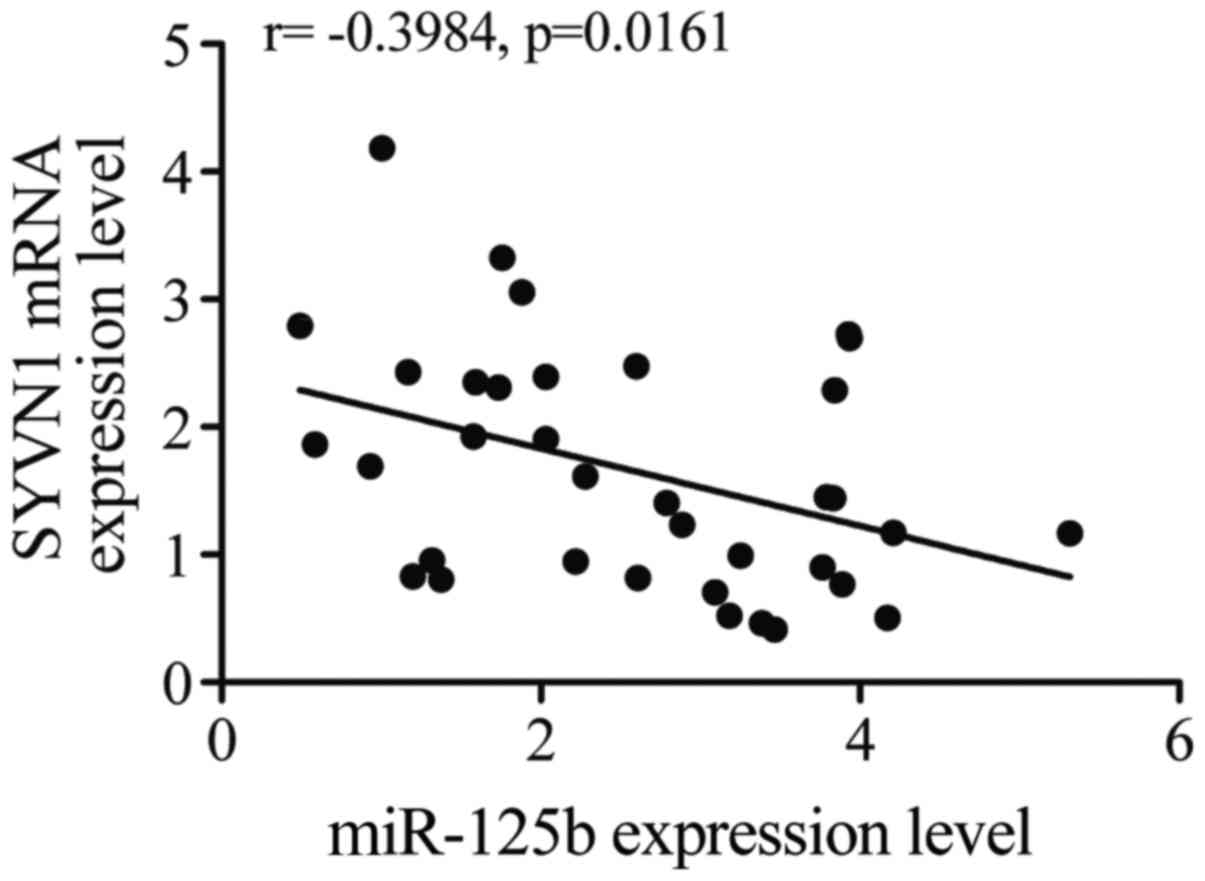
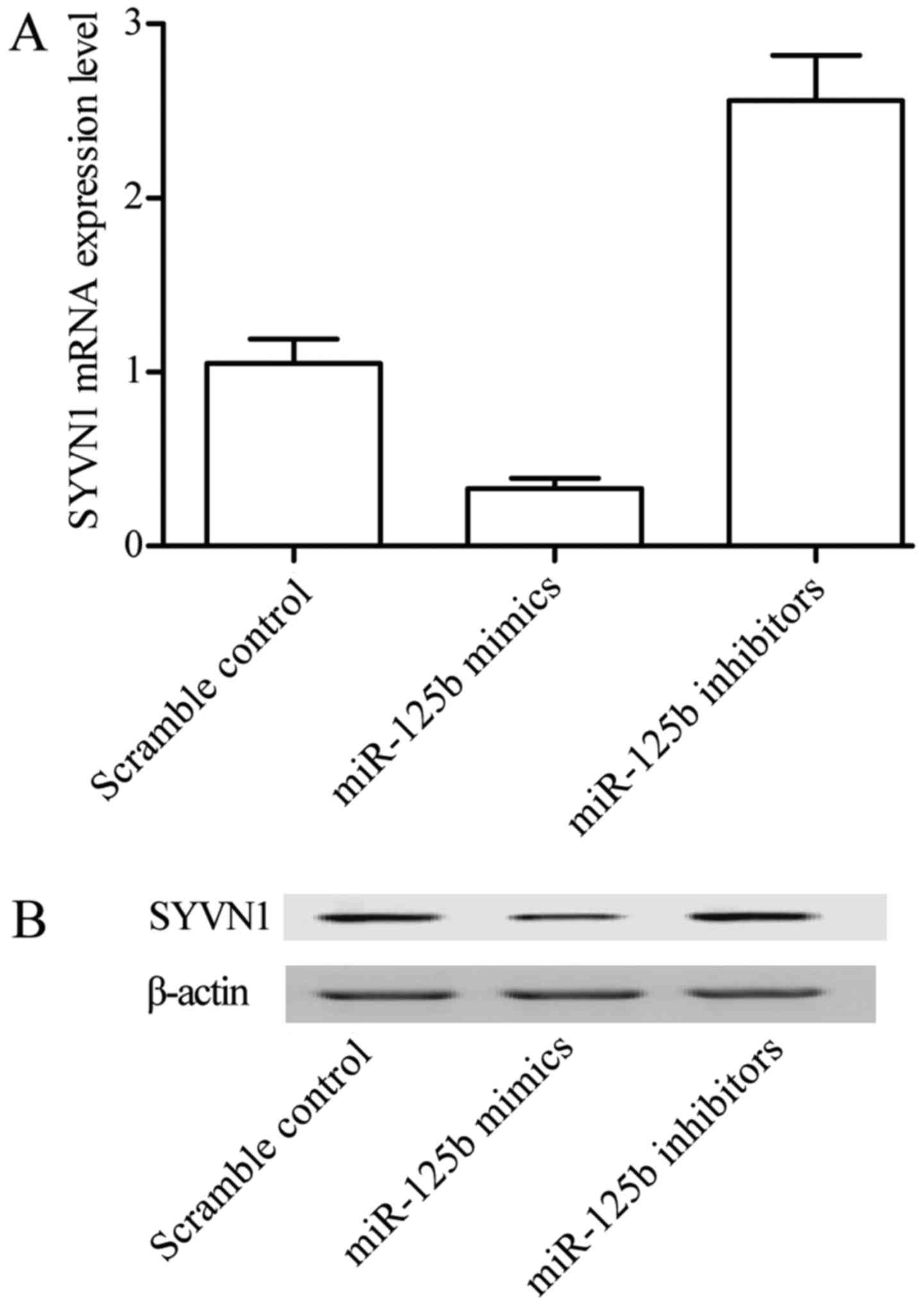
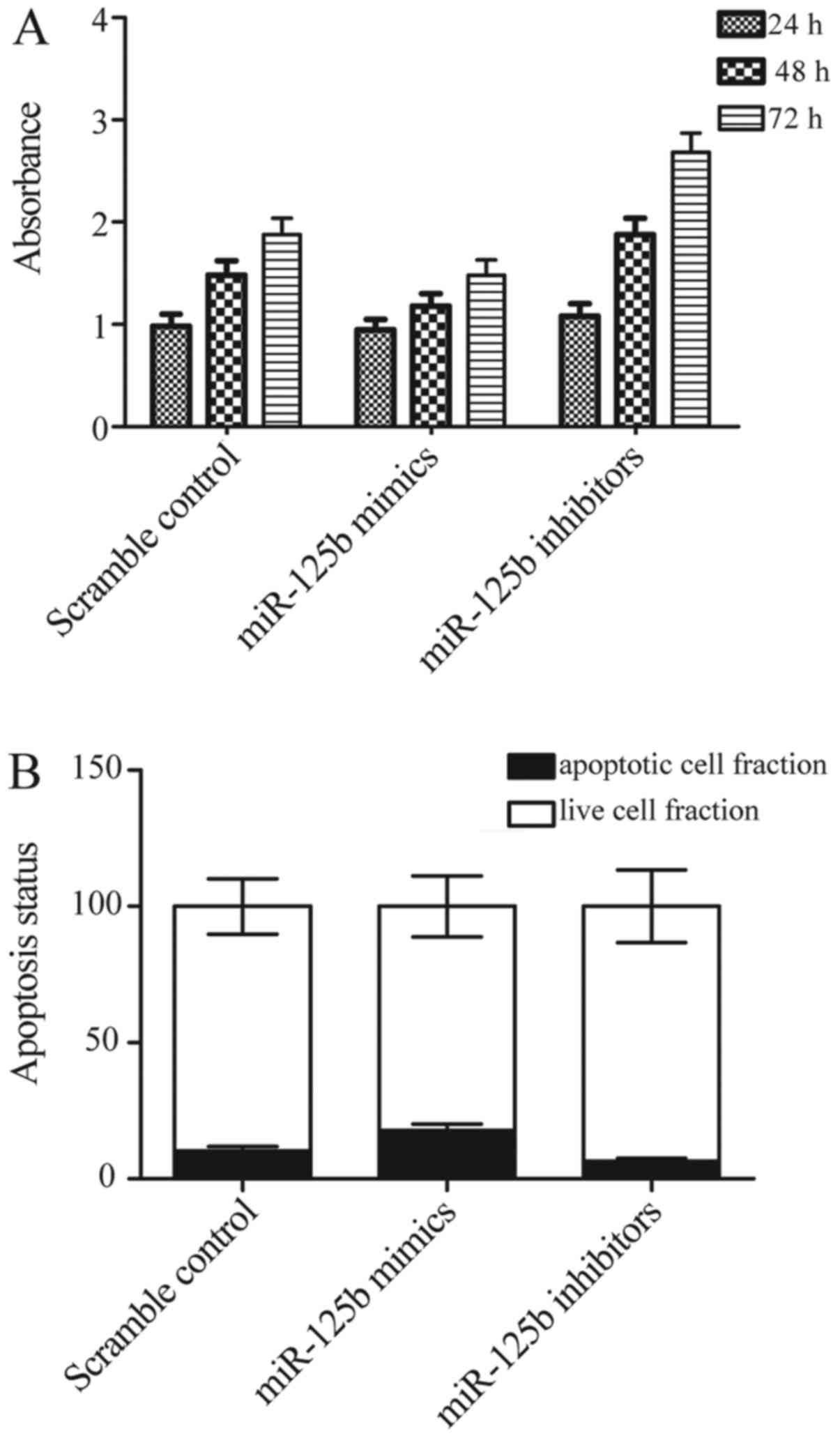
|
1
|
Schaible HG, Richter F, Ebersberger A,
Boettger MK, Vanegas H, Natura G, Vazquez E and von Segond Banchet
G: Joint pain. Exp Brain Res. 196:153–162. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lascelles BD, McFarland JM and Swann H:
Guidelines for safe and effective use of NSAIDs in dogs. Vet Ther.
6:237–251. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blanco FJ, Ochs RL, Schwarz H and Lotz M:
Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol.
146:75–85. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albina JE, Cui S, Mateo RB and Reichner
JS: Nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis in murine peritoneal
macrophages. J Immunol. 150:5080–5085. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fehsel K, Kröncke KD, Meyer KL, Huber H,
Wahn V and Kolb-Bachofen V: Nitric oxide induces apoptosis in mouse
thymocytes. J Immunol. 155:2858–2865. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farrell AJ, Blake DR, Palmer RM and
Moncada S: Increased concentrations of nitrite in synovial fluid
and serum samples suggest increased nitric oxide synthesis in
rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 51:1219–1222. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayashi T, Abe E, Yamate T, Taguchi Y and
Jasin HE: Nitric oxide production by superficial and deep articular
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 40:261–269. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Firestein GS, Yeo M and Zvaifler NJ:
Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Clin Invest.
96:1631–1638. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amano T, Yamasaki S, Yagishita N,
Tsuchimochi K, Shin H, Kawahara K, Aratani S, Fujita H, Zhang L,
Ikeda R, et al: Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel
pathogenic factor for arthropathy. Genes Dev. 17:2436–2449. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murchison EP and Hannon GJ: miRNAs on the
move: miRNA biogenesis and the RNAi machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:223–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J,
Lee J, Provost P, Rådmark O, Kim S, et al: The nuclear RNase III
Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 425:415–419. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF
and Hannon GJ: Processing of primary microRNAs by the
microprocessor complex. Nature. 432:231–235. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nam JW, Shin KR, Han J, Lee Y, Kim VN and
Zhang BT: Human microRNA prediction through a probabilistic
co-learning model of sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:3570–3581. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Swingler TE, Wheeler G, Carmont V, Elliott
HR, Barter MJ, Abu-Elmagd M, Donell ST, Boot-Handford RP,
Hajihosseini MK, Münsterberg A, et al: The expression and function
of microRNAs in chondrogenesis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
64:1909–1919. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong E and Reddi AH: MicroRNAs in
chondrogenesis, articular cartilage, and osteoarthritis:
Implications for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
18:445–453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong S, Yang B, Guo H and Kang F:
MicroRNAs regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 418:587–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dunn W, DuRaine G and Reddi AH: Profiling
microRNA expression in bovine articular cartilage and implications
for mechanotransduction. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2333–2339. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P and
Tsezou A: Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify
novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and
inflammatory networks. PLoS One. 3:e37402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu C, Chen WP and Wang XH: MicroRNA in
osteoarthritis. J Int Med Res. 39:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goldring MB and Marcu KB: Epigenomic and
microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis,
and osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. 18:109–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crowe N, Swingler TE, Le LT, Barter MJ,
Wheeler G, Pais H, Donell ST, Young DA, Dalmay T1 and Clark IM:
Detecting new microRNAs in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes
identifies miR-3085 as a human, chondrocyte-selective, microRNA.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:534–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamasaki S, Yagishita N, Tsuchimochi K,
Kato Y, Sasaki T, Amano T, Beppu M, Aoki H, Nakamura H, Nishioka K,
et al: Resistance to endoplasmic reticulum stress is an acquired
cellular characteristic of rheumatoid synovial cells. Int J Mol
Med. 18:113–117. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yagishita N and Nakajima T: Synoviolin as
a causative factor of arthropathy. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso.
51:(Suppl 10). 1298–1303. 2006.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goettsch C, Rauner M, Pacyna N, Hempel U,
Bornstein SR and Hofbauer LC: miR-125b regulates calcification of
vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol. 179:1594–1600. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean
S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, Fabbri M, Alder H, Liu CG, Calin GA, et al:
Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following
lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles
in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol.
179:5082–5089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Yao N, Zhang J and Liu Z:
MicroRNA-125b is involved in atherosclerosis obliterans in
vitro by targeting podocalyxin. Mol Med Rep. 12:561–568.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luo X, Ranade K, Talker R, Jallal B, Shen
N and Yao Y: microRNA-mediated regulation of innate immune response
in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:2102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shaham L, Binder V, Gefen N, Borkhardt A
and Izraeli S: MiR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.
Leukemia. 26:2011–2018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bousquet M, Quelen C, Rosati R, Mansat-De
Mas V, La Starza R, Bastard C, Lippert E, Talmant P,
Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Leroux D, et al: Myeloid cell differentiation
arrest by miR-125b-1 in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia with the t(2;11)(p21;q23) translocation. J Exp Med.
205:2499–2506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chapiro E, Russell LJ, Struski S, Cavé H,
Radford-Weiss I, Valle VD, Lachenaud J, Brousset P, Bernard OA,
Harrison CJ, et al: A new recurrent translocation t(11;14)(q24;q32)
involving IGH@ and miR-125b-1 in B-cell progenitor acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 24:1362–1364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang GQ, Kai M, Nakano M and Ohkura Y:
Pre-column fluorescence derivatization high-performance liquid
chromatography of opioid peptides in rat brain and its use for
enzymatic peptide characterization. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
39:126–129. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Akbari Moqadam
F, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C, Pieters R and Den
Boer ML: MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug
resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Haematologica. 96:703–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ooi AG, Sahoo D, Adorno M, Wang Y,
Weissman IL and Park CY: MicroRNA-125b expands hematopoietic stem
cells and enriches for the lymphoid-balanced and lymphoid-biased
subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:21505–21510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hampton RY, Gardner RG and Rine J: Role of
26S proteasome and HRD genes in the degradation of
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, an integral endoplasmic
reticulum membrane protein. Mol Biol Cell. 7:2029–2044. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gardner RG, Swarbrick GM, Bays NW, Cronin
SR, Wilhovsky S, Seelig L, Kim C and Hampton RY: Endoplasmic
reticulum degradation requires lumen to cytosol signaling.
Transmembrane control of Hrd1p by Hrd3p. J Cell Biol. 151:69–82.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Friedlander R, Jarosch E, Urban J,
Volkwein C and Sommer T: A regulatory link between ER-associated
protein degradation and the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell
Biol. 2:379–384. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshida H: ER stress and diseases. FEBS J.
274:630–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaneko M, Ishiguro M, Niinuma Y, Uesugi M
and Nomura Y: Human HRD1 protects against ER stress-induced
apoptosis through ER-associated degradation. FEBS Lett.
532:147–152. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ritchlin C: Fibroblast biology. Effector
signals released by the synovial fibroblast in arthritis. Arthritis
Res. 2:356–360. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|