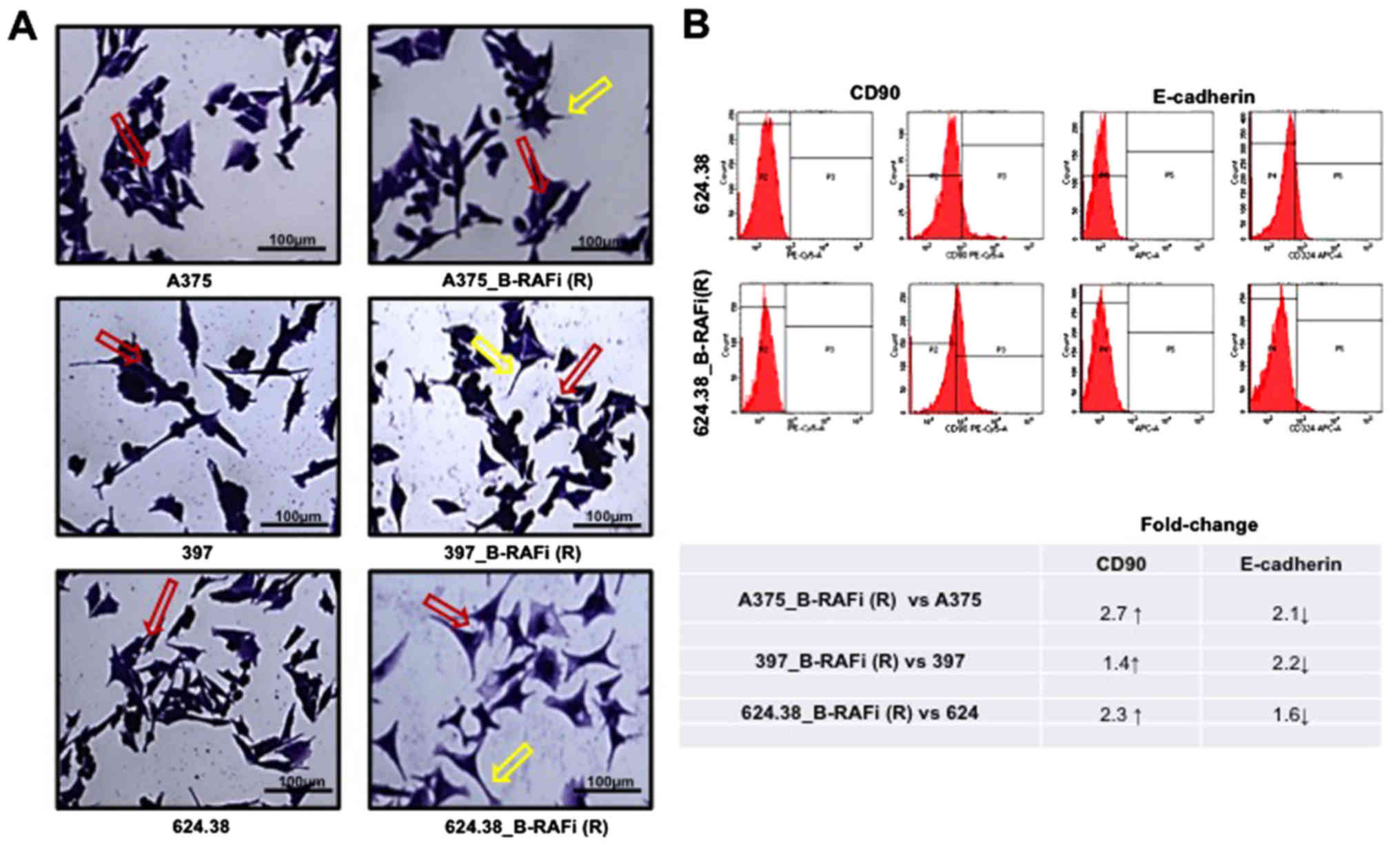
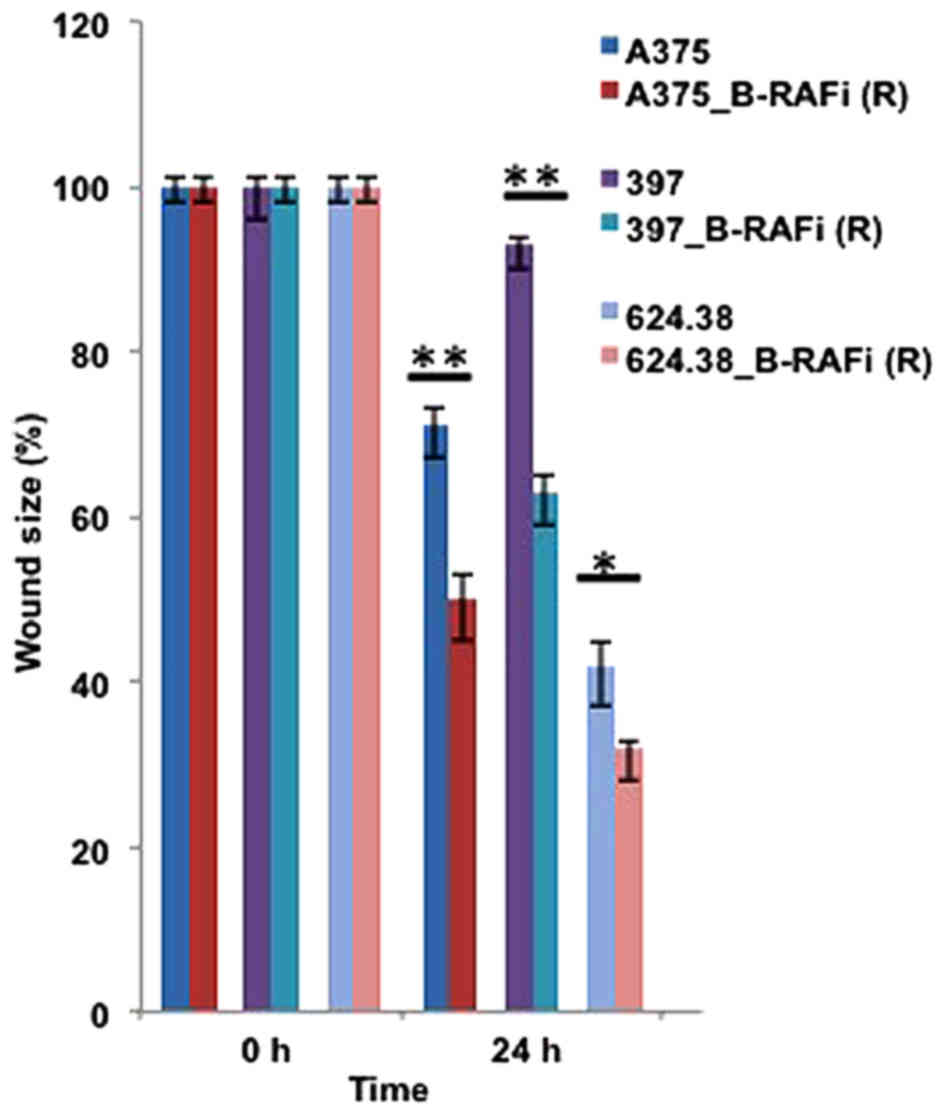
|
1
|
Carvajal RD, Marghoob AA, Kaushal A,
Kehrer JD, Ko C and Brady MS: Melanoma and other skin cancers.
Cancer Network. Home of the Journal Oncology. 1:1–23. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Tarver T: Cancer facts and figures 2012.
American Cancer Society (ACS). J Consumer Health Internet.
16:366–367. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Candido S, Rapisarda V, Marconi A,
Malaponte G, Bevelacqua V, Gangemi P, Scalisi A, McCubrey JA,
Maestro R, Spandidos DA, et al: Analysis of the
B-RafV600E mutation in cutaneous melanoma patients with
occupational sun exposure. Oncol Rep. 31:1079–1082. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Falzone L, Salemi R, Travali S, Scalisi A,
McCubrey JA, Candido S and Libra M: MMP-9 overexpression is
associated with intragenic hypermethylation of MMP9 gene in
melanoma. Aging. 8:933–944. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bernardo-Faura M, Massen S, Falk CS, Brady
NR and Eils R: Data-derived modeling characterizes plasticity of
MAPK signaling in melanoma. PLOS Comput Biol. 10:e10037952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ascierto PA, Grimaldi AM, Anderson AC,
Bifulco C, Cochran A, Garbe C, Eggermont AM, Faries M, Ferrone S,
Gershenwald JE, et al: Future perspectives in melanoma research:
Meeting report from the ‘Melanoma Bridge’, Napoli, December 5th-8th
2013. J Transl Med. 12:2772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Das Thakur M, Salangsang F, Landman AS,
Sellers WR, Pryer NK, Levesque MP, Dummer R, McMahon M and Stuart
DD: Modelling vemurafenib resistance in melanoma reveals a strategy
to forestall drug resistance. Nature. 494:251–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya
RC, Lee H, Chen Z, Lee MK, Attar N, Sazegar H, et al: Melanomas
acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS
upregulation. Nature. 468:973–977. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi H, Moriceau G, Kong X, Lee MK, Lee H,
Koya RC, Ng C, Chodon T, Scolyer RA, Dahlman KB, et al: Melanoma
whole-exome sequencing identifies (V600E)B-RAF
amplification-mediated acquired B-RAF inhibitor resistance. Nat
Commun. 3:7242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi H, Hugo W, Kong X, Hong A, Koya RC,
Moriceau G, Chodon T, Guo R, Johnson DB, Dahlman KB, et al:
Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF
inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 4:80–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rizos H, Menzies AM, Pupo GM, Carlino MS,
Fung C, Hyman J, Haydu LE, Mijatov B, Becker TM, Boyd SC, et al:
BRAF inhibitor resistance mechanisms in metastatic melanoma:
Spectrum and clinical impact. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1965–1977. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Allen EM, Wagle N, Sucker A, Treacy
DJ, Johannessen CM, Goetz EM, Place CS, Taylor-Weiner A, Whittaker
S, Kryukov GV, et al: Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group of
Germany (DeCOG): The genetic landscape of clinical resistance to
RAF inhibition in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Discov. 4:94–109.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ascierto PA, Marincola FM and Atkins MB:
What's new in melanoma? Combination! J Transl Med. 13:2132015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Caputo E, Miceli R, Motti ML, Taté R,
Fratangelo F, Botti G, Mozzillo N, Carriero MV, Cavalcanti E,
Palmieri G, et al: AurkA inhibitors enhance the effects of B-RAF
and MEK inhibitors in melanoma treatment. J Transl Med. 12:2162014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun C, Wang L, Huang S, Heynen GJ,
Prahallad A, Robert C, Haanen J, Blank C, Wesseling J, Willems SM,
et al: Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition
in melanoma. Nature. 508:118–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sanchez-Laorden B, Viros A, Girotti MR,
Pedersen M, Saturno G, Zambon A, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Turajlic S,
Hayes A, Gore M, et al: BRAF inhibitors induce metastasis in RAS
mutant or inhibitor-resistant melanoma cells by reactivating MEK
and ERK signaling. Sci Signal. 7:ra302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung JW, Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Oh ES, Park S
and Han IO: Ionising radiation induces changes associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and increased cell
motility of A549 lung epithelial cells. Eur J Cancer. 43:1214–1224.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang AD, Fan F, Camp ER, van Buren G, Liu
W, Somcio R, Gray MJ, Cheng H, Hoff PM and Ellis LM: Chronic
oxaliplatin resistance induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in colorectal cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4147–4153.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoek KS, Eichhoff OM, Schlegel NC,
Döbbeling U, Kobert N, Schaerer L, Hemmi S and Dummer R: In vivo
switching of human melanoma cells between proliferative and
invasive states. Cancer Res. 68:650–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wehbe M, Soudja SM, Mas A, Chasson L,
Guinamard R, de Tenbossche CP, Verdeil G, Van den Eynde B and
Schmitt-Verhulst AM: Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition-like and
TGFβ pathways associated with autochthonous inflammatory melanoma
development in mice. PLoS One. 7:e494192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jayachandran A, Anaka M, Prithviraj P,
Hudson C, McKeown SJ, Lo PH, Vella LJ, Goding CR, Cebon J and
Behren A: Thrombospondin 1 promotes an aggressive phenotype through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human melanoma. Oncotarget.
5:5782–5797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nawshad A, Lagamba D, Polad A and Hay ED:
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling during
epithelial-mesenchymal transformation: Implications for
embryogenesis and tumor metastasis. Cells Tissues Organs.
179:11–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gavert N and Ben-Ze'ev A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of
tumors. Trends Mol Med. 14:199–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nieto MA: The ins and outs of the
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:347–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Santisteban M, Reiman JM, Asiedu MK,
Behrens MD, Nassar A, Kalli KR, Haluska P, Ingle JN, Hartmann LC,
Manjili MH, et al: Immune-induced epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in vivo generates breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Res.
69:2887–2895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zimmerer RM, Korn P, Demougin P, Kampmann
A, Kokemüller H, Eckardt AM, Gellrich NC and Tavassol F: Functional
features of cancer stem cells in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Cell
Int. 13:782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kashyap V, Rezende NC, Scotland KB,
Shaffer SM, Persson JL, Gudas LJ and Mongan NP: Regulation of stem
cell pluripotency and differentiation involves a mutual regulatory
circuit of the NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 pluripotency transcription
factors with polycomb repressive complexes and stem cell microRNAs.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:1093–1108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wen KM, Zhang GH, Li J, Chen ZQ, Cheng YL,
Su X and Zeng QL: OCT4B1 promotes cell growth, migration and
invasion suppressing sensitivity to οxaliplatin in colon cancer.
Oncol Rep. 34:2943–2952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pennisi M, Russo G, Di Salvatore V,
Candido S, Libra M and Pappalardo F: Computational modeling in
melanoma for novel drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov.
11:609–621. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pappalardo F, Russo G, Candido S, Pennisi
M, Cavalieri S, Motta S, McCubrey JA, Nicoletti F and Libra M:
Computational modeling of PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in
melanoma cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01521042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bissell MJ and Labarge MA: Context, tissue
plasticity, and cancer: Are tumor stem cells also regulated by the
microenvironment? Cancer Cell. 7:17–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin X, Zhang BH, Zheng SS, Gao DM, Qiu SJ,
Wu WZ and Ren ZG: Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates
stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail
signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 8:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Medema JP: Cancer stem cells: The
challenges ahead. Nat Cell Biol. 15:338–344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|