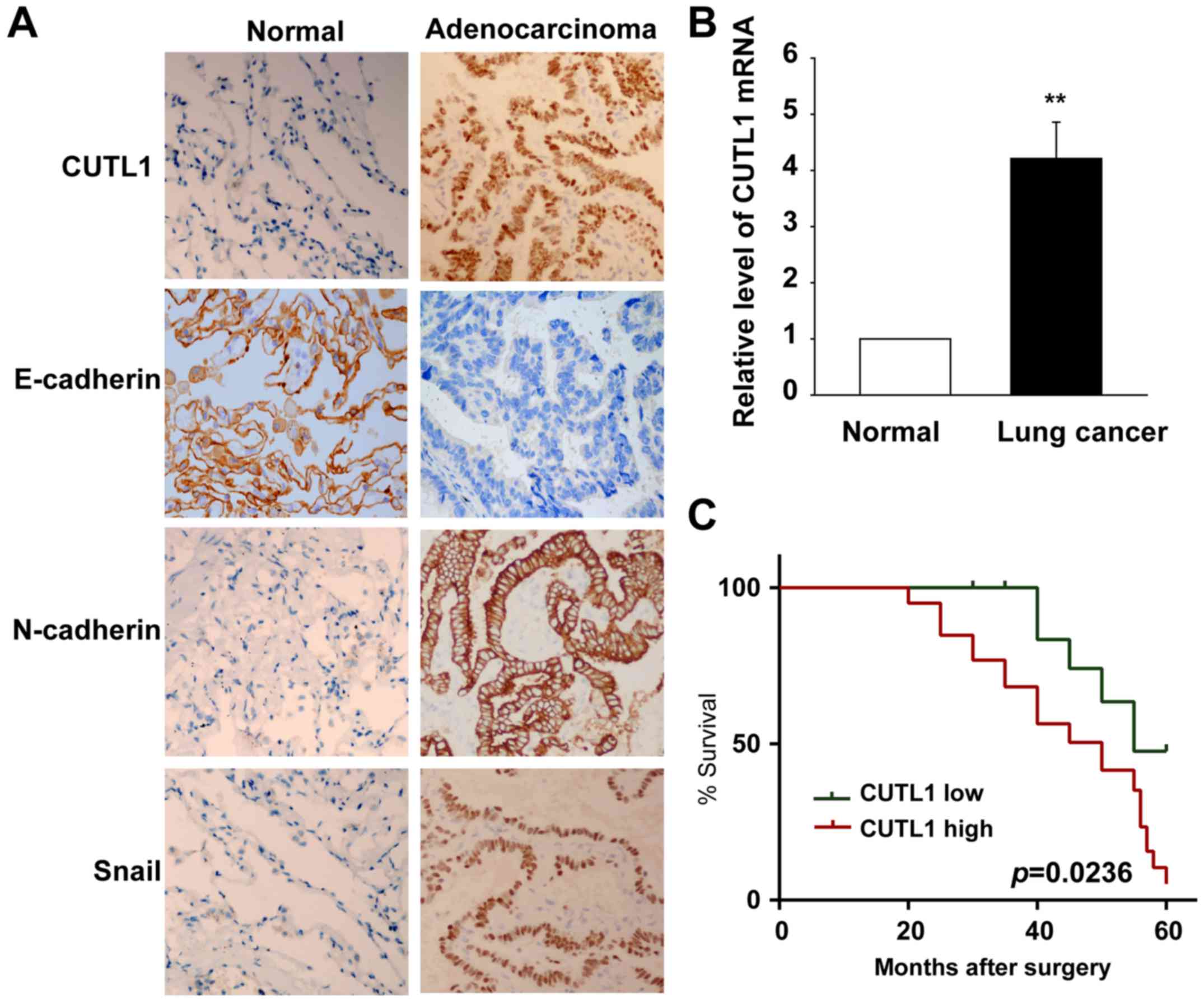
|
1
|
Shtivelman E, Hensing T, Simon GR, Dennis
PA, Otterson GA, Bueno R and Salgia R: Molecular pathways and
therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 5:1392–1433. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC and
Rabe KF: Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent
developments. Lancet. 382:709–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsiao SH, Chung CL, Chou YT, Lee HL, Lin
SE and Liu HE: Identification of subgroup patients with stage
IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer at higher risk for brain
metastases. Lung Cancer. 82:319–323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nepveu A: Role of the multifunctional
CDP/Cut/Cux homeodomain transcription factor in regulating
differentiation, cell growth and development. Gene. 270:1–15. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sansregret L and Nepveu A: The multiple
roles of CUX1: Insights from mouse models and cell-based assays.
Gene. 412:84–94. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu KC, Lin BS, Zhao M, Wang KY and Lan
XP: Cutl1: A potential target for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
25:349–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Truscott M, Raynal L, Premdas P, Goulet B,
Leduy L, Bérubé G and Nepveu A: CDP/Cux stimulates transcription
from the DNA polymerase alpha gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol.
23:3013–3028. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Gurp MF, Pratap J, Luong M, Javed A,
Hoffmann H, Giordano A, Stein JL, Neufeld EJ, Lian JB, Stein GS, et
al: The CCAAT displacement protein/cut homeodomain protein
represses osteocalcin gene transcription and forms complexes with
the retinoblastoma protein-related protein p107 and cyclin A.
Cancer Res. 59:5980–5988. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aleksic T, Bechtel M, Krndija D, von
Wichert G, Knobel B, Giehl K, Gress TM and Michl P: CUTL1 promotes
tumor cell migration by decreasing proteasome-mediated Src
degradation. Oncogene. 26:5939–5949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan X, Wang H, Zhou J, Wang S, Zhang X, Li
T, Nie Y and Liu B: The transcription factor CUTL1 is associated
with proliferation and prognosis in malignant melanoma. Melanoma
Res. 24:198–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ripka S, König A, Buchholz M, Wagner M,
Sipos B, Klöppel G, Downward J, Gress T and Michl P: WNT5A - target
of CUTL1 and potent modulator of tumor cell migration and invasion
in pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis. 28:1178–1187. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng H and Kang Y: Multilayer control of
the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 33:1755–1763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Foroni C, Broggini M, Generali D and Damia
G: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer: Role,
molecular mechanisms and clinical impact. Cancer Treat Rev.
38:689–697. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fabregat I, Fernando J, Mainez J and
Sancho P: TGF-beta signaling in cancer treatment. Curr Pharm Des.
20:2934–2947. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong S, Noh H, Teng Y, Shao J, Rehmani H,
Ding HF, Dong Z, Su SB, Shi H, Kim J, et al: SHOX2 is a direct
miR-375 target and a novel epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
inducer in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 16:279–90.e1, 5. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Michl P and Downward J: CUTL1: A key
mediator of TGFbeta-induced tumor invasion. Cell Cycle. 5:132–134.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Michl P, Ramjaun AR, Pardo OE, Warne PH,
Wagner M, Poulsom R, DArrigo C, Ryder K, Menke A, Gress T, et al:
CUTL1 is a target of TGF(beta) signaling that enhances cancer cell
motility and invasiveness. Cancer Cell. 7:521–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Christiansen JJ and Rajasekaran AK:
Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite
for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 66:8319–8326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nagathihalli NS, Massion PP, Gonzalez AL,
Lu P and Datta PK: Smoking induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in non-small cell lung cancer through HDAC-mediated
downregulation of E-cadherin. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2362–2372. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Liu G, Kang Y, Dong Z, Qian Q and
Ma X: N-cadherin expression is associated with acquisition of EMT
phenotype and with enhanced invasion in erlotinib-resistant lung
cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 8:e576922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng P, Meng HM, Gao WZ, Chen L, Liu XH,
Xiao ZQ, Liu YX, Sui HM, Zhou J, Liu YH, et al: Snail as a key
regulator of PRL-3 gene in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
12:742–749. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Signaling
networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during
embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 98:1512–1520.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shirakihara T, Saitoh M and Miyazono K:
Differential regulation of epithelial and mesenchymal markers by
deltaEF1 proteins in epithelial mesenchymal transition induced by
TGF-beta. Mol Biol Cell. 18:3533–3544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
González-Santiago AE, Mendoza-Topete LA,
Sánchez-Llamas F, Troyo-Sanromán R and Gurrola-Díaz CM: TGF-β1
serum concentration as a complementary diagnostic biomarker of lung
cancer: Establishment of a cut-point value. J Clin Lab Anal.
25:238–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|