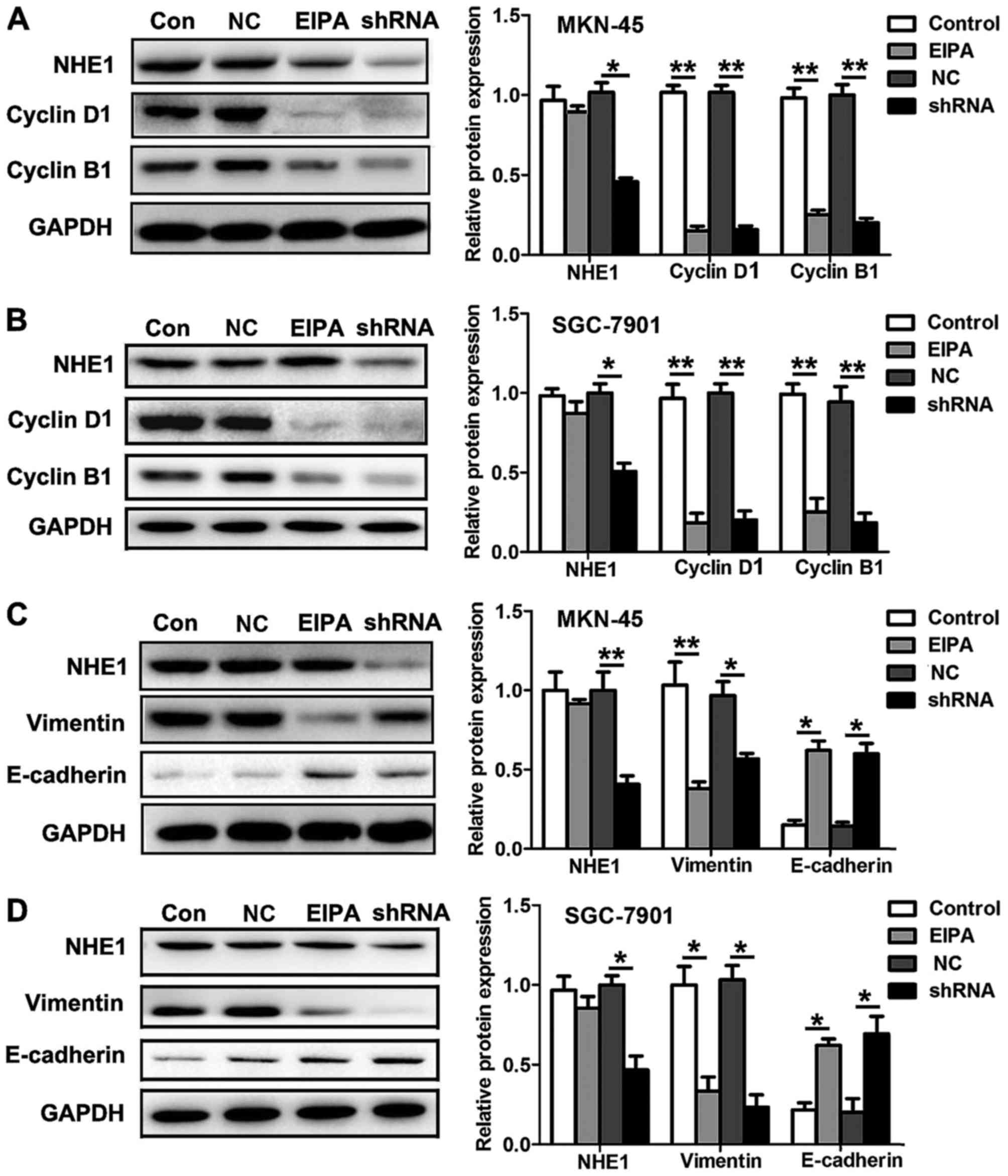
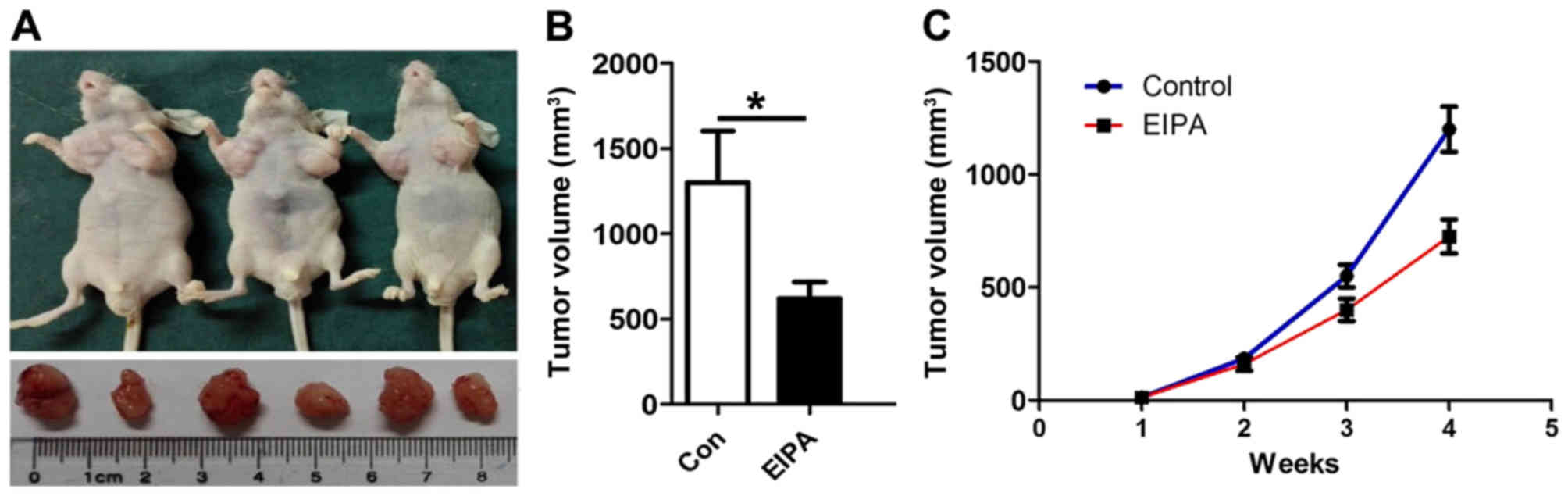
|
1
|
Ang YL, Yong WP and Tan P: Translating
gastric cancer genomics into targeted therapies. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 100:141–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Quéro L, Guillerm S and Hennequin C:
Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for gastric cancer. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 7:102–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dehal A, Smith JJ and Nash GM:
Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy: An
evidence-based review-past, present and future. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 7:143–157. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mattar R, Nonogaki S, Silva C, Alves V and
Gama-Rodrigues JJ: P53 and Rb tumor suppressor gene alterations in
gastric cancer. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 59:172–180.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kanamala M, Wilson WR, Yang M, Palmer BD
and Wu Z: Mechanisms and biomaterials in pH-responsive tumour
targeted drug delivery: A review. Biomaterials. 85:152–167. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parks SK, Cormerais Y, Marchiq I and
Pouyssegur J: Hypoxia optimises tumour growth by controlling
nutrient import and acidic metabolite export. Mol Aspects Med.
47–48, 3–14. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kato Y, Ozawa S, Miyamoto C, Maehata Y,
Suzuki A, Maeda T and Baba Y: Acidic extracellular microenvironment
and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amith SR and Fliegel L: Regulation of the
Na+/H+ Exchanger (NHE1) in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res.
73:1259–1564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu J, Ji B, Wen G, Yang Y, Jin H, Liu X,
Xie R, Song W, Song P, Dong H, et al: Na+/H+ exchanger 1, Na+/Ca2+
exchanger 1 and calmodulin complex regulates interleukin 6-mediated
cellular behavior of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 37:290–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loo SY, Chang MK, Chua CS, Kumar AP,
Pervaiz S and Clement MV: NHE-1: A promising target for novel
anti-cancer therapeutics. Curr Pharm Des. 18:1372–1382. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reshkin SJ, Cardone RA and Harguindey S:
Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer. Recent Patents
Anticancer Drug Discov. 8:85–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Slepkov E and Fliegel L: Structure and
function of the NHE1 isoform of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem Cell
Biol. 80:499–508. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Odunewu-Aderibigbe A and Fliegel L: The
Na+/H+ exchanger and pH regulation in the heart. IUBMB Life.
66:679–685. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garden OA, Musk P, Worthington-White DA,
Dewey MJ and Rich IN: Silent polymorphisms within the coding region
of human sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform-1 cDNA in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells of leukemia patients: A comparison with
healthy controls. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 120:37–43. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amith SR, Wilkinson JM and Fliegel L:
Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 regulation modulates metastatic potential and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 7:21091–21113. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Bao P, Li Z, Ouyang H, Wu C and Qian
G: Inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis induced by a Na+/H+
exchanger-1 (NHE-1) antisense gene on drug-resistant human small
cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 21:1243–1249. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Pawlik T,
Sliwowski Z, Ochmański W and Hahn EG: Duodenal mucosal protection
by bicarbonate secretion and its mechanisms. J Physiol Pharmacol.
55 Suppl 2:S5–S17. 2004.
|
|
18
|
Steffan JJ, Snider JL, Skalli O, Welbourne
T and Cardelli JA: Na+/H+ exchangers and RhoA regulate acidic
extracellular pH-induced lysosome trafficking in prostate cancer
cells. Traffic. 10:737–753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fuster DG and Alexander RT: Traditional
and emerging roles for the SLC9 Na+/H+ exchangers. Pflugers Arch.
466:61–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Amith SR and Fliegel L: Regulation of the
Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE1) in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res.
73:1259–1264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khajah MA, Almohri I, Mathew PM and
Luqmani YA: Extracellular alkaline pH leads to increased metastatic
potential of estrogen receptor silenced endocrine resistant breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e763272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boyarsky G, Hanssen C and Clyne LA:
Inadequacy of high K+/nigericin for calibrating BCECF. II.
Intracellular pH dependence of the correction. Am J Physiol.
271:C1146–C1156. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sardet C, Franchi A and Pouysségur J:
Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human
growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 56:271–280.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fliegel L: Molecular biology of the
myocardial Na+/H+ exchanger. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 44:228–237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kemp G, Young H and Fliegel L: Structure
and function of the human Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1. Channels.
2:329–336. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiang Y, Chou CY, Hsu KF, Huang YF and
Shen MR: EGF upregulates Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 by
post-translational regulation that is important for cervical cancer
cell invasiveness. J Cell Physiol. 214:810–819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stock C, Jungmann O and Seidler DG:
Decorin and chondroitin-6 sulfate inhibit B16V melanoma cell
migration and invasion by cellular acidification. J Cell Physiol.
226:2641–2650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rebillard A, Tekpli X, Meurette O, Sergent
O, LeMoigne-Muller G, Vernhet L, Gorria M, Chevanne M, Christmann
M, Kaina B, et al: Cisplatin-induced apoptosis involves membrane
fluidification via inhibition of NHE1 in human colon cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:7865–7874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jones EM, Cochrane CA and Percival SL: The
effect of pH on the extracellular matrix and biofilms. Adv Wound
Care. 4:431–439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Turk B, Dolenc I, Lenarcic B, Krizaj I,
Turk V, Bieth JG and Björk I: Acidic pH as a physiological
regulator of human cathepsin L activity. Eur J Biochem.
259:926–932. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Greco MR, Antelmi E, Busco G, Guerra L,
Rubino R, Casavola V, Reshkin SJ and Cardone RA: Protease activity
at invadopodial focal digestive areas is dependent on NHE1-driven
acidic pHe. Oncol Rep. 31:940–946. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yonezawa N, Nishida E and Sakai H: pH
control of actin polymerization by cofilin. J Biol Chem.
260:14410–14412. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang X, Wang D, Dong W, Song Z and Dou K:
Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 by 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)
amiloride reduces hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma invasion
and motility. Cancer Lett. 295:198–204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Weaver BA: How Taxol/paclitaxel kills
cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 25:2677–2681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Collins K, Jacks T and Pavletich NP: The
cell cycle and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:2776–2778. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Santo L, Siu KT and Raje N: Targeting
cyclin-dependent kinases and cell cycle progression in human
cancers. Semin Oncol. 42:788–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Putney LK, Denker SP and Barber DL: The
changing face of the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE1: Structure, regulation,
and cellular actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 42:527–552. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Smith BN and Bhowmick NA: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:E172016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ipekci T, Ozden F, Unal B, Saygin C,
Uzunaslan D and Ates E: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers
β-catenin, Snail, and E-cadherin do not predict disease free
survival in prostate adenocarcinoma: A prospective study. Pathol
Oncol Res. 21:1209–1216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yagasaki R, Noguchi M, Minami M and
Earashi M: Clinical significance of E-cadherin and vimentin
co-expression in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 9:755–761.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dorudi S, Sheffield JP, Poulsom R,
Northover JM and Hart IR: E-cadherin expression in colorectal
cancer. An immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Am J
Pathol. 142:981–986. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li K, Dan Z, Hu X, Gesang L, Ze Y and
Bianba Z: CD14 regulates gastric cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion in vitro. Oncol Rep. 30:2725–2732.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou Y, Li G, Wu J, Zhang Z, Wu Z, Fan P,
Hao T, Zhang X, Li M, Zhang F, et al: Clinicopathological
significance of E-cadherin, VEGF, and MMPs in gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 31:549–558. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|