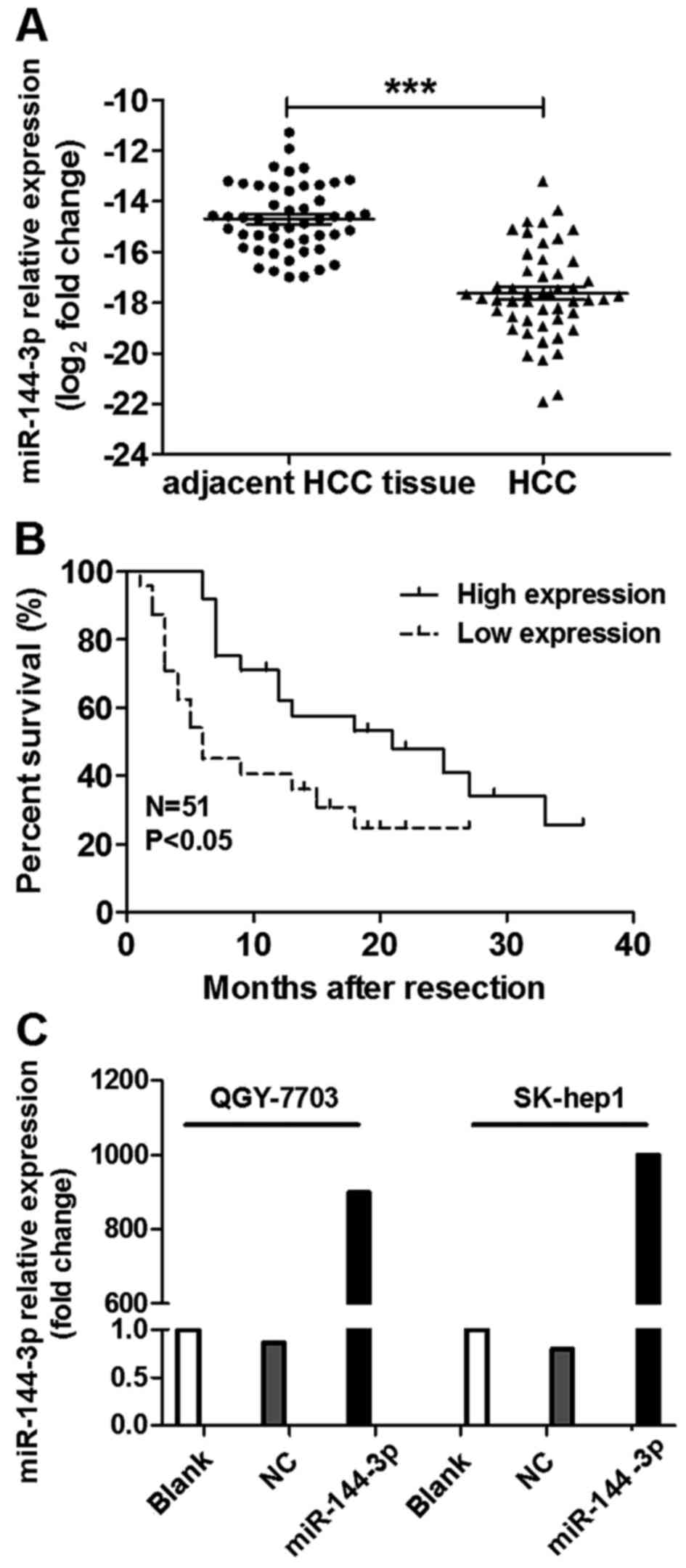
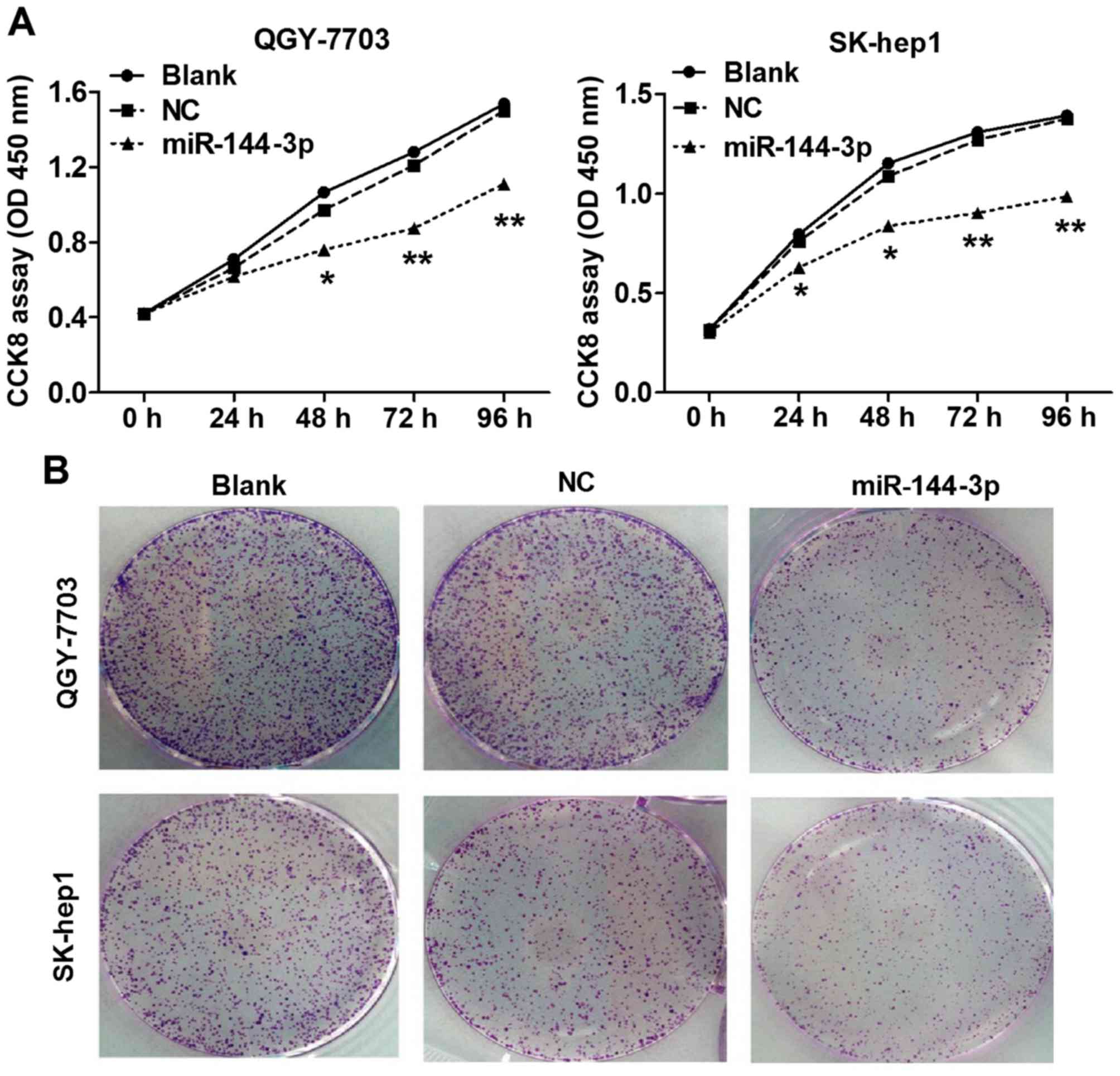
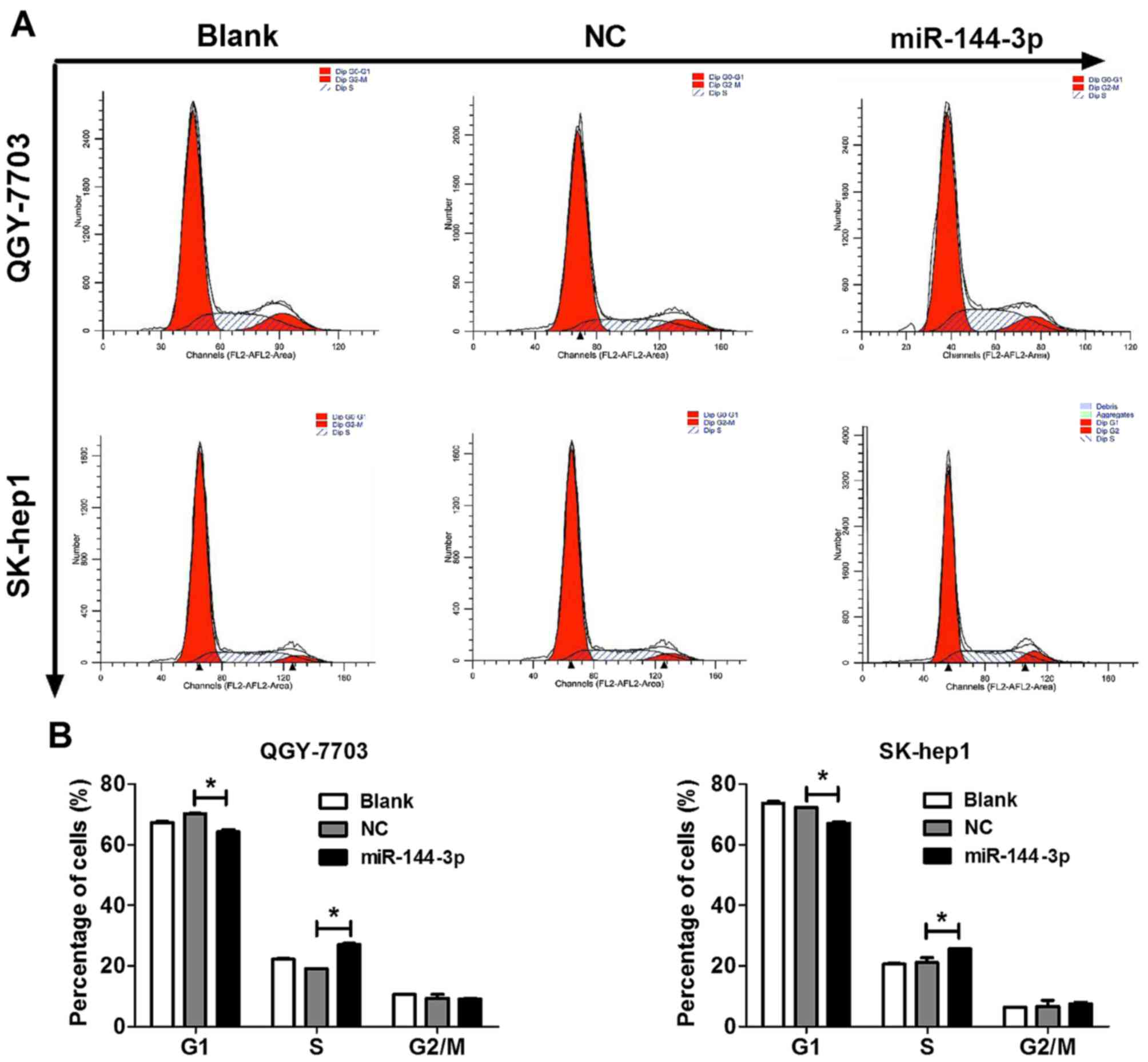
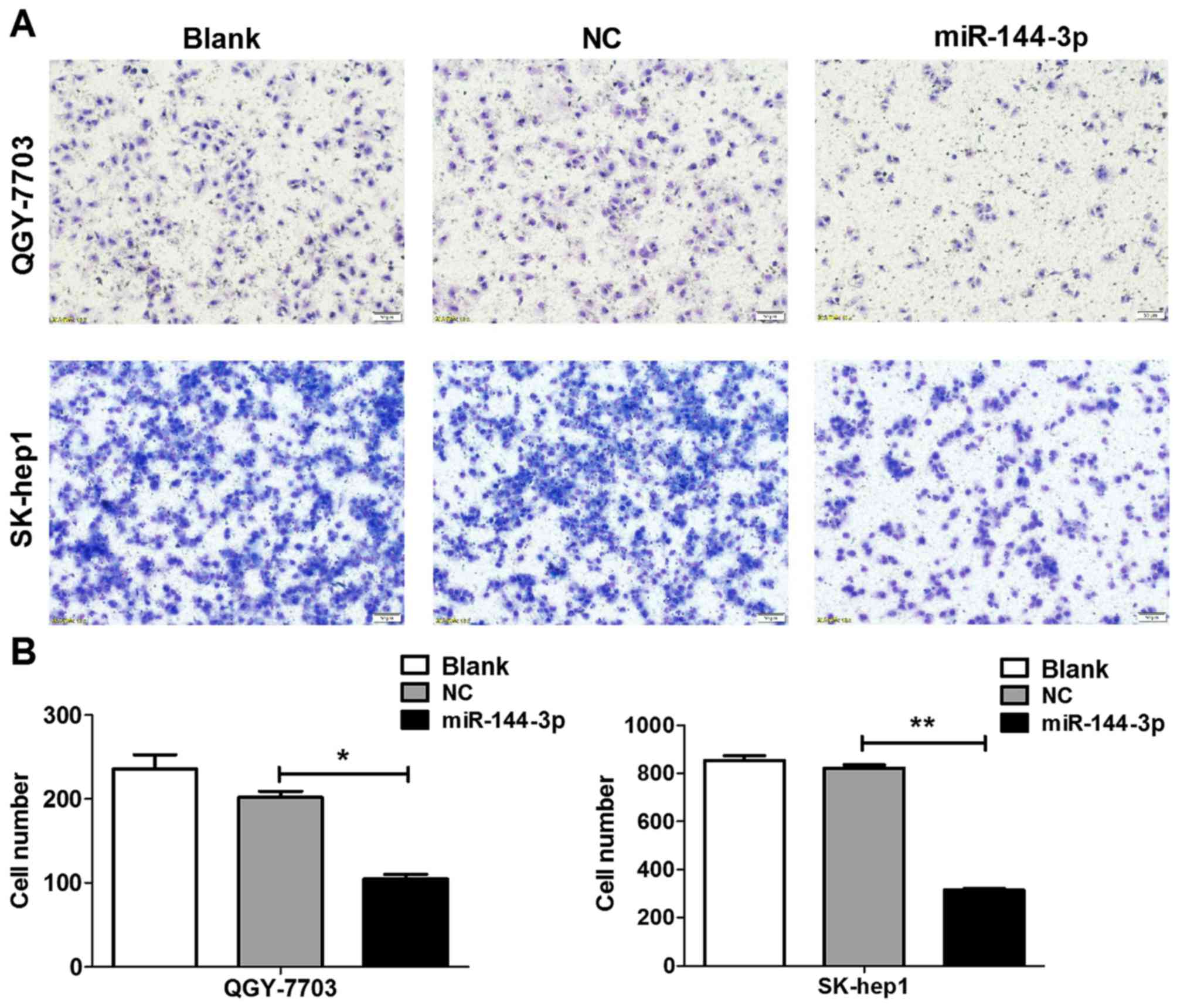
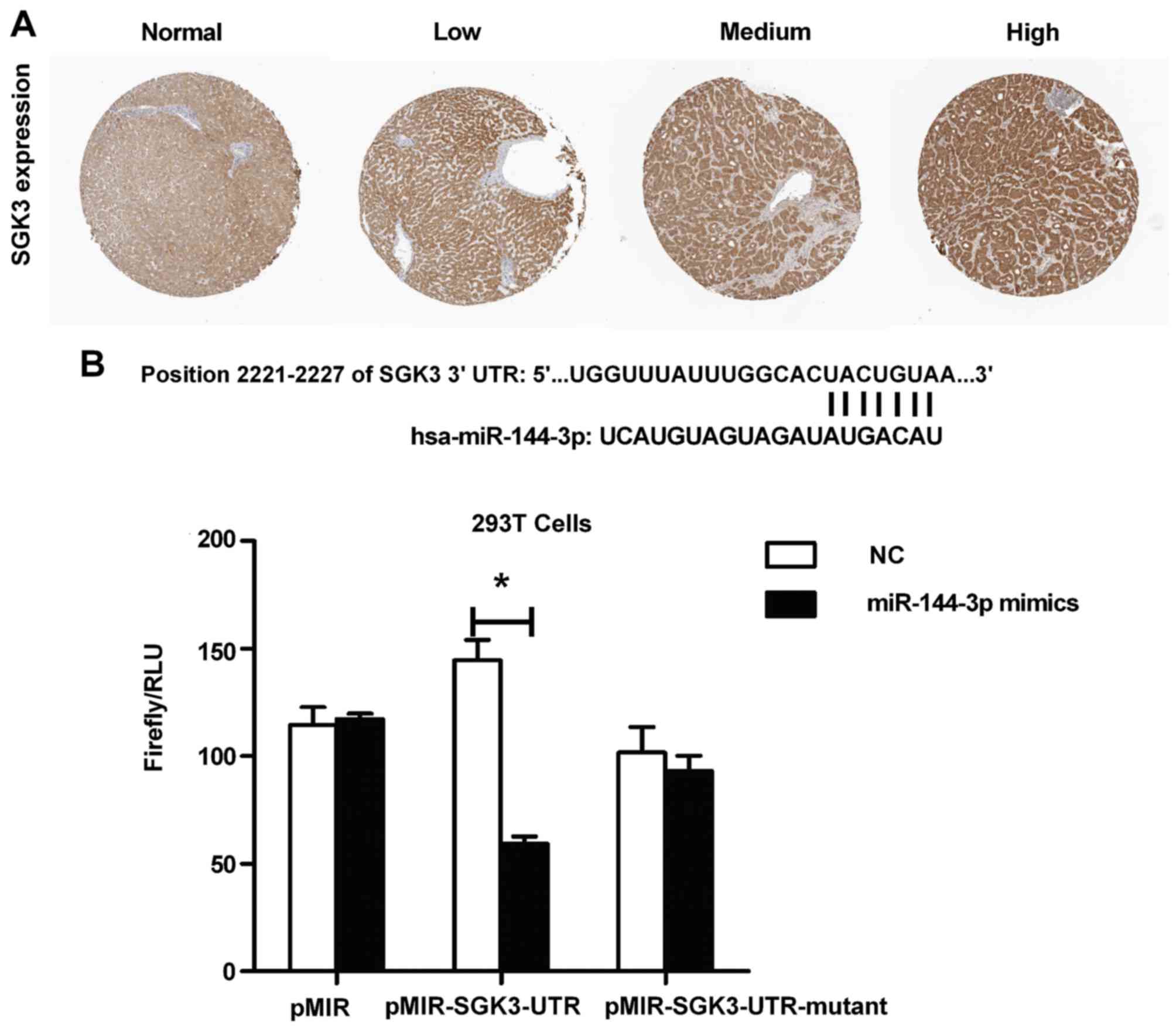
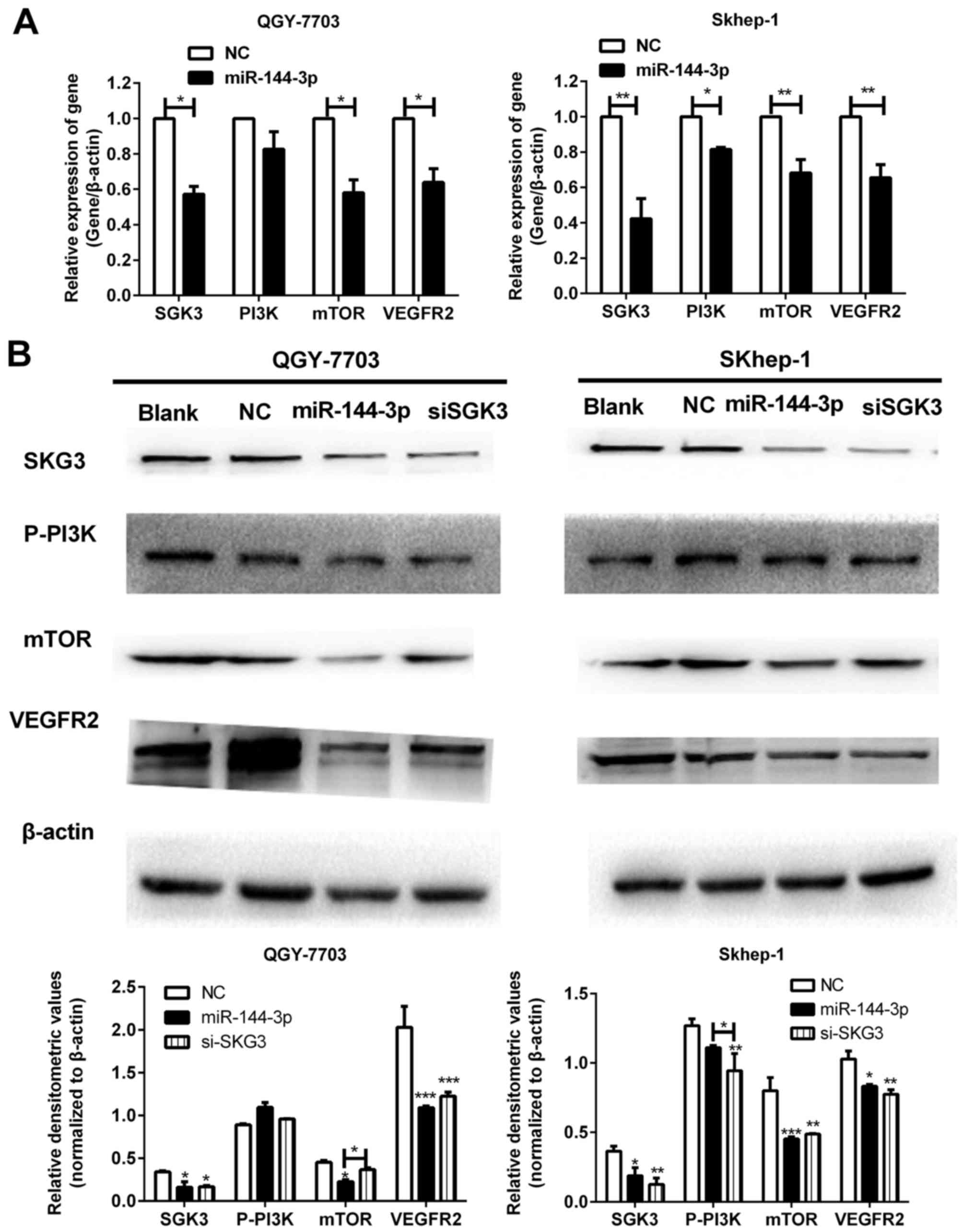
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aravalli RN, Cressman EN and Steer CJ:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma: An
update. Arch Toxicol. 87:227–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ
and Bushell M: microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol.
13:e249–e258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou X, Zhang CZ, Lu SX, Chen GG, Li LZ,
Liu LL, Yi C, Fu J, Hu W, Wen JM, et al: miR-625 suppresses tumour
migration and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 34:965–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, Wang Z, Ding G, Dong
Q, Qin L, Wu X, Zheng Y, Yang Y, et al: Identification of miRNomes
in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p
as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell.
19:232–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guan H, Liang W, Xie Z, Li H, Liu J, Liu
L, Xiu L and Li Y: Down-regulation of miR-144 promotes thyroid
cancer cell invasion by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Endocrine.
48:566–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zha W, Cao L, Shen Y and Huang M: Roles of
MiR-144-ZFX pathway in growth regulation of non-small-cell lung
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e741752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang XP, Hou J, Shen XY, Huang CY, Zhang
XH, Xie YA and Luo XL: MicroRNA-486-5p, which is downregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses tumor growth by targeting
PIK3R1. FEBS J. 282:579–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bruhn MA, Pearson RB, Hannan RD and
Sheppard KE: AKT-independent PI3-K signaling in cancer - emerging
role for SGK3. Cancer Manag Res. 5:281–292. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao T, Li H, Hu Y, Ma D and Cai X: miR-144
suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol. 35:10759–10764. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang R, Zhao N, Li S, Fang JH, Chen MX,
Yang J, Jia WH, Yuan Y and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-195 suppresses
angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
inhibiting the expression of VEGF, VAV2, and CDC42. Hepatology.
58:642–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang X, Zhang XF, Lu X, Jia HL, Liang L,
Dong QZ, Ye QH and Qin LX: MicroRNA-26a suppresses angiogenesis in
human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte growth
factor-cMet pathway. Hepatology. 59:1874–1885. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Wang G and Zheng H: Role
of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 14:e186722014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Navon R, Wang H, Steinfeld I, Tsalenko A,
Ben-Dor A and Yakhini Z: Novel rank-based statistical methods
reveal microRNAs with differential expression in multiple cancer
types. PLoS One. 4:e80032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen S, Li P, Li J, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X,
Zang W, Wang H, Chu H, Zhao G, et al: MiR-144 inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis and autophagy in lung cancer
cells by targeting TIGAR. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:997–1007. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Y, Ying L, Tian Y, Yang P, Zhu Y, Wang
Z, Qiu F and Lin J: miR-144 downregulation increases bladder cancer
cell proliferation by targeting EZH2 and regulating Wnt signaling.
FEBS J. 280:4531–4538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang LY, Lee Ho-Fun V, Wong AM, Kwong DL,
Zhu YH, Dong SS, Kong KL, Chen J, Tsao SW, Guan XY, et al:
MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN.
Carcinogenesis. 34:454–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu L, Wang S, Chen R, Wu Y, Zhang B,
Huang S, Zhang J, Xiao F, Wang M and Liang Y: Myc induced
miR-144/451 contributes to the acquired imatinib resistance in
chronic myelogenous leukemia cell K562. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
425:368–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yuan SX, Yang F, Yang Y, Tao QF, Zhang J,
Huang G, Yang Y, Wang RY, Yang S, Huo XS, et al: Long noncoding RNA
associated with microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
promotes angiogenesis and serves as a predictor for hepatocellular
carcinoma patients' poor recurrence-free survival after
hepatectomy. Hepatology. 56:2231–2241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y,
Huang X, Zhang JP, Guan XY and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-29b suppresses
tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix
metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 54:1729–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I,
Pinzani M and Bosch J: Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol.
50:604–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thomas MB, Jaffe D, Choti MM, Belghiti J,
Curley S, Fong Y, Gores G, Kerlan R, Merle P, O'Neil B, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Consensus recommendations of the National
Cancer Institute Clinical Trials Planning Meeting. J Clin Oncol.
28:3994–4005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hao CY: Angiogenesis blockade as therapy
for hepatocellular carcinoma: Progress and challenges. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:4–6. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Wang JN, Tang JM, Kong X, Yang
JY, Zheng F, Guo LY, Huang YZ, Zhang L, Tian L, et al: VEGF is
essential for the growth and migration of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 39:5085–5093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hou M, Lai Y, He S, He W, Shen H and Ke Z:
SGK3 (CISK) may induce tumor angiogenesis (Hypothesis). Oncol Lett.
10:23–26. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Catela C, Kratsios P, Hede M, Lang F and
Rosenthal N: Serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) is
necessary for vascular remodeling during angiogenesis. Dev Dyn.
239:2149–2160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zarrinpashneh E, Poggioli T, Sarathchandra
P, Lexow J, Monassier L, Terracciano C, Lang F, Damilano F, Zhou
JQ, Rosenzweig A, et al: Ablation of SGK1 impairs endothelial cell
migration and tube formation leading to decreased neo-angiogenesis
following myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 8:e802682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|