|
1
|
Moroishi T, Hansen CG and Guan KL: The
emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:73–79.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mo JS, Park HW and Guan KL: The Hippo
signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep.
15:642–656. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hong W and Guan KL: The YAP and TAZ
transcription co-activators: Key downstream effectors of the
mammalian Hippo pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:785–793. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnson R and Halder G: The two faces of
Hippo: Targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and
cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:63–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piccolo S, Dupont S and Cordenonsi M: The
biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiol Rev.
94:1287–1312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steinhardt AA, Gayyed MF, Klein AP, Dong
J, Maitra A, Pan D, Montgomery EA and Anders RA: Expression of
Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum Pathol.
39:1582–1589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zender L, Spector MS, Xue W, Flemming P,
Cordon-Cardo C, Silke J, Fan ST, Luk JM, Wigler M, Hannon GJ, et
al: Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer
using an integrative oncogenomic approach. Cell. 125:1253–1267.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim
J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, et al: Inactivation of YAP
oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact
inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 21:2747–2761.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu FX and Guan KL: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Overholtzer M, Zhang J, Smolen GA, Muir B,
Li W, Sgroi DC, Deng CX, Brugge JS and Haber DA: Transforming
properties of YAP, a candidate oncogene on the chromosome
11q22 amplicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12405–12410. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Strano S, Monti O, Pediconi N, Baccarini
A, Fontemaggi G, Lapi E, Mantovani F, Damalas A, Citro G, Sacchi A,
et al: The transcriptional coactivator Yes-associated protein
drives p73 gene-target specificity in response to DNA damage. Mol
Cell. 18:447–459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu MZ, Yao TJ, Lee NP, Ng IO, Chan YT,
Zender L, Lowe SW, Poon RT and Luk JM: Yes-associated protein is an
independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
115:4576–4585. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Dong Q, Zhang Q, Li Z, Wang E and
Qiu X: Overexpression of yes-associated protein contributes to
progression and poor prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Sci. 101:1279–1285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, George J, Deb S, Degoutin JL,
Takano EA, Fox SB, Bowtell DD and Harvey KF: AOCS Study group: The
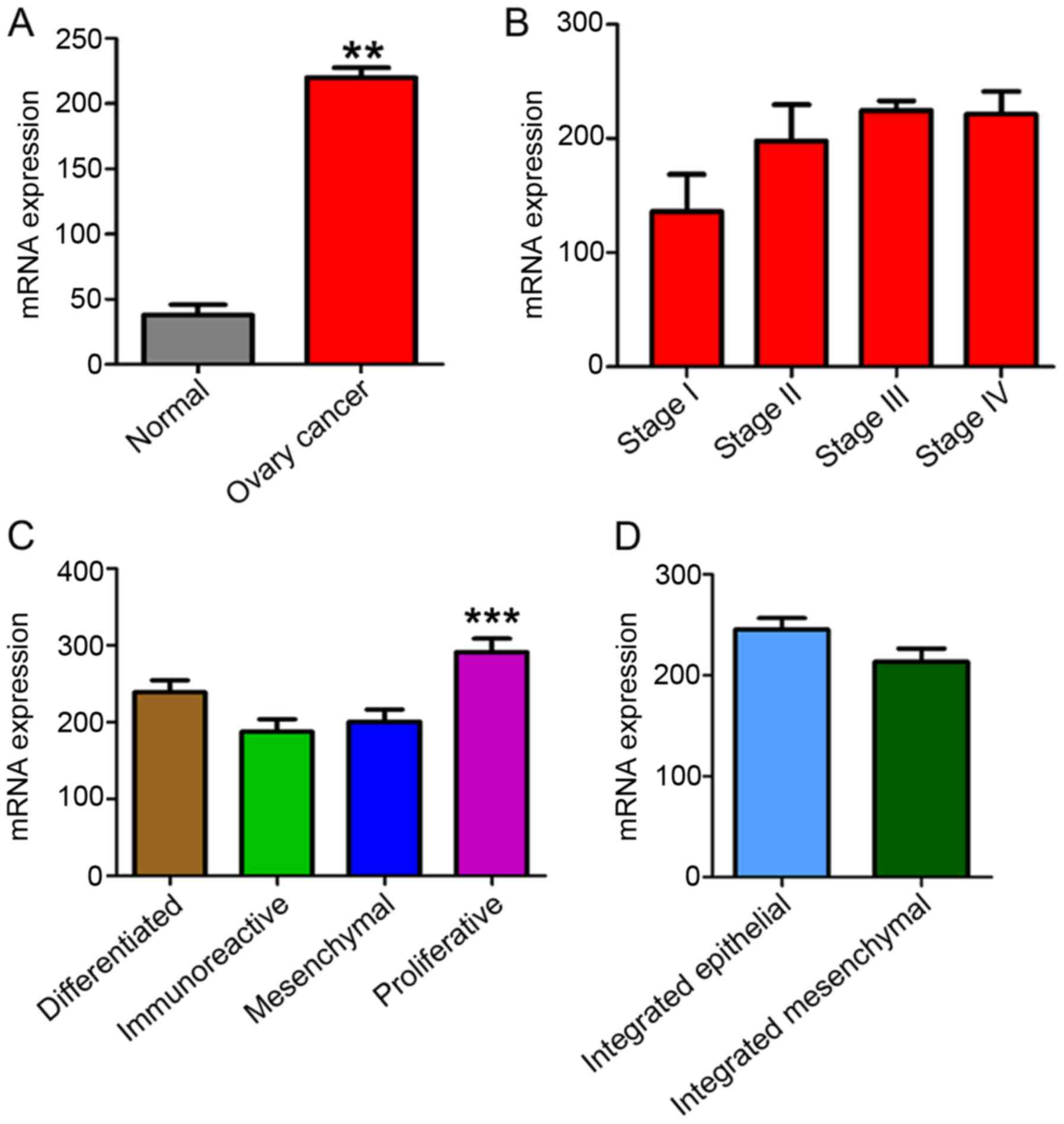
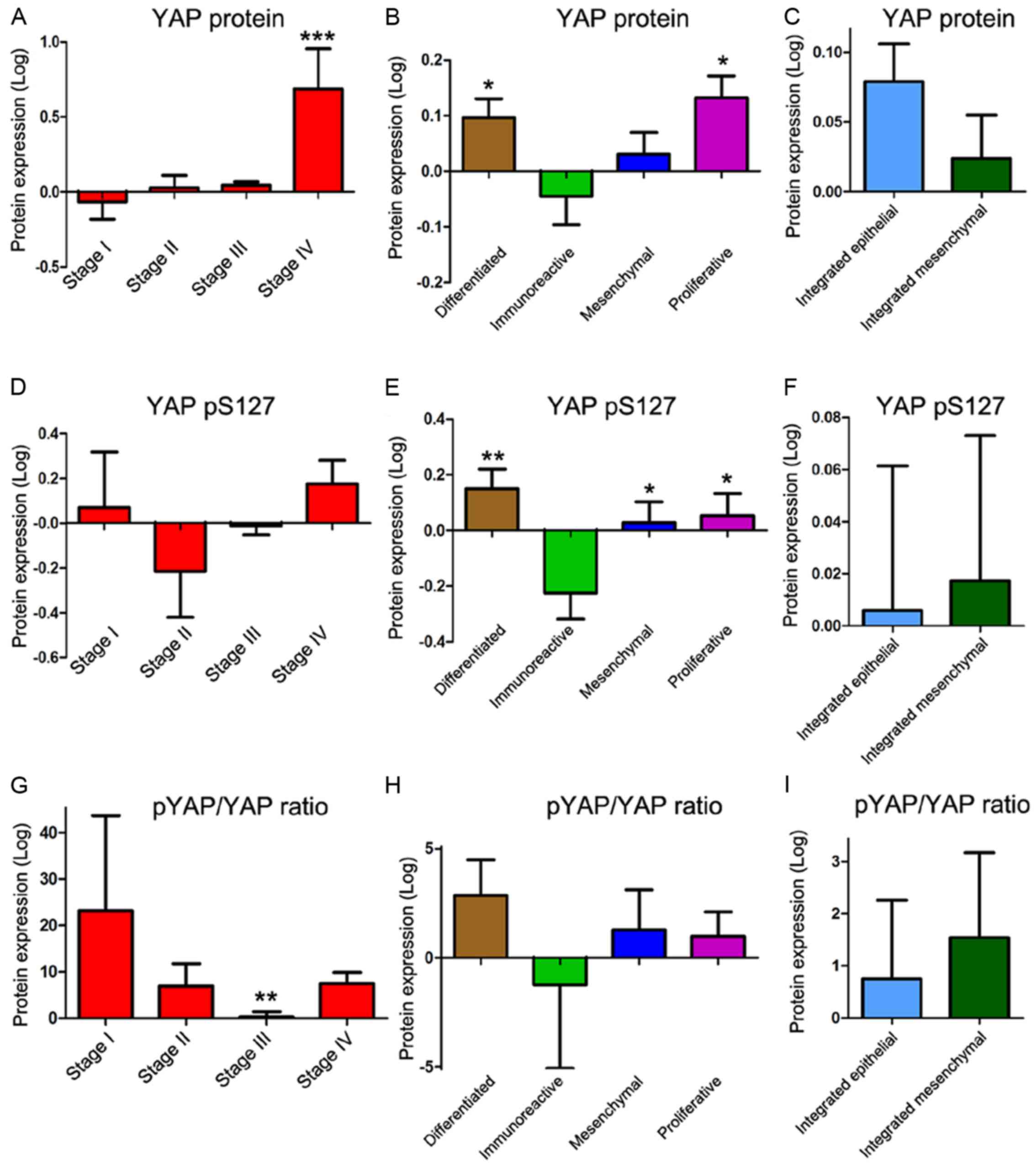
Hippo pathway transcriptional co-activator, YAP, is an ovarian
cancer oncogene. Oncogene. 30:2810–2822. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xia Y, Chang T, Wang Y, Liu Y, Li W, Li M
and Fan HY: YAP promotes ovarian cancer cell tumorigenesis and is
indicative of a poor prognosis for ovarian cancer patients. PLoS
One. 9:e917702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SI, Lim MC, Lim J, Won YJ, Seo SS,
Kang S and Park SY: Incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer
according to histologic subtypes in Korea, 1999 to 2012. J Gynecol
Oncol. 27:e52016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
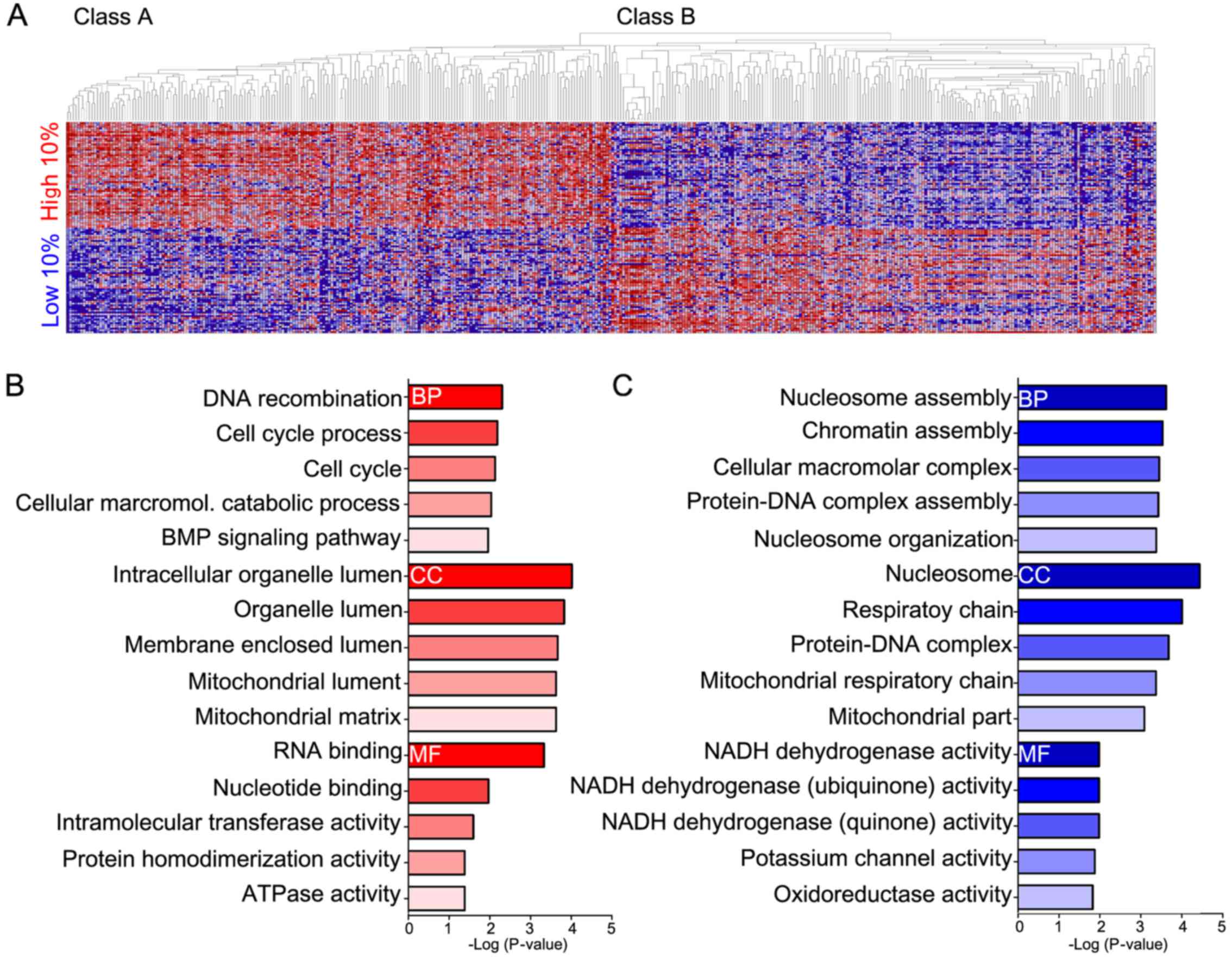
Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C,
Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML, Downing JR, Caligiuri
MA, et al: Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and
class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science.
286:531–537. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D109–D114.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang D, Sun Y, Hu L, Zheng H, Ji P, Pecot
CV, Zhao Y, Reynolds S, Cheng H, Rupaimoole R, et al: Integrated
analyses identify a master microRNA regulatory network for the
mesenchymal subtype in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell.
23:186–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bell D, Berchuck A, Birrer M, Chien J,
Cramer DW, Dao F, Dhir R, DiSaia P, Gabra H, Glenn P, et al: Cancer
Genome Atlas Research Network: Integrated genomic analyses of
ovarian carcinoma. Nature. 474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
DiMeo TA, Anderson K, Phadke P, Fan C,
Perou CM, Naber S and Kuperwasser C: A novel lung metastasis
signature links Wnt signaling with cancer cell self-renewal and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in basal-like breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 69:5364–5373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong J, Feldmann G, Huang J, Wu S, Zhang
N, Comerford SA, Gayyed MF, Anders RA, Maitra A and Pan D:
Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and
mammals. Cell. 130:1120–1133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hall CA, Wang R, Miao J, Oliva E, Shen X,
Wheeler T, Hilsenbeck SG, Orsulic S and Goode S: Hippo pathway
effector Yap is an ovarian cancer oncogene. Cancer Res.
70:8517–8525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|