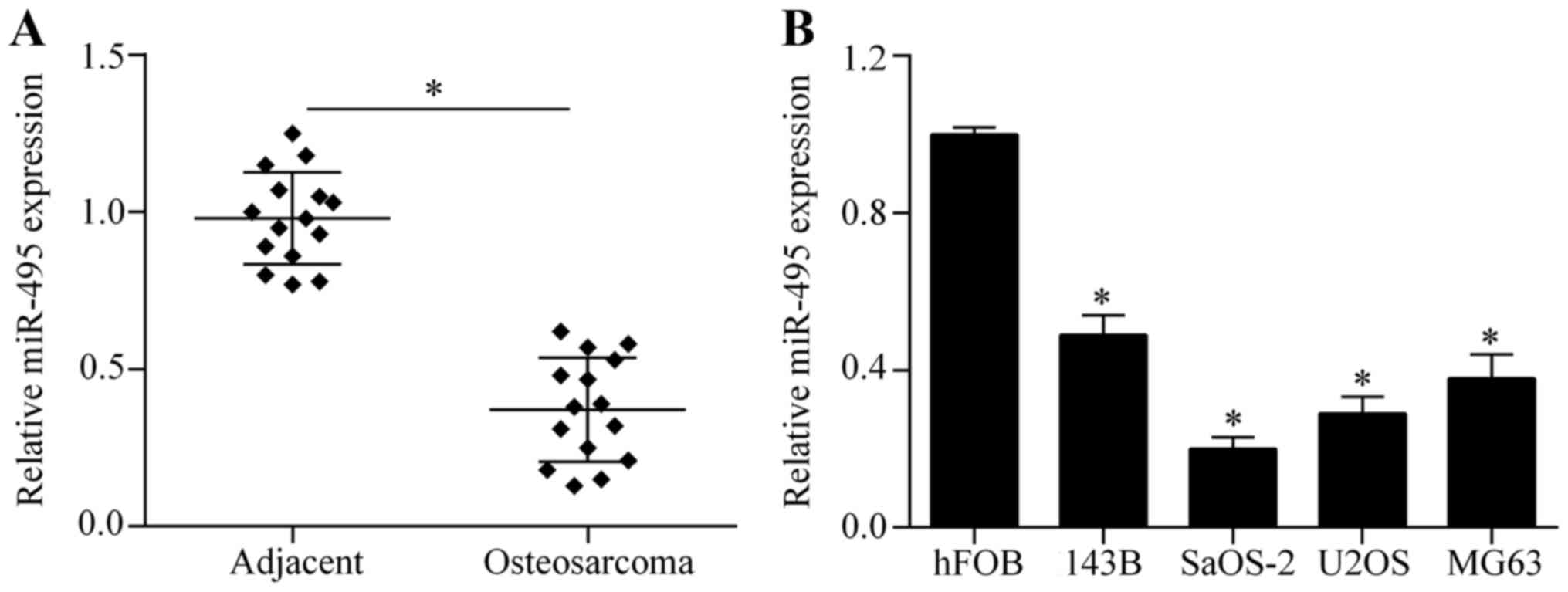
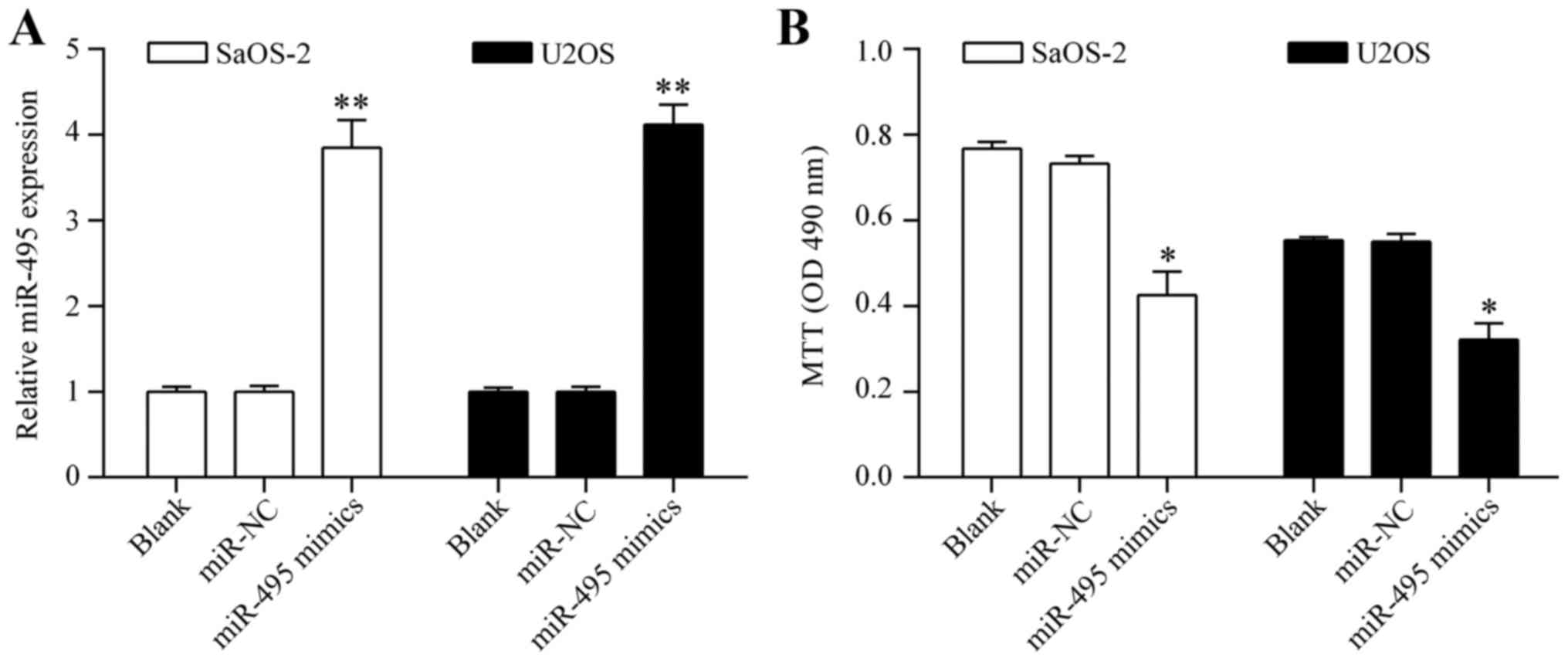
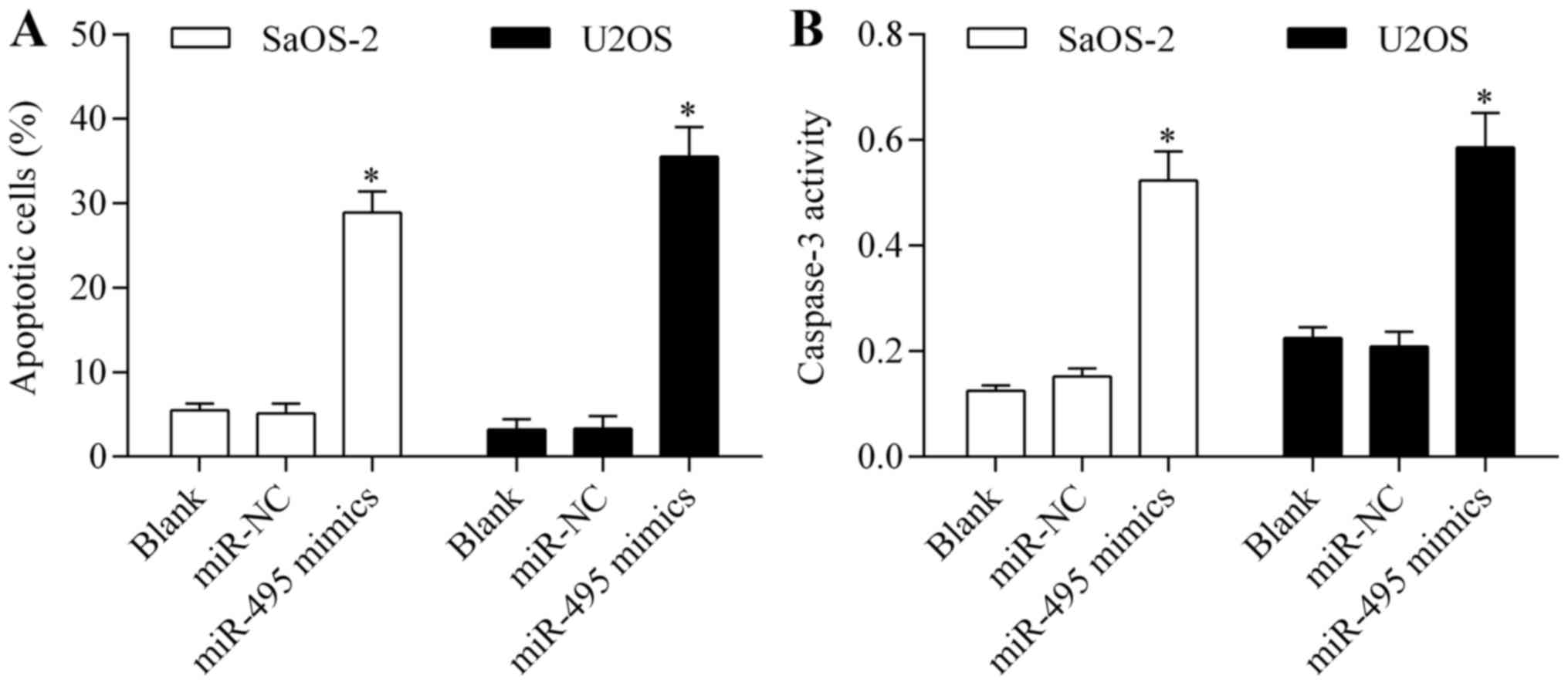
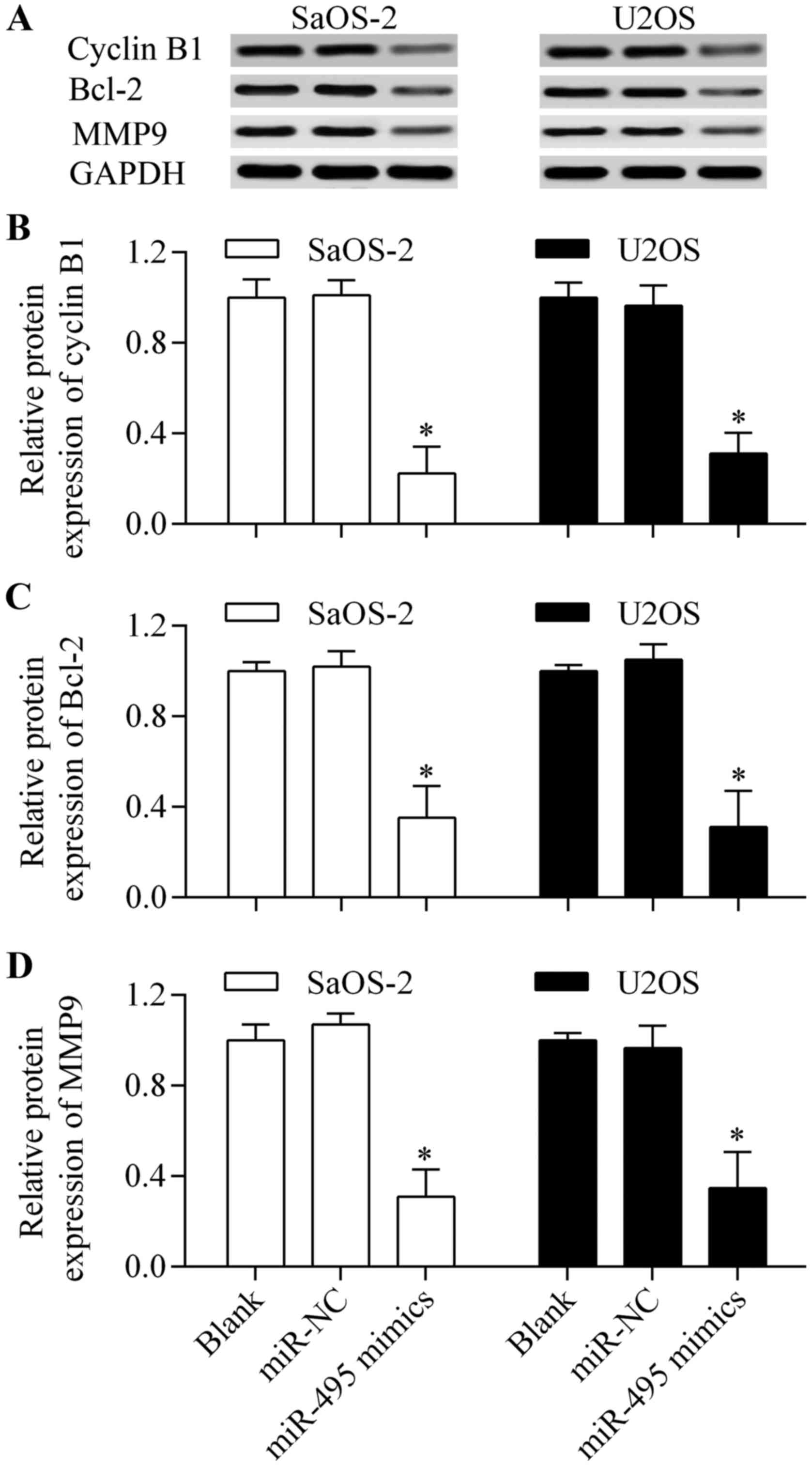
|
1
|
Botter SM, Neri D and Fuchs B: Recent
advances in osteosarcoma. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 16:15–23. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo MD, Healey
JH, Bernstein ML, Betcher D, Ferguson WS, Gebhardt MC, Goorin AM,
Harris M, et al: Children's Oncology Group: Osteosarcoma: The
addition of muramyl tripeptide to chemotherapy improves overall
survival - a report from the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin
Oncol. 26:633–638. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hughes DP: Strategies for the targeted
delivery of therapeutics for osteosarcoma. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
6:1311–1321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thomson DW, Bracken CP and Goodall GJ:
Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:6845–6853. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD and
Pushparaj PN: Oncomirs: The potential role of non-coding microRNAs
in understanding cancer. Bioinformation. 2:330–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pang JC, Kwok WK, Chen Z and Ng HK:
Oncogenic role of microRNAs in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol.
117:599–611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Silber J, James CD and Hodgson JG:
microRNAs in gliomas: Small regulators of a big problem.
Neuromolecular Med. 11:208–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kushlinskii NE, Fridman MV and Braga EA:
Molecular mechanisms and microRNAs in osteosarcoma pathogenesis.
Biochemistry. 81:315–328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Yan YG, Wang C, Zhang SJ, Yu XH
and Wang WJ: MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta. 444:9–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS and
Kolb EA: MicroRNAs and potential targets in osteosarcoma: Review.
Front Pediatr. 3:692015.Review. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rochman M, Malicet C and Bustin M:
HMGN5/NSBP1: A new member of the HMGN protein family that affects
chromatin structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:86–92.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Z, Tang R, Wu D and Sun X: Research
advances in HMGN5 and cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:1531–1539. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hock R, Furusawa T, Ueda T and Bustin M:
HMG chromosomal proteins in development and disease. Trends Cell
Biol. 17:72–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shirakawa H, Landsman D, Postnikov YV and
Bustin M: NBP-45, a novel nucleosomal binding protein with a
tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression. J Biol
Chem. 275:6368–6374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
King LM and Francomano CA:
Characterization of a human gene encoding nucleosomal binding
protein NSBP1. Genomics. 71:163–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Postnikov Y and Bustin M: Regulation of
chromatin structure and function by HMGN proteins. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1799:62–68. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu J, Yan R, Chen J, Xu T, Zhou J, Wang M,
Chen C, Yan Y and Lu Y: HMGN5: A potential oncogene in
gliomas. J Neurooncol. 104:729–736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang N, Zhou LQ and Zhang XY:
Downregulation of the nucleosome-binding protein 1 (NSBP1) gene can
inhibit the in vitro and in vivo proliferation of prostate cancer
cells. Asian J Androl. 12:709–717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ji SQ, Yao L, Zhang XY, Li XS and Zhou LQ:
Knockdown of the nucleosome binding protein 1 inhibits the growth
and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro and
in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weng M, Song F, Chen J, Wu J, Qin J, Jin T
and Xu J: The high-mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5 is
highly expressed in breast cancer and promotes the proliferation
and invasion of breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 36:959–966. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wahafu W, He ZS, Zhang XY, Zhang CJ, Yao
K, Hao H, Song G, He Q, Li XS and Zhou LQ: The nucleosome binding
protein NSBP1 is highly expressed in human bladder cancer and
promotes the proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 32:931–939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Yuan B, Yuan W, Wang C, Gao R and
Wang J: The expression and clinical significance of high mobility
group nucleosome binding domain 5 in human osteosarcoma. Tumour
Biol. 35:6539–6547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chu H, Chen X, Wang H, Du Y, Wang Y, Zang
W, Li P, Li J, Chang J, Zhao G, et al: MiR-495 regulates
proliferation and migration in NSCLC by targeting MTA3. Tumour
Biol. 35:3487–3494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao M, Nie W, Li J, Zhang Y, Yan X, Guan
X, Chen X, Zen K, Zhang CY, Jiang X, et al: MicroRNA-495 induces
breast cancer cell migration by targeting JAM-A. Protein Cell.
5:862–872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Liu JL, Yu L, Liu XX, Wu HM, Lei
FY, Wu S and Wang X: Downregulated miR-495 [corrected] inhibits the
G1-S phase transition by targeting Bmi-1 in breast cancer.
Medicine. 94:e7182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li JZ, Wang ZL, Xu WH, Li Q, Gao L and
Wang ZM: MicroRNA-495 regulates migration and invasion in prostate
cancer cells via targeting Akt and mTOR signaling. Cancer Invest.
34:181–188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Widodo Djati MS and Rifa'i M: Role of
MicroRNAs in carcinogenesis that potential for biomarker of
endometrial cancer. Ann Med Surg. 7:9–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mishra S, Srivastava AK, Suman S, Kumar V
and Shukla Y: Circulating miRNAs revealed as surrogate molecular
signatures for the early detection of breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
369:67–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano
D, Finazzi-Agro' E, Levine AJ, Bernardini S, Garabadgiu AV, Melino
G and Candi E: MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c,
miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p,
mapped to the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis,
migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells.
Oncogene. 33:5173–5182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang X, Huang H, Li Z, He C, Li Y, Chen
P, Gurbuxani S, Arnovitz S, Hong GM, Price C, et al: miR-495 is a
tumor-suppressor microRNA down-regulated in MLL-rearranged
leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:19397–19402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Z, Cao Y, Jie Z, Liu Y, Li Y, Li J, Zhu
G, Liu Z, Tu Y, Peng G, et al: miR-495 and miR-551a inhibit the
migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by directly
interacting with PRL-3. Cancer Lett. 323:41–47. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Z, Zhang G, Li D, Jie Z, Chen H, Xiong
J, Liu Y, Cao Y, Jiang M, Le Z, et al: Methylation-associated
silencing of miR-495 inhibit the migration and invasion of human
gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PRL-3. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 456:344–350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen SM, Chen HC, Chen SJ, Huang CY, Chen
PY, Wu TW, Feng LY, Tsai HC, Lui TN, Hsueh C, et al: MicroRNA-495
inhibits proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells by
downregulating cyclin-dependent kinase 6. World J Surg Oncol.
11:872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nie S, Li K, Huang Y, Hu Q, Gao X and Jie
S: miR-495 mediates metabolic shift in glioma cells via targeting
Glut1. J Craniofac Surg. 26:e155–e158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang C, Yun Z, Zhao T, Liu X and Ma X:
MiR-495 is a predictive biomarker that downregulates GFI1
expression in medulloblastoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1430–1439.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang B, Yuan F, Liu J, Li Y, Zhou F, Liu
X, Hao Z, Li Q, Zheng Y and Wang W: Hsa-miR-495 acts as a tumor
suppressor gene in glioma via the negative regulation of MYB. Mol
Med Rep. 14:977–982. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song L, Li Y, Li W, Wu S and Li Z: miR-495
enhances the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to
platinum by modulation of copper-transporting P-type adenosine
triphosphatase A (ATP7A). J Cell Biochem. 115:1234–1242. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu YY, Tian J, Hao Q and Yin LR:
MicroRNA-495 downregulates FOXC1 expression to suppress cell growth
and migration in endometrial cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:239–251. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hwang-Verslues WW, Chang PH, Wei PC, Yang
CY, Huang CK, Kuo WH, Shew JY, Chang KJ, Lee EY and Lee WH: miR-495
is upregulated by E12/E47 in breast cancer stem cells, and promotes
oncogenesis and hypoxia resistance via downregulation of E-cadherin
and REDD1. Oncogene. 30:2463–2474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee SH, Jung YD, Choi YS and Lee YM:
Targeting of RUNX3 by miR-130a and miR-495 cooperatively increases
cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis in gastric cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 6:33269–33278. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang XY, Guo ZQ, Ji SQ, Zhang M, Jiang N,
Li XS and Zhou LQ: Small interfering RNA targeting HMGN5 induces
apoptosis via modulation of a mitochondrial pathway and Bcl-2
family proteins in prostate cancer cells. Asian J Androl.
14:487–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gan Y, Tan J, Yang J, Zhou Y, Dai Y, He L,
Yao K and Tang Y: Knockdown of HMGN5 suppresses the viability and
invasion of human urothelial bladder cancer 5637 cells in vitro and
in vivo. Med Oncol. 32:1362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen P, Wang XL, Ma ZS, Xu Z, Jia B, Ren
J, Hu YX, Zhang QH, Ma TG, Yan BD, et al: Knockdown of HMGN5
expression by RNA interference induces cell cycle arrest in human
lung cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3223–3228. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Norbury C and Nurse P: Animal cell cycles
and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 61:441–470. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aizawa K, Ueki K, Suzuki S, Yabusaki H,
Kanda T, Nishimaki T, Suzuki T and Hatakeyama K: Apoptosis and
Bbcl-2 expression in gastric carcinomas: Correlation
withclinicopathological variables, p53 expression, cell
proliferation and prognosis. Int J Oncol. 14:85–91. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Belotti D, Paganoni P, Manenti L, Garofalo
A, Marchini S, Taraboletti G and Giavazzi R: Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP9 and MMP2) induce the release of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by ovarian carcinoma cells:
Implications for ascites formation. Cancer Res. 63:5224–5229.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang C, Gao R, Wang J, Yuan W, Wang C and
Zhou X: High-mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5 increases
drug resistance in osteosarcoma through upregulating autophagy.
Tumour Biol. 35:6357–6363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yao K, He L, Gan Y, Zeng Q, Dai Y and Tan
J: MiR-186 suppresses the growth and metastasis of bladder cancer
by targeting NSBP1. Diagn Pathol. 10:1462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wei P, Qiao B, Li Q, Han X, Zhang H, Huo Q
and Sun J: microRNA-340 suppresses tumorigenic potential of
prostate cancer cells by targeting high-mobility group
nucleosome-binding domain 5. DNA Cell Biol. 35:33–43. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li D, Du X, Liu A and Li P: Suppression of
nucleosome-binding protein 1 by miR-326 impedes cell proliferation
and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
35:1117–1124. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|