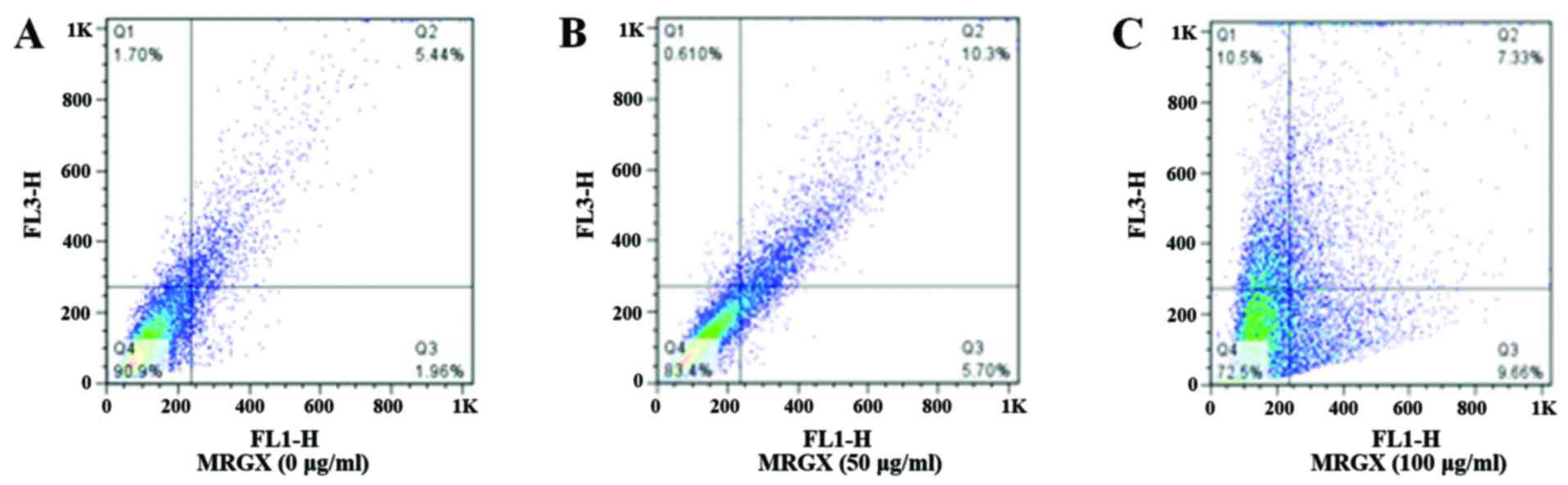
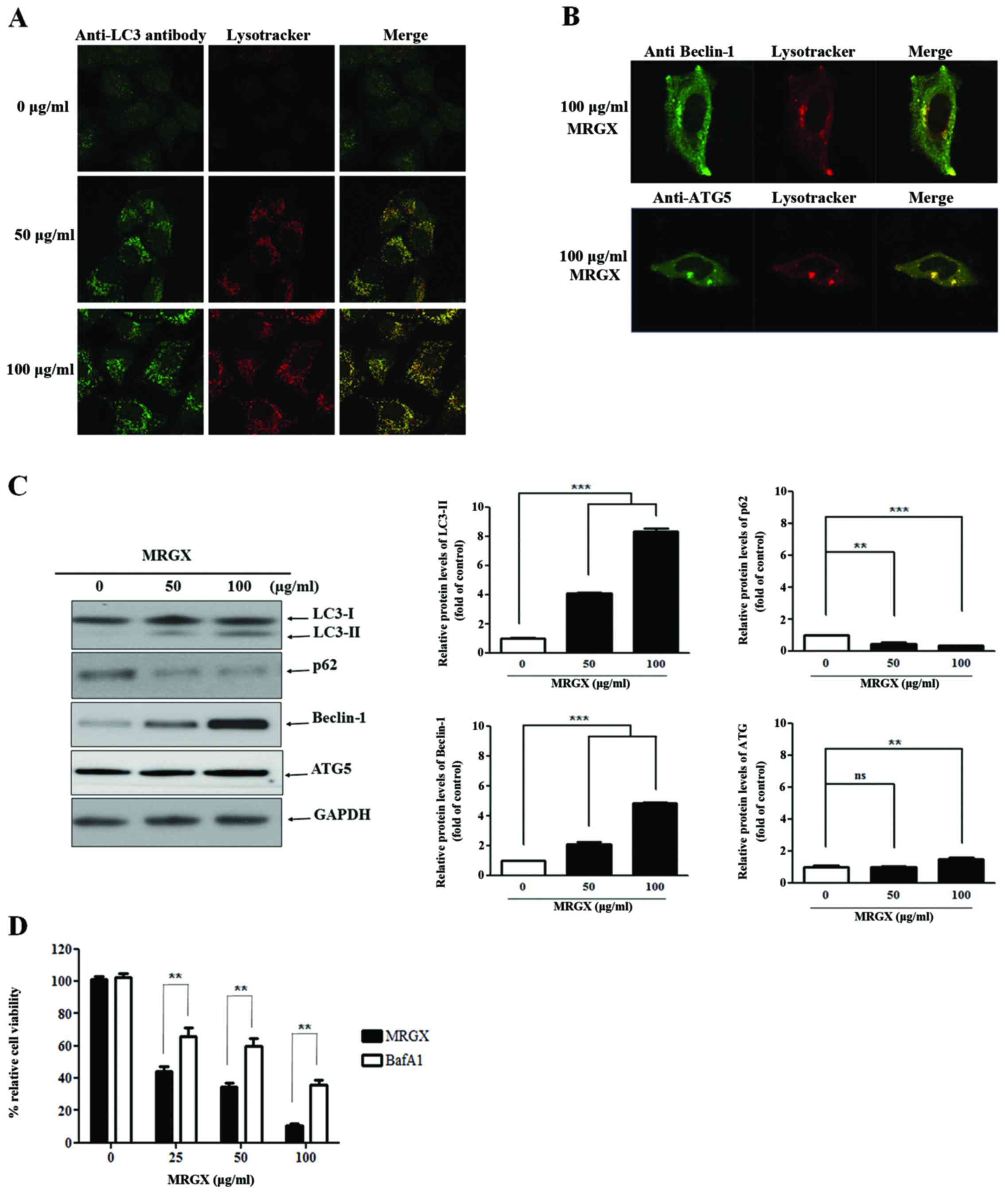
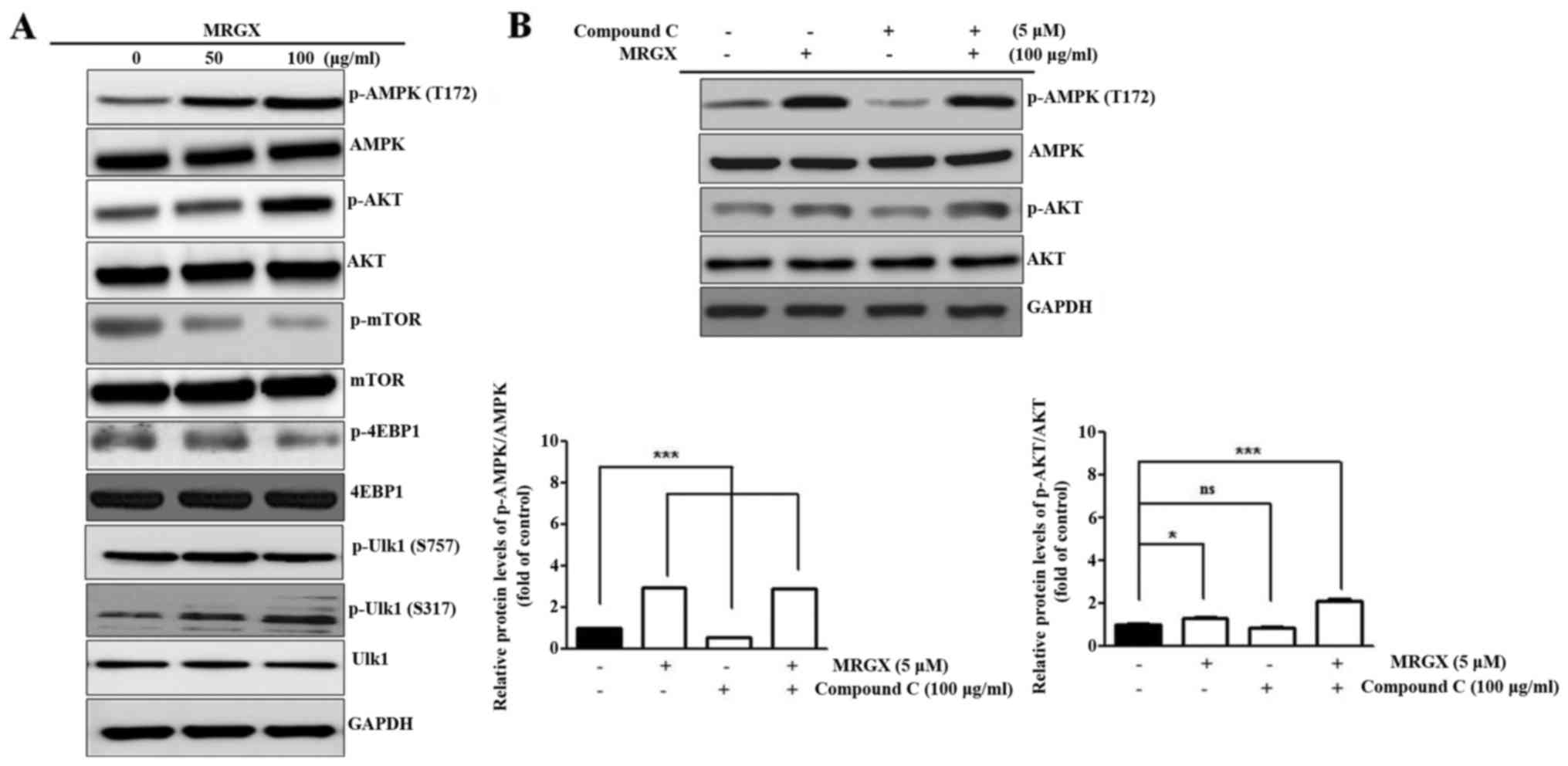
|
1
|
Ang-Lee MK, Moss J and Yuan CS: Herbal
medicines and perioperative care. JAMA. 286:208–216. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nag SA, Qin JJ, Wang W, Wang MH, Wang H
and Zhang R: Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: In vitro and in
vivo activities, structure-activity relationships, and molecular
mechanisms of action. Front Pharmacol. 3:252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwon YK, Lee SY, Kang HS, Sung JS, Cho CK,
Yoo HS, Shin S, Choi JS, Lee YW and Jang IS: Differential
expression of gene profiles in MRGX-treated lung cancer. J
Pharmacopuncture. 16:30–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kim KH, Choi I, Lee YW, Cho CK, Yoo HS,
Lee SB, Ho Choi S, Kwon KR and Jang JH: Target genes involved in
antiproliferative effect of modified ginseng extracts in lung
cancer A549 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 46:441–449. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jang SI, Lee YW, Cho CK, Yoo HS and Jang
JH: Identification of target genes involved in the
antiproliferative effect of enzyme-modified ginseng extract in
HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cell. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:5025682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwang JW, Baek YM, Jang IS, Yang KE, Lee
DG, Yoon SJ, Rho J, Cho CK, Lee YW, Kwon KR, et al: An
enzymatically fortified ginseng extract inhibits proliferation and
induces apoptosis of KATO3 human gastric cancer cells via
modulation of Bax, mTOR, PKB and IκBα. Mol Med Rep. 11:670–676.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stinchcombe TE, Lee CB and Socinski MA:
Current approaches to advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer:
First-line therapy in patients with a good functional status. Clin
Lung Cancer. 7 Suppl 4:S111–S117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yun TK: Panax ginseng - a
non-organ-specific cancer preventive? Lancet Oncol. 2:49–55. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee DG, Jang SI, Kim YR, Yang KE, Yoon SJ,
Lee ZW, An HJ, Jang IS, Choi JS and Yoo HS: Anti-proliferative
effects of ginsenosides extracted from mountain ginseng on lung
cancer. Chin J Integr Med. 22:344–352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gustafsson AB and Gottlieb RA: Recycle or
die: The role of autophagy in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
44:654–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kundu M and Thompson CB: Autophagy: Basic
principles and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:427–455.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie Z, Zhang J, Wu J, Viollet B and Zou
MH: Upregulation of mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 by the
AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells attenuates
oxidative stress in diabetes. Diabetes. 57:3222–3230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Colombo SL and Moncada S: AMPKalpha1
regulates the antioxidant status of vascular endothelial cells.
Biochem J. 421:163–169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vellai T: Autophagy genes and ageing. Cell
Death Differ. 16:94–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stockert JC, Blázquez-Castro A, Cañete M,
Horobin RW and Villanueva A: MTT assay for cell viability:
Intracellular localization of the formazan product is in lipid
droplets. Acta Histochem. 114:785–796. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi IK, Cho YS, Jung HJ and Kwon HJ:
Autophagonizer, a novel synthetic small molecule, induces
autophagic cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:849–854.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hwang JW, Baek YM, Yang KE, Yoo HS, Cho
CK, Lee YW, Park J, Eom CY, Lee ZW, Choi JS, et al: Lactobacillus
casei extract induces apoptosis in gastric cancer by inhibiting
NF-κB and mTOR-mediated signaling. Integr Cancer Ther. 12:165–173.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hammond EM, Brunet CL, Johnson GD,
Parkhill J, Milner AE, Brady G, Gregory CD and Grand RJ: Homology
between a human apoptosis specific protein and the product of APG5,
a gene involved in autophagy in yeast. FEBS Lett. 425:391–395.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheong H, Wu J, Gonzales LK, Guttentag SH,
Thompson CB and Lindsten T: Analysis of a lung defect in
autophagy-deficient mouse strains. Autophagy. 10:45–56. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z: Lysosomal
proton pump activity: Supravital cell staining with acridine orange
differentiates leukocyte subpopulations. Methods Cell Biol.
41:185–194. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoon JH, Her S, Kim M, Jang IS and Park J:
The expression of damage-regulated autophagy modulator 2 (DRAM2)
contributes to autophagy induction. Mol Biol Rep. 39:1087–1093.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Xia H, Kim M, Xu L, Li Y, Zhang L,
Cai Y, Norberg HV, Zhang T, Furuya T, et al: Beclin1 controls the
levels of p53 by regulating the deubiquitination activity of USP10
and USP13. Cell. 147:223–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guévin C, Manna D, Bélanger C, Konan KV,
Mak P and Labonté P: Autophagy protein ATG5 interacts transiently
with the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase (NS5B) early during
infection. Virology. 405:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Egan D, Kim J, Shaw RJ and Guan KL: The
autophagy initiating kinase ULK1 is regulated via opposing
phosphorylation by AMPK and mTOR. Autophagy. 7:643–644. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
Cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan CS, Wu JA and Osinski J: Ginsenoside
variability in American ginseng samples. Am J Clin Nutr.
75:600–601. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lei J, Li X, Gong XJ and Zheng YN:
Isolation, synthesis and structures of cytotoxic ginsenoside
derivatives. Molecules. 12:2140–2150. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han M, Hou JG, Dong CM, Li W, Yu HL, Zheng
YN and Chen L: Isolation, synthesis and structures of ginsenoside
derivatives and their anti-tumor bioactivity. Molecules.
15:399–406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hwang JW, Oh JH, Yoo HS, Lee YW, Cho CK,
Kwon KR, Yoon JH, Park J, Her S, Lee ZW, et al: Mountain ginseng
extract exhibits anti-lung cancer activity by inhibiting the
nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Am J Chin Med. 40:187–202. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu D, Wu J, Xu L, Zhang R and Chen L: A
method for the establishment of a cell line with stable expression
of the GFP-LC3 reporter protein. Mol Med Rep. 6:783–786.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ding Z, Wang X, Schnackenberg L, Khaidakov
M, Liu S, Singla S, Dai Y and Mehta JL: Regulation of autophagy and
apoptosis in response to ox-LDL in vascular smooth muscle cells,
and the modulatory effects of the microRNA hsa-let-7g. Int J
Cardiol. 168:1378–1385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Roach PJ: AMPK → ULK1 → autophagy. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:3082–3084. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|