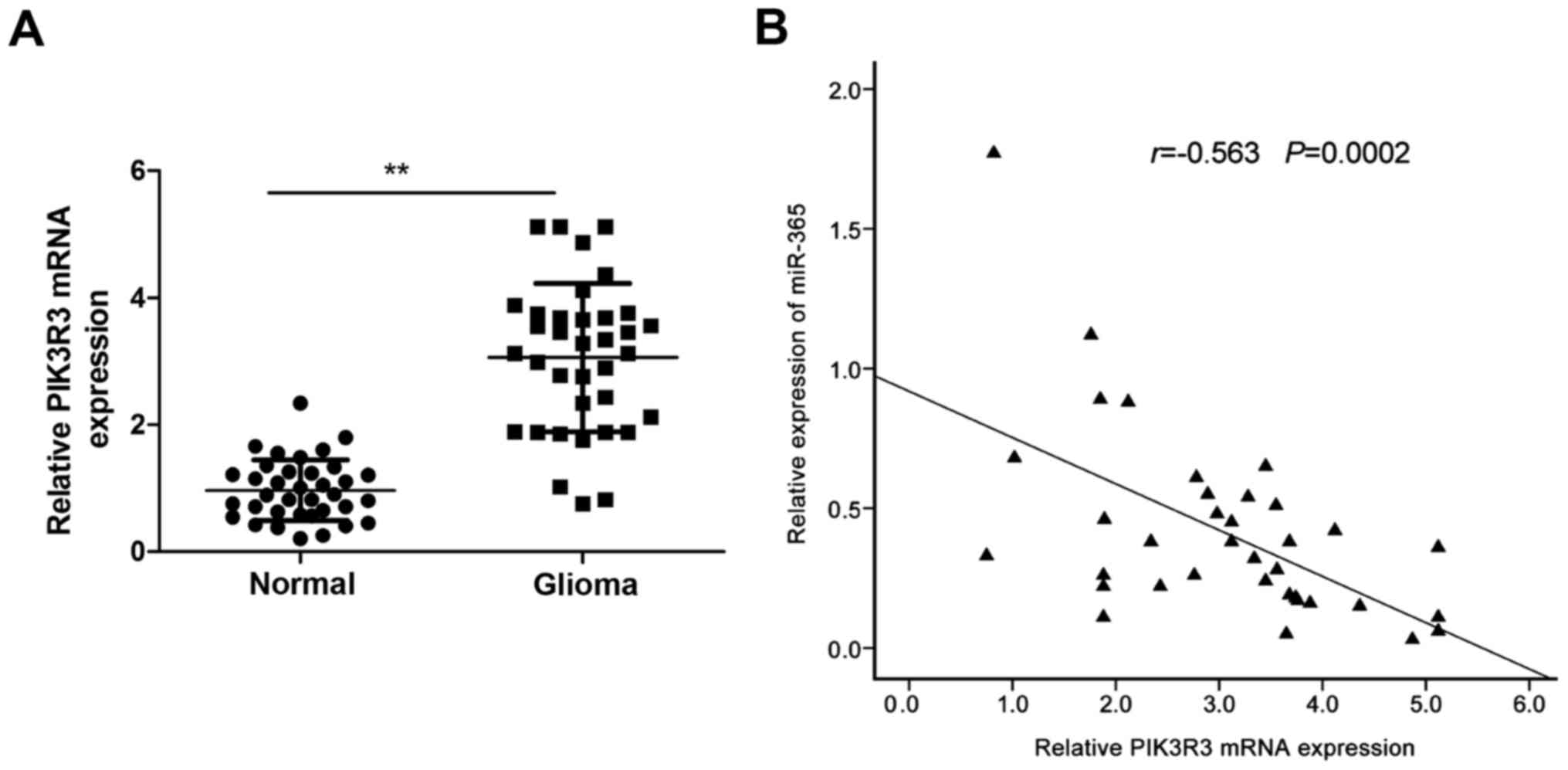
|
1
|
Reardon DA, Rich JN, Friedman HS and
Bigner DD: Recent advances in the treatment of malignant
astrocytoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:1253–1265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clarke J, Butowski N and Chang S: Recent
advances in therapy for glioblastoma. Arch Neurol. 67:279–283.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grauer OM, Wesseling P and Adema GJ:
Immunotherapy of diffuse gliomas: Biological background, current
status and future developments. Brain Pathol. 19:674–693. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Almeida MI, Reis RM and Calin GA: MicroRNA
history: Discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat
Res. 717:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McManus MT: MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 13:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
England B, Huang T and Karsy M: Current
understanding of the role and targeting of tumor suppressor p53 in
glioblastoma multiforme. Tumour Biol. 34:2063–2074. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tivnan A and McDonald KL: Current progress
for the use of miRNAs in glioblastoma treatment. Mol Neurobiol.
48:757–768. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi J, Rice SJ, Salzberg AC, Runkle EA,
Liao J, Zander DS and Mu D: MiR-365 regulates lung cancer and
developmental gene thyroid transcription factor 1. Cell Cycle.
11:177–186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun R, Liu Z, Ma G, Lv W, Zhao X, Lei G
and Xu C: Associations of deregulation of mir-365 and its target
mRNA TTF-1 and survival in patients with NSCLC. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:2392–2399. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bai J, Zhang Z, Li X and Liu H:
MicroRNA-365 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant
melanoma by targeting NRP1 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:4913–4922. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo SL, Ye H, Teng Y, Wang YL, Yang G, Li
XB, Zhang C and Yang X, Yang ZZ and Yang X: Akt-p53-miR-365-cyclin
D1/cdc25A axis contributes to gastric tumorigenesis induced by PTEN
deficiency. Nat Commun. 4:25442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao J, Zhao P, Chen X, Wang W, Li Y, Xi W,
Zhang W, Hu P, Wang T and Shan L: miR-365 inhibits proliferation
and promotes apoptosis of SOSP9607 osteosarcoma cells. Xi Bao Yu
Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 32:44–48. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nie J, Liu L, Zheng W, Chen L, Wu X, Xu Y,
Du X and Han W: microRNA-365, down-regulated in colon cancer,
inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis of colon
cancer cells by probably targeting Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2.
Carcinogenesis. 33:220–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu K, Li X, Cao Y, Ge Y, Wang J and Shi
B: MiR-132 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3R3. Int J Oncol.
47:1585–1593. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Zhao H, Feng L and Xu S:
MicroRNA-217 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting
Runx2 in human glioma. Am J Transl Res. 8:1482–1491.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao G, Dong W, Meng X, Liu H, Liao H and
Liu S: MiR-511 inhibits growth and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting PIK3R3. Tumour Biol.
36:4453–4459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Li Q, Fei G,
Luo J and Ren T: MicroRNA-7-regulated TLR9 signaling-enhanced
growth and metastatic potential of human lung cancer cells by
altering the phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 3/Akt
pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 24:42–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J,
Liang S, Hasegawa K, Giannakakis A, Poulos N, O'Brien-Jenkins A,
Katsaros D, et al: Integrative genomic analysis of
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase family identifies PIK3R3 as a
potential therapeutic target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:5314–5321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Q, Guo W, Zhang Y, Wu Y and Xiang J:
MiR-19a promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RhoB
in human glioma cells. Neurosci Lett. 628:161–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng T, Zhou L, Zuo L and Luan Y: MiR-506
functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting STAT3. Oncol
Rep. 35:1057–1064. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou M, Liu W, Ma S, Cao H, Peng X, Guo L,
Zhou X, Zheng L, Guo L, Wan M, et al: A novel onco-miR-365 induces
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:1653–1659.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hamada S, Masamune A, Miura S, Satoh K and
Shimosegawa T: MiR-365 induces gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic
cancer cells by targeting the adaptor protein SHC1 and
pro-apoptotic regulator BAX. Cell Signal. 26:179–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Klahan S, Wu MS, Hsi E, Huang CC, Hou MF
and Chang WC: Computational analysis of mRNA expression profiles
identifies the ITG family and PIK3R3 as crucial genes for
regulating triple negative breast cancer cell migration. BioMed Res
Int. 2014:5365912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xia X, Cheng A, Akinmade D and Hamburger
AW: The N-terminal 24 amino acids of the p55 gamma regulatory
subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase binds Rb and induces cell
cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1717–1725. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Chen GB, Tang YC, Sinha RA, Wu Y,
Yap CS, Wang G, Hu J, Xia X, Tan P, et al: Genetic and
bioinformatic analyses of the expression and function of PI3K
regulatory subunit PIK3R3 in an Asian patient gastric cancer
library. BMC Med Genomics. 5:342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang G, Yang X, Li C, Cao X, Luo X and Hu
J: PIK3R3 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1837–1847.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soroceanu L, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Soriano
RH, Aldape K, Misra A, Zha J, Forrest WF, Nigro JM, Modrusan Z, et
al: Identification of IGF2 signaling through
phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 as a
growth-promoting axis in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3466–3471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|