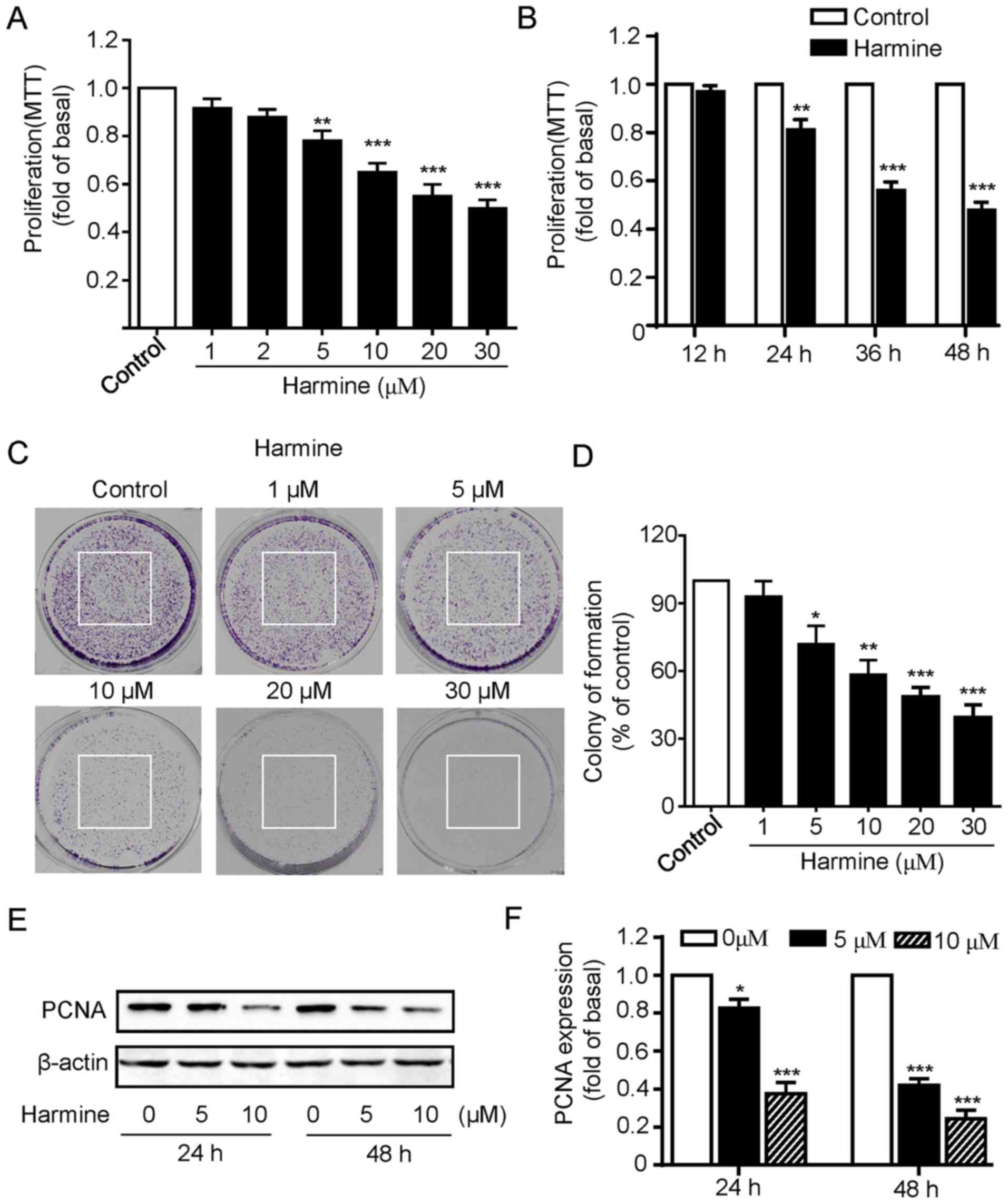
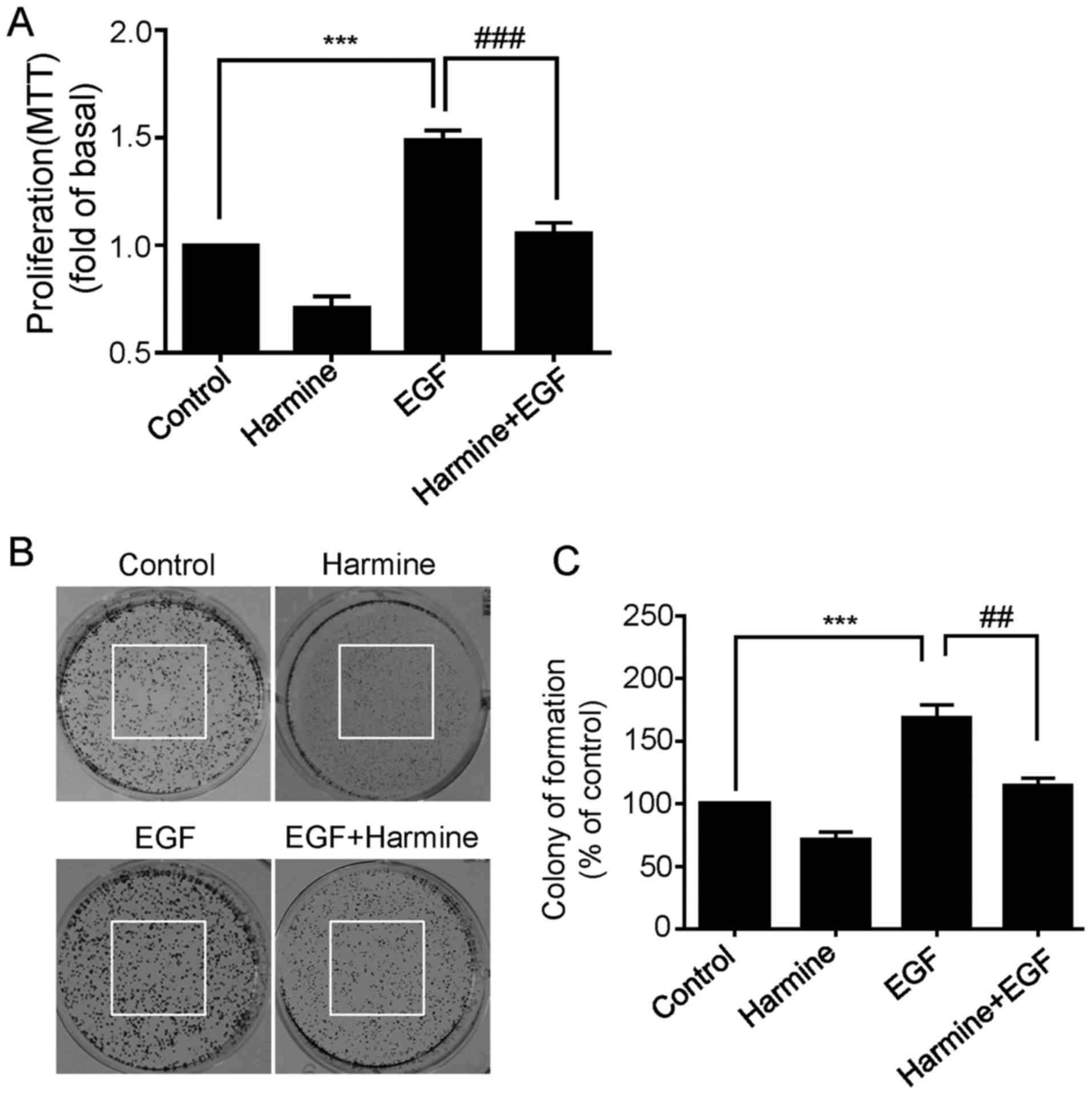
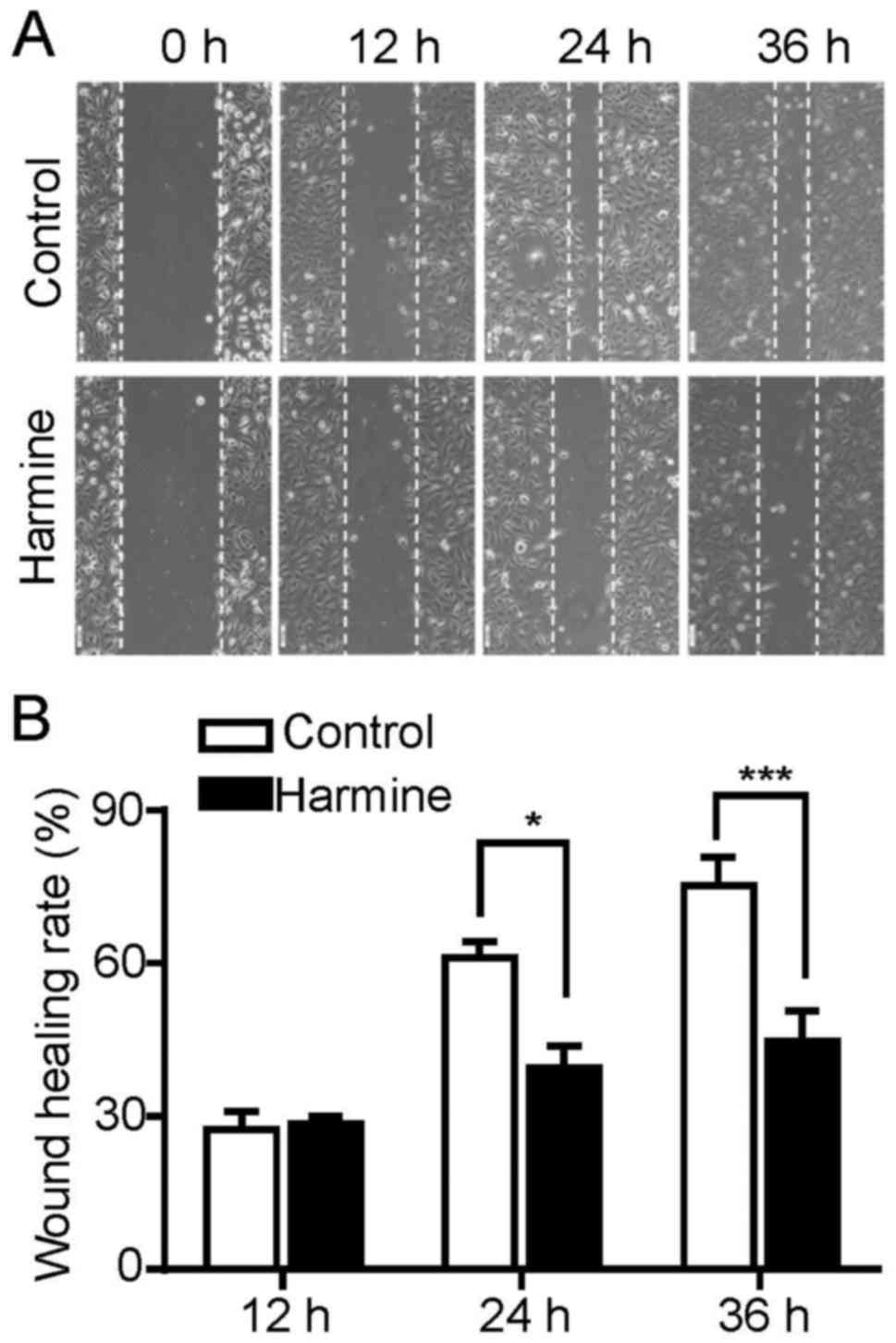
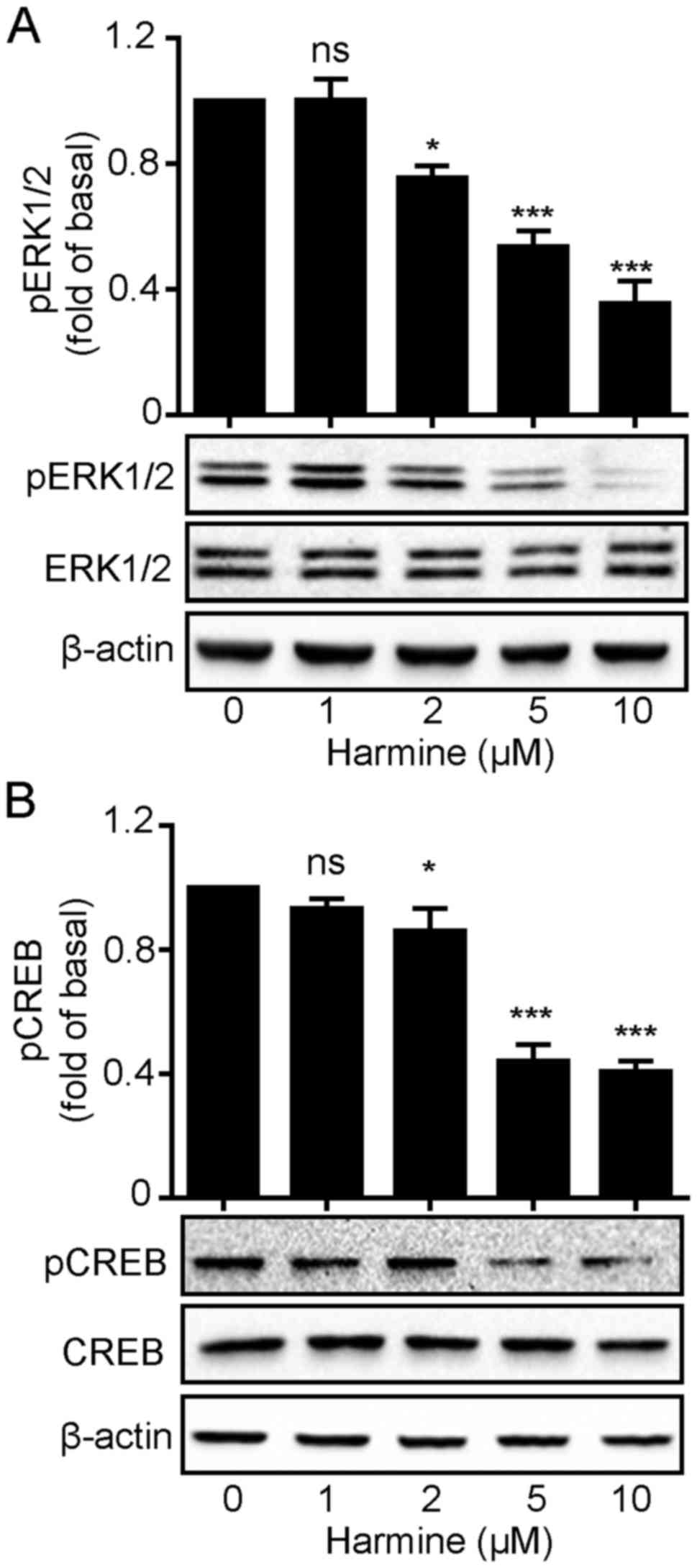
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coleman RL, Monk BJ, Sood AK and Herzog
TJ: Latest research and treatment of advanced-stage epithelial
ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:211–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mukherjee AK, Basu S, Sarkar N and Ghosh
AC: Advances in cancer therapy with plant based natural products.
Curr Med Chem. 8:1467–1486. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McChesney JD: Natural products in drug
discovery - organizing for success. P R Health Sci J. 21:91–95.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cragg GM, Newman DJ and Snader KM: Natural
products in drug discovery and development. J Nat Prod. 60:52–60.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao R, Peng W, Wang Z and Xu A:
beta-Carboline alkaloids: Biochemical and pharmacological
functions. Curr Med Chem. 14:479–500. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel K, Gadewar M, Tripathi R, Prasad SK
and Patel DK: A review on medicinal importance, pharmacological
activity and bioanalytical aspects of beta-carboline alkaloid
‘Harmine’. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2:660–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farzin D and Mansouri N:
Antidepressant-like effect of harmane and other beta-carbolines in
the mouse forced swim test. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 16:324–328.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao MR, Li Q, Liu ZL, Liu HH, Wang W, Liao
XL, Pan YL and Jiang JW: Harmine induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells
via mitochondrial signaling pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 10:599–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hamsa TP and Kuttan G: Harmine activates
intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis in B16F-10 melanoma.
Chin Med. 6:112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang P, Huang CR, Wang W, Zhang XK, Chen
JJ, Wang JJ, Lin C and Jiang JW: Harmine hydrochloride triggers G2
phase arrest and apoptosis in MGC-803 cells and SMMC-7721 cells by
upregulating p21, activating caspase-8/Bid, and downregulating
ERK/Bad pathway. Phytother Res. 30:31–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lafky JM, Wilken JA, Baron AT and Maihle
NJ: Clinical implications of the ErbB/epidermal growth factor (EGF)
receptor family and its ligands in ovarian cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1785:232–265. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu LZ, Hu XW, Xia C, He J, Zhou Q, Shi X,
Fang J and Jiang BH: Reactive oxygen species regulate epidermal
growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression through activation of
AKT and P70S6K1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
41:1521–1533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Newby AC: Matrix metalloproteinases
regulate migration, proliferation, and death of vascular smooth
muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates.
Cardiovasc Res. 69:614–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bernatchez PN, Soker S and Sirois MG:
Vascular endothelial growth factor effect on endothelial cell
proliferation, migration, and platelet-activating factor synthesis
is Flk-1-dependent. J Biol Chem. 274:31047–31054. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Demain AL and Vaishnav P: Natural products
for cancer chemotherapy. Microb Biotechnol. 4:687–699. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kummar S, Gutierrez M, Doroshow JH and
Murgo AJ: Drug development in oncology: Classical cytotoxics and
molecularly targeted agents. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 62:15–26. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fox E, Curt GA and Balis FM: Clinical
trial design for target-based therapy. Oncologist. 7:401–409. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dakic V, Maciel RM, Drummond H, Nascimento
JM, Trindade P and Rehen SK: Harmine stimulates proliferation of
human neural progenitors. PeerJ. 4:e27272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hämmerle B, Ulin E, Guimera J, Becker W,
Guillemot F and Tejedor FJ: Transient expression of Mnb/Dyrk1a
couples cell cycle exit and differentiation of neuronal precursors
by inducing p27KIP1 expression and suppressing NOTCH signaling.
Development. 138:2543–2554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D,
Jain M, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:15–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dimova I, Zaharieva B, Raitcheva S,
Dimitrov R, Doganov N and Toncheva D: Tissue microarray analysis of
EGFR and erbB2 copy number changes in ovarian tumors. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 16:145–151. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dancey JE and Freidlin B: Targeting
epidermal growth factor receptor - are we missing the mark? Lancet.
362:62–64. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lassus H, Sihto H, Leminen A, Joensuu H,
Isola J, Nupponen NN and Butzow R: Gene amplification, mutation,
and protein expression of EGFR and mutations of ERBB2 in serous
ovarian carcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 84:671–681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aggarwal S, Kim SW, Ryu SH, Chung WC and
Koo JS: Growth suppression of lung cancer cells by targeting cyclic
AMP response element-binding protein. Cancer Res. 68:981–988. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu P, Weaver VM and Werb Z: The
extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell
Biol. 196:395–406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H and
Thorgeirsson UP: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
Structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol.
74:111–122. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu P, He J, Liu S, Wang M, Pan B and Zhang
W: β2-adrenergic receptor activation promotes the proliferation of
A549 lung cancer cells via the ERK1/2/CREB pathway. Oncol Rep.
36:1757–1763. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|