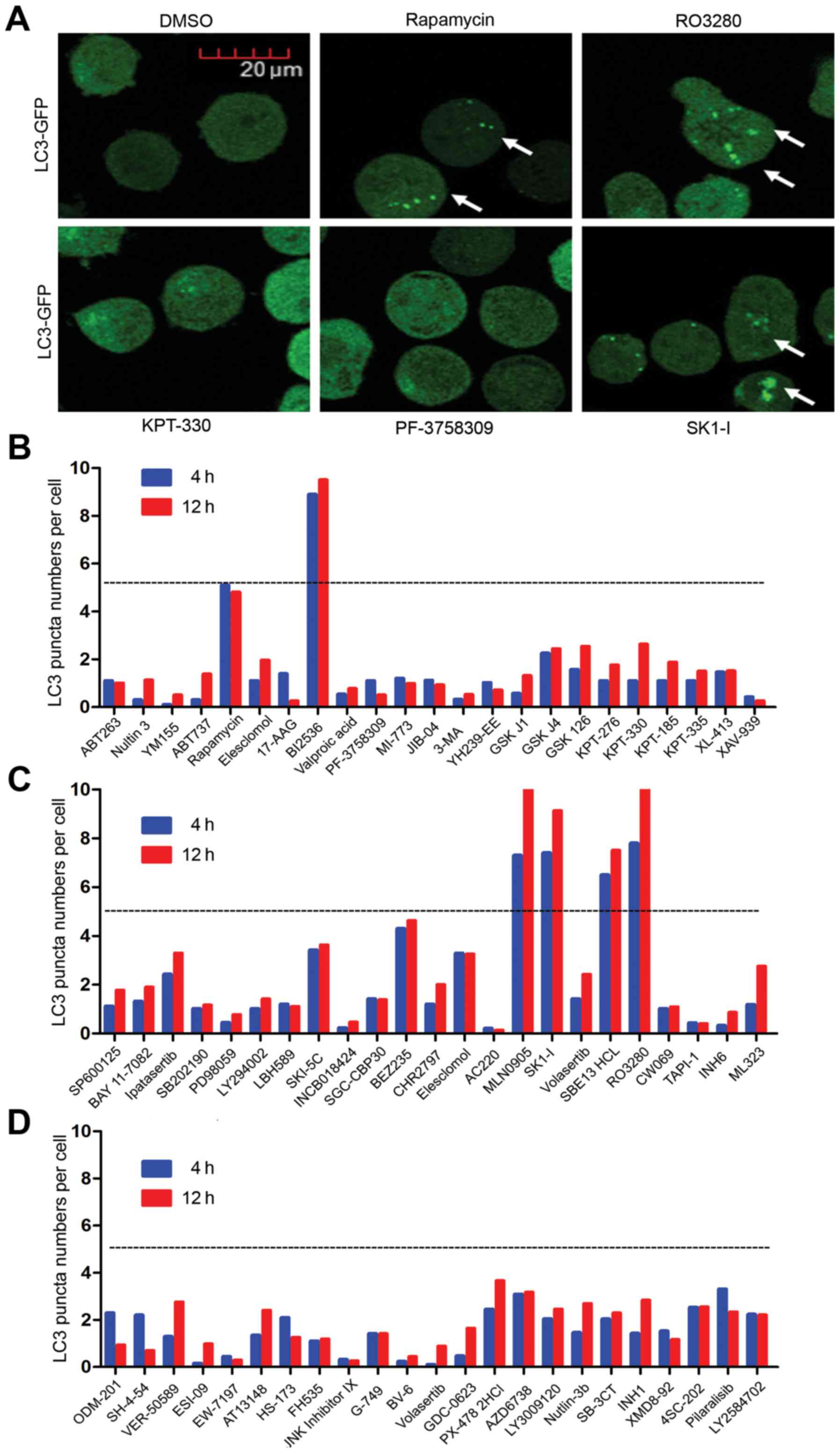
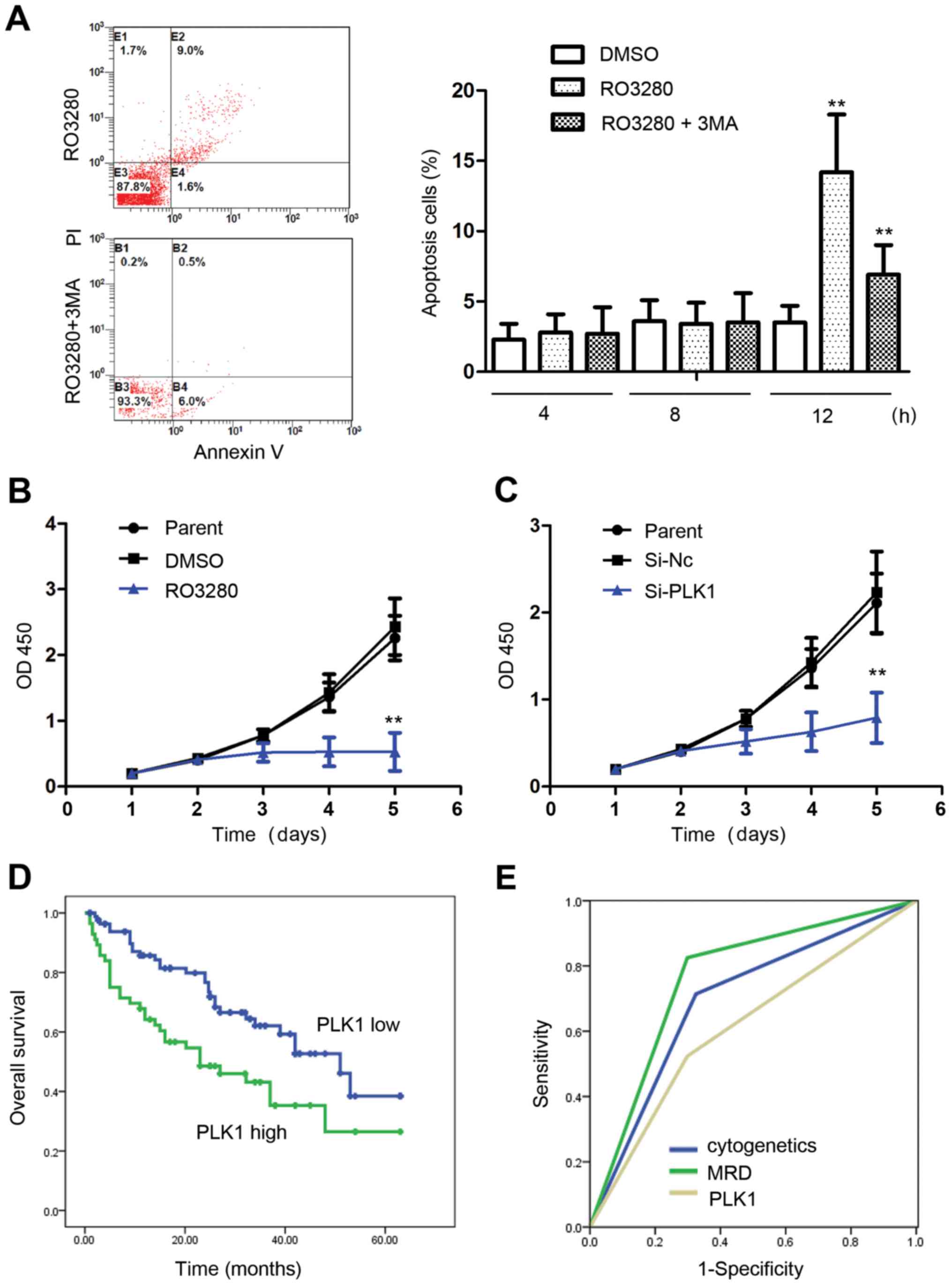
|
1
|
Watson AS, Riffelmacher T, Stranks A,
Williams O, De Boer J, Cain K, MacFarlane M, McGouran J, Kessler B,
Khandwala S, et al: Autophagy limits proliferation and glycolytic
metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov.
1:150082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Radwan SM, Hamdy NM, Hegab HM and
El-Mesallamy HO: Beclin-1 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α genes
expression: potential biomarkers in acute leukemia patients. Cancer
Biomark. 16:619–626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu B, Yue QF, Chen Y, Bu FD, Sun CY and
Liu XY: Expression of autophagy related gene BECLIN-1 and number of
autophagic vacuoles in bone marrow mononuclear cells from 40
myelodysplastic syndromes patients and their significance. Zhongguo
Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 23:146–149. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Piya S, Kornblau SM, Ruvolo VR, Mu H,
Ruvolo PP, McQueen T, Davis RE, Hail N Jr, Kantarjian H, Andreeff
M, et al: Atg7 suppression enhances chemotherapeutic agent
sensitivity and overcomes stroma-mediated chemoresistance in acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood. 128:1260–1269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim Y, Eom JI, Jeung HK, Jang JE, Kim JS,
Cheong JW, Kim YS and Min YH: Induction of cytosine
arabinoside-resistant human myeloid leukemia cell death through
autophagy regulation by hydroxychloroquine. Biomed Pharmacother.
73:87–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zare-Abdollahi D, Safari S, Movafagh A,
Ghadiani M, Tabarraee M, Riazi-Isfahani S, Gorji S, Keyvan L and
Gachkar L: Expression analysis of BECN1 in acute myeloid leukemia:
association with distinct cytogenetic and molecular abnormalities.
Int J Lab Hematol. 38:125–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bertacchini J, Heidari N, Mediani L,
Capitani S, Shahjahani M, Ahmadzadeh A and Saki N: Targeting
PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:2337–2347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng Z, Wang RY, Qiu YH, Mak DH, Coombes
K, Yoo SY, Zhang Q, Jessen K, Liu Y, Rommel C, et al: MLN0128, a
novel mTOR kinase inhibitor, disrupts survival signaling and
triggers apoptosis in AML and AML stem/progenitor cells.
Oncotarget. 7:55083–55097. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lindblad O, Cordero E, Puissant A,
Macaulay L, Ramos A, Kabir NN, Sun J, Vallon-Christersson J,
Haraldsson K, Hemann MT, et al: Aberrant activation of the
PI3K/mTOR pathway promotes resistance to sorafenib in AML.
Oncogene. 35:5119–5131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maire V, Némati F, Richardson M,
Vincent-Salomon A, Tesson B, Rigaill G, Gravier E, Marty-Prouvost
B, De Koning L, Lang G, et al: Polo-like kinase 1: a potential
therapeutic option in combination with conventional chemotherapy
for the management of patients with triple-negative breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 73:813–823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deeraksa A, Pan J, Sha Y, Liu XD, Eissa
NT, Lin SH and Yu-Lee LY: Plk1 is upregulated in
androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells and its inhibition leads
to necroptosis. Oncogene. 32:2973–2983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang G, Zhang Z and Liu Z: Polo-like
kinase 1 is overexpressed in renal cancer and participates in the
proliferation and invasion of renal cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
34:1887–1894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ackermann S, Goeser F, Schulte JH, Schramm
A, Ehemann V, Hero B, Eggert A, Berthold F and Fischer M: Polo-like
kinase 1 is a therapeutic target in high-risk neuroblastoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:731–741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Renner AG, Dos Santos C, Recher C, Bailly
C, Créancier L, Kruczynski A, Payrastre B and Manenti S: Polo-like
kinase 1 is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia and its
inhibition preferentially targets the proliferation of leukemic
cells. Blood. 114:659–662. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Du XL, Wang CJ, Lin DC, Ruan X,
Feng YB, Huo YQ, Peng H, Cui JL, Zhang TT, et al: Reciprocal
activation between PLK1 and Stat3 contributes to survival and
proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
142:521–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Behren A, Mühlen S, Sanhueza GA Acuna,
Schwager C, Plinkert PK, Huber PE, Abdollahi A and Simon C:
Phenotype-assisted transcriptome analysis identifies FOXM1
downstream from Ras-MKK3-p38 to regulate in vitro cellular
invasion. Oncogene. 29:1519–1530. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Valsasina B, Beria I, Alli C, Alzani R,
Avanzi N, Ballinari D, Cappella P, Caruso M, Casolaro A, Ciavolella
A, et al: NMS-P937, an orally available, specific small-molecule
polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor with antitumor activity in solid and
hematologic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1006–1016. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hikichi Y, Honda K, Hikami K, Miyashita H,
Kaieda I, Murai S, Uchiyama N, Hasegawa M, Kawamoto T, Sato T, et
al: TAK-960, a novel, orally available, selective inhibitor of
polo-like kinase 1, shows broad-spectrum preclinical antitumor
activity in multiple dosing regimens. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:700–709.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen S, Bartkovitz D, Cai J, Chen Y, Chen
Z, Chu XJ, Le K, Le NT, Luk KC, Mischke S, et al: Identification of
novel, potent and selective inhibitors of polo-like kinase 1.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:1247–1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gumireddy K, Reddy MV, Cosenza SC,
Boominathan R, Baker SJ, Papathi N, Jiang J, Holland J and Reddy
EP: ON01910, a non-ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor of
Plk1, is a potent anticancer agent. Cancer Cell. 7:275–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Talati C, Griffiths EA, Wetzler M and Wang
ES: Polo-like kinase inhibitors in hematologic malignancies. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 98:200–210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hao Z and Kota V: Volasertib for AML:
clinical use and patient consideration. Onco Targets Ther.
8:1761–1771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gutteridge RE, Ndiaye MA, Liu X and Ahmad
N: Plk1 inhibitors in cancer therapy: from laboratory to clinics.
Mol Cancer Ther. 15:1427–1435. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng L, Ma Y, Sun J, Shen Q, Liu L, Lu H,
Wang F, Yue Y, Li J, Zhang S, et al: YY1-MIR372-SQSTM1 regulatory
axis in autophagy. Autophagy. 10:1442–1453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang KF, Yang H, Jiang WQ, Li S and Cai
YC: Puquitinib mesylate (XC-302) induces autophagy via inhibiting
the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal cancer cells.
Int J Mol Med. 36:1556–1562. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang NN, Li ZH, Zhao H, Tao YF, Xu LX, Lu
J, Cao L, Du XJ, Sun LC, Zhao WL, et al: Molecular targeting of the
oncoprotein PLK1 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: RO3280, a
novel PLK1 inhibitor, induces apoptosis in leukemia cells. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:1266–1292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Price MM, Oskeritzian CA, Falanga YT,
Harikumar KB, Allegood JC, Alvarez SE, Conrad D, Ryan JJ, Milstien
S and Spiegel S: A specific sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor
attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a mast
cell-dependent murine model of allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 131:501–511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gjertsen BT and Schöffski P: Discovery and
development of the polo-like kinase inhibitor volasertib in cancer
therapy. Leukemia. 29:11–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X and Erikson RL: Polo-like kinase
(Plk)1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:5789–5794. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle
kinases in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 17:60–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang H, Tian C, Sun J, Chen LN, Lv Y, Yang
XD, Xiao K, Wang J, Chen C, Shi Q, et al: Overexpression of PLK3
mediates the degradation of abnormal prion proteins dependent on
chaperone-mediated autophagy. Mol Neurobiol. Jun 25–2016.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim T, Mehta SL, Kaimal B, Lyons K,
Dempsey RJ and Vemuganti R: Poststroke Induction of α-synuclein
mediates ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci. 36:7055–7065. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Petherick KJ, Conway OJ, Mpamhanga C,
Osborne SA, Kamal A, Saxty B and Ganley IG: Pharmacological
inhibition of ULK1 kinase blocks mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR)-dependent autophagy. J Biol Chem. 290:287262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan XY, Tian C, Wang H, Xu Y, Ren K, Zhang
BY, Gao C, Shi Q, Meng G, Zhang LB, et al: Activation of the
AMPK-ULK1 pathway plays an important role in autophagy during prion
infection. Sci Rep. 5:147282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Basu S, Rajakaruna S, Reyes B, Van
Bockstaele E and Menko AS: Suppression of MAPK/JNK-MTORC1 signaling
leads to premature loss of organelles and nuclei by autophagy
during terminal differentiation of lens fiber cells. Autophagy.
10:1193–1211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Evangelisti C, Evangelisti C, Bressanin D,
Buontempo F, Chiarini F, Lonetti A, Soncin M, Spartà A, McCubrey JA
and Martelli AM: Targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
in acute myelogenous leukemia. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
17:921–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Callera F, Lopes CO, Rosa ES and Mulin CC:
Lack of antileukemic activity of rapamycin in elderly patients with
acute myeloid leukemia evolving from a myelodysplastic syndrome.
Leuk Res. 32:1633–1634. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zou H, Li L, Carcedo I Garcia, Xu ZP,
Monteiro M and Gu W: Synergistic inhibition of colon cancer cell
growth with nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and PI3K/mTOR dual
inhibitor BEZ235 through apoptosis. Int J Nanomed. 11:1947–1958.
2016.
|
|
39
|
Park HS, Hong SK, Oh MM, Yoon CY, Jeong
SJ, Byun SS, Cheon J, Lee SE and Moon G: Synergistic antitumor
effect of NVP-BEZ235 and sunitinib on docetaxel-resistant human
castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
34:3457–3468. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|