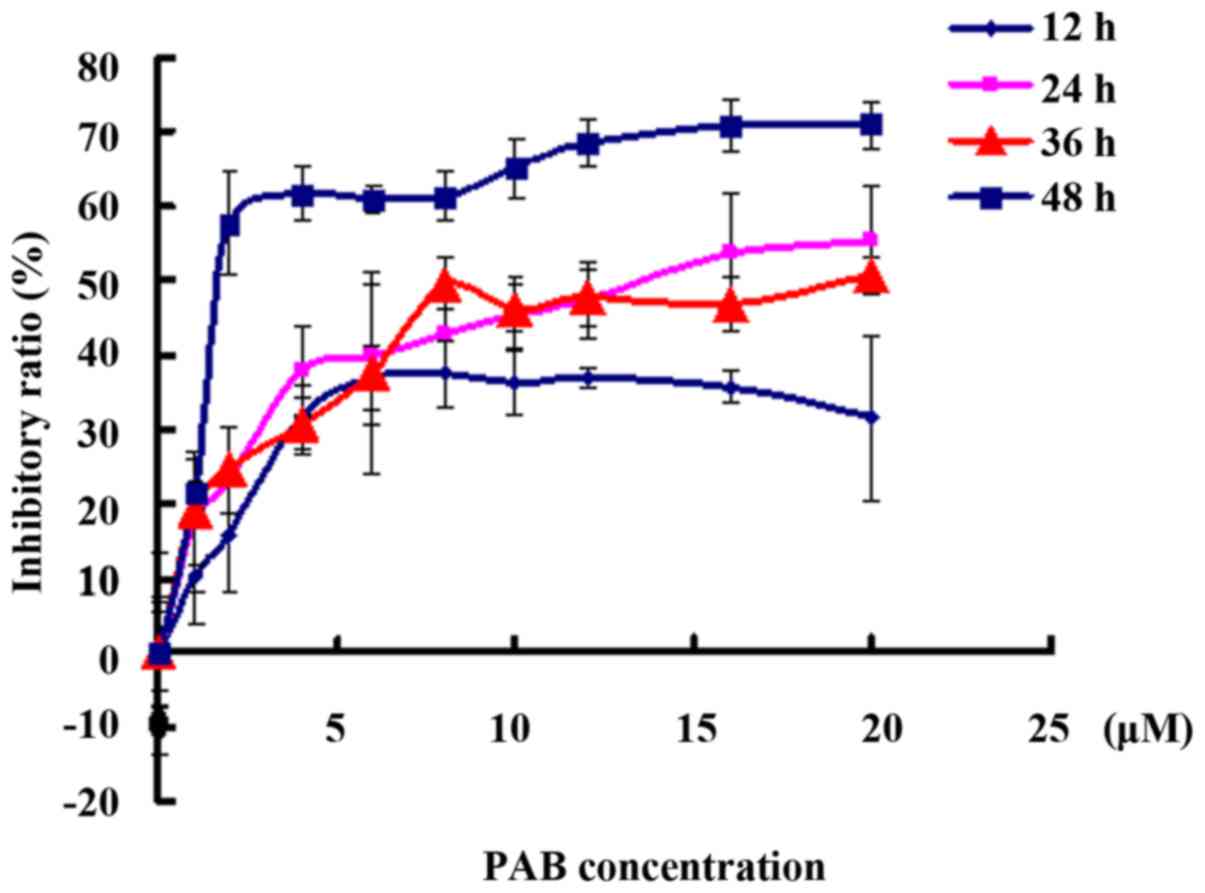
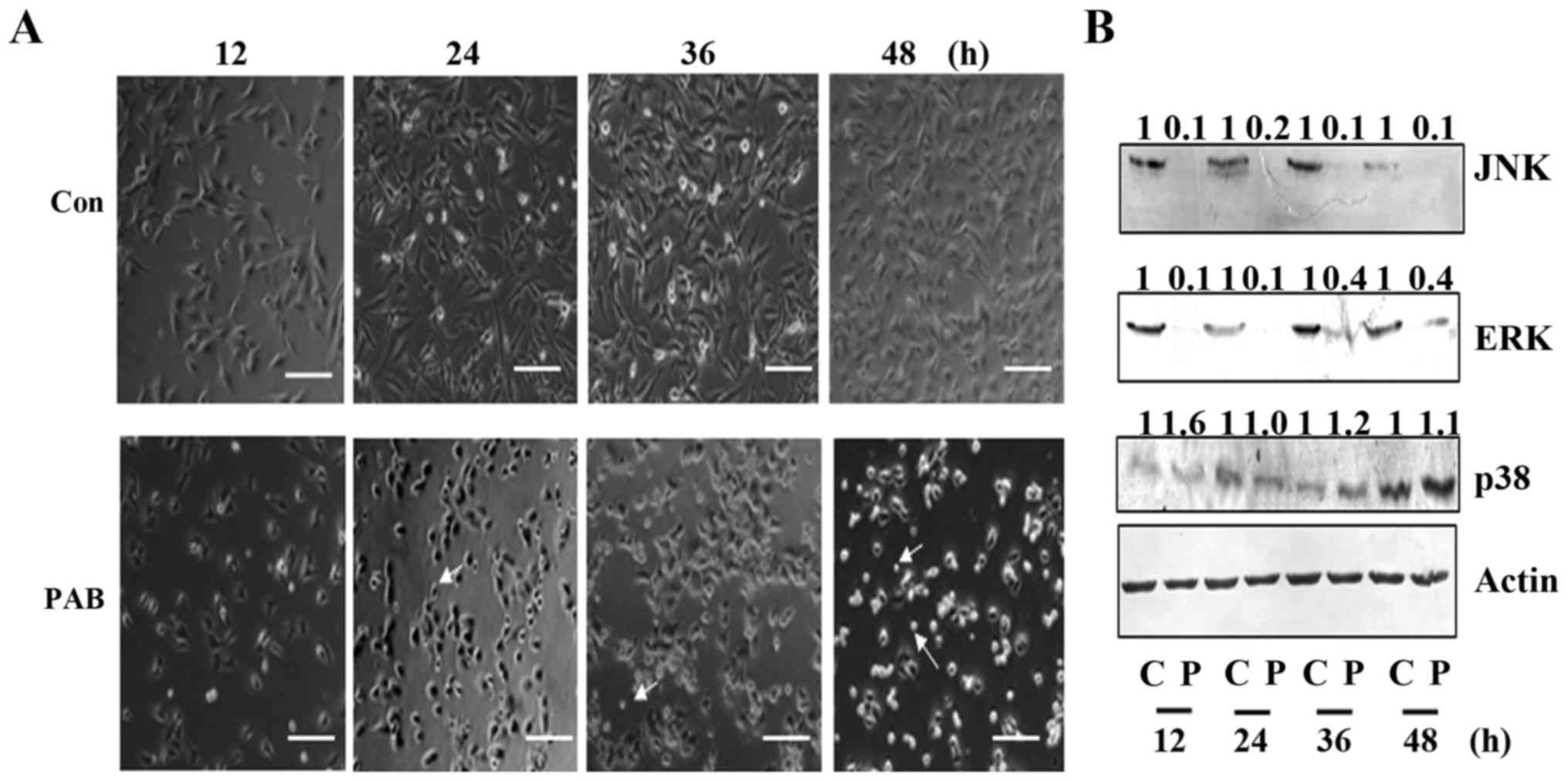
|
1
|
Gong X, Wang M, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Involvement of JNK-initiated p53 accumulation and
phosphorylation of p53 in pseudolaric acid B induced cell death.
Exp Mol Med. 38:428–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gong XF, Wang MW, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces apoptosis through p53 and
Bax/Bcl-2 pathways in human melanoma A375-S2 cells. Arch Pharm Res.
28:68–72. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pan DJ, Li ZL, Hu CQ, Chen K, Chang JJ and
Lee KH: The cytotoxic principles of Pseudolarix kaempferi:
Pseudolaric acid-A and -B and related derivatives. Planta Med.
56:383–385. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu J, Li X, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Bcl-2 family proteins were involved in pseudolaric acid
B-induced autophagy in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells. J Pharmacol
Sci. 107:295–302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu JH, Cui Q, Jiang YY, Yang W, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces apoptosis,
senescence, and mitotic arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 28:1975–1983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu JH, Wang HJ, Li XR, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Protein tyrosine kinase, JNK, and ERK involvement
in pseudolaric acid B-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer
MCF-7 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1069–1076. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shakur SF, Bit-Ivan E, Watkin WG, Merrell
RT and Farhat HI: Multifocal and multicentric glioblastoma with
leptomeningeal gliomatosis: A case report and review of the
literature. Case Rep Med. 2013:1326792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Walker C, Baborie A, Crooks D, Wilkins S
and Jenkinson MD: Biology, genetics and imaging of glial cell
tumours. Br J Radiol. 84:S90–S106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Siu IM, Gallia GL, et
al: An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma
multiforme. Science. 321:1807–1812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lozano G and Elledge SJ: p53 sends
nucleotides to repair DNA. Nature. 404:24–25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li FF, Yi S, Wen L, He J, Yang LJ, Zhao J,
Zhang BP, Cui GH and Chen Y: Oridonin induces NPM mutant protein
translocation and apoptosis in NPM1c+ acute myeloid leukemia cells
in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:806–813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qi M, Yao G, Fan S, Cheng W, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces mitotic
catastrophe followed by apoptotic cell death in murine fibrosarcoma
L929 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:16–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klekotka PA, Santoro SA, Wang H and Zutter
MM: Specific residues within the alpha 2 integrin subunit
cytoplasmic domain regulate migration and cell cycle progression
via distinct MAPK pathways. J Biol Chem. 276:32353–32361. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoon S and Seger R: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase: Multiple substrates regulate diverse
cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24:21–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hartwell LH and Weinert TA: Checkpoints:
Controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science.
246:629–634. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu J, Ren P, Zhong T, Wang Y, Yan M, Xue
B, Li R, Dai C, Liu C, Chen G, et al: Pseudolaric acid B inhibits
proliferation in SW579 human thyroid squamous cell carcinoma. Mol
Med Rep. 12:7195–7202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Chong Y, Tu Y, Liu N, Yue C, Qi Z,
Liu H, Yao Y, Liu H, Gao S, et al: CRM1/XPO1 is associated with
clinical outcome in glioma and represents a therapeutic target by
perturbing multiple core pathways. J Hematol Oncol. 9:1082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tong YG, Zhang XW, Geng MY, Yue JM, Xin
XL, Tian F, Shen X, Tong LJ, Li MH, Zhang C, et al: Pseudolarix
acid B, a new tubulin-binding agent, inhibits angiogenesis by
interacting with a novel binding site on tubulin. Mol Pharmacol.
69:1226–1233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wong VK, Chiu P, Chung SS, Chow LM, Zhao
YZ, Yang BB and Ko BC: Pseudolaric acid B, a novel
microtubule-destabilizing agent that circumvents multidrug
resistance phenotype and exhibits antitumor activity in vivo. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:6002–6011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu B, Dong H, Lin X, Yang X, Yue X, Yang
J, Li Y, Wu L, Zhu X, Zhang S, et al: RND3 promotes Snail 1 protein
degradation and inhibits glioblastoma cell migration and invasion.
Oncotarget. 7:82411–82423. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|