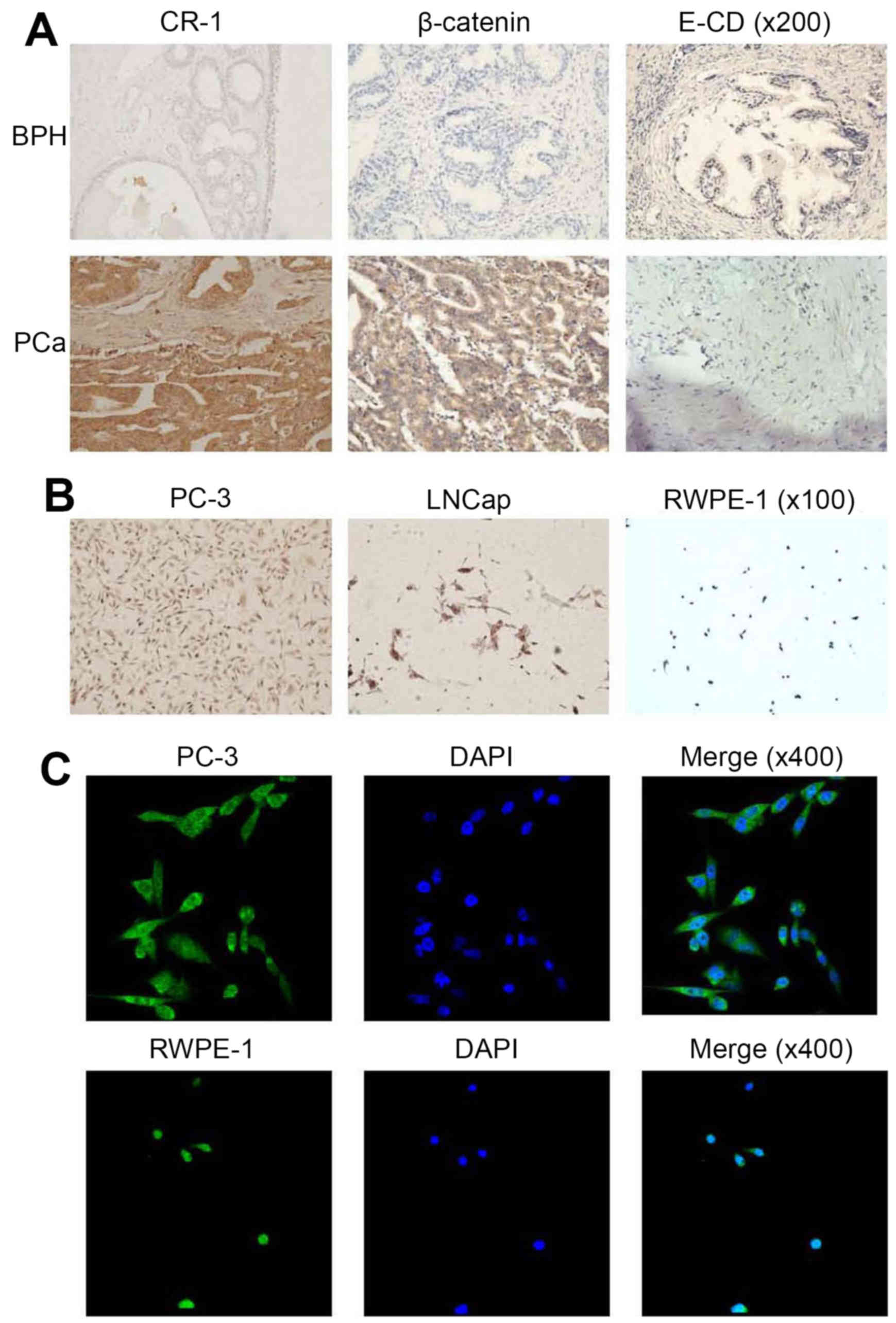
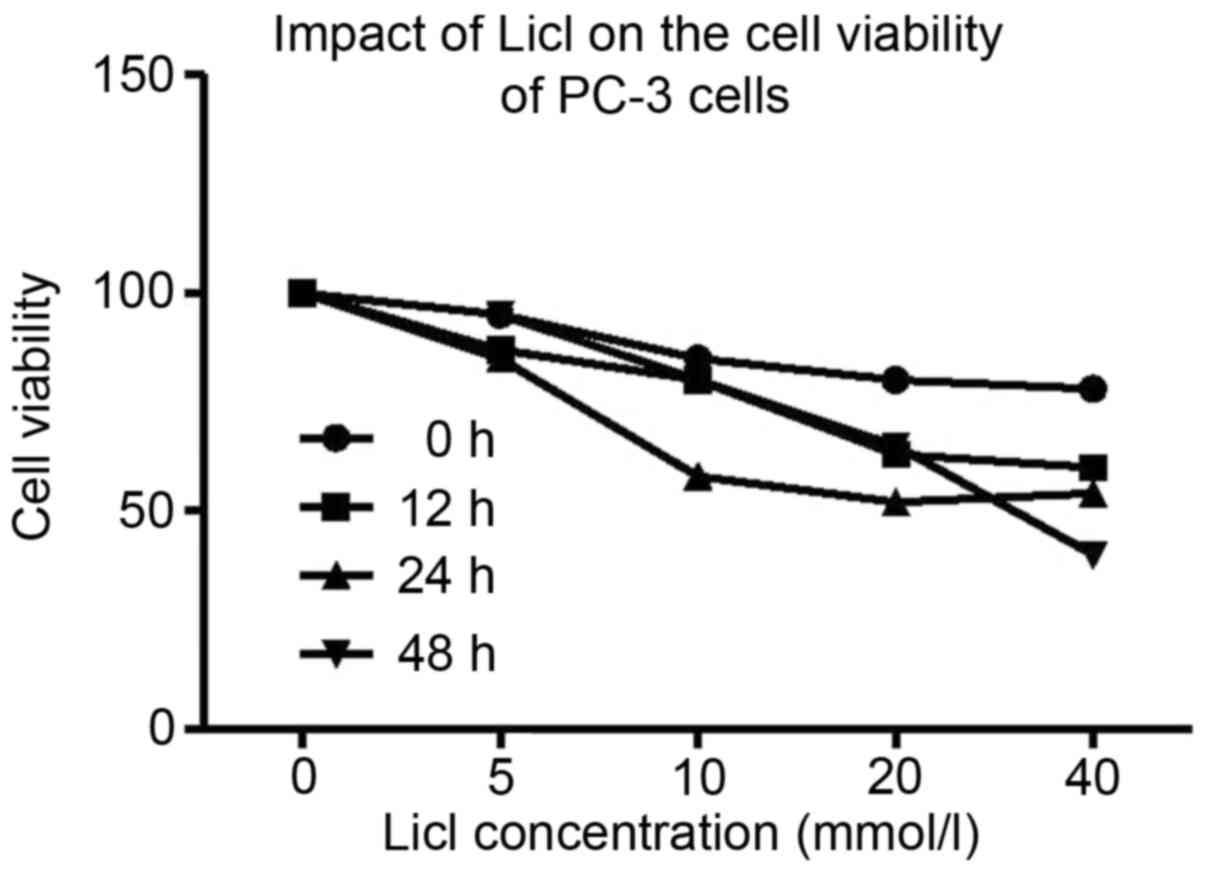
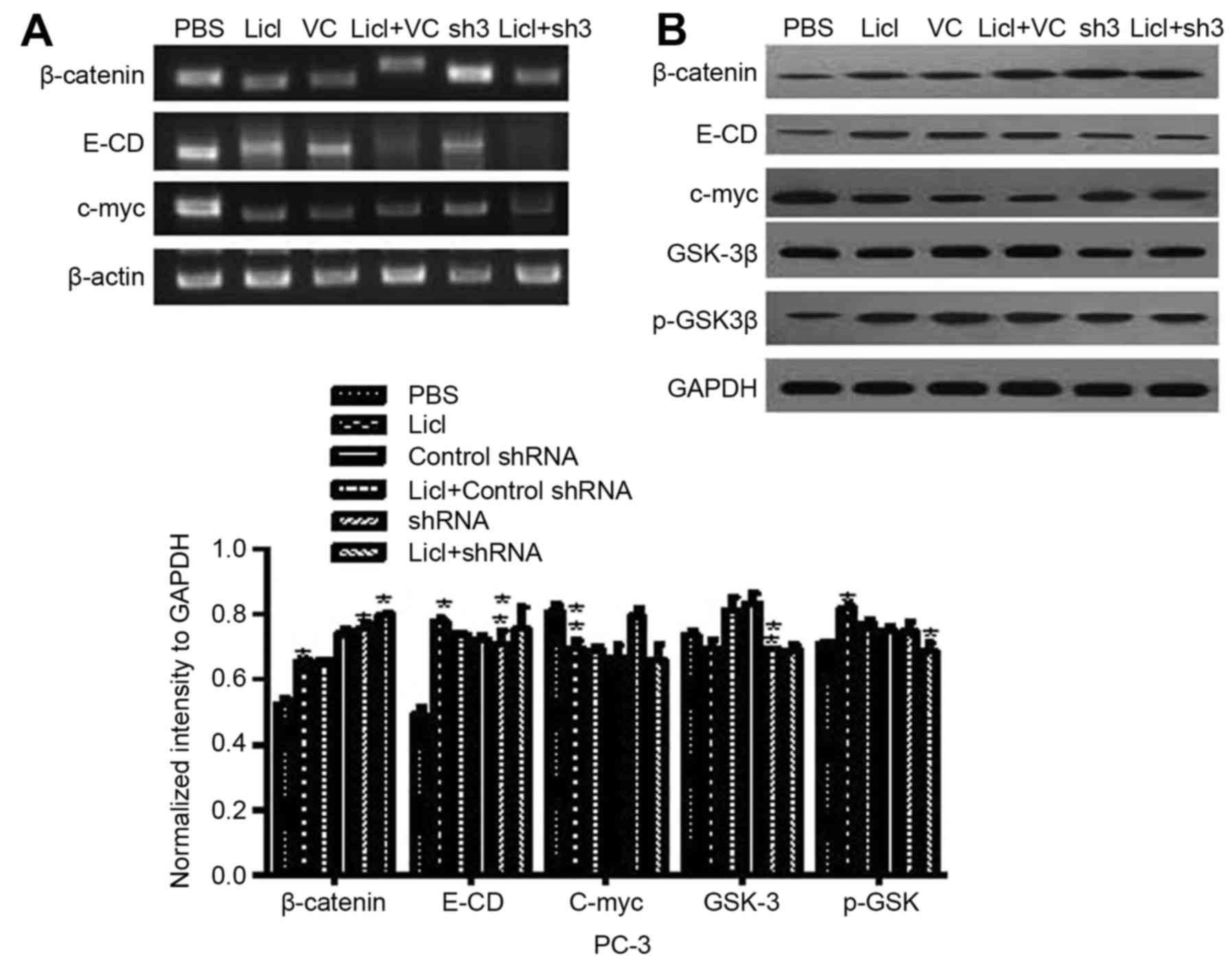
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Lortet-Tieulent J,
Ward E, Ferlay J, Brawley O and Bray F: International variation in
prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol.
61:1079–1092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Attard G, Parker C, Eeles RA, Schröder F,
Tomlins SA, Tannock I, Drake CG and de Bono JS: Prostate cancer.
Lancet. 387:70–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saloman DS, Bianco C, Ebert AD, Khan NI,
De Santis M, Normanno N, Wechselberger C, Seno M, Williams K,
Sanicola M, et al: The EGF-CFC family: Novel epidermal growth
factor-related proteins in development and cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 7:199–226. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ciccodicola A, Dono R, Obici S, Simeone A,
Zollo M and Persico MG: Molecular characterization of a gene of the
‘EGF family’ expressed in undifferentiated human NTERA2
teratocarcinoma cells. EMBO J. 8:1987–1991. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bianco C, Rangel MC, Castro NP, Nagaoka T,
Rollman K, Gonzales M and Salomon DS: Role of Cripto-1 in stem cell
maintenance and malignant progression. Am J Pathol. 177:532–540.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bianco C, Strizzi L, Normanno N, Khan N
and Salomon DS: Cripto-1: An oncofetal gene with many faces. Curr
Top Dev Biol. 67:85–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Castro NP, Rangel MC, Nagaoka T,
Salomon DS and Bianco C: Cripto-1: An embryonic gene that promotes
tumorigenesis. Future Oncol. 6:1127–1142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strizzi L, Bianco C, Normanno N, Seno M,
Wechselberger C, Wallace-Jones B, Khan NI, Hirota M, Sun Y,
Sanicola M, et al: Epithelial mesenchymal transition is a
characteristic of hyperplasias and tumors in mammary gland from
MMTV-Cripto-1 transgenic mice. J Cell Physiol. 201:266–276. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wechselberger C, Ebert AD, Bianco C, Khan
NI, Sun Y, Wallace-Jones B, Montesano R and Salomon DS: Cripto-1
enhances migration and branching morphogenesis of mouse mammary
epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 266:95–105. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wechselberger C, Strizzi L, Kenney N,
Hirota M, Sun Y, Ebert A, Orozco O, Bianco C, Khan NI,
Wallace-Jones B, et al: Human Cripto-1 overexpression in the mouse
mammary gland results in the development of hyperplasia and
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 24:4094–4105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Strizzi L, Bianco C, Normanno N and
Salomon D: Cripto-1: A multifunctional modulator during
embryogenesis and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 24:5731–5741. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rangel MC, Karasawa H, Castro NP, Nagaoka
T, Salomon DS and Bianco C: Role of Cripto-1 during
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer. Am
J Pathol. 180:2188–2200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K,
Bronner-Fraser M and Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:
The importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J
Clin Invest. 119:1438–1449. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prasad CP, Rath G, Mathur S, Bhatnagar D,
Parshad R and Ralhan R: Expression analysis of E-cadherin, Slug and
GSK3beta in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast. BMC Cancer.
9:3252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Che Q, Bian Y, Zhou Q, Jiang F, Tong
H, Ke J, Wang K and Wan XP: Autocrine motility factor promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer via MAPK
signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 47:1017–1024. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adamson ED, Minchiotti G and Salomon DS:
Cripto: A tumor growth factor and more. J Cell Physiol.
190:267–278. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bianco C, Normanno N, De Luca A, Maiello
MR, Wechselberger C, Sun Y, Khan N, Adkins H, Sanicola M,
Vonderhaar B, et al: Detection and localization of Cripto-1 binding
in mouse mammary epithelial cells and in the mouse mammary gland
using an immunoglobulin-cripto-1 fusion protein. J Cell Physiol.
190:74–82. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei B, Jin W, Ruan J, Xu Z, Zhou Y, Liang
J, Cheng H, Jin K, Huang X, Lu P, et al: Cripto-1 expression and
its prognostic value in human bladder cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
36:1105–1113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang JH, Wei W, Xu J, Guo ZX, Xiao CZ,
Zhang YF, Jian PE, Wu XL, Shi M and Guo RP: Elevated expression of
Cripto-1 correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:35116–35128. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagaoka T, Karasawa H, Castro NP, Rangel
MC, Salomon DS and Bianco C: An evolving web of signaling networks
regulated by Cripto-1. Growth Factors. 30:13–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bianco C, Castro NP, Baraty C, Rollman K,
Held N, Rangel MC, Karasawa H, Gonzales M, Strizzi L and Salomon
DS: Regulation of human Cripto-1 expression by nuclear receptors
and DNA promoter methylation in human embryonal and breast cancer
cells. J Cell Physiol. 228:1174–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shukla A, Ho Y, Liu X, Ryscavage A and
Glick AB: Cripto-1 alters keratinocyte differentiation via blockade
of transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling: Role in skin
carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 6:509–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu CH, Wang Y, Qian LH, Yu LK, Zhang XW
and Wang QB: Serum Cripto-1 is a novel biomarker for non-small cell
lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Clin Respir J. Nov
25–2015.(Epub ahead of print) doi: 10.1111/crj.12414. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gong YP, Yarrow PM, Carmalt HL, Kwun SY,
Kennedy CW, Lin BP, Xing PX and Gillett DJ: Overexpression of
Cripto and its prognostic significance in breast cancer: A study
with long-term survival. Eur J Surg Oncol. 33:438–443. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Klauzinska M, Castro NP, Rangel MC, Spike
BT, Gray PC, Bertolette D, Cuttitta F and Salomon D: The
multifaceted role of the embryonic gene Cripto-1 in cancer, stem
cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Semin Cancer Biol.
29:51–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong XY, Zhang LH, Jia SQ, Shi T, Niu ZJ,
Du H, Zhang GG, Hu Y, Lu AP, Li JY, et al: Positive association of
up-regulated Cripto-1 and down-regulated E-cadherin with tumour
progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Histopathology.
52:560–568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Strizzi L, Bianco C, Raafat A, Abdallah W,
Chang C, Raafat D, Hirota M, Hamada S, Sun Y, Normanno N, et al:
Netrin-1 regulates invasion and migration of mouse mammary
epithelial cells overexpressing Cripto-1 in vitro and in vivo. J
Cell Sci. 118:4633–4643. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou CL, Zhang ZH, Huang DL and Sun AJ:
LiCl suppresses tumor growth and inhibits DNA replication in
prostate cancer. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 41:475–478. 2012.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang F, Phiel CJ, Spece L, Gurvich N and
Klein PS: Inhibitory phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3
(GSK-3) in response to lithium. Evidence for autoregulation of
GSK-3. J Biol Chem. 278:33067–33077. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang C, Chen W, Wang X, Zhao J, Li Q and
Fu Z: Cripto-1 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:4212852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Z, Li G, Wu L, Weng D, Li X and Yao K:
Cripto-1 overexpression is involved in the tumorigenesis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:3152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|