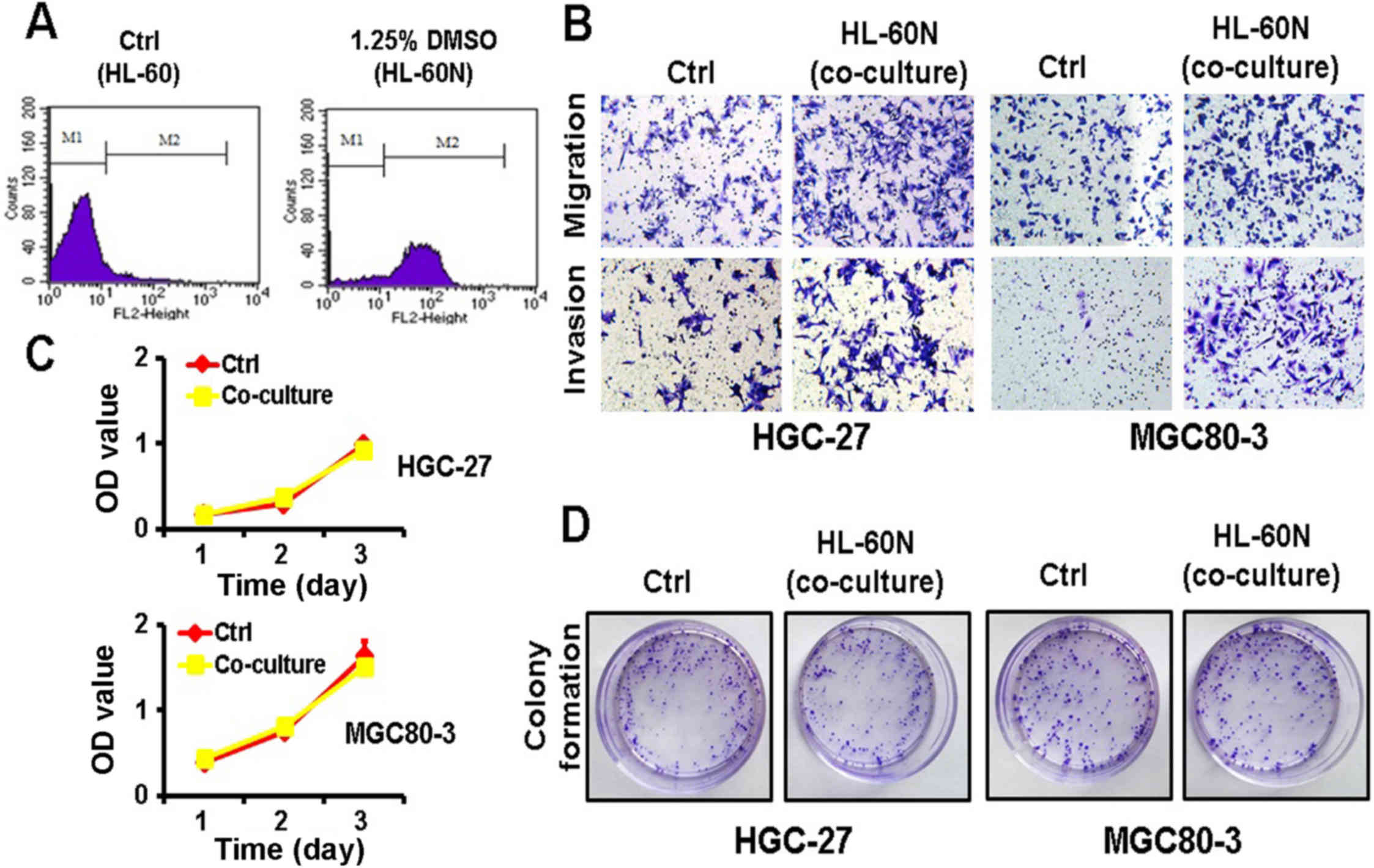
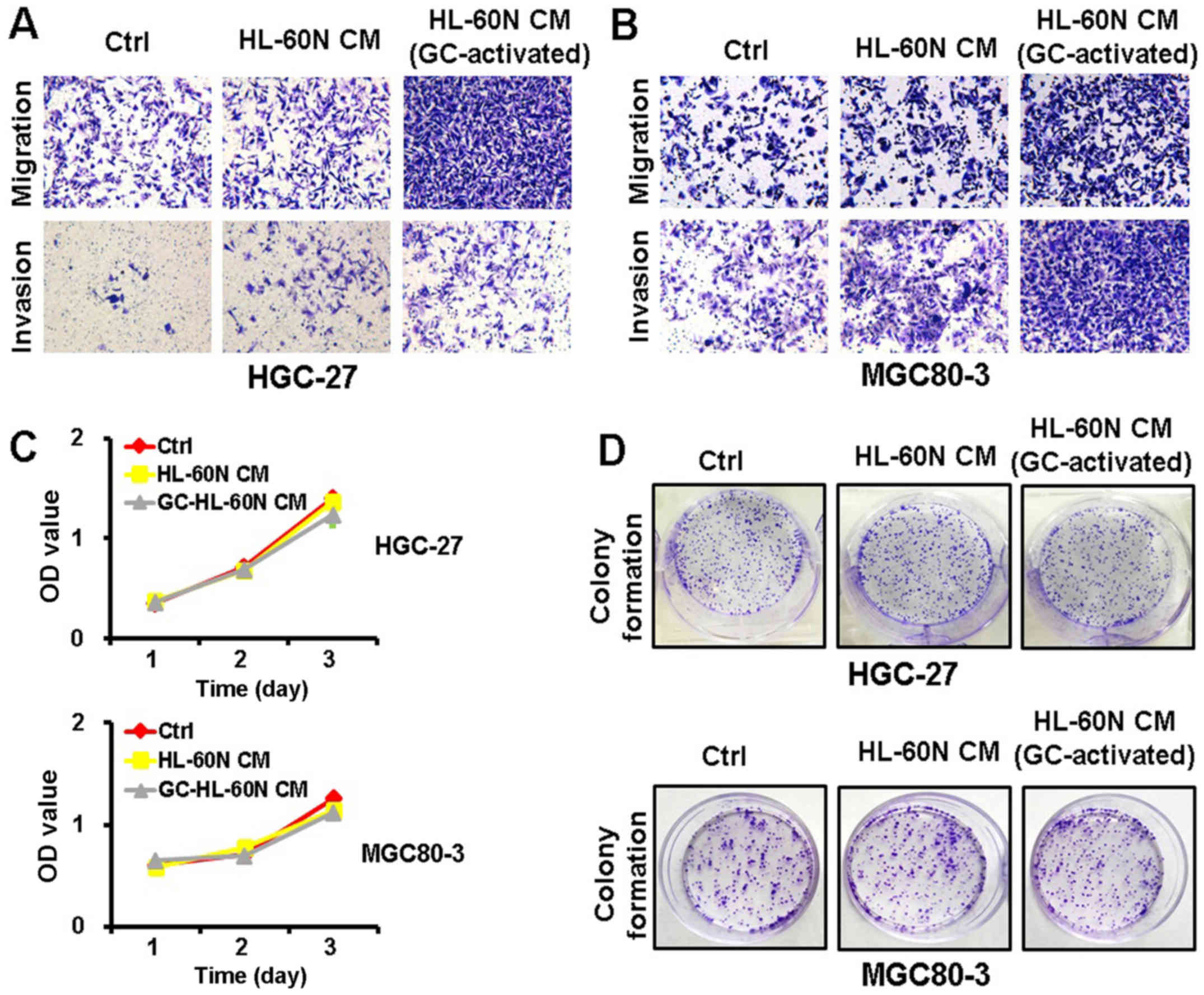
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma HY, Liu XZ and Liang CM: Inflammatory
microenvironment contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:6619–6628. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang X, Zhang W, Yuan X, Fu M, Qian H and
Xu W: Neutrophils in cancer development and progression: Roles,
mechanisms, and implications (Review). Int J Oncol. 49:857–867.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coffelt SB, Wellenstein MD and de Visser
KE: Neutrophils in cancer: Neutral no more. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:431–446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li TJ, Jiang YM, Hu YF, Huang L, Yu J,
Zhao LY, Deng HJ, Mou TY, Liu H, Yang Y, et al:
Interleukin-17-producing neutrophils link inflammatory stimuli to
disease progression by promoting angiogenesis in gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:1575–1585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang TT, Zhao YL, Peng LS, Chen N, Chen W,
Lv YP, Mao FY, Zhang JY, Cheng P, Teng YS, et al: Tumour-activated
neutrophils in gastric cancer foster immune suppression and disease
progression through GM-CSF-PD-L1 pathway. Gut. Mar 8–2017.(Epud
ahead of print). doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313075. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Powell DR and Huttenlocher A: Neutrophils
in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 37:41–52. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gordon-Weeks AN, Lim SY, Yuzhalin AE,
Jones K, Markelc B, Kim KJ, Buzzelli JN, Fokas E, Cao Y, Smart S,
et al: Neutrophils promote hepatic metastasis growth through
fibroblast growth factor 2-dependent angiogenesis in mice.
Hepatology. 65:1920–1935. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW,
Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS, Verstegen NJM, Ciampricotti M,
Hawinkels LJAC, Jonkers J and de Visser KE: IL-17-producing γδ T
cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 522:345–348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He M, Peng A, Huang XZ, Shi DC, Wang JC,
Zhao Q, Lin H, Kuang DM, Ke PF and Lao XM: Peritumoral stromal
neutrophils are essential for c-Met-elicited metastasis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoImmunology. 5:e12198282016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grégoire M, Guilloton F, Pangault C,
Mourcin F, Sok P, Latour M, Amé-Thomas P, Flecher E, Fest T and
Tarte K: Neutrophils trigger a NF-κB dependent polarization of
tumor-supportive stromal cells in germinal center B-cell lymphomas.
Oncotarget. 6:16471–16487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu Q, Zhang X, Zhang L, Li W, Wu H, Yuan
X, Mao F, Wang M, Zhu W, Qian H, et al: The IL-6-STAT3 axis
mediates a reciprocal crosstalk between cancer-derived mesenchymal
stem cells and neutrophils to synergistically prompt gastric cancer
progression. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El Rayes T, Catena R, Lee S, Stawowczyk M,
Joshi N, Fischbach C, Powell CA, Dannenberg AJ, Altorki NK, Gao D,
et al: Lung inflammation promotes metastasis through neutrophil
protease-mediated degradation of Tsp-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:pp. 16000–16005. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Queen MM, Ryan RE, Holzer RG, Keller-Peck
CR and Jorcyk CL: Breast cancer cells stimulate neutrophils to
produce oncostatin M: Potential implications for tumor progression.
Cancer Res. 65:8896–8904. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Glogauer JE, Sun CX, Bradley G and
Magalhaes MA: Neutrophils increase oral squamous cell carcinoma
invasion through an invadopodia-dependent pathway. Cancer Immunol
Res. 3:1218–1226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Freisinger CM and Huttenlocher A: Live
imaging and gene expression analysis in zebrafish identifies a link
between neutrophils and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS
One. 9:e1121832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu P, Shen M, Zhang P, Zheng C, Pang Z,
Zhu L and Du J: Intratumoral neutrophil granulocytes contribute to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:7789–7796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gaida MM, Steffen TG, Günther F,
Tschaharganeh DF, Felix K, Bergmann F, Schirmacher P and Hänsch GM:
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils promote dyshesion of tumor cells and
elastase-mediated degradation of E-cadherin in pancreatic tumors.
Eur J Immunol. 42:3369–3380. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mayer C, Darb-Esfahani S, Meyer AS, Hübner
K, Rom J, Sohn C, Braicu I, Sehouli J, Hänsch GM and Gaida MM:
Neutrophil granulocytes in ovarian cancer - induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition and tumor cell migration. J
Cancer. 7:546–554. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang L, Wu RL and Xu AM:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Am J Transl
Res. 7:2141–2158. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu Y, Zhao Q, Peng C, Sun L, Li XF and
Kuang DM: Neutrophils promote motility of cancer cells via a
hyaluronan-mediated TLR4/PI3K activation loop. J Pathol.
225:438–447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou Q, Wang X, Yu Z, Wu X, Chen X, Li J,
Zhu Z, Liu B and Su L: Transducin (β)-like 1 X-linked receptor 1
promotes gastric cancer progression via the ERK1/2 pathway.
Oncogene. 36:1873–1886. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li XF, Chen DP, Ouyang FZ, Chen MM, Wu Y,
Kuang DM and Zheng L: Increased autophagy sustains the survival and
pro-tumourigenic effects of neutrophils in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 62:131–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|