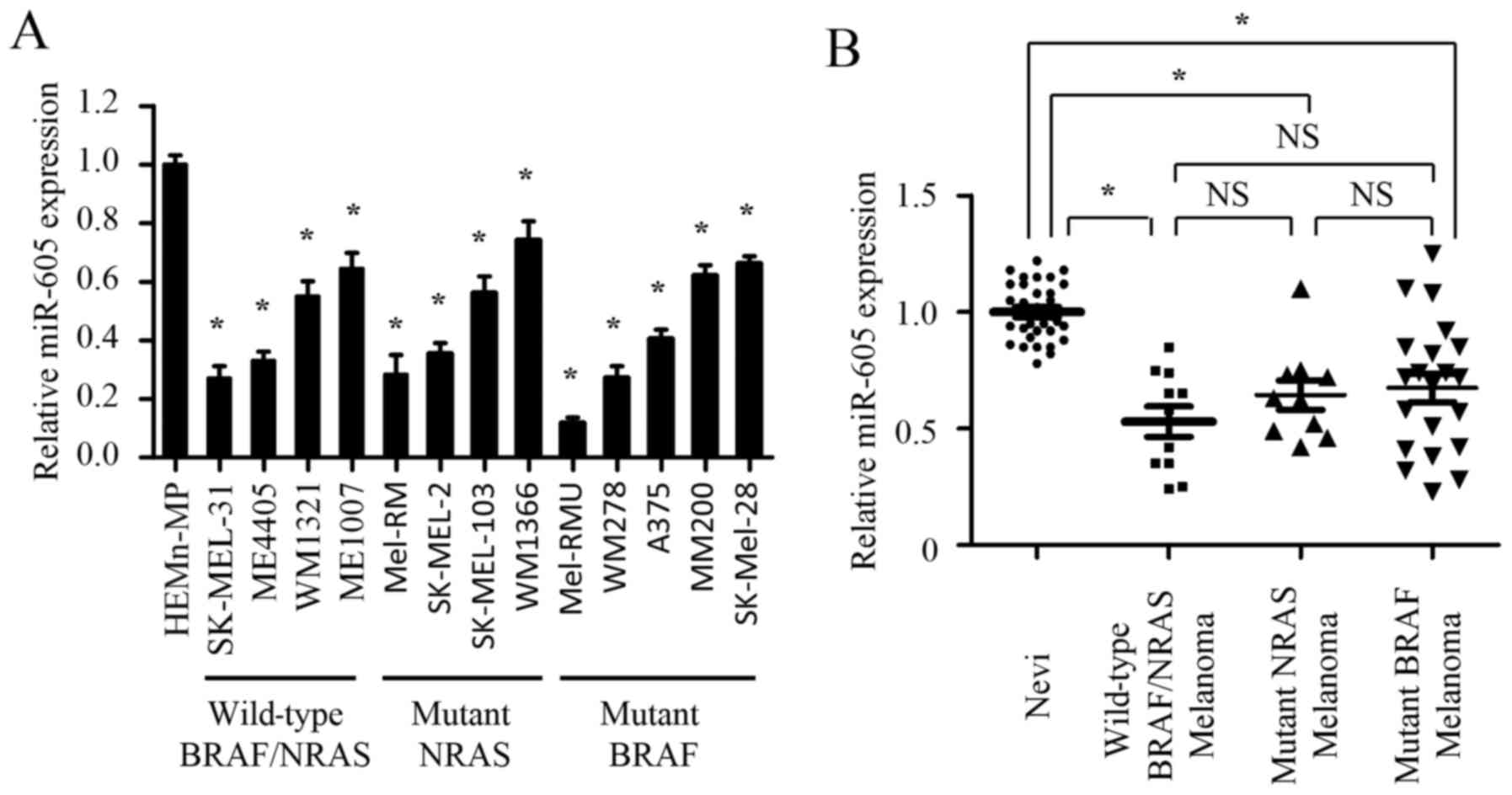
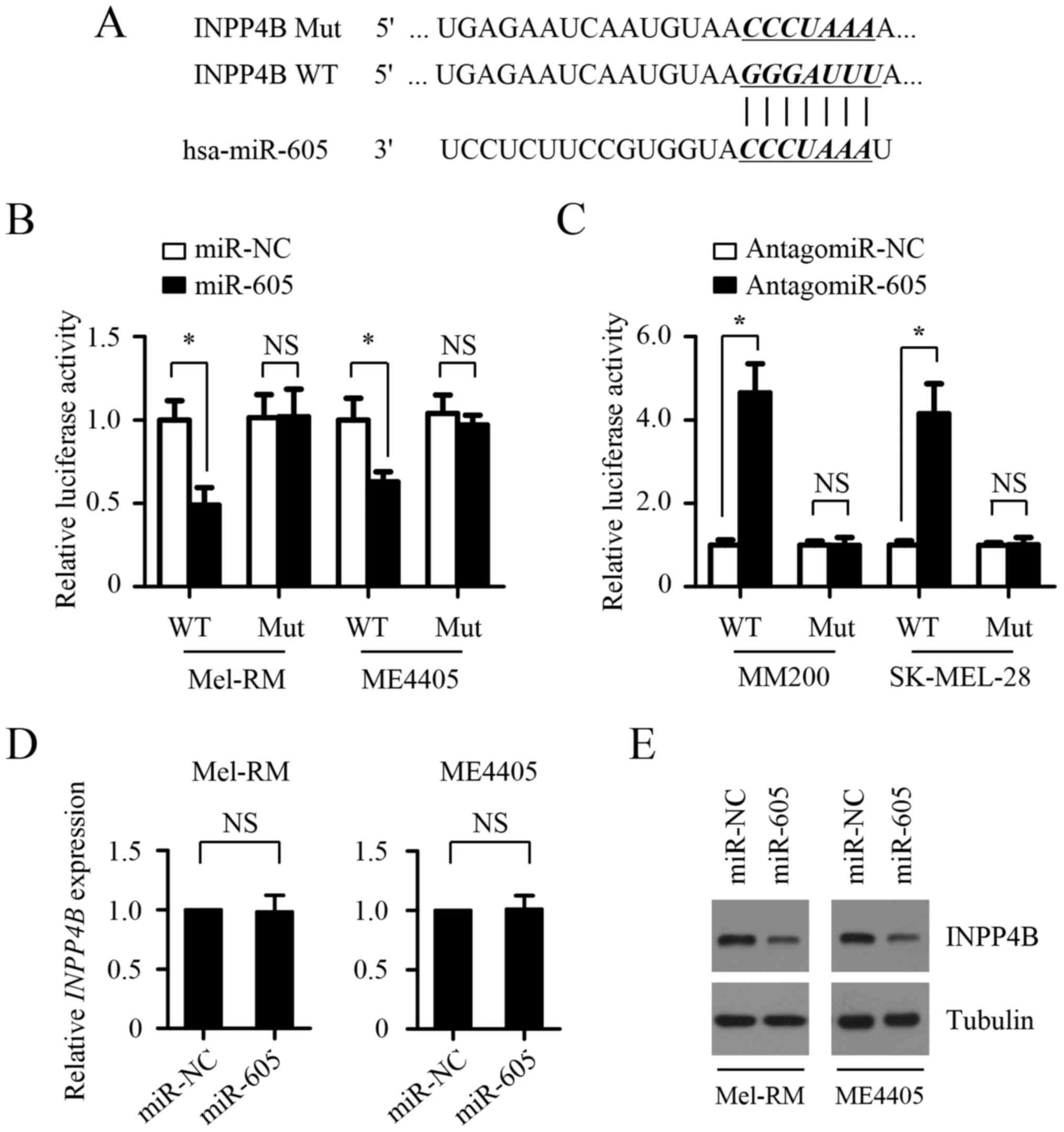
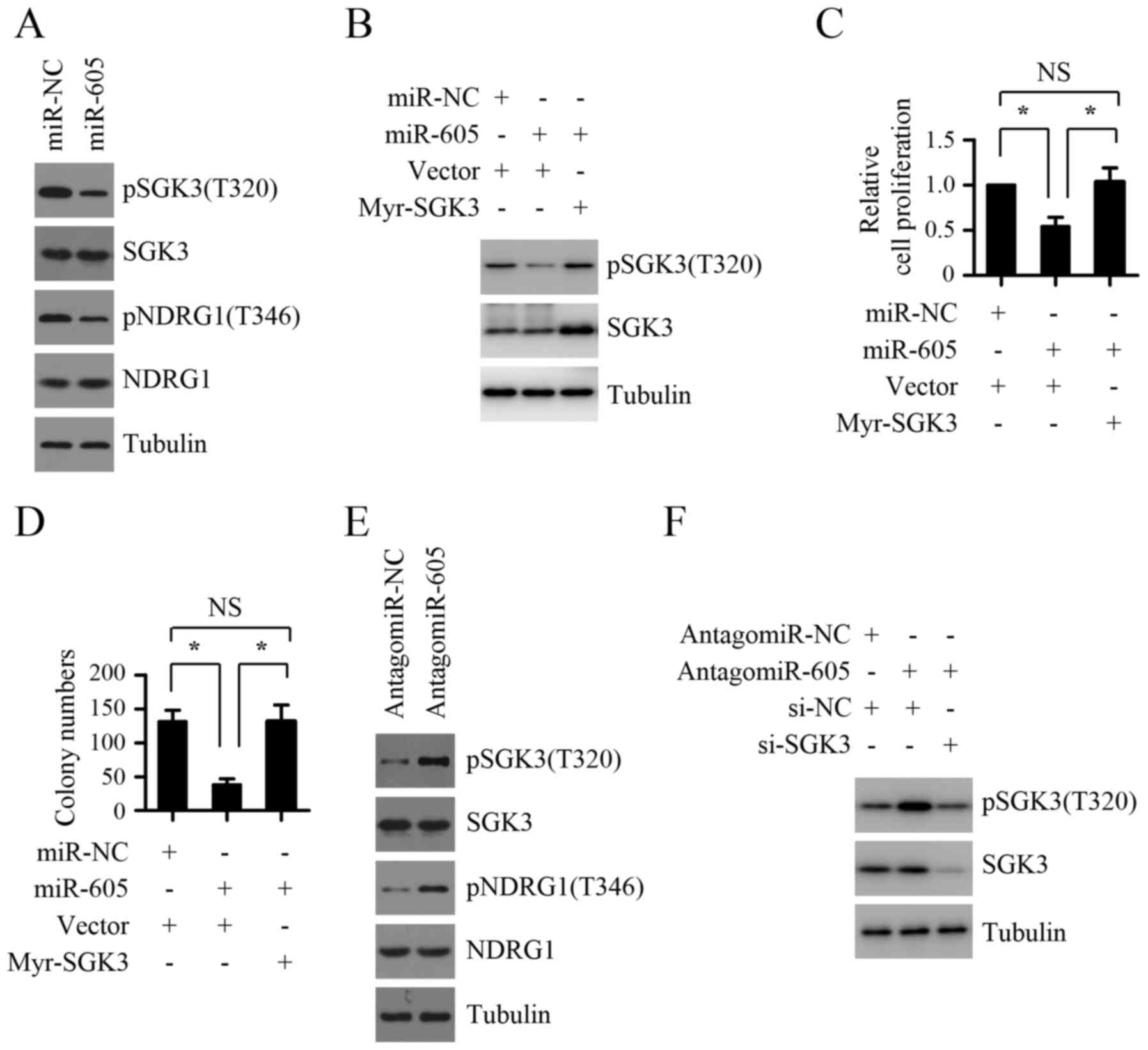
|
1
|
Arrangoiz R, Dorantes J, Cordera F, Juarez
MM and Paquentin EM: Melanoma review: Epidemiology, risk factors,
diagnosis and staging. J Cancer Treat Res. 4:1–15. 2016.doi:
10.11648/j.jctr.20160401.11. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W: Cancer statistics: updated cancer
burden in China. Chin J Cancer Res. 27:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holderfield M, Deuker MM, McCormick F and
McMahon M: Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated
melanoma and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:455–467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agoulnik IU, Hodgson MC, Bowden WA and
Ittmann MM: INPP4B: The new kid on the PI3K block. Oncotarget.
2:321–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Zeng D, Chen Y, Li N, Lv Y, Li Y,
Xu X and Xu G: miR-937 contributes to the lung cancer cell
proliferation by targeting INPP4B. Life Sci. 155:110–115. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rynkiewicz NK, Fedele CG, Chiam K, Gupta
R, Kench JG, Ooms LM, McLean CA, Giles GG, Horvath LG and Mitchell
CA: INPP4B is highly expressed in prostate intermediate cells and
its loss of expression in prostate carcinoma predicts for
recurrence and poor long term survival. Prostate. 75:92–102. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu I, Yeh CR, Slavin S, Miyamoto H, Netto
GJ, Tsai YC, Muyan M, Wu XR, Messing EM, Guancial EA, et al:
Estrogen receptor alpha prevents bladder cancer via INPP4B
inhibited akt pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget.
5:7917–7935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Perez-Lorenzo R, Gill KZ, Shen CH, Zhao
FX, Zheng B, Schulze HJ, Silvers DN, Brunner G and Horst BA: A
tumor suppressor function for the lipid phosphatase INPP4B in
melanocytic neoplasms. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1359–1368. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dzneladze I, He R, Woolley JF, Son MH,
Sharobim MH, Greenberg SA, Gabra M, Langlois C, Rashid A, Hakem A,
et al: INPP4B overexpression is associated with poor clinical
outcome and therapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
29:1485–1495. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fedele CG, Ooms LM, Ho M, Vieusseux J,
O'Toole SA, Millar EK, Lopez-Knowles E, Sriratana A, Gurung R,
Baglietto L, et al: Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase II
regulates PI3K/Akt signaling and is lost in human basal-like breast
cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:22231–22236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gasser JA, Inuzuka H, Lau AW, Wei W,
Beroukhim R and Toker A: SGK3 mediates INPP4B-dependent PI3K
signaling in breast cancer. Mol Cell. 56:595–607. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chi MN, Guo ST, Wilmott JS, Guo XY, Yan
XG, Wang CY, Liu XY, Jin L, Tseng HY, Liu T, et al: INPP4B is
upregulated and functions as an oncogenic driver through SGK3 in a
subset of melanomas. Oncotarget. 6:39891–39907. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bruhn MA, Pearson RB, Hannan RD and
Sheppard KE: AKT-independent PI3-K signaling in cancer - emerging
role for SGK3. Cancer Manag Res. 5:281–292. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Zhou D, Phung S, Masri S, Smith D
and Chen S: SGK3 is an estrogen-inducible kinase promoting
estrogen-mediated survival of breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol.
25:72–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Zhou D and Chen S: SGK3 is an
androgen-inducible kinase promoting prostate cancer cell
proliferation through activation of p70 S6 kinase and up-regulation
of cyclin D1. Mol Endocrinol. 28:935–948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu H, Li C, Shen C, Yin F, Wang K, Liu Y,
Zheng B, Zhang W, Hou X, Chen X, et al: MiR-212-3p inhibits
glioblastoma cell proliferation by targeting SGK3. J Neurooncol.
122:431–439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu M, Chen L, Chan TH, Wang J, Li Y, Li
Y, Zeng TT, Yuan YF and Guan XY: Serum and glucocorticoid kinase 3
at 8q13.1 promotes cell proliferation and survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 55:1754–1765. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scortegagna M, Lau E, Zhang T, Feng Y,
Sereduk C, Yin H, De SK, Meeth K, Platt JT, Langdon CG, et al: PDK1
and SGK3 contribute to the growth of BRAF-mutant melanomas and are
potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Res. 75:1399–1412. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haflidadóttir BS, Bergsteinsdóttir K,
Praetorius C and Steingrímsson E: miR-148 regulates Mitf in
melanoma cells. PLoS One. 5:e115742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, Reavie
L, Zou X, Alvarez-Diaz S, Zakrzewski J, Blochin E, Rose A,
Bogunovic D, et al: Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma
metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated
transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1814–1819. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Bottero L,
Segnalini P, Stoppacciaro A, Biffoni M, Felli N, Mattia G, Petrini
M, Colombo MP, et al: The promyelocytic leukemia zinc
finger-microRNA-221/−222 pathway controls melanoma progression
through multiple oncogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res. 68:2745–2754.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo C, Merz PR, Chen Y, Dickes E, Pscherer
A, Schadendorf D and Eichmüller SB: MiR-101 inhibits melanoma cell
invasion and proliferation by targeting MITF and EZH2. Cancer Lett.
341:240–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo C, Tetteh PW, Merz PR, Dickes E,
Abukiwan A, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Holland-Cunz S, Sinnberg T, Schittek
B, Schadendorf D, et al: miR-137 inhibits the invasion of melanoma
cells through downregulation of multiple oncogenic target genes. J
Invest Dermatol. 133:768–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S, Tetzlaff MT, Cui R and Xu X:
miR-200c inhibits melanoma progression and drug resistance through
down-regulation of BMI-1. Am J Pathol. 181:1823–1835. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao J, Lin H, Luo X, Luo X and Wang Z:
miR-605 joins p53 network to form a p53:miR-605:Mdm2 positive
feedback loop in response to stress. EMBO J. 30:524–532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang MW, Jin MJ, Yu YX, Zhang SC, Liu B,
Jiang X, Pan YF, Li QI, Ma SY and Chen K: Associations of
lifestyle-related factors, hsa-miR-149 and hsa-miR-605 gene
polymorphisms with gastrointestinal cancer risk. Mol Carcinog.
51:(Suppl 1). E21–E31. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang SP, Levesque E, Guillemette C, Yu
CC, Huang CY, Lin VC, Chung IC, Chen LC, Laverdière I, Lacombe L,
et al: Genetic variants in microRNAs and microRNA target sites
predict biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in
localized prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 135:2661–2667. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin Z, Li H, Cui Z, Ren Y, Li X, Wu W,
Guan P, Qian B, Rothman N, Lan Q, et al: Polymorphisms in pre-miRNA
genes and cooking oil fume exposure as well as their interaction on
the risk of lung cancer in a Chinese nonsmoking female population.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:395–401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Tian F, Li D, Chen J, Jiang P, Zheng
S, Li X and Wang S: MiR-605 represses PSMD10/Gankyrin and inhibits
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell progression. FEBS Lett.
588:3491–3500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen L, Liu T, Tu Y, Rong D and Cao Y:
Cul1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation by promoting DEPTOR
degradation and enhancing cap-dependent translation. Oncol Rep.
35:1049–1056. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hao S, Luo C, Abukiwan A, Wang G, He J,
Huang L, Weber CE, Lv N, Xiao X, Eichmüller SB, et al: miR-137
inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by targeting PAK2. Exp
Dermatol. 24:947–952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang X, Zhang H, Lian S and Zhu W:
miR-137 suppresses tumor growth of malignant melanoma by targeting
aurora kinase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 475:251–256. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen QH, Wang QB and Zhang B: Ethnicity
modifies the association between functional microRNA polymorphisms
and breast cancer risk: a HuGE meta-analysis. Tumour Biol.
35:529–543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alhasan AH, Scott AW, Wu JJ, Feng G, Meeks
JJ, Thaxton CS and Mirkin CA: Circulating microRNA signature for
the diagnosis of very high-risk prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:10655–10660. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guo ST, Chi MN, Yang RH, Guo XY, Zan LK,
Wang CY, Xi YF, Jin L, Croft A, Tseng HY, et al: INPP4B is an
oncogenic regulator in human colon cancer. Oncogene. 35:3049–3061.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bago R, Sommer E, Castel P, Crafter C,
Bailey FP, Shpiro N, Baselga J, Cross D, Eyers PA and Alessi DR:
The hVps34-SGK3 pathway alleviates sustained PI3K/Akt inhibition by
stimulating mTORC1 and tumour growth. EMBO J. 35:1902–1922. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, Nathan P,
Garbe C, Milhem M, Demidov LV, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, Mohr P, et
al: METRIC Study Group: Improved survival with MEK inhibition in
BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 367:107–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|