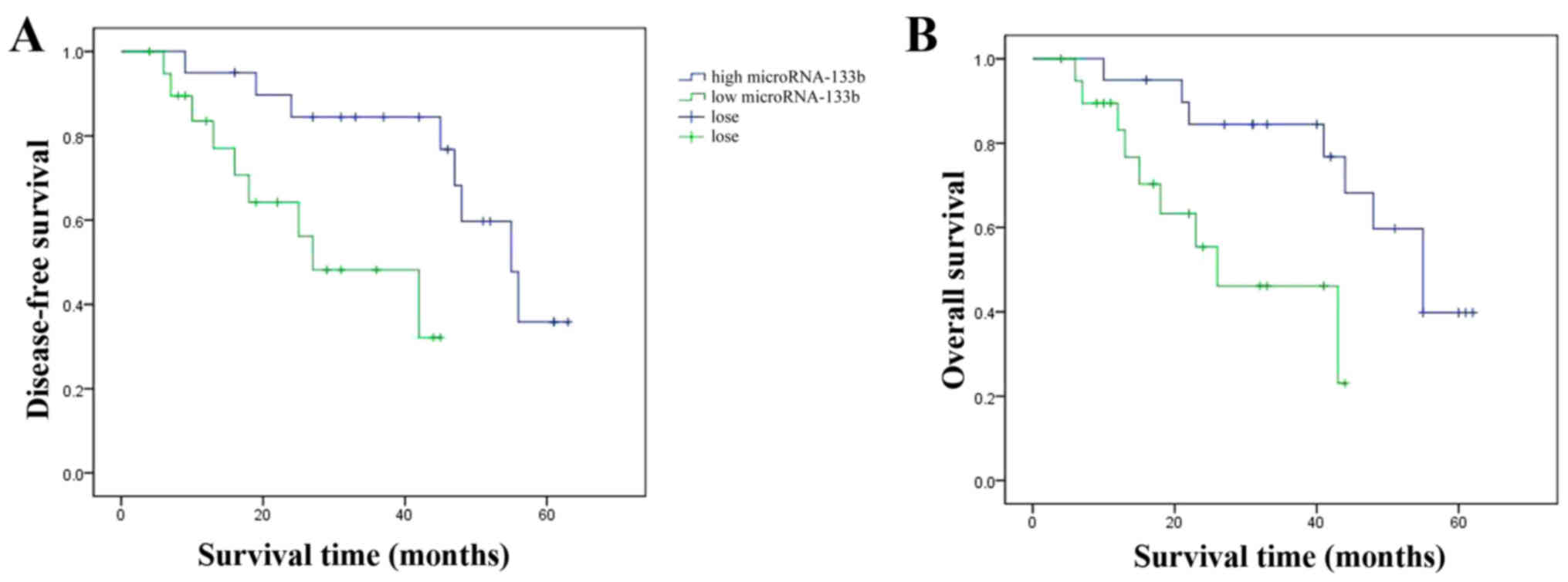
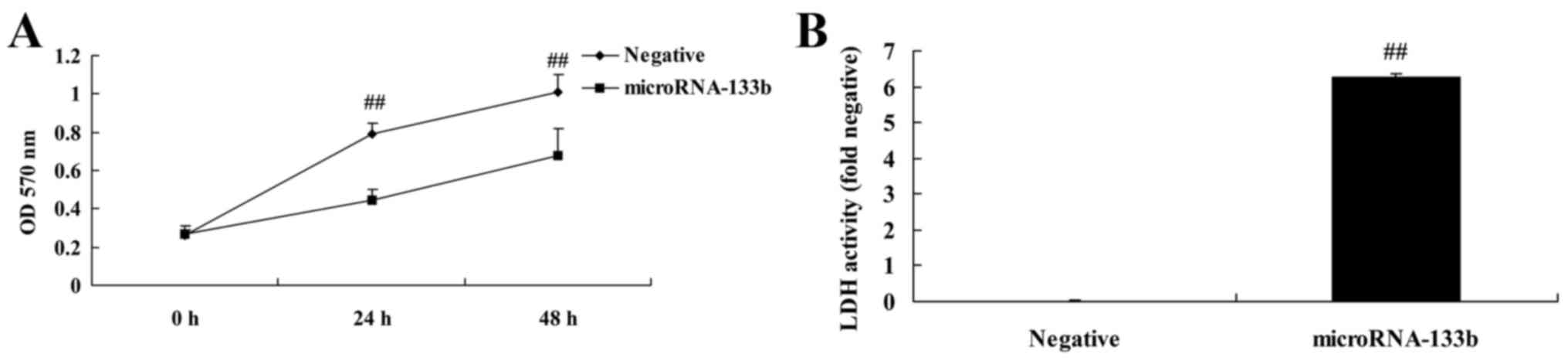
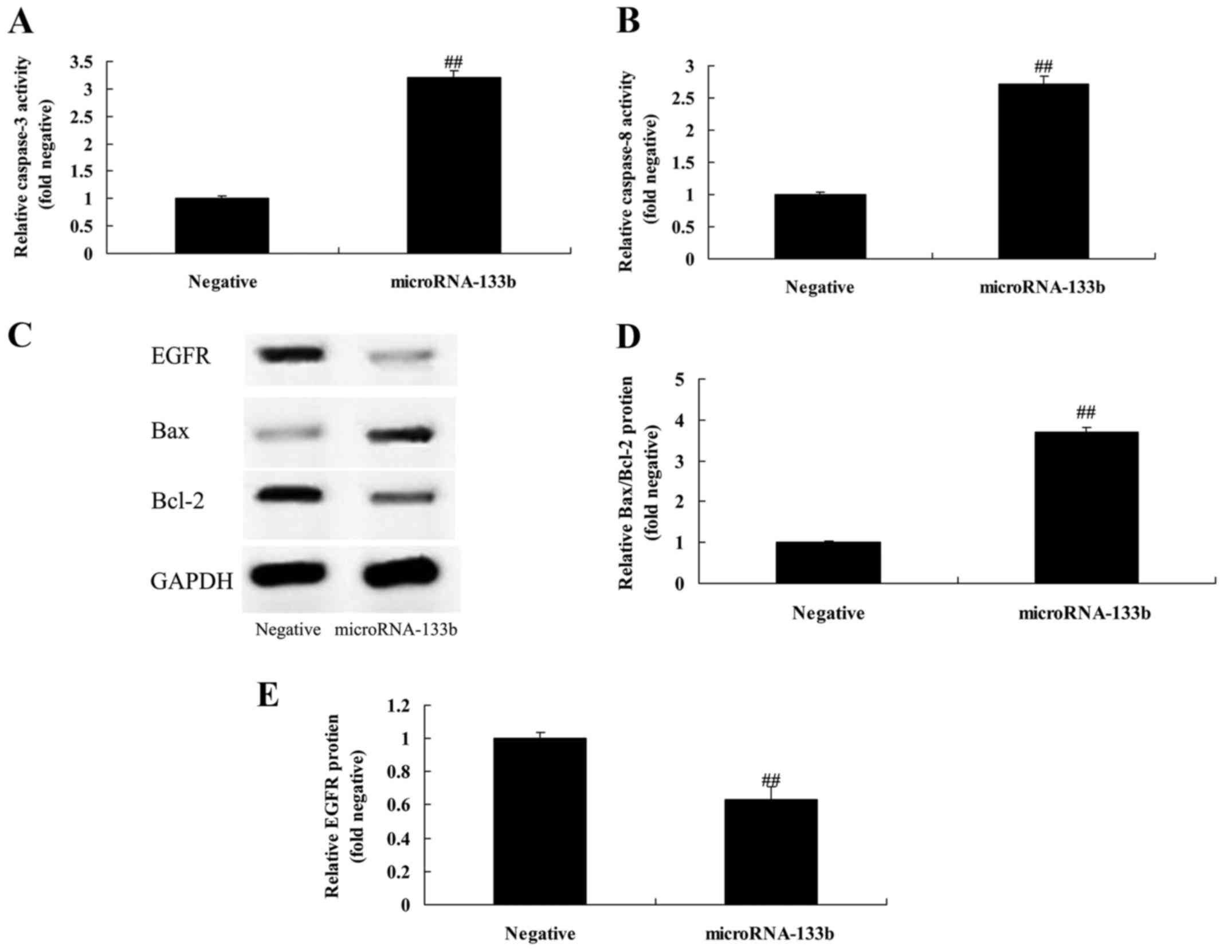
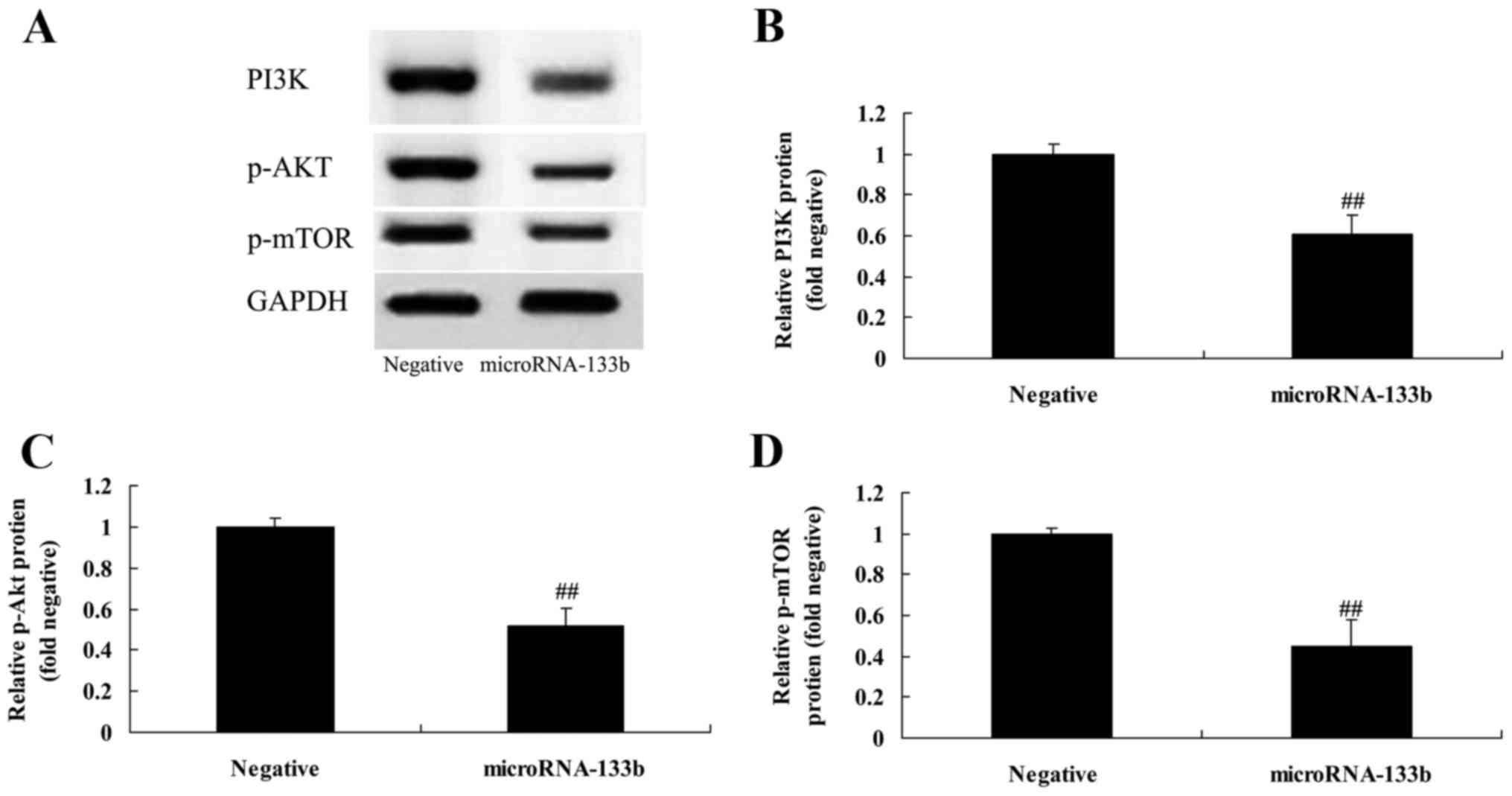
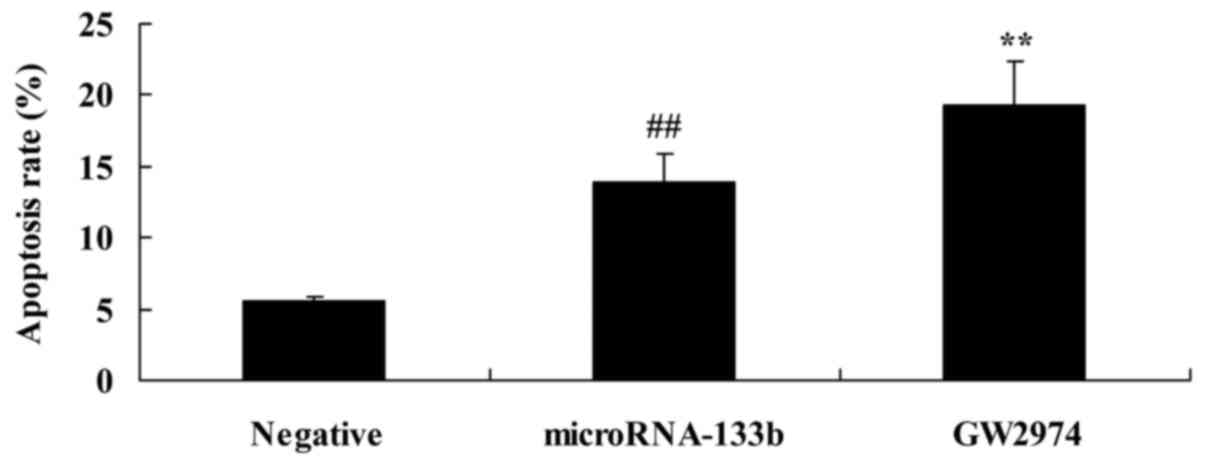
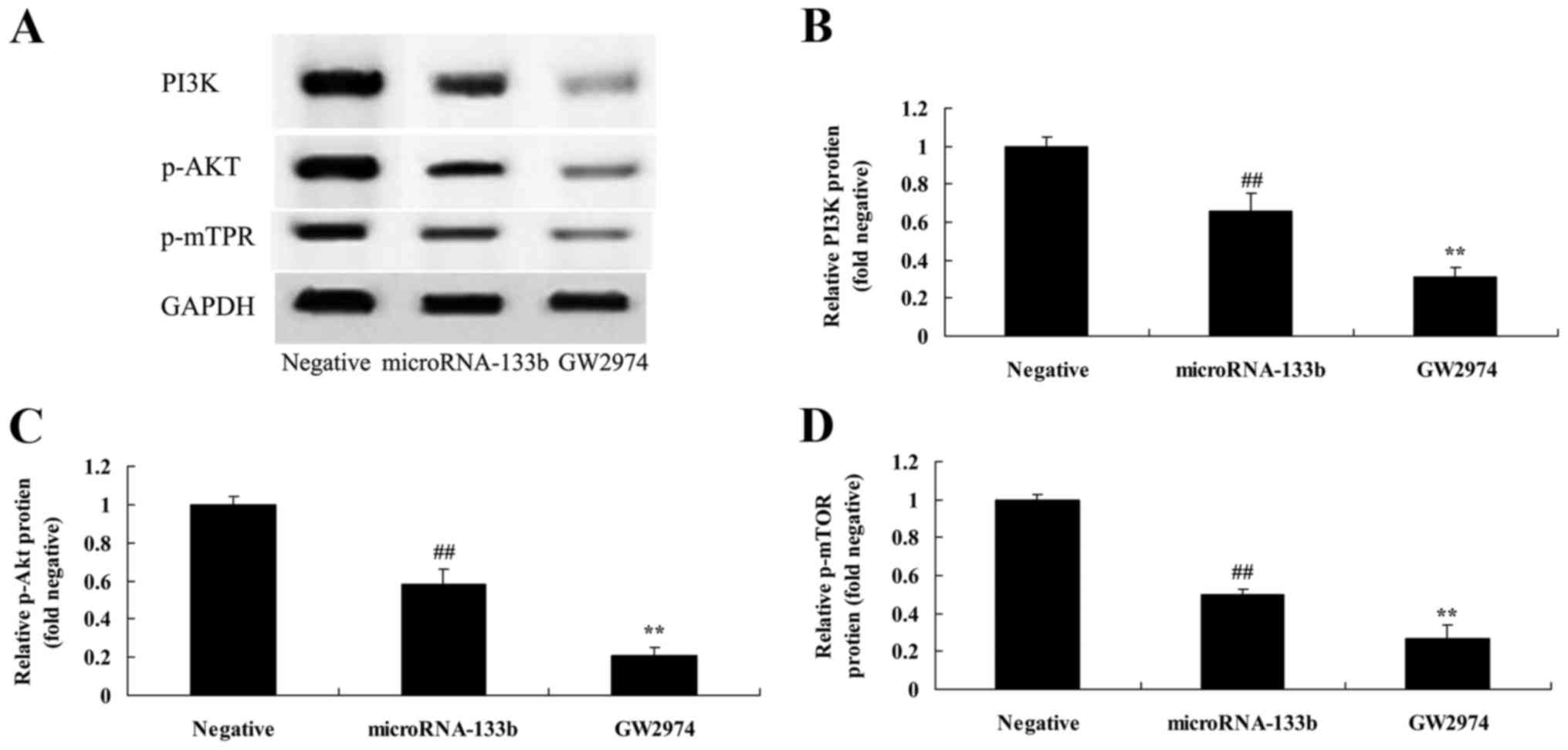
|
1
|
Geissler EK, Schnitzbauer AA, Zülke C,
Lamby PE, Proneth A, Duvoux C, Burra P, Jauch KW, Rentsch M, Ganten
TM, et al: Sirolimus use in liver transplant recipients with
hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized, multicenter, open-label
phase 3 trial. Transplantation. 100:116–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Erhardt A, Kolligs F, Dollinger M, Schott
E, Wege H, Bitzer M, Gog C, Lammert F, Schuchmann M, Walter C, et
al: TACE plus sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Results of the multicenter, phase II SOCRATES trial.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:947–954. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Ge NL, Chen Y, Xie XY, Yin X, Gan
YH, Zhang BH, Zhang JB, Chen RX, Wang YH, et al: Long-term outcomes
and prognostic analysis of radiofrequency ablation for small
hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year follow-up in Chinese patients.
Med Oncol. 32:772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirokawa F, Hayashi M, Miyamoto Y, Asakuma
M, Shimizu T, Komeda K, Inoue Y and Uchiyama K: Predictors of poor
prognosis by recurrence patterns after curative hepatectomy for
hepatocellular carcinoma in Child-Pugh classification A.
Hepatogastroenterology. 62:164–168. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu BS, Zhao G, Yu HF, Chen K, Dong JH and
Tan JW: High expression of AP-4 predicts poor prognosis for
hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy. Tumour Biol.
34:271–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu F, Zhang Y, Peng Z, Gao H, Xu L and
Chen M: High expression of high mobility group box 1 (hmgb1)
predicts poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
hepatectomy. J Transl Med. 10:1352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang C, Xiang H, Si H, Guo D and Sun M:
High expression of myofibrillogenesis regulator-1 predicts poor
prognosis for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
hepatectomy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14818–14823. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hirokawa F, Hayashi M, Asakuma M, Shimizu
T, Inoue Y and Uchiyama K: Risk factors and patterns of early
recurrence after curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Surg Oncol. 25:24–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang SL, Liu LP, Sun YF, Yang XR, Fan J,
Ren JW, Chen GG and Lai PB: Distinguished prognosis after
hepatectomy of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma with or without
cirrhosis: A long-term follow-up analysis. J Gastroenterol.
51:722–732. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wada H, Yamamoto H, Kim C, Uemura M, Akita
H, Tomimaru Y, Hama N, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Eguchi H, et al:
Association between ephrin-A1 mRNA expression and poor prognosis
after hepatectomy to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
45:1051–1058. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobayashi A, Takahashi S, Ishii H, Konishi
M, Nakagohri T, Gotohda N, Satake M, Furuse J and Kinoshita T:
Factors predicting survival in advanced T-staged hepatocellular
carcinoma patients treated with reduction hepatectomy followed by
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Eur J Surg Oncol.
33:1019–1024. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ahn S, Hyeon J and Park CK: Metadherin is
a prognostic predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
hepatectomy. Gut Liver. 7:206–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mizuguchi Y, Takizawa T, Yoshida H and
Uchida E: Dysregulated miRNA in progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol Res. 46:391–406. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang JT, Liu SM, Ma H, Yang Y, Zhang X,
Sun H, Zhang X, Xu J and Wang J: Systematic review and
meta-analysis: Circulating miRNAs for diagnosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 231:328–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mahgoub A and Steer CJ: MicroRNAs in the
evaluation and potential treatment of liver diseases. J Clin Med.
5:pii: E522016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Leng C, Zhang ZG, Chen WX, Luo HP, Song J,
Dong W, Zhu XR, Chen XP, Liang HF and Zhang BX: An integrin
beta4-EGFR unit promotes hepatocellular carcinoma lung metastases
by enhancing anchorage independence through activation of FAK-AKT
pathway. Cancer Lett. 376:188–196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang YP, Huang LY, Sun WM, Zhang ZZ, Fang
JZ, Wei BF, Wu BH and Han ZG: Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase
substrate activates EGFR/ERK signalling pathway and promotes cell
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 337:96–106.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu H, Gao L, Wang C, Li Y, Ma H, Chen L,
Qin J, Liu B, Liu Y and Liang C: Lower serum soluble-EGFR is a
potential biomarker for metastasis of HCC demonstrated by
N-glycoproteomic analysis. Discov Med. 19:333–341. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li T, Dong ZR, Guo ZY, Wang CH, Zhi XT,
Zhou JW, Li DK, Chen ZT, Chen ZQ and Hu SY: Mannose-mediated
inhibitory effects of PA-MSHA on invasion and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma via EGFR/Akt/IκBβ/NF-κB pathway. Liver
Int. 35:1416–1429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Yu C, Chen M, Li
Z, Tian S and Sun C: MicroRNA-3127 promotes cell proliferation and
tumorigenicity in hepatocellular carcinoma by disrupting of
PI3K/AKT negative regulation. Oncotarget. 6:6359–6372. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pellegrino R, Calvisi DF, Neumann O,
Kolluru V, Wesely J, Chen X, Wang C, Wuestefeld T, Ladu S, Elgohary
N, et al: EEF1A2 inactivates p53 by way of PI3K/AKT/mTOR-dependent
stabilization of MDM4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
59:1886–1899. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu M, Guo J, Li W, Xia H, Lu Y, Dong X,
Chen Y, Xie X, Fu S and Li M: HBx induced AFP receptor expressed to
activate PI3K/AKT signal to promote expression of Src in liver
cells and hepatoma cells. BMC Cancer. 15:3622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang Q, Zhan L, Cao H, Li J, Lyu Y, Guo
X, Zhang J, Ji L, Ren T, An J, et al: Increased mitochondrial
fission promotes autophagy and hepatocellular carcinoma cell
survival through the ROS-modulated coordinated regulation of the
NFKB and TP53 pathways. Autophagy. 12:999–1014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brandi G, De Rosa F, Agostini V, di
Girolamo S, Andreone P, Bolondi L, Serra C, Sama C, Golfieri R,
Gramenzi A, et al: Italian Liver Cancer (ITA.LI.CA) Group:
Metronomic capecitabine in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
patients: A phase II study. Oncologist. 18:1256–1257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lanaya H, Natarajan A, Komposch K, Li L,
Amberg N, Chen L, Wculek SK, Hammer M, Zenz R, Peck-Radosavljevic
M, et al: EGFR has a tumour-promoting role in liver macrophages
during hepatocellular carcinoma formation. Nat Cell Biol.
16:972–981. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu J, Jia L, Ma H, Li Y, Ma Z and Zhao Y:
Axl gene knockdown inhibits the metastasis properties of
hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/Akt-PAK1 signal pathway. Tumour
Biol. 35:3809–3817. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang X, Zeng L, Huang J, Zhou H and Liu
Y: Arctigenin, a natural lignan compound, induces apoptotic death
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppression of PI3-K/Akt
signaling. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:458–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Zhang C, Xu L, Zang K, Ning Z,
Jiang F, Chi H, Zhu X and Meng Z: Bufalin suppresses hepatocellular
carcinoma invasion and metastasis by targeting HIF-1α via the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 7:20193–20208. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nemazanyy I, Espeillac C, Pende M and
Panasyuk G: Role of PI3K, mTOR and Akt2 signalling in hepatic
tumorigenesis via the control of PKM2 expression. Biochem Soc
Trans. 41:917–922. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Guo X, Xiong L, Yu L, Li Z, Guo
Q, Li Z, Li B and Lin N: Comprehensive analysis of
microRNA-regulated protein interaction network reveals the tumor
suppressive role of microRNA-149 in human hepatocellular carcinoma
via targeting AKT-mTOR pathway. Mol Cancer. 13:2532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horn D, Hess J, Freier K, Hoffmann J and
Freudlsperger C: Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances
radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 19:795–805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Makinoshima H, Takita M, Saruwatari K,
Umemura S, Obata Y, Ishii G, Matsumoto S, Sugiyama E, Ochiai A, Abe
R, et al: Signaling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
(PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis is responsible for
aerobic glycolysis mediated by glucose transporter in epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J Biol
Chem. 290:17495–17504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ooft ML, Braunius WW, Heus P, Stegeman I,
van Diest PJ, Grolman W, Zuur CI and Mayems SM: Prognostic
significance of the EGFR pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomarkers Med. 9:997–1010.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, Athar
M, Ghazizadeh S, Simon M, O'Banion MK and Ma L: Soluble E-cadherin:
A critical oncogene modulating receptor tyrosine kinases, MAPK and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Oncogene. 33:225–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|