R and Bernard OA: AF6q21, a novel partner of the MLL gene in
t(6;11)(q21;q23), defines a forkhead transcriptional factor
subfamily. Blood. 90:3714–3719. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parry P, Wei Y and Evans G: Cloning and
characterization of the t(X;11) breakpoint from a leukemic cell
line identify a new member of the forkhead gene family. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 11:79–84. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hatini V, Tao W and Lai E: Expression of
winged helix genes, BF-1 and BF-2, define adjacent domains within
the developing forebrain and retina. J Neurobiol. 25:1293–1309.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pierrou S, Hellqvist M, Samuelsson L,
Enerbäck S and Carlsson P: Cloning and characterization of seven
human forkhead proteins: Binding site specificity and DNA bending.
EMBO J. 13:5002–5012. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hatini V, Huh SO, Herzlinger D, Soares VC
and Lai E: Essential role of stromal mesenchyme in kidney
morphogenesis revealed by targeted disruption of Winged Helix
transcription factor BF-2. Genes Dev. 10:1467–1478. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Levinson RS, Batourina E, Choi C,
Vorontchikhina M, Kitajewski J and Mendelsohn CL: Foxd1-dependent
signals control cellularity in the renal capsule, a structure
required for normal renal development. Development. 132:529–539.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Herrera E, Marcus R, Li S, Williams SE,
Erskine L, Lai E and Mason C: Foxd1 is required for proper
formation of the optic chiasm. Development. 131:5727–5739. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gumbel JH, Patterson EM, Owusu SA, Kabat
BE, Jung DO, Simmons J, Hopkins T and Ellsworth BS: The forkhead
transcription factor, Foxd1, is necessary for pituitary luteinizing
hormone expression in mice. PLoS One. 7:e521562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao YF, Zhao JY, Yue H, Hu KS, Shen H,
Guo ZG and Su XJ: FOXD1 promotes breast cancer proliferation and
chemotherapeutic drug resistance by targeting p27. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 456:232–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y and
Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Forkhead Box M1 transcription factor
leads to the inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis of pancreatic
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:8293–8300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaneda H, Arao T, Tanaka K, Tamura D,
Aomatsu K, Kudo K, Sakai K, De Velasco MA, Matsumoto K, Fujita Y,
et al: FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and enhances
tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:2053–2063. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ray PS, Wang J, Qu Y, Sim MS, Shamonki J,
Bagaria SP, Ye X, Liu B, Elashoff D, Hoon DS, et al: FOXC1 is a
potential prognostic biomarker with functional significance in
basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3870–3876. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y,
Ding Z, Miao L, Tothova Z, Horner JW, Carrasco DR, et al: FoxOs are
lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate
endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell. 128:309–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Balli D, Ustiyan V, Zhang Y, Wang IC,
Masino AJ, Ren X, Whitsett JA, Kalinichenko VV and Kalin TV: Foxm1
transcription factor is required for lung fibrosis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J. 32:231–244. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Humphreys BD, Lin SL, Kobayashi A, Hudson
TE, Nowlin BT, Bonventre JV, Valerius MT, McMahon AP and Duffield
JS: Fate tracing reveals the pericyte and not epithelial origin of
myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 176:85–97. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koga M, Matsuda M, Kawamura T, Sogo T,
Shigeno A, Nishida E and Ebisuya M: Foxd1 is a mediator and
indicator of the cell reprogramming process. Nat Commun.
5:31972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fetting JL, Guay JA, Karolak MJ, Iozzo RV,
Adams DC, Maridas DE, Brown AC and Oxburgh L: FOXD1 promotes
nephron progenitor differentiation by repressing decorin in the
embryonic kidney. Development. 141:17–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|