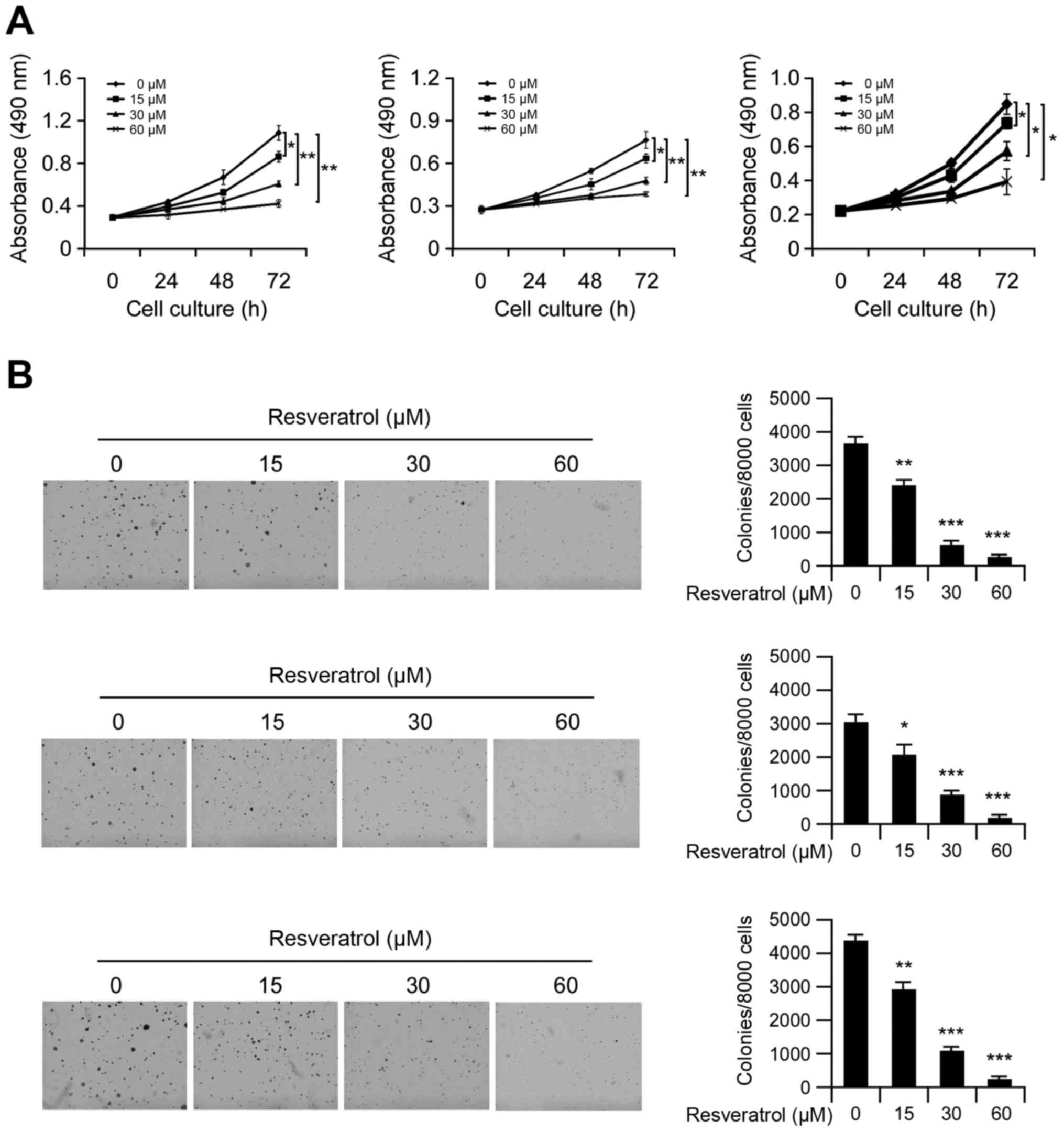
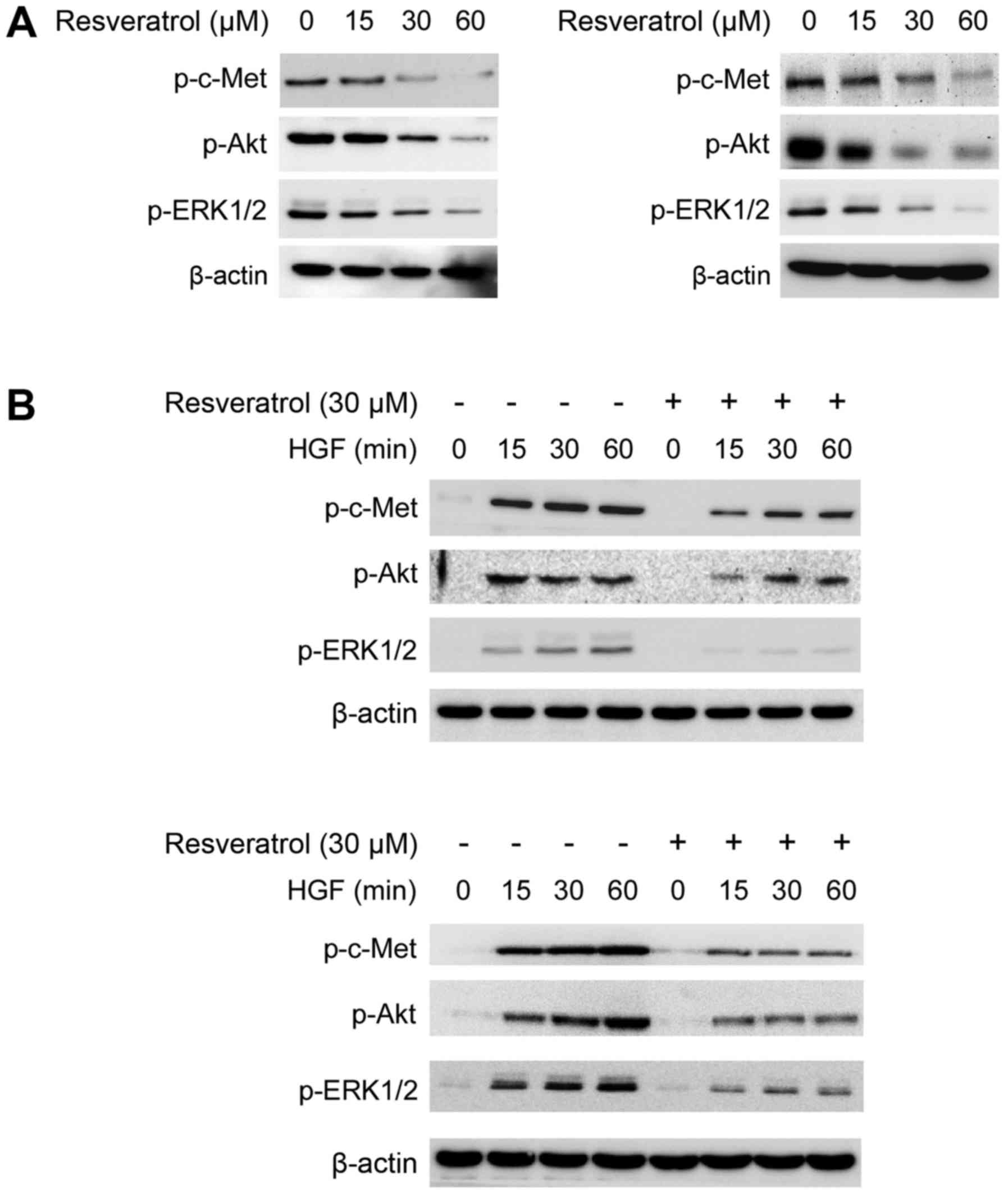
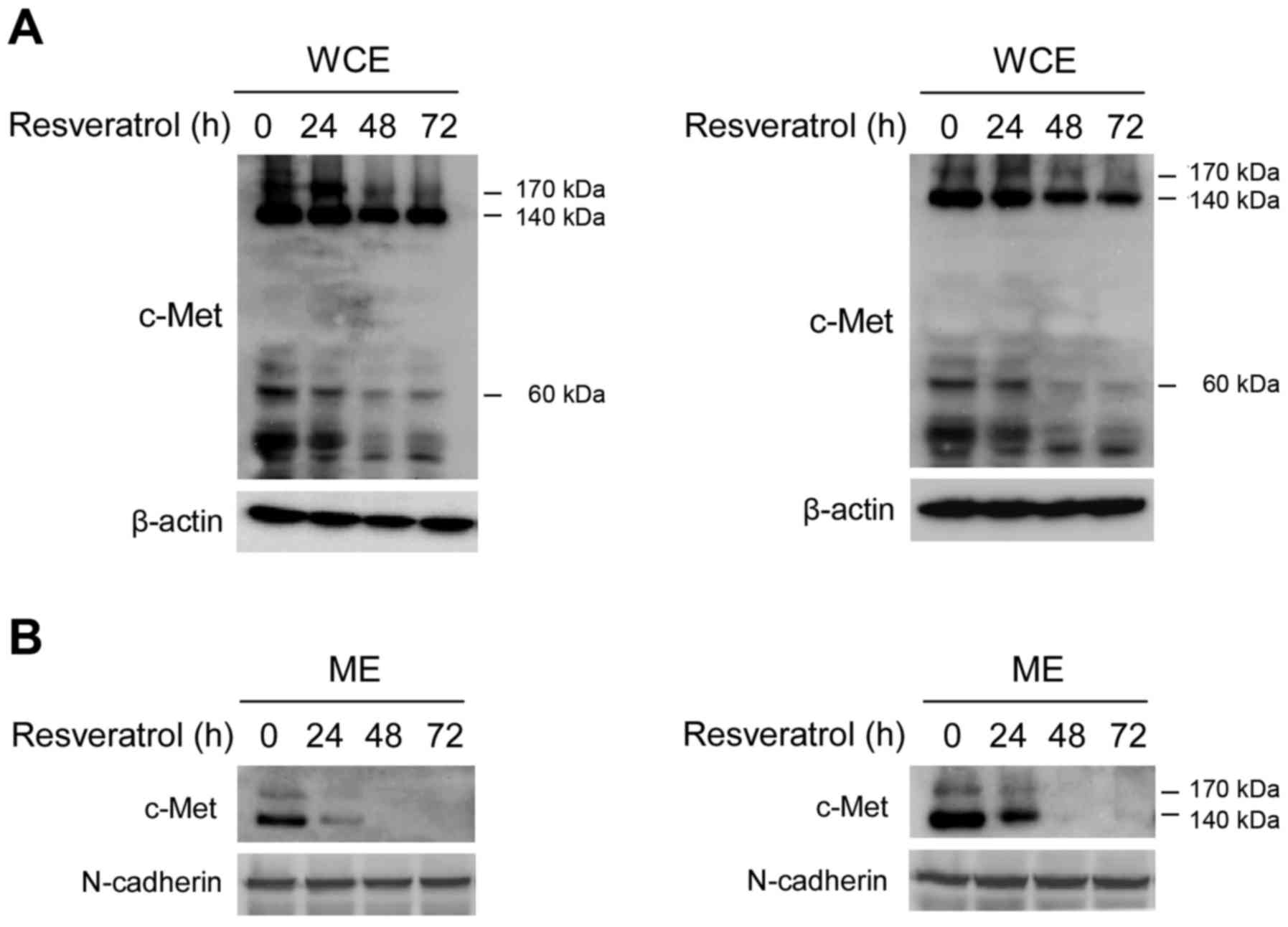
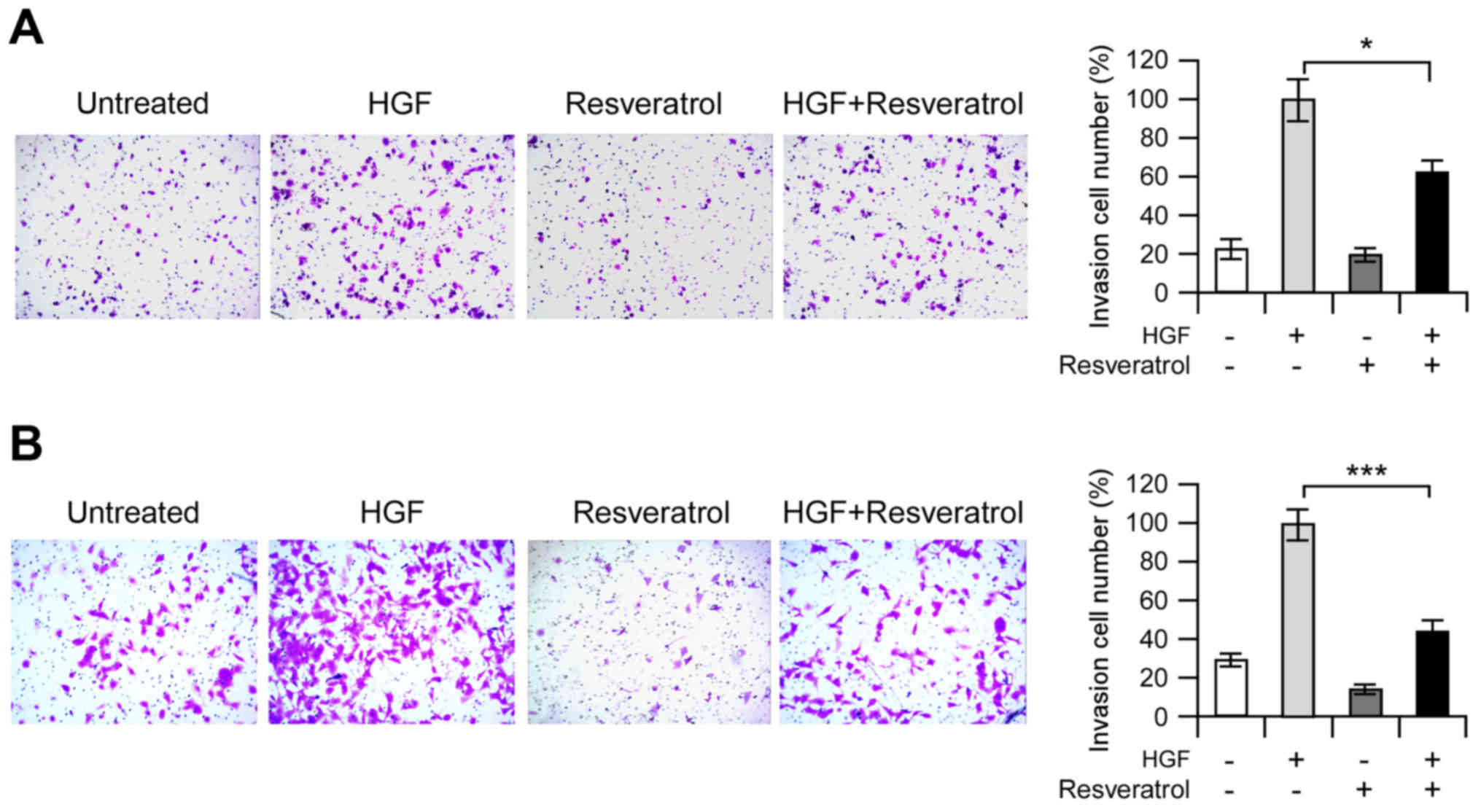
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA,
Hutin YJ and Bell BP: The contributions of hepatitis B virus and
hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer
worldwide. J Hepatol. 45:529–538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seton-Rogers S: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Gender differences. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:578–579. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goyal L, Muzumdar MD and Zhu AX: Targeting
the HGF/c-MET pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2310–2318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Villanueva A, Lachenmayer A and
Finn RS: Advances in targeted therapies for hepatocellular
carcinoma in the genomic era. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:408–424. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forner A, Gilabert M, Bruix J and Raoul
JL: Treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 11:525–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Wang Q, Yang G, Marando C, Koblish
HK, Hall LM, Fridman JS, Behshad E, Wynn R, Li Y, et al: A novel
kinase inhibitor, INCB28060, blocks c-MET-dependent signaling,
neoplastic activities, and cross-talk with EGFR and HER-3. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:7127–7138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peters S and Adjei AA: MET: A promising
anticancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 9:314–326. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C and
Woude G Vande: Targeting MET in cancer: Rationale and progress. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:89–103. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
You H, Ding W, Dang H, Jiang Y and
Rountree CB: c-Met represents a potential therapeutic target for
personalized treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
54:879–889. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim IH, Lee IH, Lee JE, Hong SH, Kim TJ,
Lee KY, Kim YK, Kim SJ, Sung SW, Park JK, et al: Prognostic impact
of multiple clinicopathologic risk factors and c-Met overexpression
in patients who have undergone resection of stage IB non-small-cell
lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 17:e31–e43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Burggraaf J, Kamerling IM, Gordon PB,
Schrier L, de Kam ML, Kales AJ, Bendiksen R, Indrevoll B, Bjerke
RM, Moestue SA, et al: Detection of colorectal polyps in humans
using an intravenously administered fluorescent peptide targeted
against c-Met. Nat Med. 21:955–961. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Otte A, Rauprich F, von der Ohe J, Yang Y,
Kommoss F, Feuerhake F, Hillemanns P and Hass R: c-Met inhibitors
attenuate tumor growth of small cell hypercalcemic ovarian
carcinoma (SCCOHT) populations. Oncotarget. 6:31640–31658.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xing F, Liu Y, Sharma S, Wu K, Chan MD, Lo
HW, Carpenter RL, Metheny-Barlow LJ, Zhou X, Qasem SA, et al:
Activation of the c-Met pathway mobilizes an inflammatory network
in the brain microenvironment to promote brain metastasis of breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 76:4970–4980. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marano L, Chiari R, Fabozzi A, De Vita F,
Boccardi V, Roviello G, Petrioli R, Marrelli D, Roviello F and
Patriti A: c-Met targeting in advanced gastric cancer: An open
challenge. Cancer Lett. 365:30–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Z, Zhu X, Cui K, Mancuso J, Federley
R, Fischer K, Teng GJ, Mittal V, Gao D, Zhao H, et al: In vivo
visualization and characterization of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast tumors. Cancer Res. 76:2094–2104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Organ SL and Tsao MS: An overview of the
c-MET signaling pathway. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 3:(Suppl). S7–S19.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Medina-Aguilar R, Pérez-Plasencia C,
Marchat LA, Gariglio P, García Mena J, Rodríguez Cuevas S,
Ruíz-García E, Astudillo-de la Vega H, Hernández Juárez J,
Flores-Pérez A, et al: Methylation landscape of human breast cancer
cells in response to dietary compound resveratrol. PLoS One.
11:e01578662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Buhrmann C, Shayan P, Popper B, Goel A and
Shakibaei M: Sirt1 is required for resveratrol-mediated
chemopreventive effects in colorectal cancer cells. Nutrients.
8:1452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gwak H, Kim S, Dhanasekaran DN and Song
YS: Resveratrol triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis by disrupting
N-linked glycosylation of proteins in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 371:347–353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahin E, Baycu C, Koparal AT, Donmez D
Burukoglu and Bektur E: Resveratrol reduces IL-6 and VEGF secretion
from co-cultured A549 lung cancer cells and adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Tumour Biol. 37:7573–7582. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taniguchi T, Iizumi Y, Watanabe M, Masuda
M, Morita M, Aono Y, Toriyama S, Oishi M, Goi W and Sakai T:
Resveratrol directly targets DDX5 resulting in suppression of the
mTORC1 pathway in prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22112016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh CK, Ndiaye MA and Ahmad N:
Resveratrol and cancer: Challenges for clinical translation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1178–1185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu X, Deng Q, Li W, Xiao L, Luo X, Liu X,
Yang L, Peng S, Ding Z, Feng T, et al: Neoalbaconol induces cell
death through necroptosis by regulating RIPK-dependent autocrine
TNFα and ROS production. Oncotarget. 6:1995–2008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li W, Peng C, Lee MH, Lim D, Zhu F, Fu Y,
Yang G, Sheng Y, Xiao L, Dong X, et al: TRAF4 is a critical
molecule for Akt activation in lung cancer. Cancer Res.
73:6938–6950. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kulkarni SS and Cantó C: The molecular
targets of resveratrol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1114–1123. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Davis GL, Dempster J, Meler JD, Orr DW,
Walberg MW, Brown B, Berger BD, O'Connor JK and Goldstein RM:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Management of an increasingly common
problem. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 21:266–280. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cui SX, Shi WN, Song ZY, Wang SQ, Yu XF,
Gao ZH and Qu XJ: Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin antagonizes the
effects of Sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma through
activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.
Oncotarget. 7:36767–36782. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li K, Shen B, Cheng X, Ma D, Jing X, Liu
X, Yang W, Peng C and Qiu W: Phenotypic and signaling consequences
of a novel aberrantly spliced transcript FGF receptor-3 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 76:4205–4215. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lanaya H, Natarajan A, Komposch K, Li L,
Amberg N, Chen L, Wculek SK, Hammer M, Zenz R, Peck-Radosavljevic
M, et al: EGFR has a tumour-promoting role in liver macrophages
during hepatocellular carcinoma formation. Nat Cell Biol.
16:972–981, 971–977. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lau EY, Lo J, Cheng BY, Ma MK, Lee JM, Ng
JK, Chai S, Lin CH, Tsang SY, Ma S, et al: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts regulate tumor-initiating cell plasticity in
hepatocellular carcinoma through c-Met/FRA1/HEY1 signaling. Cell
Rep. 15:1175–1189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu F, Wu L, Zheng S, Ding W, Teng L, Wang
Z, Ma Z and Zhao W: The clinical value of hepatocyte growth factor
and its receptor - c-met for liver cancer patients with
hepatectomy. Dig Liver Dis. 38:490–497. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Suzuki K, Hayashi N, Yamada Y, Yoshihara
H, Miyamoto Y, Ito Y, Ito T, Katayama K, Sasaki Y, Ito A, et al:
Expression of the c-met protooncogene in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 20:1231–1236. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi KJ, Baik IH, Ye SK and Lee YH:
Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Present
status and future directions. Biol Pharm Bull. 38:986–991. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Torrecilla S and Llovet JM: New molecular
therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 39:(Suppl 1). S80–S85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Suzuki M, Shiraha H, Fujikawa T, Takaoka
N, Ueda N, Nakanishi Y, Koike K, Takaki A and Shiratori Y:
Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin is a potential autologous growth
factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 280:6409–6415.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Spano D, Heck C, De Antonellis P,
Christofori G and Zollo M: Molecular networks that regulate cancer
metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:234–249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mehlen P and Puisieux A: Metastasis: A
question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:449–458. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng Y, Thiagarajan PS and Ma PC: MET
signaling: Novel targeted inhibition and its clinical development
in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:459–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wu YQ, Chen J, Wang J,
Tang XL, Mou H, Hu HZ, Song J, Yan J, et al: MiR-206 inhibits
HGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in
non-small cell lung cancer via c-Met/PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:18247–18261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Zhan Z, Jiang X, Peng X, Shen Y,
Chen F, Ji Y, Liu W, Shi Y, Duan W, et al: Simm530, a novel and
highly selective c-Met inhibitor, blocks c-Met-stimulated signaling
and neoplastic activities. Oncotarget. 7:38091–38104.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Horiguchi N, Takayama H, Toyoda M, Otsuka
T, Fukusato T, Merlino G, Takagi H and Mori M: Hepatocyte growth
factor promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through c-Met autocrine
activation and enhanced angiogenesis in transgenic mice treated
with diethylnitrosamine. Oncogene. 21:1791–1799. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ogunwobi OO, Puszyk W, Dong HJ and Liu C:
Epigenetic upregulation of HGF and c-Met drives metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e637652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T,
Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen
J, et al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung
cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jo M, Stolz DB, Esplen JE, Dorko K,
Michalopoulos GK and Strom SC: Cross-talk between epidermal growth
factor receptor and c-Met signal pathways in transformed cells. J
Biol Chem. 275:8806–8811. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Puri N and Salgia R: Synergism of EGFR and
c-Met pathways, cross-talk and inhibition, in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Carcinog. 7:92008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Sun MY, Chen CT,
Tang L, Song L, Zeng Z, Shah M, Christensen JG, Rosen N, Solit DB,
et al: HER kinase activation confers resistance to MET tyrosine
kinase inhibition in MET oncogene-addicted gastric cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3499–3508. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Varkaris A, Gaur S, Parikh NU, Song JH,
Dayyani F, Jin JK, Logothetis CJ and Gallick GE: Ligand-independent
activation of MET through IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling. Int J Cancer.
133:1536–1546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peter B, Bosze S and Horvath R:
Biophysical characteristics of proteins and living cells exposed to
the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCg): Review
of recent advances from molecular mechanisms to nanomedicine and
clinical trials. Eur Biophys J. Jun 16–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Khan F, Niaz K, Maqbool F, Hassan F
Ismail, Abdollahi M, Venkata KC Nagulapalli, Nabavi SM and Bishayee
A: Molecular targets underlying the anticancer effects of
quercetin: An update. Nutrients. 8(pii): E5292016.doi:
10.3390/nu8090529. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|